0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views23 pagesFire Extinguishing Systems on Ships
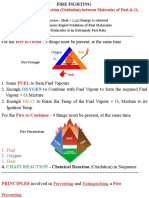
This document provides information on various fire protection systems used on ships. It discusses water firefighting systems, including their components, operation, and requirements. It also describes sprinkler systems, water spray systems, steam extinguishing systems, and powder fire extinguishing systems. The document outlines different types of gaseous fire suppression systems, including carbon dioxide and inert gas systems. It explains how these systems work to reduce oxygen levels and suppress combustion. Requirements for firefighting system capacities according to vessel type and size are also mentioned.
Uploaded by
vincentCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
72 views23 pagesFire Extinguishing Systems on Ships
This document provides information on various fire protection systems used on ships. It discusses water firefighting systems, including their components, operation, and requirements. It also describes sprinkler systems, water spray systems, steam extinguishing systems, and powder fire extinguishing systems. The document outlines different types of gaseous fire suppression systems, including carbon dioxide and inert gas systems. It explains how these systems work to reduce oxygen levels and suppress combustion. Requirements for firefighting system capacities according to vessel type and size are also mentioned.
Uploaded by
vincentCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd