Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. Macroscopic
Uploaded by
cayla mae carlosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Approaches: 1. Clinical Diagnosis 2. Laboratory Diagnosis 2 Phases: 1. Macroscopic
Uploaded by
cayla mae carlosCopyright:
Available Formats
MICROPARA LAB Routine fecalysis
2 approaches: 2 phases:
1. Clinical Diagnosis 1. Macroscopic
2. Laboratory Diagnosis - Color
- Most common= Stool - Form & Consistency
- Half of the parasitical infections are
intestinal.
2 steps:
1. Detection of parasite
2. Identification of parasite
Stool Sample Collection
- Avoid taking foods and substances
(barium, oil, bismuth, iron, cooked 2. Microscopic
blood, oil and fatty materils) - With microscope
- Properly collected specimens must
(DFS) Direct Fecal Smear
be delivered immediately to the
lab. - Emulsify on saline solution (2-3
- Place adequate amount of stool drops) until it formed
into a correct container. homogenous…
- Midportion should be taken; - And, observe on microscope.
consider bloody mucoid part.
- Avoid mixture of urine, dirt, cotton, Katho- Thick smear
fibers, tissue paper. - Intestinal and not suitable for
- Stool must be thumb/pea sized protozoan or liquid smears.
- Watery stool should be delivered - Use of transparent cellophane tape.
immediately in the lab. Because the - Visualize under microscope
trophozoite forms would die within - Permanent, stained fresh fecal
30 minutes. smear
- Urinate fist before collecting stool. - Concentration methods
- Defecate on a bedpan
Iodine solution or NSS sol.
- Will give contrast
Amoeba
- Permanent, stained fresh fecal
smear
- For better visualization
Low- grade parasitemia
- Concentration methods
- Whatever is submitted, ise it all and
concentrate it.
2 types of CM:
1. Floatation
- Higher density 2 gametocytes:
- Weight of ova will float
1. Micro- male gametes
- Can get to the surface
2. Macro- female gametes
- Topmost
- Outer surface of tube Crescent shaped gametocytes= Plasmodium
- Ex: zinc sulfate floatation technique falciparum
2. Sedimentation
- Lower density solution of ova
- Will be on the bottom
- Ex: formalin ether technique
concentration
BLOOD
Malaria
Screening: thick and thin smearing Entamoeba Histolytica
1. Thick= detection for the presence of Trophozoite:
parasite. (close to one another)
2. Thin= identification of parasite of - 1 nucleus have ingested RBC’s
species.
Cyst:
Plasmodium
- 4 nuclei
- Intraerythrocytic
- Trophozoite: ringforms
- cigar shaped/ round ended.
Axoneme
- interior portion of flagella
Giardia Lamblia
- rocket shaped
- axoneme = central portion
- trophozite: 2 nuclei
- Cyst: 2-4 nuclei with thick coat Balantidium coli
- Cyst and trophozoite:
Micro nucleus- involved in sexual
repro.
Macro nucleus- involved in diff.
metabolism, and respiration
- Cystosome = mouth part
- Cystopage = anus- like
- Longer in anterior
- Shorter in posterior Cilia
Trichomonas Hominis
- Anterior part is the flagella
- Cystosome; mouth part of the
parasite
- No cyst form
- Undulating Membrane
- Jerky motility
- 1 nuclei
- 3-5 flagella anterior
- 1 posterior
Ctto: notes ni bethel
You might also like
- Arasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeDocument5 pagesArasitology: Intestinal AmoebaeMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Activity Tabulation ParasitologyDocument18 pagesActivity Tabulation ParasitologyStephen YorNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument18 pagesParasitologyLudwig359100% (2)
- Philippine Textbook of Medical Parasitology 2nd Ed - Belizario - 1 PDFDocument256 pagesPhilippine Textbook of Medical Parasitology 2nd Ed - Belizario - 1 PDFPamela Castillo83% (6)
- Parasitology Reviewer: Monica Kristine ReyesDocument34 pagesParasitology Reviewer: Monica Kristine ReyesMariel Yanes Garcia75% (4)
- MCQs in Medical MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesMCQs in Medical Microbiologysidharta_chatterjee100% (8)
- Para Lec ReviewerDocument18 pagesPara Lec ReviewerRudolph MendozaNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cardiovascular DisordersDocument9 pagesPediatric Cardiovascular Disorderscayla mae carlos0% (1)
- Newborn Disorders - : Small For Gestational Age (Sga) NewbornDocument11 pagesNewborn Disorders - : Small For Gestational Age (Sga) Newborncayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Newborn Disorders - : Small For Gestational Age (Sga) NewbornDocument11 pagesNewborn Disorders - : Small For Gestational Age (Sga) Newborncayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument9 pagesMicrobiology and ParasitologyDefensor Pison Gringgo0% (1)
- Pediatric Genitourinary DisordersDocument7 pagesPediatric Genitourinary Disorderscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Animal AmoebiasisDocument22 pagesAnimal Amoebiasissufian abdo jiloNo ratings yet
- PROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyDocument7 pagesPROTOZOA (Sarcodina) : ProtozoologyReyven Niña DyNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Lec 7 Lung FlukesDocument5 pagesParasitology-Lec 7 Lung Flukesapi-3743217100% (1)
- Stool AnalysisDocument8 pagesStool AnalysisLuciaGomez100% (1)
- Medical Technology Assessment Program: Mycology Review NotesDocument6 pagesMedical Technology Assessment Program: Mycology Review NotesMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Para Lab Merge FileDocument72 pagesPara Lab Merge Fileehehe agikNo ratings yet
- Practice Application of Nursing InformaticsDocument3 pagesPractice Application of Nursing Informaticscayla mae carlos100% (3)
- Case Study of AmoebiasisDocument7 pagesCase Study of Amoebiasisbuzz Q75% (4)
- Protista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Document6 pagesProtista (Subdivision Protozoa) : Bütschlii), or Pathogenic (E. Histolytica)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Parasites by Apple TanDocument16 pagesParasites by Apple TanOlivia LimNo ratings yet
- Tabular Parasitology MICROPARADocument19 pagesTabular Parasitology MICROPARAJerlyn FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Intro To para Lab Part 2Document1 pageIntro To para Lab Part 2Vanessa May BlancioNo ratings yet
- Taenia Saginata-Opistorchis FelineusDocument5 pagesTaenia Saginata-Opistorchis FelineusKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- (PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument6 pages(PARA) 1.5 - Blood and Tissue FlagellatesGuia De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Dientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesDocument4 pagesDientamoeba Fragilis: Intestinal FlagellatesRitz CelsoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Review On FlagellatesDocument2 pagesParasitology Review On FlagellatesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- E. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesDocument11 pagesE. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesCorinne MandrezaNo ratings yet
- Ameba and E.histolyticaDocument18 pagesAmeba and E.histolyticapenonia.abegailashleyNo ratings yet
- Trematodes: 2. MiracidiaDocument3 pagesTrematodes: 2. MiracidiaBikram ChohanNo ratings yet
- Histo - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesDocument4 pagesHisto - Fresh Tissue Examination and Intro To Histological TechniquesBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- Balantidum Coli: EBON, SISON - 2017Document5 pagesBalantidum Coli: EBON, SISON - 2017Abcd ReyesNo ratings yet
- MBP Lab ReviewerDocument9 pagesMBP Lab ReviewerTrisha PaolaNo ratings yet
- MLS 306 Week 3Document2 pagesMLS 306 Week 3Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Mycovi1 L1Document3 pagesMycovi1 L1MHEKAELLA SAMSONNo ratings yet
- Protozoa-RevisionDocument6 pagesProtozoa-RevisionIssam HadiNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myDocument35 pagesBlood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Free-Living Amoebas & Ciliates (Lab)Document10 pagesFree-Living Amoebas & Ciliates (Lab)Xie LianNo ratings yet
- Amoeba: Ms. Helga SyDocument7 pagesAmoeba: Ms. Helga Syanti romantic txtNo ratings yet
- Short Writing Assignment 4Document5 pagesShort Writing Assignment 4Troi JeraoNo ratings yet
- AMOEBADocument11 pagesAMOEBAMicaella RemilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Coccidian PDFDocument11 pagesLesson 6 - Coccidian PDFAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Free Living AmoebaDocument5 pagesFree Living AmoebaEiveren Mae SutillezaNo ratings yet
- TERMINOLOGIESDocument3 pagesTERMINOLOGIESYsabella PolanaNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases Tableanushkasingh300806No ratings yet
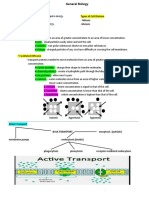
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisDocument4 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisAlex SerdeñaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Blood and Tissue FlagellatesDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Blood and Tissue FlagellatesaemancarpioNo ratings yet
- Hemoflagellates Protozoa: Scientific Name Disease Commune NameDocument6 pagesHemoflagellates Protozoa: Scientific Name Disease Commune Nameaust austNo ratings yet
- Parasitology LectureDocument7 pagesParasitology Lectureangela verayeNo ratings yet
- Intestinal FlukesDocument3 pagesIntestinal FlukesStephany Polinar0% (1)
- HR1Document6 pagesHR1Rose CitcoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Blood and Tissue ProtozoansDocument42 pagesActivity 2 Blood and Tissue ProtozoansRaven TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Apparatus For Practical of MSC Class Semester IDocument8 pagesApparatus For Practical of MSC Class Semester Iranaateeq100% (1)
- Week 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument4 pagesWeek 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris LumbricoidesHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)Document4 pages1.3 Hemoflagellates and Ciliates (Limpin)arvinkennethdelacruzNo ratings yet
- S. Japonicum or Oriental Lung FlukeDocument4 pagesS. Japonicum or Oriental Lung FlukeMon Kristoper CastilloNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFDocument23 pagesPlatyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFAbdulla Hil KafiNo ratings yet
- 6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsDocument35 pages6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsHeyzel joy FabianNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Para Lab Part 1Document2 pagesPara Lab Part 1Vanessa May BlancioNo ratings yet
- Plus 2 PracticalDocument16 pagesPlus 2 Practicaljayantaroy783360No ratings yet
- Miscellaneous Protozoa1Document5 pagesMiscellaneous Protozoa1Haki TozakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 IntegumentaryDocument3 pagesChapter 6 IntegumentaryLiane LomioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer On EukaryotesDocument6 pagesReviewer On EukaryotesAlaica Joice B. JaboneteNo ratings yet
- Parasites High YoieldDocument4 pagesParasites High Yoieldnreena aslamNo ratings yet
- Microbiology A Laboratory Manual 11th Edition Cappuccino Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesMicrobiology A Laboratory Manual 11th Edition Cappuccino Solutions Manualbegravebasnetvp8su100% (19)
- Dwnload Full Microbiology A Laboratory Manual 11th Edition Cappuccino Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Microbiology A Laboratory Manual 11th Edition Cappuccino Solutions Manual PDFyoreoakling.9vtk0y100% (10)
- Histology - Git Table 1Document1 pageHistology - Git Table 1lcrujidoNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument4 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology I and Parasitology IIDocument46 pagesParasitology I and Parasitology IIkhaledNo ratings yet
- OkieDocument3 pagesOkieFebeval CastilloNo ratings yet
- Semi Final TransesDocument17 pagesSemi Final TransesCAÑADA, JOHANNELYN M.No ratings yet
- Method of Preparation and Systematic Examination of A Direct Fecal SmearDocument3 pagesMethod of Preparation and Systematic Examination of A Direct Fecal SmearCelne CentinoNo ratings yet
- PlacardsDocument18 pagesPlacardscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Local Anaesthetic Dosing For Male CircumcisionDocument4 pagesLocal Anaesthetic Dosing For Male CircumcisionAssenav ZednemNo ratings yet
- 1 General3 815notrimsDocument46 pages1 General3 815notrimsShuvashishSunuwarNo ratings yet
- Anthropogenic Disasters: Complex Human Emergencies Technological DisastersDocument2 pagesAnthropogenic Disasters: Complex Human Emergencies Technological Disasterscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Emergency and Disaster NursingDocument144 pagesEmergency and Disaster Nursingcayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- 601 Floor Plan FDocument1 page601 Floor Plan Fcayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- For Learners Handwashing StepsDocument1 pageFor Learners Handwashing Stepscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Cop - Unit Ii - Foundations of CaringDocument3 pagesCop - Unit Ii - Foundations of Caringcayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- The WASH Benefits Bangladesh, WASH Benefits Kenya, and SHINE Trials: A Summary of Their FindingsDocument2 pagesThe WASH Benefits Bangladesh, WASH Benefits Kenya, and SHINE Trials: A Summary of Their Findingscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Arrythmias 2-3Document4 pagesArrythmias 2-3cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Extraordinary Measures Jop 13 346Document1 pageExtraordinary Measures Jop 13 346cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- HIVST Provides An Empowering Opportunity For People Who Are Left Behind by Other HIV Testing ServicesDocument1 pageHIVST Provides An Empowering Opportunity For People Who Are Left Behind by Other HIV Testing Servicescayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Hematologic Disorders - : Blood Blood CoagulationDocument6 pagesPediatric Hematologic Disorders - : Blood Blood Coagulationcayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- TLE 6 - Q2-Pic5Document1 pageTLE 6 - Q2-Pic5cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- The COVIDDocument2 pagesThe COVIDcayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Respiratory Disorders General InterventionsDocument2 pagesPediatric Respiratory Disorders General Interventionscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Open PrayerDocument1 pageOpen Prayercayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Cop Lec - Unit Iv - Physical Care of OlderDocument3 pagesCop Lec - Unit Iv - Physical Care of Oldercayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document5 pagesActivity 1cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Problems With Eating and Feeding, Incontinence, Confusion, Evidence of Falls, and Skin BreakdownDocument1 pageProblems With Eating and Feeding, Incontinence, Confusion, Evidence of Falls, and Skin Breakdowncayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Lumad's Belief and ValuesDocument1 pageLumad's Belief and Valuescayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Exercise Which Keeps The Heart Pumping and Working Steadily For About 20 Minutes Per Day Improves FitnessDocument3 pagesExercise Which Keeps The Heart Pumping and Working Steadily For About 20 Minutes Per Day Improves Fitnesscayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Chinese General Hospital Colleges: Cayla Mae M. Carlos BSN 2-C Mr. Marc Levane B. BerdinDocument1 pageChinese General Hospital Colleges: Cayla Mae M. Carlos BSN 2-C Mr. Marc Levane B. Berdincayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- List of Documents Need For Filing 2021 Mayors Permit and Itr 2020Document1 pageList of Documents Need For Filing 2021 Mayors Permit and Itr 2020cayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Subject Code Subject Title Course Grade Numeric EquivalentDocument2 pagesSubject Code Subject Title Course Grade Numeric Equivalentcayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Update On Laboratory Diagnosis of AmoebiasisDocument24 pagesUpdate On Laboratory Diagnosis of AmoebiasisMedical WarriorNo ratings yet
- Intestinal and Commensal AmoebaDocument9 pagesIntestinal and Commensal AmoebaFuture TrekingNo ratings yet
- Para Lec Lesson2Document9 pagesPara Lec Lesson2Tolentino, Edron E.No ratings yet
- (CGPT) B11M4.1Document12 pages(CGPT) B11M4.1adriennemartha.barrientosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocument73 pagesIntroduction To ParasitologyKarylle CateNo ratings yet
- Commensal AmebaeDocument11 pagesCommensal AmebaeGladys Mary MarianNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Part 1Document66 pagesMicrobiology Part 1Authentic IdiotNo ratings yet
- MICP211 LEC - CombinedDocument40 pagesMICP211 LEC - CombinedJULIANA NICOLE TUIBUENNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Protozoa (Ibrahim Qadir)Document112 pagesParasitology Protozoa (Ibrahim Qadir)Alan H BamokiNo ratings yet
- 4.animalkingdom ResonanceDocument80 pages4.animalkingdom ResonanceEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Pearsons Federal Taxation 2020 Individuals 33rd Edition Timothy J Rupert Kenneth e AndersonDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Pearsons Federal Taxation 2020 Individuals 33rd Edition Timothy J Rupert Kenneth e AndersonRobertMedinawnkt100% (40)
- Mdparas NotesDocument46 pagesMdparas NotesnamkimseoNo ratings yet
- ProtozoaDocument81 pagesProtozoaabigail correNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ParasitologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To ParasitologyJoyce LeeNo ratings yet
- Course Outline ParasitologyDocument6 pagesCourse Outline ParasitologyNichole SilverioNo ratings yet
- Medt25 01 Module Rubrics Urinalysis FecalysisDocument13 pagesMedt25 01 Module Rubrics Urinalysis Fecalysissharon agorNo ratings yet
- Parasitology PartialDocument8 pagesParasitology Partialcayla mae carlosNo ratings yet
- Parasites SanguinsDocument14 pagesParasites Sanguinsmebarki mohamedNo ratings yet
- Parasitology: By: Jahre Mark Toledo, RMT, Maed BioDocument50 pagesParasitology: By: Jahre Mark Toledo, RMT, Maed BioJahre Mark Toledo100% (1)