Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(Système International D'Unités) : 'Technical Data
Uploaded by
ilo iloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(Système International D'Unités) : 'Technical Data
Uploaded by
ilo iloCopyright:
Available Formats
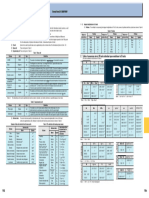
’TECHNICAL DATA»
SI(SYSTÈME INTERNATIONAL D’UNITÉS)EXCERPT FROM JIS Z 8203(1985)
1.International units SI and the method of use 1-3. Integral multiplication in SI units
1-1. Sphere of application This standard specifies how to use the International System of Units(SI)and other international unitary systems, Prefixes The multiple for composing the integral multiplication of 10 in SI units, names of prefixed and their symbols are shown in Table 4.
as well as units used in correlation with units from international systems, and other units which may be used. Table 4. Prefixes
1-2. Terminology and definitions Terminology used in this specification and definitions thereof are as follows: Multiple to be Prefixes Multiple to be Prefixes Multiple to be Prefixes
(1)International System Coherent system of units adopted and recommended by the International Committee on Weights and combined with unit Name Sign combined with unit Name Sign combined with unit Name Sign
of Units(SI) Measures. It contains base units and supplementary units,units derived from them, and their integral
exponents to the 10th power. 10 18 Exsa E 10 2 Hect h 10 -9 Nano n
(2)SI unit SI is the abbreviation of Systeme International d'Unites(International System of Units)
. 10 15 Peta P 10 Deca da 10-12 Pico p
10 12 Tera T 10-1 Deci d 10-15 Femt f
(3)Base unit Those units given in Table 1. 10 9 Giga G 10-2 Centi c 10-18 Ato a
(4)Supplementary unit Those units given in Table 2. 10 6 Mega M 10-3 Milli m
10 3 Kilo k 10-6 Micro O
Table 1. Base unit
Volume Unit Sign Definition 2.Table of conversion rate of JIS units attendant upon switchover to SI units
The units contained in bold lines are SI units.
Length Meter m The meter is the distance light travels in 1/299,792,458 of a second in a vacuum.
N dyn kgf PaCs cP P
The kilogram is a unit of mass(not weight nor force) , equal to the mass
Mass Kilogram kg
Viscosity
of an international prototype stored in Sevres, France. 1 1M10 5 1.019 72M10 -1 1 1M10 3 1M10
Force
Time Second s
The second is a fundamental unit of time, equal to 9, 192, 631, 770 periods of radiation corresponding 1M10-5 1 1.019 72M10 -6 1M10-3 1 1M10-2
to the transition between two superfine levels of the ground state of an atom of cesium-133.
9.806 65 9.806 65M10 5
1 1M10-1 1M10 2 1
The ampere is a unit of electric current, defined as a 2M10-7newton force of attraction
Electric current Ampere A exerted at 1 meter intervals between two parallel current-carrying linear conductors 2
Note)1P=1dynCs/cm =1g/cmCs
that are infinitely small in circular cross-sectional area and infinitely long in length. 2
The kelvin is a unit of absolute temperature equal to 1/273.16 of the absolute 1PaCs=1NCS/m, 1cP=1mPaCs
Thermodynamic Kelvin K
temperature temperature of the triple point of water.
Pa or N/m 2 MPa or N/mm 2 kgf/mm 2 kgf/cm 2 m 2 /s cSt St
The mole is the amount of substance of a system(with a specific composition)which contains
Amount
Kinematic
viscosity
of substance Mole mol as many elementary units(1)as there are atoms of carbon in 0.012 kilogram of pure nuclide 1 1M10-6 1.019 72M10 -7 1.019 72M10 -5 1 1M10 6 1M10 4
carbon12. The mole is used to specify both the elementary unit and system.
Stress
1M10 6 1 1.019 72M10 -1 1.019 72M10 1M10 -6 1 1M10-2
The candela is a unit of luminous intensity, defined as the luminous intensity of
Luminous Candela cd a steradian light source which emits a monochrome radiation at a frequency 6 2 1M10 -4
1M10 2
1
intensity 9.806 65M10 9.806 65 1 1M10
of 540M1012 Hz, in a specified direction and at a force equal to 1/683 watts.
9.806 65M10 4 9.806 65M10 -2 1M10-2 1 Note)1St=1cm 2 /s, 1cSt=1mm/S 2
Note(1): The elementary unit must be specified and must be an atom, molecule, ion, electron, photon or a specified group of such units.
Note)1Pa=1N/m2, 1Mpa=1N/mm2
Table 2. Supplementary unit
Volume Unit Sign Definition
mmHg
Plane angle Radian rad The radian is a unit of plane angle, defined as the central angle of a circle Pa kPa MPa bar kgf/cm 2 atm mmH 2 0 or
determined by two radii and an arc joining them, all of the same length. Torr
The steradian is the unit of measurement for solid angles, equal to the solid angle subtended center of a 1 1M10 -3 1M10 -6 1M10 -5 1.019 72M10 -5 9.869 23M10 -6 1.019 72M10 -1 7.500 62M10 -3
Solid angle Steradian sr
sphere by a portion of the surface of the sphere whose area equals the square of the sphere's radius.
3 -3 -2 -2 -3 2
1M10 1 1M10 1M10 1.019 72M10 9.869 23M10 1.019 72M10 7.500 62
(5)
Pressure
Derived units The units of derived quantity in International units. Those are expressed algebraically in terms of the base
units and supplementary units. Besides, the derived units that have proper names are shown in Table 3. 1M10 6 1M10 3 1 1M10 1.019 72M10 9.869 23 1.019 72M10 5 7.500 62M10 3
1M10 5 1M10 2 1M10 -1 1 1.019 72 9.869 23M10 -1 1.019 72M10 4 7.500 62M10 2
Examples of the units derived from the base units Table 3. The derived units having proper names
9.806 65M10 4 9.806 65M10 9.806 65M10 -2 9.806 65M10 -1 1 9.678 41M10 -1 1M10 4 7.355 59M10 2
Derived units Derived units Expressing method
Volume by derived unit 1.013 25M10 5 1.013 25M10 2 1.013 25M10 -1 1.013 25 1.033 23 1 1.033 23M10 4 7.600 00M10 2
Unit Sign Volume -3 -6 -5 -4 -5
Unit Sign
or supplementary 9.806 65 9.806 65M10 9.806 65M10 9.806 65M10 1M10 9.678 41M10 1 7.355 59M10 -2
Area Square m2 unit/others 2 -1 -4 -3 -3 -3
1.333 22M10 1.333 22M10 1.333 22M10 1.333 22M10 1.359 51M10 1.315 79M10 1.359 51M10 1
Volume Cubic m3 Frequency Hertz Hz 1Hz=1s-1
Velocity Meter/second m/s Force Newton N 1N=1kgCm/s 2 Note)1Pa=1N/m 2
Acceleration Meter/second 2 m/s 2 Pressure, stress Pascal Pa 1Pa=1N/m 2
J kWCh kgfCm kcal W/(mCK) kcal/(mChCA)
conductivity
Wave numbers Every meter m-1 Energy, work, heat Joule J 1J=1NCm
quantity of heat
Thermal
Work, energy,
Density Kilogram every cubic meter kg/m 3 Work rate, process rate, power, electric power Watt W 1W=1J/s 1 2.777 78M10 -7 1.019 72M10 -1 2.388 89M10 -4 1 8.600 0M10 -1
Electric charge, quantity of electricity Coulomb C 1C=1ACs M10 6 5
8.600 0 M10 2 1.162 79 1
Electric current density Ampere every square meter A/m 2 3.600 1 3.670 98M10
Potential, potential difference, voltage, electromotive force Voltage V 1V=1J/C
Magnetic field strength Ampere every meter A/m 9.806 65 2.724 07M10 -6 1 2.342 70M10 -3
Electrostatic capacity, capacitance Farad F 1F=1C/V
Concentration of substance Mole every cubic meter mol/m 3 4.186 05M10 3 1.162 79M10 -3 4.268 58M10 2
1 2
W/(m CK)
2
kcal/(mChC A)
heat transfer
Coefficient of
Electric resistance Ohm q 1q=1V/A
Specific volume Cubic meter every kilogram m 3 /kg 1S=1q-1
Conductance Siemens S Note)1J=1WCs, 1J=1NCm 1 8.600 0M10 -1
Luminance Candela every square meter cd/m 2 Magnetic flux Weber Wb 1Wb=1VCs 1.162 79 1
Magnetic flux density, magnetic induction Tesla T 1T=1Wb/m 2 W kgfCm/s PS kcal/h
heat flow rate
Inductance Henry H 1H=1Wb/A 1 1.019 72M10 -1 1.359 62M10 -3 8.600 0 M10 -1
Power,
kcal/(kgCA)
J/(kgCK)
Specified heat
Celsius temperature Celsius degree
or Degree A 1tA=(t+273.15)k 9.806 65 1 1.333 33M10 -2 8.433 71 cal/(gCA)
Light flux Lumen lm 1lm=1cdCsr 1 2.388 89M10 -4
7.355 M10 2 7.5 M10 1 6.325 29M10 2
Illumination Lux lx 1lx=1lm/m 2 4.186 05M10 -3 1
-1 -3
Radioactivity Becquerel Bq 1Bq=1s-1 1.162 79 1.185 72M10 1.580 95M10 1
Quantity of absorption radio Gray Gy 1Gy=1J/kg Note)1W=1J/s, PS:French horsepower
Radio equivalent Sievert Sv 1Sv=1J/kg
You might also like
- Units & DetailsDocument1 pageUnits & DetailssantoshcipetNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design Technical Infomation - 2Document15 pagesMechanical Design Technical Infomation - 2Paco LMNo ratings yet
- SI (International System of Units) : (Technical Data)Document1 pageSI (International System of Units) : (Technical Data)anoopkntpcNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design Technical InfomationDocument36 pagesMechanical Design Technical InfomationPaco LMNo ratings yet
- FMDS0912Document10 pagesFMDS0912Cesar RomeroNo ratings yet
- VM Apr 30 l2Document9 pagesVM Apr 30 l2SomilNo ratings yet
- 1.3 The International System of Units: TABLE 1-1Document2 pages1.3 The International System of Units: TABLE 1-1noman581No ratings yet
- Recommended Unit Symbols, SI Prefixes, and Abbreviations: A VIIDocument3 pagesRecommended Unit Symbols, SI Prefixes, and Abbreviations: A VIIBOURAS Ihabe - بوراس إيهابNo ratings yet
- Rolling Bearings For Industrial Machinery Part E Appendix TableDocument14 pagesRolling Bearings For Industrial Machinery Part E Appendix TableInamMuradNo ratings yet
- SI Unit EDocument1 pageSI Unit EEvangelin GuardamanoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument135 pagesPhysicspraveen reddyNo ratings yet
- Iso 1000Document32 pagesIso 1000choirulbiNo ratings yet
- TPFREP D00B Terminal Performance Report Implementation Guide - Hapag-Llo...Document33 pagesTPFREP D00B Terminal Performance Report Implementation Guide - Hapag-Llo...Aijaz Sabir HussainNo ratings yet
- SI UnitsDocument1 pageSI UnitsluameiacheiaNo ratings yet
- Iso 10005:1994Document29 pagesIso 10005:1994Razvan IonescuNo ratings yet
- Units and MeasurementsDocument8 pagesUnits and Measurementsernestnyondo63No ratings yet
- Units and Measurements: PhysicsDocument80 pagesUnits and Measurements: PhysicsAmit Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Kolhan University BBA SEM 5 Previous Year Question Papers of 2018 and 2022Document19 pagesKolhan University BBA SEM 5 Previous Year Question Papers of 2018 and 2022rahulmehtagamesNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document17 pagesWa0001BORN TO DIENo ratings yet
- ROS Window: 2008 SeminarDocument3 pagesROS Window: 2008 SeminarJagadeesh PvsnNo ratings yet
- IEEE Recommended Practice For Preferred Metric Units For Use in Electrical and Electronics Science and TechnologyDocument20 pagesIEEE Recommended Practice For Preferred Metric Units For Use in Electrical and Electronics Science and Technologyأمين توات الجزائريNo ratings yet
- Glossary PDFDocument40 pagesGlossary PDFFaseeshNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 NotesDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 1 NotesNicole de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- MPR-E R2 1 SNMPSysSpec - Wind Profiled - It10Document61 pagesMPR-E R2 1 SNMPSysSpec - Wind Profiled - It10Tap Zoo CatelloNo ratings yet
- Itu-T: Enhanced Telecom Operations Map (eTOM)Document14 pagesItu-T: Enhanced Telecom Operations Map (eTOM)lazaro maizNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and Measurements PresentationDocument60 pagesPhysical Quantities and Measurements Presentation金 Abigail RodriguezNo ratings yet
- TCAP MessageDocument2 pagesTCAP MessageSubhajit GhoshNo ratings yet
- Panel Data AnalysisDocument39 pagesPanel Data Analysisalaa_h1No ratings yet
- Use of SI (Metric) Units in Maritime Applications (Committee F-25 Supplement To IEEE/ASTM SI 10)Document12 pagesUse of SI (Metric) Units in Maritime Applications (Committee F-25 Supplement To IEEE/ASTM SI 10)தர்மா வெங்கடேசன்No ratings yet
- 58 - The SI Metric System of Units and SPE Metric StandardDocument39 pages58 - The SI Metric System of Units and SPE Metric Standardrizal tri susiloNo ratings yet
- Walgreens 810Document146 pagesWalgreens 810Sri VarriNo ratings yet
- MetricationDocument60 pagesMetricationLhizel ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- The SI Prefixes or Metric Prefixes Are An Indicator That Precedes A Basic Unit of Measure To Indicate A Multiple or Sub-Multiple of The UnitDocument3 pagesThe SI Prefixes or Metric Prefixes Are An Indicator That Precedes A Basic Unit of Measure To Indicate A Multiple or Sub-Multiple of The UnitMathilda YapNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1Document66 pagesPhysics - 1Aj EstoleNo ratings yet
- ANSI X12 - DELJIT - 862 - V4010 - O - v1.0 - 20090225Document22 pagesANSI X12 - DELJIT - 862 - V4010 - O - v1.0 - 20090225MaraJadeBackstoneNo ratings yet
- Network 2030 Terms and DefinitionsDocument18 pagesNetwork 2030 Terms and DefinitionsRyandika AfdilaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Gear Technology PDFDocument10 pagesElements of Gear Technology PDFGaneshan Mathan RajNo ratings yet
- T Rec G.1081 200810 I!!pdf eDocument14 pagesT Rec G.1081 200810 I!!pdf eCahyadi AswajaNo ratings yet
- Iso 10360 12 2016Document12 pagesIso 10360 12 2016Abdulaziz AlrawiNo ratings yet
- E D03a Coparn HSDG V1.1Document60 pagesE D03a Coparn HSDG V1.1Amir ArshadNo ratings yet
- T Rec G.8081 201202 I!!pdf eDocument60 pagesT Rec G.8081 201202 I!!pdf eHaziq AbbasNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Use of The International System of Units (SI) : NIST Special Publication 811 2008 EditionDocument89 pagesGuide For The Use of The International System of Units (SI) : NIST Special Publication 811 2008 EditionCarlos TrejoNo ratings yet
- Guide For The Use of The International System of UnitsDocument89 pagesGuide For The Use of The International System of UnitsAndré Dias BrochadoNo ratings yet
- T Rec E.804.1 202010 P!!PDF eDocument29 pagesT Rec E.804.1 202010 P!!PDF eKOUHON Derou FabriceNo ratings yet
- Supplement 1 - Interim View of An Interpreter's Guide For eTOM and ITIL Practitioners PDFDocument54 pagesSupplement 1 - Interim View of An Interpreter's Guide For eTOM and ITIL Practitioners PDFShantamNo ratings yet
- Appendix02 - The SI Metric System of Units and SPE Metric Standard PDFDocument38 pagesAppendix02 - The SI Metric System of Units and SPE Metric Standard PDFluisinho100% (1)
- T Rec G.987.1 201001 I!!pdf eDocument52 pagesT Rec G.987.1 201001 I!!pdf emesuge2No ratings yet
- 13 - Compass For DD - Tools Exercise - 061005Document3 pages13 - Compass For DD - Tools Exercise - 061005ebrahimNo ratings yet
- ETSI TR 102 071: Mobile Commerce (M-COMM) Requirements For Payment Methods For Mobile CommerceDocument16 pagesETSI TR 102 071: Mobile Commerce (M-COMM) Requirements For Payment Methods For Mobile CommerceShahzeb AmjadNo ratings yet
- Unidades y DimensionesDocument10 pagesUnidades y DimensionesVanessa Paulino GarciaNo ratings yet
- Panel 101Document40 pagesPanel 101aleknaekNo ratings yet
- R2-1906688 TS 36.331 Propagating Changes Due To TS 38.331 R2-1902709Document50 pagesR2-1906688 TS 36.331 Propagating Changes Due To TS 38.331 R2-1902709Mini PourNo ratings yet
- Itu PTP Rec 8256.1Document30 pagesItu PTP Rec 8256.1Kristofer GarciaNo ratings yet
- T Rec G.8121 201811 I!!pdf eDocument168 pagesT Rec G.8121 201811 I!!pdf egsplmcrtechnicalNo ratings yet
- Etsi TS 125 432Document11 pagesEtsi TS 125 432Vikrant PathakNo ratings yet
- T Rec G.870 201611 I!!pdf eDocument16 pagesT Rec G.870 201611 I!!pdf eMoss SehlabiNo ratings yet
- Telecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunications TermsFrom EverandTelecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunications TermsNo ratings yet
- Retaining Rings C Type: (Technical Data)Document1 pageRetaining Rings C Type: (Technical Data)ilo iloNo ratings yet
- Hexagon Socket Set Screws Flat Type Hexagon Bolts: (Technical Data) (Technical Data)Document1 pageHexagon Socket Set Screws Flat Type Hexagon Bolts: (Technical Data) (Technical Data)ilo iloNo ratings yet
- Hexagon Nuts/Cotter Pins Spring Pins/Retaining Rings E Type: (Technical Data) (Technical Data)Document1 pageHexagon Nuts/Cotter Pins Spring Pins/Retaining Rings E Type: (Technical Data) (Technical Data)ilo iloNo ratings yet
- Bolt Tightening ForceDocument1 pageBolt Tightening Forceiwanguna71No ratings yet
- Hexagon Socket Head Cap Screws: (Technical Data)Document1 pageHexagon Socket Head Cap Screws: (Technical Data)ilo iloNo ratings yet
- 09 Mo1509 PDFDocument2 pages09 Mo1509 PDFilo iloNo ratings yet
- 09 Mo1509 PDFDocument2 pages09 Mo1509 PDFilo iloNo ratings yet
- 09 Mo1509 PDFDocument2 pages09 Mo1509 PDFilo iloNo ratings yet
- 09 Mo1509 PDFDocument2 pages09 Mo1509 PDFilo iloNo ratings yet
- (Système International D'Unités) : 'Technical DataDocument1 page(Système International D'Unités) : 'Technical Datailo iloNo ratings yet
- 09 Mo1509 PDFDocument2 pages09 Mo1509 PDFilo iloNo ratings yet
- 09 Mo1509 PDFDocument2 pages09 Mo1509 PDFilo iloNo ratings yet
- Calculus Integrals CHeat SheetDocument1 pageCalculus Integrals CHeat Sheetwhiskey13No ratings yet
- Derivatives Cheat SheetDocument1 pageDerivatives Cheat SheetbythekiloNo ratings yet
- Material Test and Different Mix DesignDocument118 pagesMaterial Test and Different Mix DesignBekele MekonenNo ratings yet
- Group 8 Heat Excahnger ReportDocument35 pagesGroup 8 Heat Excahnger ReportHardik PanchalNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Overhauser Effect (NOE)Document5 pagesNuclear Overhauser Effect (NOE)Salustiano JurandiNo ratings yet
- Fluke Infrared Thermometer 59 MiniDocument1 pageFluke Infrared Thermometer 59 MiniRashidNo ratings yet
- Efficiency and Application of Alternative Low Cost Construction Technologies in BuildingDocument133 pagesEfficiency and Application of Alternative Low Cost Construction Technologies in BuildingkidusNo ratings yet
- Afa 2Document134 pagesAfa 2Muhammad AdjiNo ratings yet
- Physics Laws NotesDocument3 pagesPhysics Laws NotesYEO MING HUI Moe100% (1)
- Temperature - Matter & Heat - WorksheetsDocument4 pagesTemperature - Matter & Heat - WorksheetsjacafyNo ratings yet
- Functions and Characteristics of InstrumentsDocument29 pagesFunctions and Characteristics of InstrumentsMarion AlyssaNo ratings yet
- ITR HV CablesDocument2 pagesITR HV CablesYulianti Rahmi PurnamawatiNo ratings yet
- Inverse Square & Cosine LawDocument12 pagesInverse Square & Cosine LawAdisu0% (1)
- Distance Learning Programme: Jee (Main) : Leader Test Series / Joint Package CourseDocument8 pagesDistance Learning Programme: Jee (Main) : Leader Test Series / Joint Package CourseAnupam SinghNo ratings yet
- Fem Formulae PDFDocument12 pagesFem Formulae PDFvamsi krishnaNo ratings yet
- Arnitel® EM550, TPC-ET - DSM Engineering Plastics - Plastics FinderDocument5 pagesArnitel® EM550, TPC-ET - DSM Engineering Plastics - Plastics FinderFaiz AnsariNo ratings yet
- How To Cite An Honors Thesis ApaDocument4 pagesHow To Cite An Honors Thesis Apamonroeandertonsaltlakecity100% (2)
- Free Vibration of SDOFDocument11 pagesFree Vibration of SDOFADOBONo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Central Science 12th Edition Brown Test BankDocument39 pagesChemistry The Central Science 12th Edition Brown Test Bankrubydac7a9h05100% (30)
- CPSC 542f NotesDocument10 pagesCPSC 542f NotesSofia VegaNo ratings yet
- Class 22 - Determinant, Adjoint, Inverse, Identity MatrixDocument8 pagesClass 22 - Determinant, Adjoint, Inverse, Identity MatrixJada BrownNo ratings yet
- Lesson #15 Centroid of Plane Areas and of Solids of Revolution-1Document20 pagesLesson #15 Centroid of Plane Areas and of Solids of Revolution-1yveeshNo ratings yet
- Astm D3294 PtefDocument6 pagesAstm D3294 PtefIsabella RomeroNo ratings yet
- Introverted SensingDocument7 pagesIntroverted Sensinganand__08100% (1)
- Question bank-MASS TRANSFER-II MECDocument10 pagesQuestion bank-MASS TRANSFER-II MECkishore.21uchNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetice and Reactor DESIGN (CH-322) : by H. Scott Fogler Fourth EditionDocument140 pagesReaction Kinetice and Reactor DESIGN (CH-322) : by H. Scott Fogler Fourth EditionTEZ ANALYSIS AND STORIESNo ratings yet
- MEMS IMU For AHRS ApplicationsDocument7 pagesMEMS IMU For AHRS ApplicationsFrank FrunkNo ratings yet
- 2 - Stresses in Shells - Bending - Stress (Mechanics)Document1 page2 - Stresses in Shells - Bending - Stress (Mechanics)Abr's ReservedWorldNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures Study Book 3Document14 pagesSteel Structures Study Book 3ELMER EDINSON FLORES PONCENo ratings yet
- FM 1 Unit Test 6 Elastic Collisions in Two DimensionsDocument4 pagesFM 1 Unit Test 6 Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions张婧雯No ratings yet
- Jee 2024Document8 pagesJee 2024Md ArabiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Solution 1Document8 pagesAssignment Solution 1Ayush KumarNo ratings yet