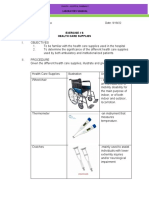
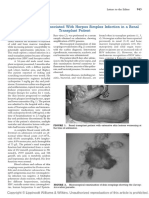
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
478 views9 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines
Here are the answers to the questions:
1. The signs and symptoms associated with toxic alcohol exposures differ based on the specific alcohol ingested:
- Ethylene glycol: signs include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, CNS depression. Metabolic acidosis and kidney failure can occur.
- Isopropanol: signs include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, CNS depression including dizziness. Respiratory depression is less common.
- Methanol: signs include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, visual disturbances including blurring of vision, CNS depression. Metabolic acidosis, blindness and death can occur.
2. The active chemicals in the following cosmetics are:
a. Cold wave lotion: Am
Uploaded by
Ashley DayagCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
478 views9 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines
Here are the answers to the questions:
1. The signs and symptoms associated with toxic alcohol exposures differ based on the specific alcohol ingested:
- Ethylene glycol: signs include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, CNS depression. Metabolic acidosis and kidney failure can occur.
- Isopropanol: signs include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, CNS depression including dizziness. Respiratory depression is less common.
- Methanol: signs include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, visual disturbances including blurring of vision, CNS depression. Metabolic acidosis, blindness and death can occur.
2. The active chemicals in the following cosmetics are:
a. Cold wave lotion: Am
Uploaded by
Ashley DayagCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd