Professional Documents
Culture Documents
7a Anand
Uploaded by
Nomunbileg Kh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesOriginal Title
7a Anand.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pages7a Anand
Uploaded by
Nomunbileg KhCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
China (Chinese: 中国; pinyin: Zhōngguó), officially
the People's Republic of China(PRC), is a country
in East Asia and is the world's most populous
country, with a population of around 1.428 billion in
2017. Covering approximately 9,600,000 square
kilometers (3,700,000 sq mi), it is the third
largest country by area.[j] Governed by
the Communist Party of China, the state exercises
jurisdiction over 22 provinces,[k]five autonomous
regions, four direct-controlled
municipalities (Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai,
and Chongqing), and the special administrative
regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
China emerged as one of the world's first
civilizations, in the fertile basin of the Yellow
River in the North China Plain. For millennia,
China's political system was based on hereditary
monarchies, or dynasties, beginning with the semi-
mythical Xia dynastyin 21st century BCE. Since
then, China has expanded, fractured, and re-
unifiednumerous times. In the 3rd century BCE, the
Qin reunited core China and established the first
Chinese empire. The succeeding Han dynasty,
which ruled from 206 BCE until 220 CE, saw some
of the most advanced technology at that time,
including papermaking and the compass, along with
agricultural and medical improvements. The
invention of gunpowder and movable type in
the Tang dynasty (618–907) and Northern
Song (960–1127) completed the Four Great
Inventions. Tang culture spread widely in Asia, as
the new Silk Route brought traders to as far
as Mesopotamia and the Horn of Africa. Dynastic
rule ended in 1912 with the Xinhai Revolution, when
the Republic of China (ROC) replaced the Qing
dynasty. China, as a whole, was ravaged by feudal
warlordism and Japan during World War II. The
subsequent Chinese Civil War resulted in a division
of territory in 1949 when the Communist Party of
China led by Mao Zedong established the People's
Republic of China on mainland China while
the Kuomintang-led nationalist government
retreated to the island of Taiwan where it governed
until 1996 when Taiwan transitioned to democracy.
The political status of Taiwan remains disputed to
this day.
China is a unitary one-party socialist republicand is
one of the few existing socialist states. Political
dissidents and human rights groups have
denounced and criticized the Chinese
government for human rights abuses, suppression
of religious and ethnic
minorities, censorship and mass surveillance, and
cracking down on protests such as in 1989. The
Chinese government says that the right to
subsistence and economic development is a
prerequisite to other types of human rights and that
the notion of human rights should take into account
a country's present economic level.
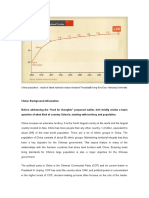
Since the introduction of economic reforms in
1978, China's economy has been one of the
world's fastest-growing with annual growth rates
consistently above 6 percent. According to the
World Bank, China's GDP grew from $150 billion in
1978 to $12.24 trillion by 2017. According to official
data, China's GDP in 2018 was 90 trillion Yuan
($13.5 trillion). Since 2010, China has been the
world's second-largest economy by nominal GDP,
and since 2014, the largest economy in the world
by purchasing power parity. China is also the
world's largest exporter and second-largest
importer of goods. China is a recognized nuclear
weapons state and has the world's largest standing
army, the People's Liberation Army, and
the second-largest defense budget. The PRC is
a permanent member of the United Nations Security
Council as it replaced the ROC in 1971, as well as
an active global partner of ASEAN Plus mechanism.
Since 2019, China has the highest number of rich
people in the world. Written by Anand
You might also like
- Car Wars 6e Vehicle Record SheetDocument1 pageCar Wars 6e Vehicle Record SheetBoyd KleenNo ratings yet
- BattleTech - Record Sheets 3055 Upgrades UnabridgedDocument283 pagesBattleTech - Record Sheets 3055 Upgrades UnabridgedJohn David Balingit100% (8)
- BOWMEN of ENGLAND PenSword Military Classics by Donald Featherstone - 5 Star Book ReviewDocument4 pagesBOWMEN of ENGLAND PenSword Military Classics by Donald Featherstone - 5 Star Book ReviewNeill HendersonNo ratings yet
- Codex: Adeptus Mechanicus: The Cult of The Machine GodDocument21 pagesCodex: Adeptus Mechanicus: The Cult of The Machine GodGaming With the Boys0% (1)
- Panzer Tracts 09-03 - Jagdpanther Panzerjaeger Panther (8.8 Em) (SD - Kfz.173) PDFDocument96 pagesPanzer Tracts 09-03 - Jagdpanther Panzerjaeger Panther (8.8 Em) (SD - Kfz.173) PDFBohdan Mohylny100% (5)
- Civil and Commercial Laws / Civil Procedure Law of the People's Republic of China: Laws and Regulations of the People's Republic of ChinaFrom EverandCivil and Commercial Laws / Civil Procedure Law of the People's Republic of China: Laws and Regulations of the People's Republic of ChinaNo ratings yet
- A Research Proposal Presented To The Gumaca National High School Gumaca, QuezonDocument33 pagesA Research Proposal Presented To The Gumaca National High School Gumaca, QuezonPanopio Sean Vincent A.100% (3)
- TMMI Feb 23Document68 pagesTMMI Feb 23Ognjen Močevič100% (2)
- Coast Artillery Journal - Aug 1948Document84 pagesCoast Artillery Journal - Aug 1948CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Classification: SECRET (BGX Directive) UNSC SPARTAN Field ManualDocument23 pagesClassification: SECRET (BGX Directive) UNSC SPARTAN Field Manualcdenton958025100% (4)
- Thrown Weapons in Ancient EgyptDocument139 pagesThrown Weapons in Ancient EgyptArchaeologist100% (2)
- Analysis of A Miracle ChinaDocument6 pagesAnalysis of A Miracle ChinaPhranxies Jean Loay BlayaNo ratings yet
- China (China (PRCDocument1 pageChina (China (PRCOrgito LekaNo ratings yet
- China (: Zhōngguó Lit. "Middle Kingdom" or "Central State"), OfficiallyDocument1 pageChina (: Zhōngguó Lit. "Middle Kingdom" or "Central State"), OfficiallyJoshua WacanganNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument2 pagesChinaMarius CiobanuNo ratings yet
- China, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is ADocument1 pageChina, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is ARafael DomínguezNo ratings yet
- China: A Brief History of the World's Most Populous NationDocument1 pageChina: A Brief History of the World's Most Populous NationFrasie SergiuNo ratings yet
- China's history, government, and economic riseDocument1 pageChina's history, government, and economic riseRadhika PrasadNo ratings yet
- China: (CITATION Wik1 /L 1048)Document2 pagesChina: (CITATION Wik1 /L 1048)Florentina IvanNo ratings yet
- Research On COVIDDocument2 pagesResearch On COVIDdivya kashyapNo ratings yet
- China's History, Government and EconomyDocument1 pageChina's History, Government and EconomyNokkiko EieiNo ratings yet
- China, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is ADocument1 pageChina, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is AHello BabyNo ratings yet
- China: by Melwin MarkDocument12 pagesChina: by Melwin MarkMelwinNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument5 pagesChinaabhishekkr26jNo ratings yet
- COUNTRY AND TOPIC RESEARCH Ilyas BagdatovDocument5 pagesCOUNTRY AND TOPIC RESEARCH Ilyas BagdatovIlyas BagdatovNo ratings yet
- WikiDocument1 pageWikiJasonNo ratings yet
- China, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), in Asia, Is The World'sDocument1 pageChina, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), in Asia, Is The World'sBishwo KhatriNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument3 pagesChinaplayingpiano2100No ratings yet
- Today'S China: The Emerging Superpower Executive SummaryDocument9 pagesToday'S China: The Emerging Superpower Executive SummaryMuhammad Umar KhanNo ratings yet
- China Economy Overview China IntrodutionDocument6 pagesChina Economy Overview China IntrodutionDamian CarlaNo ratings yet
- China Constitution - PreambleDocument2 pagesChina Constitution - PreambleCamille LopezNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument2 pagesChinaCristiana TemelieNo ratings yet
- China DictatorshipDocument3 pagesChina DictatorshipDaminNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentyedsatNo ratings yet
- China: Background InformationDocument2 pagesChina: Background InformationAmanda Amelia MendesNo ratings yet
- Mod 15 ChinaDocument26 pagesMod 15 ChinaPatrick CruzNo ratings yet
- Cina PPWDocument7 pagesCina PPWemma cabizzaNo ratings yet
- China: A Brief History of the World's Most Populous CountryDocument1 pageChina: A Brief History of the World's Most Populous CountryyedsatNo ratings yet
- China's History, Government and GeographyDocument1 pageChina's History, Government and GeographyCorina Taraș-LunguNo ratings yet
- International Marketing: Submitted To: Dr. (Prof.) D. DaveDocument61 pagesInternational Marketing: Submitted To: Dr. (Prof.) D. DaveAagam ShahNo ratings yet
- China's Economic Reforms Under Deng XiaopingDocument4 pagesChina's Economic Reforms Under Deng XiaopingMalini JwalaNo ratings yet
- China Country ProfileDocument6 pagesChina Country Profileapi-98469116No ratings yet
- History: China, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is ADocument2 pagesHistory: China, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is AjmaroseguitarteNo ratings yet
- China: LocationDocument6 pagesChina: Locationakshara pradeepNo ratings yet
- Country Profile ChinaDocument23 pagesCountry Profile Chinaa78ryNo ratings yet
- China ReportDocument25 pagesChina ReportUzairNo ratings yet
- Navneet's Ibm AssignmentDocument16 pagesNavneet's Ibm AssignmentNavneet KumarNo ratings yet
- China Government PDFDocument15 pagesChina Government PDFabhijeet nafriNo ratings yet
- China OverviewDocument20 pagesChina OverviewmanandpatelNo ratings yet
- China Geography Map: Physical Features, Regions & RiversDocument8 pagesChina Geography Map: Physical Features, Regions & RiversGovind ParmarNo ratings yet
- CHINADocument78 pagesCHINAUinNo ratings yet
- China, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is ADocument1 pageChina, Officially The People's Republic of China (PRC), Is ARam Krishna AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Soong Ch'ing-Ling - Sixteen Years of LiberationDocument13 pagesSoong Ch'ing-Ling - Sixteen Years of LiberationbNo ratings yet
- Topic 5: Political InstitutionDocument11 pagesTopic 5: Political InstitutionMondrich GabrienteNo ratings yet
- China Is A Country Located in East Asia With An Area of 9,596,960 KMDocument6 pagesChina Is A Country Located in East Asia With An Area of 9,596,960 KMRealRyanXDNo ratings yet
- Эдийн засагDocument1 pageЭдийн засагTuya MtsNo ratings yet
- NO COMMUNISTS Wikipedia Democratic Federation of ChinaDocument58 pagesNO COMMUNISTS Wikipedia Democratic Federation of Chinahazelfaras333No ratings yet
- China PresentationDocument2 pagesChina PresentationBenjamin BringardNo ratings yet
- China Russia RelationsDocument22 pagesChina Russia RelationsYassine Afilal Elalami IdrissiNo ratings yet
- China'S Foreign PolicyDocument20 pagesChina'S Foreign PolicyshahzaibNo ratings yet
- China (: Gònghéguó PRC), Is A Country inDocument1 pageChina (: Gònghéguó PRC), Is A Country inRichard NixonNo ratings yet
- CHINA'S RISEDocument12 pagesCHINA'S RISERehman Khan JatoiNo ratings yet
- How Communist Party Operates in Chinese Society: Victoria CGA 2013059087Document2 pagesHow Communist Party Operates in Chinese Society: Victoria CGA 2013059087Victoria VCNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument101 pagesChinaShairuz Caesar Briones DugayNo ratings yet
- China, Officially The People's Republic of China (PR China or PRC), Is ADocument5 pagesChina, Officially The People's Republic of China (PR China or PRC), Is Afitra watiNo ratings yet
- Informacion Resumida de ChinaDocument3 pagesInformacion Resumida de ChinaWareNo ratings yet
- Chinese Party, State and SocietyDocument3 pagesChinese Party, State and SocietyRosalia Ortiz SalazarNo ratings yet
- SoftDocument5 pagesSoftPaulo DuarteNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2.2 Country AnalysisDocument2 pagesAssignment 2.2 Country AnalysisCorazon DyNo ratings yet
- Ancient Chinese Dynasties and the Evolution of Chinese PoliticsDocument22 pagesAncient Chinese Dynasties and the Evolution of Chinese PoliticsSwapneel ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument3 pagesChinaNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- Anand 7aDocument3 pagesAnand 7aNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- Anand 7a HobbyDocument9 pagesAnand 7a HobbyNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- Measures Temperature Temperature Gradient Mercury-In-Glass ThermometerDocument4 pagesMeasures Temperature Temperature Gradient Mercury-In-Glass ThermometerNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- 7a AnandDocument3 pages7a AnandNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- ChinaDocument3 pagesChinaNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- Anand 7a HobbyDocument9 pagesAnand 7a HobbyNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- Anand 7aDocument3 pagesAnand 7aNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- Measures Temperature Temperature Gradient Mercury-In-Glass ThermometerDocument4 pagesMeasures Temperature Temperature Gradient Mercury-In-Glass ThermometerNomunbileg KhNo ratings yet
- GR Phase 1 2021-List of CasesDocument11 pagesGR Phase 1 2021-List of Caseskamal62747No ratings yet
- XxsaojenfpfxynmkriifDocument140 pagesXxsaojenfpfxynmkriiferrgrthyNo ratings yet
- Jonathan Smele - The Russian Civil Wars, 1916-1926 Ten Years That Shook The WorldDocument460 pagesJonathan Smele - The Russian Civil Wars, 1916-1926 Ten Years That Shook The WorldBrunoNo ratings yet
- Peloponnese - WikipediaDocument33 pagesPeloponnese - Wikipediamae mahiyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 01 Instructor: Samiya Shahzad: Student DetailsDocument3 pagesAssignment No. 01 Instructor: Samiya Shahzad: Student DetailsBilal SheikhNo ratings yet
- Weapons StatsDocument91 pagesWeapons StatsElouan Berthome LavignotteNo ratings yet
- SEC Vs Subic Bay GoldDocument2 pagesSEC Vs Subic Bay GoldBrokenNo ratings yet
- Local Study of Biak-na-Bato National Park Under ThreatDocument6 pagesLocal Study of Biak-na-Bato National Park Under ThreatMay Anne BarlisNo ratings yet
- Aprt BataviaDocument62 pagesAprt Bataviaimam17No ratings yet
- KD, Kaod Úohd, H - FLD U: 1 JK TallhDocument9 pagesKD, Kaod Úohd, H - FLD U: 1 JK TallhChandima K PriyamalNo ratings yet
- 02 February 1987Document80 pages02 February 1987Neville KempNo ratings yet
- GunulaDocument2 pagesGunula2ooneyNo ratings yet
- Individual Remembering and Collective MemoryDocument11 pagesIndividual Remembering and Collective MemoryDebbie GoldgaberNo ratings yet
- Court Martial Jurisdiction ChallengedDocument17 pagesCourt Martial Jurisdiction ChallengedChoi ChoiNo ratings yet
- French Revolution Question and Answers Part 1Document5 pagesFrench Revolution Question and Answers Part 1IyzSpookyNo ratings yet
- Jerusalem Center For Public Affairs Annual ReportDocument22 pagesJerusalem Center For Public Affairs Annual ReportDaniel LevinNo ratings yet
- Global Positioning System (GPS)Document13 pagesGlobal Positioning System (GPS)ratheeshbrNo ratings yet
- Terrorism in Punjab Grassroots Reality - by Puri, Sekhon, JudgeDocument100 pagesTerrorism in Punjab Grassroots Reality - by Puri, Sekhon, JudgeadNo ratings yet
- Jjohn Vincent S. Paz and Natalie T. de CastroDocument7 pagesJjohn Vincent S. Paz and Natalie T. de CastroNatalie De castroNo ratings yet
- SF000003 Close Quarters Battle CQBDocument39 pagesSF000003 Close Quarters Battle CQBfoxbat1988No ratings yet