Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Daily Lesson Plan CSS 1
Daily Lesson Plan CSS 1
Uploaded by
kenneth llorente0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesOriginal Title
Daily Lesson Plan CSS 1.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan CSS 1
Daily Lesson Plan CSS 1
Uploaded by
kenneth llorenteCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
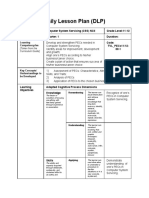
Daily Lesson Plan (DLP)
Learning Area: TLE Computer System Servicing (CSS) NCII Grade Level: 11-12
iPlan No.: 1 Quarter: 1 Duration:
Learning Discuss the relevance of the course; Explain Code:
Competency/ies: basic concepts, theories and core competencies TVL_PECS8/12-00-
[Taken from the in computer hardware servicing; Explore 1
Curriculum Guide] opportunities in computer hardware servicing as
a career
Key Concepts/ 1) Relevance of the course
Understandings 2) Basic concepts and core competencies in Computer System
to be Developed Servicing
3) Career opportunities
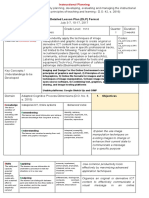
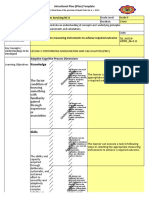
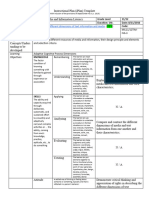
Learning Adapted Cognitive Process Dimensions
Objectives
Knowledge Remembering The learner can Recognize basic
The factor or condition recall information
and retrieve concepts,
of knowing something
with familiarity gained relevant underlying theories
knowledge from
through experience or
long-term
and core
association competencies in
memory: identify,
retrieve, computer systems
recognize,
duplicate, list,
and networks.
memorize,
repeat, describe,
reproduce
Understanding The learner can
construct
meaning from
oral, written and
graphic
messages:
interpret,
exemplify,
classify,
summarize, infer,
compare,
explain,
paraphrase,
discuss
Skills Applying The learner can Demonstrate
The ability and use information
to undertake a understanding of
capacity acquired
through deliberate, procedure in basic concepts,
familiar situations
systematic, and
or in a way:
underlying theories
sustained effort to and core
smoothly and execute,
adaptively carry out implement, competencies in
demonstrate,
complex activities or..
dramatize,
computer systems
the ability, coming
from one’s knowledge, interpret, solve, and networks.
practice, aptitude, etc., use, illustrate,
convert, discover
to do something Analyzing The learner can Distinguish quality
distinguish
between parts and marketable
and determine service in computer
how they relate
to one another,
hardware servicing
and the overall in terms of computer
structure and systems and
purpose:
differentiate,
networks
distinguish, installation, and
compare, diagnoses and
contrast,
organize, outline, troubleshoots
attribute, computer systems
deconstruct as prescribed by
TESDA Training
Regulations.
Evaluating The learner can
make judgments
and justify
decisions:
coordinate,
measure, detect,
defend, judge,
argue, debate,
describe,
critique,
appraise,
evaluate
Creating The learner can
put elements
together to form
a functional
whole, create a
new product or
point of view:
generate,
hypothesize,
plan, design,
develop,
produce,
construct,
formulate,
assemble, devise
Attitude A settled way of thinking or feeling Impart theories and
about someone or something, core competencies
typically one that is reflected in a
person’s behavior: in computer
systems and
networks in the web.
Values [RA 849]
· A learner principles or Maka-Diyos
standards of behavior;
one’s judgment of
what is important in Maka-tao
life.
· Go beyond learner’s
Makakalikasan
Makabansa
life on earth, include
more than wealth and
fame and would affect
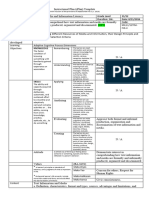
Resources Listing of all resources Book, computer system unit, projector, laptop,
needed
Needed internet, photocopy etc.
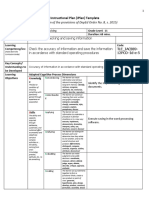
METHODOLOGY
Introductory Activity Concept mapping. Identify the icons related to
This part introduces the lesson content. Although computer tech and career.
at times optional, it is usually included to serve as
a warm-up activity to give the learners zest for the
incoming lesson and an idea about what it to
follow. One principle in learning is that learning
occurs when it is conducted in a pleasurable and
comfortable atmosphere.
Activity Group Activity. Recite keywords related to
This is an interactive strategy to elicit learner’s computer technology, career, marketable services
prior learning experience. It serves as springboard
for new learning. It illustrates the principle that etc.
learning starts where the learners are. Carefully 1. Can you recognize the use of computer in its
structured activities such as individual or group
assessment, dyadic or triadic interactions,
marketable services?
puzzles, simulations or role-play, cybernetics 2. Does the user connect to the internet using
exercise, gallery walk and the like may be created. his mobile gadgets?
Clear instructions should be considered in this
part of the lesson.
3. Can you use the computer in updating your
career opportunities?
4. What are the skills the users could develop in
Computer Hardware Servicing?
5. How importance Computer Hardware
Servicing business?
Analysis Peer-to-peer Activity. Ask and answer the following
Essential questions are included to serve as a questions:
guide for the teacher in clarifying key
understandings about the topic at hand. Critical 1. Does a computer technician know problems
points are organized to structure the discussion related to computer?
allowing the learners to maximize instructions and 2. If yes or no, why can you say it?
sharing of ideas and opinions about expected
issues. Affective questions are included to elicit 3. How computer helps the business industry?
the feelings of the learners about the activity or 4. In your own words, how your skills in
the topic. The last questions or points taken
should lead the learners to understand the new
computer could help you in establishing your
concepts or skills that are to be presented in the business?
next part of the lesson.
Abstraction Verse Recitation. Computer Skills can help build
This outlines the key concepts, important skills career opportunities, can help develop good ways in
that should be enhanced, and the proper attitude
that should be emphasized. This is organized as a computer hardware servicing, and can help find
lecturette that summarizes the learning ways of a fruitful course.
emphasized from the activity, analysis and new
inputs in this part of the lesson.
Application Pen & Paper Activity. Use One-half Crosswise and
This part is structured to ensure the commitment answer the following:
of the learners to do something to apply their new 1. Enumerate the skills competencies that can
learning in their own environment.
develop career opportunity.
2. State the relevance of the course in your
chosen career specialization.
Assessment Summative Test. Questionnaire is distributed and
For the Teacher to: one half lengthwise is used.
1. Assesses whether learning objectives have been
met for a specified duration Improvised Test Questions are derived from K to 12
2. Remediate and/or enrich with appropriate Basic Education Curriculum Technology and
strategies as needed Livelihood Education Grade 10 Information and
3. Evaluate whether learning intentions and
success criteria have been met Communications Technology authored by Rosalie
[Reminder: Formative Assessment may be given Lujero et. al. shall be administered by the teacher
before, during or after the lesson.]
Assignment Reinforcing/
Note: Fill-in any of the strengthening the
four purposes day’s lesson
Enhancing/
inspiring the day’
lesson
Preparing for the Make a research on Personal Entrepreneurial
new lesson Competencies PECs(PC)
Concluding Closing Quote. The teacher reads the quotation.
Activity The number one benefit of information technology is that it empowers
This is usually a brief people to do what they want to do. It lets people be creative. It lets people
but effective closing
activity such as a
be productive. It lets people learn things they didn't think they could learn
strong quotation, a before, and so in a sense it is all about potential.
short song, an By Steve Ballmer
anecdote, parable or a Read more at:
letter that inspires the
learners to do http://www.brainyquote.com/quotes/keywords/information_technology.html
something to practice
their new learning.
You might also like
- Agreement For An Easement of Right of WayDocument2 pagesAgreement For An Easement of Right of Wayjuvpilapil100% (45)
- United Nation PPT PresentationDocument37 pagesUnited Nation PPT PresentationDeo Emmanuel Aguillon90% (10)
- Investor Deck - Doctor Insta PDFDocument28 pagesInvestor Deck - Doctor Insta PDFSamarjit Samanta100% (3)
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper: Anthropological Foundations of Education in The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesReflection Paper: Anthropological Foundations of Education in The PhilippinesFajarito PamNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan CSS 2Document4 pagesDaily Lesson Plan CSS 2kenneth llorenteNo ratings yet
- Iplan No. 16 in Tle CssDocument5 pagesIplan No. 16 in Tle CssRgen Al VillNo ratings yet
- Perform Testing DocumentationDocument5 pagesPerform Testing DocumentationGerald E Baculna100% (1)
- Ict-9 LP SampleDocument2 pagesIct-9 LP Samplejohn kingNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Gerald E BaculnaNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document4 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- 2.5.1 Establish Information Requirements For Internet SearchDocument3 pages2.5.1 Establish Information Requirements For Internet Searchjayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan)Document6 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan)Earl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Principles in Performing Computer OperationsDocument3 pagesConcepts and Principles in Performing Computer Operationsjayson reyesNo ratings yet
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 08Document4 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 08Glycelle Urlanda MapiliNo ratings yet
- Milq2 LC7Document3 pagesMilq2 LC7Michael PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 15Document3 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 15Måřïä Ļà ĞŕëàthaNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Principles in Performing Computer OperationsDocument4 pagesConcepts and Principles in Performing Computer Operationsjayson reyesNo ratings yet
- CSS Lesson Plan Q1Document6 pagesCSS Lesson Plan Q1Kuyawan kulbaanNo ratings yet
- Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content CodeDocument9 pagesLearning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content CodeJuvyGonzalesNo ratings yet
- Iplan L3.2.2-ADocument4 pagesIplan L3.2.2-Ajayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Iplan L3.2.2Document4 pagesIplan L3.2.2jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 12Document4 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 12Glycelle Urlanda MapiliNo ratings yet
- IP of Subtraction of IntegersDocument4 pagesIP of Subtraction of IntegersAnonymous 45yUH2ONcTNo ratings yet
- Milq1 LC2Document4 pagesMilq1 LC2Paron MarNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 Iplan Lesson 2 LO2-1.1Document4 pages2.1.1 Iplan Lesson 2 LO2-1.1jayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Milq2 LC8Document5 pagesMilq2 LC8Michael PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideJoely E. De TorresNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Understanding SDocument3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Understanding SAnalie Imbing CabanlitNo ratings yet
- Knowledge: The Factor Condition of Knowing Something With Familiarity Gained Through Experience or AssociationDocument4 pagesKnowledge: The Factor Condition of Knowing Something With Familiarity Gained Through Experience or Associationjayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Media and Literacy DLP Q1 Week1 Day 2Document3 pagesMedia and Literacy DLP Q1 Week1 Day 2macgigaonlinestoreNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts CodeDocument3 pagesInstructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts Codejayson reyesNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts CodeDocument3 pagesInstructional Plan: Learning Area: Grade Level: Iplan No.: Quarter: Duration: Content Key Concepts Codejayson reyes100% (1)
- Speech Context and StylesDocument4 pagesSpeech Context and Stylestamara canalejaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan: (Taken From The Curriculum Guide)Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan: (Taken From The Curriculum Guide)raziel yuragNo ratings yet
- Milq1 LC2Document4 pagesMilq1 LC2Jennifer AlbaradoNo ratings yet
- Milq4 LC7Document2 pagesMilq4 LC7Maribel MarmitoNo ratings yet
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015marjunampoNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- Pe2 DLP Lesson 13Document4 pagesPe2 DLP Lesson 13Glycelle Urlanda MapiliNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document5 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Pangangan NHSNo ratings yet
- DLP FBS 5Document3 pagesDLP FBS 5Christine Rose Villanueva VargasNo ratings yet
- Milq2 LC9Document5 pagesMilq2 LC9renzmarion.penalesNo ratings yet
- Milq2 LC4Document6 pagesMilq2 LC4renzmarion.penalesNo ratings yet
- Instructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)Document3 pagesInstructional Plan (Iplan) : (With Inclusion of The Provision of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015)raziel yuragNo ratings yet
- Milq2 LC3Document5 pagesMilq2 LC3renzmarion.penalesNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Curriculum GuideJoely E. De TorresNo ratings yet
- With Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Document5 pagesWith Inclusion of The Provisions of Deped Order No. 8, S. 2015Wil-Ly de la CernaNo ratings yet
- Media-and-Literacy-DLP-Q1-Week2 Day-4Document4 pagesMedia-and-Literacy-DLP-Q1-Week2 Day-4macgigaonlinestoreNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q1 W4 D3 WhenIsWorkDoneDocument3 pagesScience8 Q1 W4 D3 WhenIsWorkDoneLenlen NamocNo ratings yet
- Milq2 LC7Document3 pagesMilq2 LC7renzmarion.penalesNo ratings yet
- Milq4 LC19Document3 pagesMilq4 LC19JOHN MC RAE RACINESNo ratings yet
- Instructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatDocument14 pagesInstructional Planning: Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) FormatTina VillaNo ratings yet
- Milq4 LC3Document5 pagesMilq4 LC3Maribel MarmitoNo ratings yet
- Knowledge: The Factor Condition of Knowing Something With Familiarity Gained Through Experience or AssociationDocument4 pagesKnowledge: The Factor Condition of Knowing Something With Familiarity Gained Through Experience or AssociationJamaica PondaraNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasNo ratings yet
- Stray Dog ManagementDocument9 pagesStray Dog Managementvware dNo ratings yet
- Nation Building SpeechDocument2 pagesNation Building SpeechAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Status 2nd FormatDocument26 pagesMaterial Status 2nd FormatMohamed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Halal Assurance Develop and ImpleementingDocument42 pagesHalal Assurance Develop and ImpleementingDaru KalokaNo ratings yet
- Subject:: DENR Administrative Order No. 2000-05 Series of 1994Document23 pagesSubject:: DENR Administrative Order No. 2000-05 Series of 1994geraldNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Science Crops SBA 2017-2018Document16 pagesAgricultural Science Crops SBA 2017-2018Ravin BoodhanNo ratings yet
- Exit Exam 10 4Document14 pagesExit Exam 10 4Yanyan Alfante100% (1)
- DLSAA Card Application FormDocument1 pageDLSAA Card Application FormJian CassiusNo ratings yet
- Phil HealthDocument92 pagesPhil HealthJoshua LoyolaNo ratings yet
- 12 Ways To Ask PermissionDocument2 pages12 Ways To Ask PermissionNico Pérez CamoteNo ratings yet
- Court of Ages Armistice and AccordDocument3 pagesCourt of Ages Armistice and AccordCindy Kay CurrierNo ratings yet
- Seeing With New EyesDocument2 pagesSeeing With New EyesdjubinvilleNo ratings yet
- Plaintiff,: Regional Trial CourtDocument5 pagesPlaintiff,: Regional Trial CourtRaffy Monencillo LafuenteNo ratings yet
- Adil Najam - Trade & EnvironmentDocument278 pagesAdil Najam - Trade & EnvironmentJack BagelzNo ratings yet
- George Kubler The Shape of Time Remarks On The History of Things 1 PDFDocument145 pagesGeorge Kubler The Shape of Time Remarks On The History of Things 1 PDFMarcela B. TavaresNo ratings yet
- Report of Work Done Jaydeep Mehta August 2016Document1 pageReport of Work Done Jaydeep Mehta August 2016api-193311681No ratings yet
- Online Healthcare Information Adoption Assessment Using Text Mining TechniquesDocument6 pagesOnline Healthcare Information Adoption Assessment Using Text Mining TechniquesRizqi AUNo ratings yet
- Construction Site Security Tips: Hanover Risk SolutionsDocument2 pagesConstruction Site Security Tips: Hanover Risk SolutionsjusticeNo ratings yet
- Saep 51Document39 pagesSaep 51Anonymous 4IpmN7OnNo ratings yet
- Vogel TulipDocument4 pagesVogel TulipAnonymous j6UCsdBPNo ratings yet
- Module 9Document4 pagesModule 9Quenie De la CruzNo ratings yet
- 5 Dance As A Competition-2021Document27 pages5 Dance As A Competition-2021Tricia Angela A. MunarNo ratings yet
- College Language Association CLA Journal: This Content Downloaded From 106.199.80.82 On Sat, 07 Apr 2018 12:00:47 UTCDocument12 pagesCollege Language Association CLA Journal: This Content Downloaded From 106.199.80.82 On Sat, 07 Apr 2018 12:00:47 UTCJINSHAD ALI K PNo ratings yet
- Perspective EssayDocument3 pagesPerspective Essayapi-393071505No ratings yet
- TESTING & Bem Guide 2018Document50 pagesTESTING & Bem Guide 2018Samir BounabNo ratings yet
- Curricular Statement: Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesCurricular Statement: Lesson PlanJacqueline ButlerNo ratings yet