Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet: by Via
Uploaded by
Johann Sebastian CruzOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet: by Via
Uploaded by
Johann Sebastian CruzCopyright:
Available Formats
Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet
by heatherisawesome (x0xheather_) via cheatography.com/41810/cs/12657/
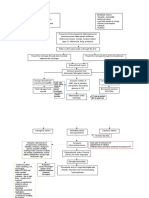
MENINGITIS LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT
Epidemiology/Facts Etiology
- 1.2 million cases every year worldwide - most common reason patients seek medical attention
-30% to 50% of survivors develop neurologic disabilities - pneumonia most common infectious cause of death in the US
- usually follows colonization of the upper respiratory tract with potential
Risk Factors
pathogens
- passive and active exposure to cigarette smoke
Pathophysiology
- children with cholera implants
- sickle cell disease - inhaled aerosolized particles
- URI, otitis media - enter lung via bloodstream from extra pulmonary infection
- alcoholism - aspiration of oropharyngeal contents
- immunosuppression
Organisms & Risk Factors
Organisms
Acute Bronchitis viral, self-limiting
- Strep pneumoniae (available vaccine)
Chronic Bronchitis environmental, bacterial
- Neisseria meningitidis (vaccine available)
- Haemophilus influenzae (vaccine available) Influenza
- Listeria monocytogenes (between 1 month and 60 years) Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV): newborns (baseline health status)
- Herpes Simplex Virus
CAP S.pneumonia
- West Nile Virus
H. flu
Infection process originates with nasopharyngeal colinations and N. Menin
translocation M. cattar
Signs/Symptoms HAP/HCAP S. aureus
- fever, chills, vomiting GNR
- headache, photophobia resistance
- nuchal rigidity Aspiration PNA oropharyngeal (CAP) + anaerobes
- Brudzinkski sign
- Kernig sign
- altered mental status, seizure
- lethargy, drowsiness
Diagnostics
- abnormal CSF chemistries
a.) elevated WBC count (>100 cells/mm3)
b.) elevated protein (>50 mg/dL)
c.) decreased glucose levels (<40 mg/dL)
- CSF gram stain & cultures
By heatherisawesome Published 2nd September, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(x0xheather_) Last updated 12th September, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
cheatography.com/x0xheather/ Page 1 of 5. https://apollopad.com
Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet
by heatherisawesome (x0xheather_) via cheatography.com/41810/cs/12657/
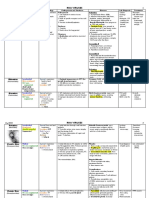
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT (cont) BONE AND JOINT INFECTION (cont)
Signs & Symptoms - elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein
(CRP), and white blood cell (WBC) count, positive blood cultures, synovial
- cough
build analysis (increased WBC, cultures)
- coryza
- rhinitis - bone changes observed on radiographs 10-14 days after the onset of
- sore throat infection
- malaise - contrasted CT scans positive even sooner
- fatigue
- headache
INTRA-ABDOMINAL INFECTION
- fever
- fever rhonchi Pathophysiology
- coarse bilateral rales - Defect in the GI tract (polymicrobic)
- wheezing purulent sputum - Necrotizing pancreatitis (polymicrobic)
- hemoptysis
- Perforated ulcer (polymicrobic)
- chest pain - Appendicitis (polymicrobic)
- dense infiltrate on CXR (pneumonia only) - Penetrating trauma (polymicrobic)
- increased WBC - IBD (polymicrobic)
- WBC
- Peritoneal dialysis (eg: staphylococcus auerus)
- decreased O2 saturation
- labored breathing - Cirrhosis (eg: e. coli)
- tachycardia Signs & Symptoms
- tachypnea
- Fever
Diagnostics - Hypoactive bowel sounds
- sputum gram stain & cultures - Abdominal distension/tenderness
- rapid flu swabs - Nausea/vomiting
CXR - Elevated WBC
- Hypovolemic shock
BONE AND JOINT INFECTION - Ascites fluid (eg: high WBC, high protein, gram stain)
Organisms
Osteomyelitis & infectious arthritis Staphylococcus aureus (usually)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
streptococcus
e. coli
staphylococcus epidermis
anaerobes all can be isolated
Hematogenous vs. contiguous spread
Signs & Symptoms
- significan tenderness, pain, swelling, fever, chills, decreased motion, and
malaise
By heatherisawesome Published 2nd September, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(x0xheather_) Last updated 12th September, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
cheatography.com/x0xheather/ Page 2 of 5. https://apollopad.com
Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet
by heatherisawesome (x0xheather_) via cheatography.com/41810/cs/12657/
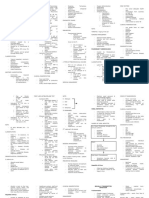
URINARY TRACT INFECTION UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
Patho & Organisms Epidemiology
- E. coli (85%) - most URI's have a viral etiology and resolved spontaneously
- Staph saprophyticus a.) sinusitis, pharyngitis, otitis
- Proteus spp. b.) symptoms lasting more than 7 days = bacterial?
- Klebsiella spp. - antibiotic use puts recipient at increased risk of selection/carriage of
- pseudomonas aeruginosa resistant organisms and future antibiotic failure
- enterococcus - bacterial infection may follow viral infection
- Recurrent UTIs (reinfection more than two weeks apart) Otitis
- Relapse less than two weeks (due to unsuccessful treatment, resistant
- day-care attendance
organisms, anatomical abnormalities)
- recent antibiotic exposure
Risk Factors - age younger than 2 years
Uncomplicated Often post-coital; healthy adult female - frequent bouts of otitis media
- often follows viral nasopharyngeal infection that causes eustachian tub
Complicataed Male, kids dysfunction
Diabetes - otalgia, fever, irritability, tugging ears, discolored (grey), thickened,
Immunocompromised bulging eardrum
Pregnancy - S. pneumoniae
Device-related (foley catheter) - H. influenzae
Menopause - M. catarrhalis
Lower UTI Signs/Symptoms (Cystic) - S. aureus
- S. progenies
- Dysuria
- P. aeruginosa
- Urgency
- Frequency Sinusitis
- Nocturia - nasal discharge/congestion
- Suprapubic heaviness - maxillary tooth pain
- Hematuria - facial or sinus pain that may radiate
Upper UTI Signs/Symptoms (Pyelonephritis) - cough
- nasal discharge
- Systemic symptoms
- often follows visual URI that leads to inflamed nasal passages, trapping
- Fever
bacterial in sinuses
- Nausea
- chronic/recurrent infections occur three to four times a year
- Vomiting
- S. pneumoniae and H. influenza
- Flank pain
Pharyngitis
Diagnostics (Urinalysis)
- Significant bacteriuria
- > 100,000 (10^5)/mL
- > 10^2/mL + symptoms
- RBCs
- WBCs
- Nitrites
By heatherisawesome Published 2nd September, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(x0xheather_) Last updated 12th September, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
cheatography.com/x0xheather/ Page 3 of 5. https://apollopad.com
Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet
by heatherisawesome (x0xheather_) via cheatography.com/41810/cs/12657/
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS (cont) SKIN & SOFT TISSUE INFECTION
- viruses, group A strep, S. pyogenes Organisms
- seasonal outbreaks occur in winter and early spring, spread via direct
Folliculitis, furnucles Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
contact with droplets
(boils), and carbuncles*
- sore throat, odynophagia, fever, headache
- erythma/inflammation of the tonsils and pharynx with or without patch Erysipelas Streptococcus pyogenes
exudates Impetigo* Staphylococcus aureus
- enlarged, tender lymph nodes
Lymphangitis S. pyogenes
- red swollen uvula
- petechiae on the soft palate Cellulitis S. pyogenes and S. aureus
- rapid antigen test for GAS
Necrotizing Faciitis S. progenes
Diabetic Foot Infections, Staphylococci, streptococci, enteric gram
ENDOCARDIDTIS
Decubitus Ulcers negative bacilli, and anaerobes
Organisms & Risk Factors
HUman/Animal Bite Pasteurella multocida, eikenella
- Cardia valve abnormalities: regurgutation, prosthetic heart valves Wounds ocrrodens, S. aureus, and anaerobes
- intravenous drug abuse
* Highly Contagious *
- viridian's streptococci
Notes
- Streptococcus bovis
- Staphylococcus aureus - use caution with "spider bites"
- fungal - many of these infections originate as minor trauma, scratches (soap and
- HACEK: haemophilus, aggregatibacter, cardiobacterium, eikenella water)
corrodens, kingella - predisposing factors: diabetes mellitus, local trauma or infection, recent
surgery
Diagnostics
- MRSA tips: transmission on fomites
- persistent bacteremia/fungemia
- echocardiography: valvular vegetation
Signs/Symptoms
- fever & murmur
- osler nodes
- infective emboli: renal, pulmonary, CNS
By heatherisawesome Published 2nd September, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(x0xheather_) Last updated 12th September, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
cheatography.com/x0xheather/ Page 4 of 5. https://apollopad.com
Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections Cheat Sheet
by heatherisawesome (x0xheather_) via cheatography.com/41810/cs/12657/
GASTROINTESTINAL INFECTION SEPSIS
Key Facts Definition: life-threatening organ dysfunction due to a dysregulated host
response to infection; it arises when the body's response to an infection
Diarrhea is eg: E. coli
injures its own tissues and organs
Usually Viral eg: Shigella
eg: campylobacter Infection + Quick Sepsis Organ Failure Assessment
eg: salmonella
Altered Mental Status GSC < 15
eg: clostridium
Fast Respiratory Rate > 22 BPM
Patient education & prevention strategies are key
Low Blood Pressure < 100 SBP
eg: traveller's diarrhea
eg: food poisoning Increased O2 Consumption
eg: vaccination
Decreased O2 Delivery
Pathophysiology: inflammatory secretion Procalcitonin Levels
Signs/Symptoms
Healthy 0.01
- nausea
Local Infection 0.1 - 0.5
- abdominal pain
Systemic Infection 0.5 - 2.0
- cramping
- bloating Severe Sepsis 2.0 - 10
- dehydration Septic Shock > 10
fever
C-Reactive Protein (mg/L)
- frequent urge to evacuate
- fever blood & severe dehydration Minor Infection 10 - 20
Risk Factors Moderate Infection 20- 50
- ingestion of raw or undercooked seafood (eg: vibrio cholera or Severe Infection > 50
noroviruses)
- use of antibiotics (eg: c. diff)
- use of PPI
- travel to tropical areas(eg: parasitic infections like guard, entamoeba,
strongyloides, and cryptosporidium)
- travel to endemic areas (eg: vibrio cholera)
By heatherisawesome Published 2nd September, 2017. Sponsored by ApolloPad.com
(x0xheather_) Last updated 12th September, 2017. Everyone has a novel in them. Finish Yours!
cheatography.com/x0xheather/ Page 5 of 5. https://apollopad.com
You might also like
- X0xheather - Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections PDFDocument5 pagesX0xheather - Pathophysiology of Bacterial Infections PDFAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- S. Aureus Pneumonia Often Complicates Illness Caused by Influenza VirusesDocument14 pagesS. Aureus Pneumonia Often Complicates Illness Caused by Influenza VirusesRia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MBL 1 Bacterial PneumoniaDocument5 pagesMBL 1 Bacterial PneumoniaFadhlina OmarNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Tests and Pneumonia DiagnosisDocument7 pagesLower Respiratory Tests and Pneumonia DiagnosisSofronio OmboyNo ratings yet
- (4.1) Meningitis & EncephalitisDocument36 pages(4.1) Meningitis & EncephalitisFarhaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial PneumoniaDocument4 pagesBacterial PneumoniaPabinaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobials Drugs: Dr. Mohammed Al-KhawlaniDocument19 pagesAntimicrobials Drugs: Dr. Mohammed Al-Khawlaniخالد الشرعبيNo ratings yet
- Anchalee Pulmonary Manifestation in AIDSDocument105 pagesAnchalee Pulmonary Manifestation in AIDSsuho exoNo ratings yet
- Meningitis Risk Factors and TreatmentDocument2 pagesMeningitis Risk Factors and Treatmentedrian02No ratings yet
- Adult Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Infectious DiseasesDocument163 pagesAdult Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Infectious DiseasesRuthaliya IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Harrison ManuallDocument105 pagesHarrison Manuallale maril100% (1)
- 1.acute Respiratory Disease: DDX: Kawasaki, Strep. InfectionDocument5 pages1.acute Respiratory Disease: DDX: Kawasaki, Strep. InfectionSheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- IM PULMO - PneumoniaDocument9 pagesIM PULMO - PneumoniaJorelyn FriasNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: DR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,Spp.,Dtce.,Mars Fk-Uwk, 1 April 2011Document42 pagesPneumonia: DR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,Spp.,Dtce.,Mars Fk-Uwk, 1 April 2011Nurfatin adilah kamarudinNo ratings yet
- Preventive and Social MedicineDocument14 pagesPreventive and Social MedicineSuresh GuduruNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: DR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,Spp.,Dtce.,Mars Fk-Uwk, 1 April 2011Document35 pagesPneumonia: DR - Dr. Tahan P.H.,Spp.,Dtce.,Mars Fk-Uwk, 1 April 2011IqbalRazifNo ratings yet
- 6.pneumonia (New)Document104 pages6.pneumonia (New)Ryana Fitriana IINo ratings yet
- Cytotoxic Killing Cell Apoptosis. F Liver Inflammation Liver Damage 1-6 MONTHSDocument21 pagesCytotoxic Killing Cell Apoptosis. F Liver Inflammation Liver Damage 1-6 MONTHSKyla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Medicine & Pediatric SMLE Notes: Key Points for ExamsDocument23 pagesMedicine & Pediatric SMLE Notes: Key Points for Examsanmar alkhudhri100% (1)
- Salmonela Thyposa: Disease Etiology Unique S&S Brief Patophysiology Diagnostic Treatment / Plan OthersDocument8 pagesSalmonela Thyposa: Disease Etiology Unique S&S Brief Patophysiology Diagnostic Treatment / Plan OthersNatalia_WiryantoNo ratings yet
- Pathogens That Involve The Respiratory TractDocument28 pagesPathogens That Involve The Respiratory TractLeeShauran100% (2)
- Bronsiolita Pneumonia Comunitara Pneumonii AtipiceDocument49 pagesBronsiolita Pneumonia Comunitara Pneumonii AtipiceTeodora LupuNo ratings yet
- ncm112 FinalsDocument18 pagesncm112 FinalsAbegail MierNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument3 pagesTuberculosisJennyu YuNo ratings yet
- Important Terms - Tropical InfectionDocument8 pagesImportant Terms - Tropical InfectionTimothy JordanNo ratings yet
- Fever of Unknown Origin - Clinical Overview of Classic - and - Current ConceptsDocument20 pagesFever of Unknown Origin - Clinical Overview of Classic - and - Current ConceptsPedro Luz da RosaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology PinkDocument3 pagesMicrobiology PinkBenjamin GaliaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Microbiology GuideDocument15 pagesPneumonia Microbiology GuidepuniariNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Diagnosis, Types, Pathogenesis & TreatmentDocument78 pagesPneumonia Diagnosis, Types, Pathogenesis & Treatment404notfoundNo ratings yet
- Cns Infections MbbsDocument40 pagesCns Infections MbbsSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Report Pathophysiology Problem-Based Learning Case 1Document5 pagesReasoning Report Pathophysiology Problem-Based Learning Case 1Yen ChouNo ratings yet
- Sweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesDocument7 pagesSweat Chloride Test: 1. Splenic Rupture 2. Avoid Sports and Physical Activity 3. Atypical LymphocytesAnonymous GfqHQ5SNwNo ratings yet
- Rna Viruses: EnterovirusDocument4 pagesRna Viruses: EnterovirusYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- 1 Urtd+eviDocument76 pages1 Urtd+eviIfabiyi OlaniyiNo ratings yet
- Approach to PUO: What's New in 2020Document9 pagesApproach to PUO: What's New in 2020RONALDO OSIRIS CRUZ ALFARONo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases: Bacteria, Viruses, Mycetes & ParasitesDocument137 pagesInfectious Diseases: Bacteria, Viruses, Mycetes & ParasitesWendielynne MillomedaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PresentationDocument23 pagesPneumonia Presentationapi-546694141No ratings yet
- 4e8ae48410.TERAPI ISPA DAN ISPBDocument56 pages4e8ae48410.TERAPI ISPA DAN ISPBAbd HarisNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and Associated DiseasesDocument7 pagesBacteria and Associated DiseasesAhmed ALiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Infectious DiseasesDocument407 pagesSummary of Infectious DiseasesMh HmNo ratings yet
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Document29 pagesHuman Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)Stiffany GlenNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors, Signs, Symptoms and Management of InfluenzaDocument8 pagesRisk Factors, Signs, Symptoms and Management of InfluenzaAila HinlogNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 1 NotesDocument11 pagesMed Surg 1 NotesMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- Safe Handling, Packaging & Shipping of Infectious SubstancesDocument96 pagesSafe Handling, Packaging & Shipping of Infectious SubstancesGeoffrey RufinNo ratings yet
- Summary of Infectious DiseasesDocument415 pagesSummary of Infectious DiseasesAlston Foods BVNo ratings yet
- Pertussis, Meningococcal meningitis, Strept pharyngitis, Diphtheria, Pulmonary TBDocument14 pagesPertussis, Meningococcal meningitis, Strept pharyngitis, Diphtheria, Pulmonary TBAhmed MansourNo ratings yet
- Exposures and Nursing Care for Pneumonia in ChildrenDocument1 pageExposures and Nursing Care for Pneumonia in ChildrenAlcala, Mariaden A.100% (1)
- Infection (Course)Document72 pagesInfection (Course)Asmaa RagabNo ratings yet
- Bakteri SSPDocument69 pagesBakteri SSPCiendy ShintyaNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument65 pagesMeningitisA. Pathak100% (7)
- Enterococci: S. AureusDocument2 pagesEnterococci: S. AureusShift UallNo ratings yet
- Chronic Dry CoughDocument119 pagesChronic Dry CoughUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 13 Respiratory Infectious DiseasesDocument12 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 13 Respiratory Infectious DiseasesViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia and Hospital-Acquired PneumoniaDocument15 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia and Hospital-Acquired PneumoniafaisalNo ratings yet
- Week 1 TropMedDocument96 pagesWeek 1 TropMedmyqurandiaryNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 1Document28 pagesRespiratory 1Howell MathewNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Diagnosis and PathogenesisDocument104 pagesPneumonia Diagnosis and PathogenesissallykartikaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology MnemonicsFritzel SusbillaNo ratings yet
- NTG Reviewer '13Document413 pagesNTG Reviewer '13RuiVanNo ratings yet
- Neurologic ExaminationDocument6 pagesNeurologic ExaminationJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- PDF Thomason CapstoneDocument10 pagesPDF Thomason CapstoneJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Correia Balance Outcome MeasDocument28 pagesCorreia Balance Outcome MeasJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- God's Prayer for Serenity, Courage and WisdomDocument1 pageGod's Prayer for Serenity, Courage and WisdomJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- 210wk7massage PDFDocument30 pages210wk7massage PDFMileNo ratings yet
- Compression Rubric PDFDocument1 pageCompression Rubric PDFJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- SR Iv PDFDocument8 pagesSR Iv PDFJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument5 pagesWelcomeCatNo ratings yet
- Fma Ue English PDFDocument3 pagesFma Ue English PDFnistaraNo ratings yet
- PT 1 Midterm RubricDocument3 pagesPT 1 Midterm RubricJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Medicine The American Journal of SportsDocument7 pagesMedicine The American Journal of SportsJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy Modalities PDFDocument31 pagesPhysical Therapy Modalities PDFArjun S RajNo ratings yet
- Principles of ChartingDocument7 pagesPrinciples of ChartingJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- WelcomeDocument5 pagesWelcomeCatNo ratings yet
- SR OF CVsDocument16 pagesSR OF CVsJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Stroke Impact Scale SISDocument6 pagesStroke Impact Scale SISJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- PT research manual week 1 tasksDocument5 pagesPT research manual week 1 tasksJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- KINESIOLOGY - Carmina Cortez, MD - September 27, 2017Document9 pagesKINESIOLOGY - Carmina Cortez, MD - September 27, 2017Johann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- RA 7277 - Magna Carta of Disabled PersonsDocument18 pagesRA 7277 - Magna Carta of Disabled PersonsVanny Joyce Baluyut100% (3)
- The Skeletal & Articular SystemsDocument11 pagesThe Skeletal & Articular SystemsJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Hispanic CultureDocument76 pagesHispanic CultureJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Final MD HGD ReportDocument100 pagesFinal MD HGD ReportJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck - MusclesDocument3 pagesHead and Neck - MusclesJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- The Ability of The Landing Error Scoring System To Detect Changes in Landing Mechanics: A Critically Appraised TopicDocument9 pagesThe Ability of The Landing Error Scoring System To Detect Changes in Landing Mechanics: A Critically Appraised TopicJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- The African American Culture: An OverviewDocument61 pagesThe African American Culture: An OverviewJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy Ethics - Gabard, Donald L. (SRG)Document210 pagesPhysical Therapy Ethics - Gabard, Donald L. (SRG)Eva Bella93% (15)
- Medicine The American Journal of SportsDocument7 pagesMedicine The American Journal of SportsJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Description PDFDocument1 pageDescription PDFJohann Sebastian CruzNo ratings yet
- Pelaksanaan Perawatan Luka Post Operasi Sectio Caesarea Sesuai Standar Operasional ProsedurDocument9 pagesPelaksanaan Perawatan Luka Post Operasi Sectio Caesarea Sesuai Standar Operasional Prosedural ghaisaniNo ratings yet
- ICPR 5 1 WebDocument96 pagesICPR 5 1 WebAndreea-Luciana UrzicăNo ratings yet
- Hazard Awareness Training PresentationDocument29 pagesHazard Awareness Training Presentationutibe_7No ratings yet
- Cholera Mindmap: Understanding The Disease, Symptoms, and PreventionDocument1 pageCholera Mindmap: Understanding The Disease, Symptoms, and PreventionUlysse BerraNo ratings yet
- F. FeasibilityDocument2 pagesF. Feasibilitypatricia gunioNo ratings yet
- V154 BSBLDR602 Assessment Task - 1Document3 pagesV154 BSBLDR602 Assessment Task - 1Briyidt Alejandra CaroNo ratings yet
- CBTDocument2 pagesCBTTanvi ManjrekarNo ratings yet
- Leyna Slivka-5Document1 pageLeyna Slivka-5api-490419585No ratings yet
- An Introduction To API 653 PDFDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To API 653 PDFGiorgi KOGOSHVILINo ratings yet
- Hand Radiology ABC PDFDocument4 pagesHand Radiology ABC PDFJames Carvajal AcostaNo ratings yet
- Metallic BiomaterialsDocument34 pagesMetallic BiomaterialsHarshil Dave100% (1)
- Effects of Smoking on Lung CapacityDocument9 pagesEffects of Smoking on Lung CapacityMohammad MashhoodNo ratings yet
- IFEA IES Endodontic and Dental Practice During COVID-19Document24 pagesIFEA IES Endodontic and Dental Practice During COVID-19Mohammed TarekNo ratings yet
- Anna University Industrial Relations Question Bank BA7034Document45 pagesAnna University Industrial Relations Question Bank BA7034Shupiksha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- BRAC Internship ApplicationDocument4 pagesBRAC Internship ApplicationShahanaj S. TanniNo ratings yet
- Peh 11 FidpDocument15 pagesPeh 11 FidpCris SimonNo ratings yet
- Geriatrics QuestionsDocument3 pagesGeriatrics QuestionsMary JaneNo ratings yet
- Empirical Treatment of Sepsis in AdultsDocument11 pagesEmpirical Treatment of Sepsis in AdultsMarnia SulfianaNo ratings yet
- Academic style nominalisationDocument2 pagesAcademic style nominalisationJamie Leigh McGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Films that bring the issue of waste to lightDocument7 pagesFilms that bring the issue of waste to lightLaudianeSant'AnnaNo ratings yet
- Capitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityDocument2 pagesCapitol University: College of Nursing Cagayan de Oro CityChaine Agolito100% (1)
- Folate Vit B12 AccuBind VAST ELISA Rev2Document4 pagesFolate Vit B12 AccuBind VAST ELISA Rev2Clari MalpartidaNo ratings yet
- Secrets To Write For The Self-Help MarketDocument14 pagesSecrets To Write For The Self-Help Marketobaidullah omerNo ratings yet
- Care Plan: Assessment DataDocument15 pagesCare Plan: Assessment Dataapi-509452165No ratings yet
- History of Medical Technology: From Ancient Diagnostics to Modern Lab MedicineDocument5 pagesHistory of Medical Technology: From Ancient Diagnostics to Modern Lab MedicineJose KruzNo ratings yet
- Has The Philippines Undergone The Demographic TransitionDocument2 pagesHas The Philippines Undergone The Demographic TransitionKaren Recla100% (10)
- Lutz, Nutrition and Diet Therapy 6e ETBDocument15 pagesLutz, Nutrition and Diet Therapy 6e ETBShelly-ann Richards-FrancisNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Public Health Research and DevelopmentDocument1 pageIndian Journal of Public Health Research and DevelopmentNusa karya engineeringNo ratings yet
- At The Dentist British English StudentDocument4 pagesAt The Dentist British English StudentАнгелина СветличнаяNo ratings yet
- FICHA TECNICA Thinner No. 36 (Preliminary)Document2 pagesFICHA TECNICA Thinner No. 36 (Preliminary)Cesar Augusto Cama SaitoNo ratings yet
- Breaking the Habit of Being YourselfFrom EverandBreaking the Habit of Being YourselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1456)
- The Happiest Baby on the Block: The New Way to Calm Crying and Help Your Newborn Baby Sleep LongerFrom EverandThe Happiest Baby on the Block: The New Way to Calm Crying and Help Your Newborn Baby Sleep LongerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- How to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipFrom EverandHow to Talk to Anyone: Learn the Secrets of Good Communication and the Little Tricks for Big Success in RelationshipRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1135)
- Deep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!From EverandDeep Sleep Meditation: Fall Asleep Instantly with Powerful Guided Meditations, Hypnosis, and Affirmations. Overcome Anxiety, Depression, Insomnia, Stress, and Relax Your Mind!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Summary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissFrom EverandSummary of The 4-Hour Body: An Uncommon Guide to Rapid Fat-Loss, Incredible Sex, and Becoming Superhuman by Timothy FerrissRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (81)
- Really Very Crunchy: A Beginner's Guide to Removing Toxins from Your Life without Adding Them to Your PersonalityFrom EverandReally Very Crunchy: A Beginner's Guide to Removing Toxins from Your Life without Adding Them to Your PersonalityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (27)
- The Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityFrom EverandThe Stress-Proof Brain: Master Your Emotional Response to Stress Using Mindfulness and NeuroplasticityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (109)
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouFrom EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- 369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESFrom Everand369: Manifesting Through 369 and the Law of Attraction - METHODS, TECHNIQUES AND EXERCISESRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (50)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Creation Frequency: Tune In to the Power of the Universe to Manifest the Life of Your DreamsFrom EverandThe Creation Frequency: Tune In to the Power of the Universe to Manifest the Life of Your DreamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (549)
- Body Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomFrom EverandBody Love Every Day: Choose Your Life-Changing 21-Day Path to Food FreedomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Allen Carr's Easy Way to Quit Vaping: Get Free from JUUL, IQOS, Disposables, Tanks or any other Nicotine ProductFrom EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way to Quit Vaping: Get Free from JUUL, IQOS, Disposables, Tanks or any other Nicotine ProductRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (31)
- Deep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingFrom EverandDeep Sleep Hypnosis: Guided Meditation For Sleep & HealingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (103)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingFrom EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- Allen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodFrom EverandAllen Carr's Easy Way for Women to Lose Weight: The original Easyway methodRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Bedtime Stories for Adults: Tales to Soothe the Tired SoulsFrom EverandBedtime Stories for Adults: Tales to Soothe the Tired SoulsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Ikigai Journey: A Practical Guide to Finding Happiness and Purpose the Japanese WayFrom EverandThe Ikigai Journey: A Practical Guide to Finding Happiness and Purpose the Japanese WayRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (27)
- The Self-Care Solution: A Year of Becoming Happier, Healthier, and Fitter—One Month at a TimeFrom EverandThe Self-Care Solution: A Year of Becoming Happier, Healthier, and Fitter—One Month at a TimeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- The Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeFrom EverandThe Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (13)
- Midnight Meditations: Calm Your Thoughts, Still Your Body, and Return to SleepFrom EverandMidnight Meditations: Calm Your Thoughts, Still Your Body, and Return to SleepRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingFrom EverandThe Food Lover's Cleanse: 140 Delicious, Nourishing Recipes That Will Tempt You Back into Healthful EatingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Glucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarFrom EverandGlucose Revolution: The Life-Changing Power of Balancing Your Blood SugarRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (349)