Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris Lumbricoides
Uploaded by
Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 2 (Lec-Lab) Mls 306 Clinical Parasitology Bsmls 3A: Ascaris Lumbricoides
Uploaded by
Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoCopyright:
Available Formats
WEEK 2 (LEC-LAB) MLS 306** CLINICAL PARASITOLOGY BSMLS 3A
PHYLUM NEMATHELMINTHES
General Characteristics - Roundworms
- Long, cylindrical & elongated
- Anterior end : with hooks, teeth, plates & papillae ( abrasion; tearing – attachment & sensory response)
- Supporting wall : outer, hyaline, non-cellular cuticle ; subcuticular epithelium; layer of muscle cells.
- With separate sexes, although some may be parthenogenic
- With Amphids (sensory organ sa Anterior end) & Phasmids (sensory organ sa Posterior end)
◼ 3 aphasmid worms (w/out sensory organ at the posterior end, chemoreceptor-not provided) : Trichuris, trichinella, capillaria
◼ Phasmid worms : hookworms, strongyloides, wuchereria, bragia malayi
- w/ alimentary tract; no circulatory system
- Life cycle : egg stage – larval stage – adult stage
- Some of the nematodes are:
◼ Oviparous – Ascaris lumbricoides
◼ Ovoviviparous/Oviviparous – Enterobius vermicularis
◼ Viviparous/larviparous – Trichinella spiralis; filaria
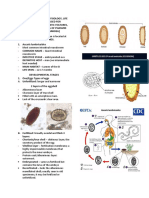
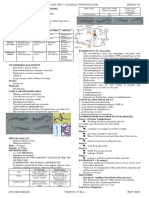
Ascaris lumbricoides
Common name: Giant/ Large Intestinal Roundworm
General Characteristics Habitat Their eggs & its characteristics Life cycle Pathology Diagnosis Epidemiology Treatment, Prevention &
Control
- Resembles the common - Adult female can produce 200,00 - - Ascariasis Direct Fecal Smear - Endemic in many countries - Deworming : 3x a year for 3
earthworm 240,000 eggs per day - Usual infection of 10-20 worms w/ warm moist climate years ( Mebendazole,
- Soil transmitted helminth / - 65 million fertilized eggs may not show symptoms 1.Fecal sample (Southeast Asia, Africa, Albendazole, Pyrantel
geohelminth - Lifespan: 1-2 years (12-20 months) - Causes Ascaris pneumonitis : 2.Formed stool - add one drop of central & south America); pamoate, levamisole,
- Parasite specific for man chest pain, cough, fever, Normal Saline Solution in the slide cosmopolitan distribution, piperazine salts)
- Polymyarian type (many - Dryness is unfavorable for survival increased eosinophil (heart-lung 1.2 billion have ascariasis - Sanitary disposal of feces
longitudinal rows of muscles) Small intestine - Eggs are destroyed by direct sunlight migration) Watery stool – no need & 2,000 die annually - Personal hygiene
- Adult : white, cream / pinkish - Killed at temperature above 40 C - Lung infiltration, asthmatic - High prevalence in children - Avoid the use of feces as
yellow when fresh - Can survive freezing temp. attacks & edema of the lips 3.Spread the fecal sample on the slide 5 to 15 yrs old fertilizer
- Adult male : curved tail, 10- - Resistance to chemical disinfectant & - Difficulty of breathing - In the Philippines, - Thorough cooking of food
31 cm by 3mm can withstand temporary immersion in - Can be found in the brain, spinal Microscopic Exam prevalence rate is 80-90% - WASHED (water,
- Adult female : straight strong chemicals membranes, spinal cord, eyeball -Observe for Ascaris egg & quantitate in rural areas, poor slum sanitation, hygiene,
pointed posterior end, 22-35 & kidneys the ova (LPO; 3-15 egg per low power sections education in deworming
cm by 5 mm Can either be: - Decrease fat & nitrogen field) framework)
- FEMALE IS LARGER 1. Fertilized egg- 45 to 70 by 35 to 50 um; absorption Ascaris infections in animals - WOW in Binan, Laguna
THAN MALE ovoidal, golden brown, very thick egg - Increase nitrogen loss in feces It may give a negative findings in the
- Anterior end: 3 lips, triangular shell; inside is a set of organized germ - Malabsorption & intolerance of following conditions : Toxocara canis – DOG
buccal cavity; may teeth & cell lactose -Patient is free from infection Toxocara cati - CAT
sensory papillae - Due to repeated copulation (mating) - Decrease growth in children -Early stage of infection
- Mode of transmission : - 3 layers : inner vitelline membrane, - Heavy infection can cause -Larval migration
Ingestion of embryonated glycogen layer, albuminous mamillation obstruction, intussusception or -Only male worms are present in
egg (+) corticated volvulus intestine
(-) decorticated Physical effects
2. Unfertilized/infertile – 88 to 94 by 39 to Diarrhea Kato-Katz technique
44 um; irregularly ovoidal, larger, longer Vague abdominal pain - Place 50-60 grams of stool in a slide
& narrower, thin shell & irregular Nausea - Cover with cellophane (soaked in
mamillated coating. Loss of appetite glycerine malachite green for 24
- No vitelline membrane Vomited ascaris (larynx-suffocation; hours)
- With lecithin granules lungs-pulmonary gangrene; eustachian - Press with rubber stopper. Leave for
- Glycogen layer tube- titus media (luga)) 10-20 minutes. Examine.
- Albuminous mamillation; (+) corticated - May invade appendix - Kato-set : template with hole, screen,
(-) decorticated - May be seen in the bile duct, liver nylon/plastic, plastic spatula
parenchyma, gall bladder - Newspaper/glazed tile
LPU-BATANGAS TAMAYO, H.B.A RMT 2023
WEEK 2 (LEC-LAB) MLS 306** CLINICAL PARASITOLOGY BSMLS 3A
3. Embryonated egg – containing an infective - May block pancreatic duct - Microscope slides
second stage larva - Perforate the bowel % cause - Cellophane as cover slip, soaked in
acute peritonitis / chronic Glycerol-Malachite green solution
granulomatous peritonitis - Fresh stool
- May also irritate nerve ending in - Gloves
the mucosa & result in intestinal
spasm leading to intestinal - Prepare the layer glazed
obstruction tile/newspaper
- Place the template with hole in
the center of a microscope slide
- Place a small amount of fecal
material on the newspaper/ the
glazed tile
- Press the screen on top so that
some of the feces filters through
& scrape with the flat spatula
across the upper surface to
collect the filtered spaces
- Add the collected feces in the
hole of the template so that it is
completely filled.
- Remove the template carefully so
that the cylinder of feces is left on
the slide.
- Cover the fecal material with the
pre-soaked cellophane strip
- Invert the microscope slide &
firmly press the fecal sample
against the cellophane strip on a
smooth hard surface such as a
tile. The material will be spread
evenly.
- Carefully remove the slide by
gently sliding it sideways to
avoid separating the cellophane
strip. Place the slide w/ the
cellophane upwards
- FECT (formalin-ether core
technique)
LPU-BATANGAS TAMAYO, H.B.A RMT 2023
WEEK 2 (LEC-LAB) MLS 306** CLINICAL PARASITOLOGY BSMLS 3A
Trichuris trichiura
Common name: Whipworm
General Characteristics Habitat Their eggs & its characteristics Life cycle Pathology Diagnosis Epidemiology Treatment, Prevention &
Control
- Flesh colored/ pinkish - Adult female can produce 3,000 to - Can cause petechial Direct Fecal Smear - 80 to 90% in rural areas; - Deworming : 3x a year for 3
slender worms 10,000 eggs per day hemorrhages – predispose to temperate & tropical years (Mebendazole,
- Soil embryonation of the - Barrel-shaped with bipolar mucus amebic dysentery 1.Fecal sample countries but more on Albendazole, Pyrantel
egg/ova (2-3 weeks) plug; Japanese lantern, football - Mucosa is hyperemic & 2.Formed stool - add one drop of warm, moist areas pamoate, levamisole,
- Infective stage : Larva : Small Intestine shaped; lemon-shaped edematous enterorrhagia / Normal Saline Solution in the slide - 604 to 795 million are piperazine salts)
Embryonated egg Adult : Large Intestine - Thick-shelled; bile stained; intestinal bleeding is common infected - Sanitary disposal of feces
- TT47-pore forming protein (2-3 months) yellowish outer & transparent inner - Lumen of appendix may be filled Watery stool – no need - 5 to 15 years old - Personal hygiene
that allows them to imbed shell with worms - Pre-school & school-age - Avoid the use of feces as
- 4 larval stages to become - 50-54 by 22-23 microns & - Infection with over 5,000 eggs 3.Spread the fecal sample on the slide children fertilizer
adult discharged in the stool in an are symptomatic - Thorough cooking of food
- Holomyarian type (somatic unsegmented stage - Blood-streaked diarrheal stools Microscopic Exam
cells, small; numerous; - Have hyaline polar plugs - Abdominal pain & tenderness; -Observe for Ascaris egg & quantitate
closely packed cells) - Around 800 parasites (500 million nausea & vomiting the ova (LPO; 3-15 egg per low power
- Anterior end : colorless, eggs per day) - Hypoalbuminaemia field)
resembles a whip, contain a - Lifespan : 1 year - The worm is capable of causing
slender esophagus ulceration of the intestines which It may give a negative findings in the
- Posterior end : contains can lead to iron deficiency following conditions :
digestive & reproductive anemia -Patient is free from infection
organs - 0.8 to 8.6 ml of blood is loss per -Early stage of infection
- Female : slightly larger than day per Trichuris (Belizario); -Larval migration
male measuring 3.5 to 5 cm 0.005 mL – other authors -Only male worms are present in
in length; 35 to 50 mm; with - Heavy worm burden may lead to intestine
a straight/blunt posterior end prolapse of the rectum (rectal
- Male : 3 to 4.5 cm ; 30 to 45 prolapse) Kato-Katz technique
mm; the posterior end is - Place 50-60 grams of stool in a slide
coiled/curved through 360; - Poor appetite - Cover with cellophane (soaked in
with a single spicule & - Wasting glycerine malachite green for 24
retractile sheath - Stunting hours)
- Mode of transmission : - Reduced intellectual & cognitive - Press with rubber stopper. Leave for
Ingestion of embryonated development in children 10-20 minutes. Examine.
egg ; mucus plug will soften - Prognosis is very good - Kato-set : template with hole, screen,
nylon/plastic, plastic spatula
- Newspaper/glazed tile
- Microscope slides
- Cellophane as cover slip, soaked in
Glycerol-Malachite green solution
- Fresh stool
- Gloves
- Prepare the layer glazed
tile/newspaper
- Place the template with hole in
the center of a microscope slide
- Place a small amount of fecal
material on the newspaper/ the
glazed tile
- Press the screen on top so that
some of the feces filters through
LPU-BATANGAS TAMAYO, H.B.A RMT 2023
WEEK 2 (LEC-LAB) MLS 306** CLINICAL PARASITOLOGY BSMLS 3A
& scrape with the flat spatula
across the upper surface to
collect the filtered spaces
- Add the collected feces in the
hole of the template so that it is
completely filled.
- Remove the template carefully so
that the cylinder of feces is left on
the slide.
- Cover the fecal material with the
pre-soaked cellophane strip
- Invert the microscope slide &
firmly press the fecal sample
against the cellophane strip on a
smooth hard surface such as a
tile. The material will be spread
evenly.
- Carefully remove the slide by
gently sliding it sideways to
avoid separating the cellophane
strip. Place the slide w/ the
cellophane upwards
- FECT (formalin-ether core
technique)
LPU-BATANGAS TAMAYO, H.B.A RMT 2023
You might also like
- NematodesDocument2 pagesNematodesRheila DuyaNo ratings yet
- 6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsDocument35 pages6.2 2021para ReviewlocalwactsHeyzel joy FabianNo ratings yet
- 3-Intstinal HelminthesDocument27 pages3-Intstinal Helminthesademabdella38No ratings yet
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument16 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesKirstin Jan LuibNo ratings yet
- E. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesDocument11 pagesE. Histolytica: Associated DiseasesCorinne MandrezaNo ratings yet
- Nematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Document4 pagesNematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Primo GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Zotc 115 JLC NotesDocument3 pagesZotc 115 JLC NotesLeinard CucalNo ratings yet
- Parasitology-Lec 5 TrematodesDocument5 pagesParasitology-Lec 5 Trematodesapi-3743217100% (2)
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases Tableanushkasingh300806No ratings yet
- 7 - Nematodes (Aphasmids and Phasmids)Document9 pages7 - Nematodes (Aphasmids and Phasmids)Scarlet WitchNo ratings yet
- Helminth Identification and Treatment GuideDocument3 pagesHelminth Identification and Treatment GuideOmphile DansonNo ratings yet
- Modultumbuhkembang PDFDocument58 pagesModultumbuhkembang PDFMayer LoliNo ratings yet
- MODEL_ORGANISMSDocument2 pagesMODEL_ORGANISMSdefaultline25No ratings yet
- Life cycle and epidemiology of protozoan parasitesDocument2 pagesLife cycle and epidemiology of protozoan parasitesKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal NematodesDocument72 pagesIntestinal Nematodessarguss14100% (6)
- Medical Parasitology: Medina & Albano - Lecture & LaboratoryDocument9 pagesMedical Parasitology: Medina & Albano - Lecture & LaboratoryabigailNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Notes on Phasmids and AphasmidsDocument4 pagesParasitology Notes on Phasmids and AphasmidsOrhan AsdfghjklNo ratings yet
- Hookworms and Gastrointestinal Parasites of RuminantsDocument6 pagesHookworms and Gastrointestinal Parasites of RuminantsPhobos DeimosNo ratings yet
- Clinical+Parasitology-Module+8Document15 pagesClinical+Parasitology-Module+8Geresh MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFDocument23 pagesPlatyhelminthes - 6th Class PDFAbdulla Hil KafiNo ratings yet
- Nematodes Lab Reviewer PDFDocument7 pagesNematodes Lab Reviewer PDFRobi Alegre MedinaNo ratings yet
- Clinpara Lec M2Document11 pagesClinpara Lec M2eumhir7No ratings yet
- BIO 102 Introductory Biology: Phylum NematodaDocument11 pagesBIO 102 Introductory Biology: Phylum NematodaFatunbiNo ratings yet
- Morphology para Lec 2Document8 pagesMorphology para Lec 2Wyenne Faye TagapanNo ratings yet
- Concise Common Diseases TableDocument4 pagesConcise Common Diseases TableKavya SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument6 pagesReviewercloud kumoishNo ratings yet
- Semi Final TransesDocument17 pagesSemi Final TransesCAÑADA, JOHANNELYN M.No ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology in Tables PDFDocument15 pagesMedical Parasitology in Tables PDFRami Mohammed86% (7)
- Devbio Notes PDFDocument8 pagesDevbio Notes PDFcloud kumoishNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument9 pagesNematodesJessa MayNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument6 pagesCestodesKathryn JeuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - NEMATODESDocument50 pagesChapter 15 - NEMATODESmarilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myDocument35 pagesBlood and Tissue Protozoa (Con't) : DR - Mehru Nisha Mehrunisha@unikl - Edu.myNida RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalDocument21 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides (Linneaus. 1758) : NEMATODES: IntestinalPatricia CabisonNo ratings yet
- Para - Amoeba TabulatedDocument1 pagePara - Amoeba TabulatedKaoriMarieSembranoNo ratings yet
- 3) +nematodes Su20 PDFDocument67 pages3) +nematodes Su20 PDFJessica KadykNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lecture OverviewDocument17 pagesParasitology Lecture Overviewlouie100% (1)
- Module 6.5 MycologyDocument4 pagesModule 6.5 MycologyPNo ratings yet
- Taenia Saginata-Opistorchis FelineusDocument5 pagesTaenia Saginata-Opistorchis FelineusKervy Jay AgraviadorNo ratings yet
- Trematodes: Noemie N. Ardiente, RMT, MSMTDocument34 pagesTrematodes: Noemie N. Ardiente, RMT, MSMTaerin june sahagonNo ratings yet
- Para-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Document11 pagesPara-Transes Pre-Final Exam - Unit 4Aysha AishaNo ratings yet
- 4 - NematheminthesDocument3 pages4 - NematheminthesAliyah Julianne PayumoNo ratings yet
- Helminths 12Document34 pagesHelminths 12malakaiad212No ratings yet
- Medical Parasitology - FullDocument30 pagesMedical Parasitology - FullJesse Osborn100% (2)
- Student Notes: Micro 1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument5 pagesStudent Notes: Micro 1: Davao Doctors College Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody Jane PardilloNo ratings yet
- Topic Summary - Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument2 pagesTopic Summary - Ascaris Lumbricoidessakalam shipper48No ratings yet
- Cestoda: Infeksi Menel AnDocument3 pagesCestoda: Infeksi Menel Ancharlesy TNo ratings yet
- Nonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesDocument20 pagesNonpathogenic Amoebae - FlagellatesHend AtijaniNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument390 pagesParasitologyVench DemicaisNo ratings yet
- Al-Mustaqbal University Parasitology Lab NotesDocument12 pagesAl-Mustaqbal University Parasitology Lab Notesهاني عقيل حسين جوادNo ratings yet
- Cestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanDocument4 pagesCestodes (Tapeworm) : Diphyllobotium Latum - 20 Yrs Life SpanMicael Andrei MendozaNo ratings yet
- Trematodes: Blood FlukesDocument3 pagesTrematodes: Blood FlukesFrance Louie JutizNo ratings yet
- RMTnotes PARASITOLOGYDocument68 pagesRMTnotes PARASITOLOGYArvin O-CaféNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Nematodes: College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-ValenzuelaDocument29 pagesIntroduction To Nematodes: College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-ValenzuelaMichNo ratings yet
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument4 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesAliana RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument36 pagesParasitology ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Notes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Approaches to Research on the Systematics of Fish-Borne TrematodesFrom EverandApproaches to Research on the Systematics of Fish-Borne TrematodesNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 Science Tech in The PhilDocument66 pagesChap 2 Science Tech in The PhilHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- MLS 306 Week 4Document3 pagesMLS 306 Week 4Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- MLS 306 WEEK 3cDocument1 pageMLS 306 WEEK 3cHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- QUIZZESDocument2 pagesQUIZZESHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- MLS 306 Week 3Document2 pagesMLS 306 Week 3Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Intellectual Revolutions That Defined SocietyDocument39 pagesChap 3 Intellectual Revolutions That Defined SocietyHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- MLS 306 Week 1Document3 pagesMLS 306 Week 1Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- MLS 306 WEEK 3bDocument2 pagesMLS 306 WEEK 3bHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Philippine S&T Agenda Focuses on Basic Research, Health, AgricultureDocument57 pagesPhilippine S&T Agenda Focuses on Basic Research, Health, AgricultureHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Intro To ManagementDocument58 pagesIntro To ManagementHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 Sci Tech in The WorldDocument38 pagesChap 1 Sci Tech in The WorldHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Personnel Management2Document60 pagesPersonnel Management2Hannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Personnel ManagementDocument3 pagesPersonnel ManagementHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- 7a. Information ManagementDocument47 pages7a. Information ManagementHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Management Control System ExplainedDocument51 pagesManagement Control System ExplainedHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- 7b Laboratory ProtocolDocument30 pages7b Laboratory ProtocolHannah Beatrice Adame Tamayo100% (1)
- Reviewertianism HAHADocument1 pageReviewertianism HAHAHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- College Students: To Form A Customer/Problem Hypothesis: To Form A Problem/Solution HypothesisDocument1 pageCollege Students: To Form A Customer/Problem Hypothesis: To Form A Problem/Solution HypothesisHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- SOP of Gram StainDocument5 pagesSOP of Gram Stainzalam55100% (1)
- Laboratory ManagersDocument45 pagesLaboratory ManagersHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- OrganizingDocument26 pagesOrganizingHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Management PlanningDocument70 pagesManagement PlanningHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - BSMLS2A - Value Proposition CanvasDocument1 pageGroup 7 - BSMLS2A - Value Proposition CanvasHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Intro To ManagementDocument58 pagesIntro To ManagementHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Group 7 - BSMLS2A - Customer Journey MapDocument2 pagesGroup 7 - BSMLS2A - Customer Journey MapHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro To Lab MGTDocument42 pages1 Intro To Lab MGTHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Group 7 BSMLS 2A coffee shop business planDocument1 pageGroup 7 BSMLS 2A coffee shop business planHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Specialized Connective TissueDocument98 pagesSpecialized Connective TissueHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument70 pagesConnective TissuesHannah Beatrice Adame TamayoNo ratings yet
- Sect 5Document25 pagesSect 5PuneetNo ratings yet
- SupermanDocument3 pagesSupermanGlen Michael F. WongNo ratings yet
- What Is Communication: What Is Communication MEANING OF COMMUNICATION: It Is Very Difficult To Define The TermDocument12 pagesWhat Is Communication: What Is Communication MEANING OF COMMUNICATION: It Is Very Difficult To Define The Termmanik ghoshNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document4 pagesBiology 1yvonne villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Me, Myself, and My Dream CareerDocument12 pagesMe, Myself, and My Dream CareerJed CameronNo ratings yet
- CAT 6040 Hydraulic Excavator Undercarriage Service TrainingDocument18 pagesCAT 6040 Hydraulic Excavator Undercarriage Service TrainingWillian Ticlia Ruiz100% (1)
- How to Improve Your Self-Motivation Through Self-Confidence, Positive Thinking, Goal Setting and EnvironmentDocument21 pagesHow to Improve Your Self-Motivation Through Self-Confidence, Positive Thinking, Goal Setting and EnvironmentRose Anne100% (1)
- FT-IR Analysis of Hock ProcessDocument4 pagesFT-IR Analysis of Hock ProcessmohsengolestanzadehNo ratings yet
- Standardized Recipes - Doc2Document130 pagesStandardized Recipes - Doc2epic failNo ratings yet
- Application Format For Child CustodyDocument2 pagesApplication Format For Child CustodyDHUP CHAND JAISWAL100% (3)
- World Health OrganizationDocument13 pagesWorld Health OrganizationVincent Ranara Sabornido100% (1)
- Fire Flow CalculationsDocument37 pagesFire Flow CalculationsAmy CurryNo ratings yet
- Contracts Summary: 601 Totaling $4.76 BillionDocument186 pagesContracts Summary: 601 Totaling $4.76 BillionJAGUAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Harvia Sauna: Glass, light and beautiful contrast – read more about the new Harvia Claro sauna on page 11Document36 pagesHarvia Sauna: Glass, light and beautiful contrast – read more about the new Harvia Claro sauna on page 11Kadiri Olanrewaju100% (1)
- Five Brothers and Their Mother's LoveDocument4 pagesFive Brothers and Their Mother's Lovevelo67% (3)
- Electricity Merit Badge Class 1 2017Document34 pagesElectricity Merit Badge Class 1 2017RoshanNo ratings yet
- Self Esteem and The Real Body ImageDocument12 pagesSelf Esteem and The Real Body ImageChy Alcarde50% (2)
- DARACLAR 9000HP Silica Brewery Case Study 2016-WebDocument7 pagesDARACLAR 9000HP Silica Brewery Case Study 2016-WebAlia ShabbirNo ratings yet
- MA Only Notice Explains Coverage ChangeDocument2 pagesMA Only Notice Explains Coverage ChangeAnonymous Zp7kAtNo ratings yet
- Slide BP Texas City RefineryDocument20 pagesSlide BP Texas City Refineryamaleena_muniraNo ratings yet
- Periodontal DiseaseDocument4 pagesPeriodontal Diseasemojako_badboysNo ratings yet
- Marketing Environment Analysis and Trends Impacting CompaniesDocument27 pagesMarketing Environment Analysis and Trends Impacting CompaniesSamoyed KalraNo ratings yet
- Cs Varnavrat Land SlideDocument7 pagesCs Varnavrat Land SlideBIJAY KRISHNA DASNo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping in Families With Deaf Children: Terri Feher-Prout University of PittsburghDocument12 pagesStress and Coping in Families With Deaf Children: Terri Feher-Prout University of PittsburghGolfiNo ratings yet
- Crop RotationsDocument19 pagesCrop RotationsSarwar M. RasheedNo ratings yet
- Spelling Bee WordsDocument3 pagesSpelling Bee WordsDana GomezNo ratings yet
- Acromegaly: Excess Growth Hormone SecretionDocument4 pagesAcromegaly: Excess Growth Hormone SecretionKavita PathakNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance at HavellsDocument16 pagesCorporate Governance at HavellsVishal Pundir100% (1)
- IB Student's Soil Systems GuideDocument7 pagesIB Student's Soil Systems GuideYohanes Sumantri RatnodiyantoNo ratings yet
- University of Groningen MagazineDocument14 pagesUniversity of Groningen MagazineKhanh Phuong PhamNo ratings yet