Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Centrespread 8
Uploaded by
757rustamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Centrespread 8
Uploaded by
757rustamCopyright:
Available Formats
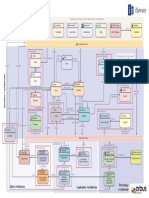
Addressing the human element during build
The operability requirements in the specification will
Effective
Productive only have an effect if the detailed design, selection of
Context of use Acceptable components, Factory Acceptance Tests (FAT),
Business The Human Element Safe installation, commissioning, and sea trials take
������������� Task Personal capabilities & limitations ���������� Operable
account of the needs, limitations and capabilities of
User Human Factors
���������������� Software Management ��������������� the crew. Evaluation of the developing systems is
Hardware Supervision
Crew interactions required, taking into account how the equipment will
Organisational Environment
Physical Environment Communications Full operation be used, the crew's competence and motivation, their
Crew training/familiarisation training, the procedures that they will be following and
Class notation
Type the type of supervision.
Special Features Type approval does not fully address ergonomic
Service Restrictions Whole ship system
(Task, ‘Fit for purpose’) issues. Design is more about reduction of costs, and
�������������� system integration is (at best) about making sure that
���������������� ������������������ everything is working on the day the ship is delivered.
Therefore, additional monitoring is required if the
VALIDATION
�������������������������
Workstations Human Element is to be successfully addressed
�������������������������� Displays
during build. That is to say:
Controls
��������������������������
• Has the manufacturer followed the standards for the
�
Habitability Accommodation
���
Maintainability Galleys
Workability
intrinsic ergonomic properties of working and living
Recreational spaces
Controllability Organization spaces and equipment? This includes health and
������ Manoeuvrability
Survivability
Policies safety issues from Class, Flag and ILO.
Procedures
������������ Manuals • Has the designer taken account of necessary
VERIFICATION
���
����������� Checklists attributes, context of use (user, task, physical and
Charts
��������� social environment) and maintainability of the layout
Drawings
�������������� and ship's sub-systems? In addition to good
���
Publications
Information Technology operational design this includes the requirements of
������������� Class, Flag and ILO, for operational safety.
������������������
����
• Can typical crew perform the intended working
���������� procedures with the provided equipment? Is the ship
������� operable in terms of the effectiveness, productivity,
��������� Unit/Sub-system
��
Checklist acceptability and safety of the crew's work?
Type Approval against:
���������� IMO
Basic design for people
The crew form an essential part of the operational ship
Standards
IEC
���
Regulation system. Integration includes ensuring that they are
ISO
ITU recruited, trained and worked according to the
(Class, Flag, Notified Body) assumptions behind the specification. ISM requires
��
assessment of the risk to operability from
ECYCLE
any change.
F
����
I
���
������
L
�������������������� Why evaluate operability? Because it
������������������� affects the bottom line. Poor
����� nsible stakehol
��
spo de effectiveness means human
DE
�������� Component R e rs
SIG
error. Lack of productivity
��
N
FE
SA UCT
&B
Pro
jec N D E means inefficient use of
CO F TH
UILD
t
Inte Mana
�� gra ger,
tor
O HIP
S limited manpower.
Safety problems mean
compensation or
USE
Master
����� grator
increased premiums.
DEVEL
s, Inte
Owner
������������������� SA
DEL FE & T Low acceptability
IVER IME
Y O LY decreases motivation.
OP
CAR F TH
�������� er
at
or GO E
Op
Su
tor nt,
pe Mas
era de
rin te
NE
Op inten
te r
Project
nd
ED
r
pe
en
Manager,
t
Su
,
Integrator
RT
DI O
SP PP
DEVEL TE SU
OS
E OP / DESIGN / UPDA
MAINTAIN
����������������������������
You might also like
- Operational Acceptance Testing WhitepaperDocument11 pagesOperational Acceptance Testing WhitepaperAryanNo ratings yet
- Cause and EffectDocument1 pageCause and EffectJeevan JyotiNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping MKKPDocument1 pageMind Mapping MKKPErita ShafiraNo ratings yet
- The 2008 IAM Competences Framework: Defining Competence Requirements For People Working in Asset ManagementDocument2 pagesThe 2008 IAM Competences Framework: Defining Competence Requirements For People Working in Asset ManagementColorinNadaMasNo ratings yet
- GSM PS Performance Evaluation and Optimization GuideDocument21 pagesGSM PS Performance Evaluation and Optimization GuidemohyeNo ratings yet
- Annex 4 - Tier Certification of Operational Sustainability - PresentationDocument12 pagesAnnex 4 - Tier Certification of Operational Sustainability - PresentationKamran SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Asset Management TriangleDocument1 pageAsset Management TriangleMathias OnosemuodeNo ratings yet
- Risk AssessmentDocument14 pagesRisk AssessmentApm FoumilNo ratings yet
- Persona Profile/Permission SetDocument2 pagesPersona Profile/Permission SettestNo ratings yet
- E01 - Machinery Operation CoordinationDocument10 pagesE01 - Machinery Operation Coordinationshahrul azwanNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument13 pagesReport0No ratings yet
- 06-BDE-1038 - Control A Field Artillery Unit MoveDocument6 pages06-BDE-1038 - Control A Field Artillery Unit MoveChengchang TsaiNo ratings yet
- CONSOLIDATEDDocument269 pagesCONSOLIDATEDNelce MiramonteNo ratings yet
- Description of Risk/Impact Counter Measure Outcome of Countermeasure Contingent Actions (In Case Risk Comes About) and Trigger DatesDocument1 pageDescription of Risk/Impact Counter Measure Outcome of Countermeasure Contingent Actions (In Case Risk Comes About) and Trigger DatesABINOU OUNIBANo ratings yet
- Steps in The Process Group: Initial StartDocument1 pageSteps in The Process Group: Initial StartProsenjitNo ratings yet
- Clm-Smaw Ncii Uc4 - CommonDocument2 pagesClm-Smaw Ncii Uc4 - CommonAlcantara CastilloNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument8 pagesReportfoxbat1988No ratings yet
- Working at Height Risk Assessment Form WHS78Document5 pagesWorking at Height Risk Assessment Form WHS78JUAN NICANOR ALIAGA GIRONNo ratings yet
- TOGAF 9.1 MetamodelDocument1 pageTOGAF 9.1 Metamodelcreamz100% (1)
- TRB For Print 2022Document13 pagesTRB For Print 2022Ralfh De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis Action Plan Energy Isolation Standard (Updated 27.03.2020)Document2 pagesGap Analysis Action Plan Energy Isolation Standard (Updated 27.03.2020)Alaa El-shafei100% (1)
- People Soft HCM 9.0 Business Process MapsDocument198 pagesPeople Soft HCM 9.0 Business Process MapslokeshmehraNo ratings yet
- Motherson Sumi Systems Limited: Competency Analysis (Applicable To E3 & Above)Document1 pageMotherson Sumi Systems Limited: Competency Analysis (Applicable To E3 & Above)Toshi VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Amit Kumar CompDocument1 pageAmit Kumar CompToshi VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Operator Training SystemDocument2 pagesOperator Training SystemQuý TrầnNo ratings yet
- Clm-Smaw Ncii Uc1 - CoreDocument2 pagesClm-Smaw Ncii Uc1 - CoreAlcantara CastilloNo ratings yet
- Manager and Delivered To The Appropriate IT Team To Install On The Database Server.)Document2 pagesManager and Delivered To The Appropriate IT Team To Install On The Database Server.)Mihaela GNo ratings yet
- Parameter Tuning - Prediction of Supply Chain Parameters Such As Lead Time and YieldDocument1 pageParameter Tuning - Prediction of Supply Chain Parameters Such As Lead Time and YieldPriyam DasNo ratings yet
- Cdp-Forms Institutional SectorDocument9 pagesCdp-Forms Institutional SectorElaiza San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - SKK-11: Allocation Time: 62 X 45 MinutesDocument3 pagesSyllabus - SKK-11: Allocation Time: 62 X 45 MinuteswahyudinNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Training: Yusuff Zain A. AbubakarDocument1 pageCertificate of Training: Yusuff Zain A. AbubakarAbdullah MundasNo ratings yet
- FCA WCM Academy 2016 ENG CatalogueDocument17 pagesFCA WCM Academy 2016 ENG CatalogueConcurseiro Carioca50% (2)
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI) Planning: IBM Maximo Asset Management Best PracticesDocument20 pagesKey Performance Indicator (KPI) Planning: IBM Maximo Asset Management Best PracticesJacky MoraudNo ratings yet
- Language Syntax: Training PlanDocument3 pagesLanguage Syntax: Training PlanAlex JamesNo ratings yet
- Closing Meeting Presentation - IndiaDocument33 pagesClosing Meeting Presentation - IndiaAnonymous cKdbnUHNo ratings yet
- Office: Office of The Media Research and Development Staff Consolidated Output On Risk and Opportunity MatrixDocument4 pagesOffice: Office of The Media Research and Development Staff Consolidated Output On Risk and Opportunity MatrixYanro FerrerNo ratings yet
- 105 165903 HFX2023Roles3Document2 pages105 165903 HFX2023Roles3sujoyNo ratings yet
- Tambahan 12 Oktober 2023Document4 pagesTambahan 12 Oktober 2023Immanuel Teja HarjayaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Uc 8 CLMDocument3 pages8 - Uc 8 CLMmariaestercampos22No ratings yet
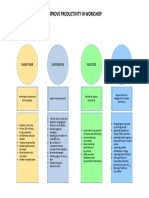
- Improve Productivity in Workshop: Points To ConsiderDocument1 pageImprove Productivity in Workshop: Points To ConsiderSirajudeen AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Curriculum MapDocument3 pagesGrade 7 Curriculum MapRussell SanicoNo ratings yet
- Ia 2011 5953607Document8 pagesIa 2011 5953607JesusNo ratings yet
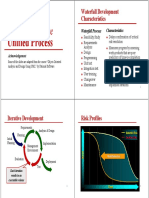
- Unified Process: Introduction To TheDocument8 pagesUnified Process: Introduction To TheSevNo ratings yet
- Report 3Document7 pagesReport 3foxbat1988No ratings yet
- CP Noss BaruuDocument3 pagesCP Noss BaruuMuhammad nazrien NizamNo ratings yet
- Sphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionDocument9 pagesSphereface: Deep Hypersphere Embedding For Face RecognitionMoxlyNo ratings yet
- 2022x SIMULIA StructuresAndDurability HandoutDocument4 pages2022x SIMULIA StructuresAndDurability HandoutNikhil NaikadeNo ratings yet
- SAM Igla - SimulatorDocument16 pagesSAM Igla - SimulatorCornelius IntVeldNo ratings yet
- Integrated CLMtemplateDocument2 pagesIntegrated CLMtemplateRodel P. PilloNo ratings yet
- Fidp 5Document2 pagesFidp 5Jon Jon Redoblado RosalesNo ratings yet
- Final Requirement: Re Entry Program: Industry: Mining IndustryDocument2 pagesFinal Requirement: Re Entry Program: Industry: Mining IndustryLhealyn Matibag BantugonNo ratings yet
- EvalForm ChopSueyDocument1 pageEvalForm ChopSueyLouie JayNo ratings yet
- MindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert CISSP Application Development MindMapjayarajanNo ratings yet
- Sip ResumeDocument2 pagesSip Resume7702609801No ratings yet
- CSS CidamDocument11 pagesCSS CidamAurel Buco100% (2)
- Sourav Pathak: Career ObjectiveDocument2 pagesSourav Pathak: Career ObjectivespsouravpathakNo ratings yet
- New 2.hirac Matrix For ExerciseDocument9 pagesNew 2.hirac Matrix For Exercisejrchshn26No ratings yet
- Service-Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and ArchitectureFrom EverandService-Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and ArchitectureNo ratings yet
- Model-Driven Online Capacity Management for Component-Based Software SystemsFrom EverandModel-Driven Online Capacity Management for Component-Based Software SystemsNo ratings yet
- There Is Someone at Work Who Encourages My Development.: Help Me GrowDocument2 pagesThere Is Someone at Work Who Encourages My Development.: Help Me Grow757rustamNo ratings yet
- Learner Needs Analysis Template: What'S The Point of This Template?Document13 pagesLearner Needs Analysis Template: What'S The Point of This Template?757rustamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource Concepts Lesson 3 - Recruiting, Selection, and OrientationDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource Concepts Lesson 3 - Recruiting, Selection, and Orientation757rustamNo ratings yet
- BPM Team Building Toolkit 2019Document84 pagesBPM Team Building Toolkit 2019757rustamNo ratings yet
- 2 Wellbeing at Work My Role As A Manager or Team LeaderDocument2 pages2 Wellbeing at Work My Role As A Manager or Team Leader757rustamNo ratings yet
- Stress Talking ToolkitDocument24 pagesStress Talking Toolkit757rustamNo ratings yet
- Recognition Toolkit For LeadersDocument2 pagesRecognition Toolkit For Leaders757rustam100% (1)
- IICF Volunteer Team Leader Website Guide: Sign Up For Year-Round Volunteer Projects As Well As The Annual Week of Giving!Document6 pagesIICF Volunteer Team Leader Website Guide: Sign Up For Year-Round Volunteer Projects As Well As The Annual Week of Giving!757rustamNo ratings yet
- Point-of-Care: Leadership Tips and Tools For NursesDocument6 pagesPoint-of-Care: Leadership Tips and Tools For Nurses757rustamNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Leaders GuideDocument44 pages2015 - Leaders Guide757rustamNo ratings yet
- Team Leader Guide: Prepared byDocument9 pagesTeam Leader Guide: Prepared by757rustamNo ratings yet
- Task Force & Strike Team Leader Guidebook: Updated For 2020 COVID-19 EnvironmentDocument34 pagesTask Force & Strike Team Leader Guidebook: Updated For 2020 COVID-19 Environment757rustamNo ratings yet
- Action Team Leader ToolkitDocument20 pagesAction Team Leader Toolkit757rustamNo ratings yet
- Leading and Managing People Trainers' Toolkit: Building A TeamDocument36 pagesLeading and Managing People Trainers' Toolkit: Building A Team757rustam100% (1)
- (eBook-EN) Make UX MeasurableDocument34 pages(eBook-EN) Make UX Measurable757rustamNo ratings yet
- Career Conversations: Employee-Driven. Development-Oriented. SimpleDocument12 pagesCareer Conversations: Employee-Driven. Development-Oriented. Simple757rustamNo ratings yet
- Manager'S Guide To Building A Successful Learning Path Using UlearnitDocument1 pageManager'S Guide To Building A Successful Learning Path Using Ulearnit757rustamNo ratings yet
- Team Leader Guide: Thank You For Accepting The Role of Team Leader!Document7 pagesTeam Leader Guide: Thank You For Accepting The Role of Team Leader!757rustamNo ratings yet
- The Proper Way To Do On The Job TrainingDocument1 pageThe Proper Way To Do On The Job Training757rustamNo ratings yet
- GG202x: Mindfulness and Resilience To Stress at Work: Team Leader GuideDocument10 pagesGG202x: Mindfulness and Resilience To Stress at Work: Team Leader Guide757rustamNo ratings yet
- Centrespread 33 PDFDocument1 pageCentrespread 33 PDF757rustamNo ratings yet
- Janitorial Safety Training Guide: Ership, ActDocument32 pagesJanitorial Safety Training Guide: Ership, Act757rustam100% (2)
- A Rough Guide To MLC 2006 Regulation 3.1: HabitabilityDocument1 pageA Rough Guide To MLC 2006 Regulation 3.1: Habitability757rustamNo ratings yet
- Competency-Based On-The-Job Training For Aviation Maintenance and Inspection) A Human Factors ApproachDocument11 pagesCompetency-Based On-The-Job Training For Aviation Maintenance and Inspection) A Human Factors Approach757rustamNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Human Error Probability of Disc Brake Unit Assembly and Wheel Set Maintenance of Railway BogieDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Human Error Probability of Disc Brake Unit Assembly and Wheel Set Maintenance of Railway Bogie757rustamNo ratings yet
- SIBUR - 1H 2020 - Results - PresentationDocument22 pagesSIBUR - 1H 2020 - Results - Presentation757rustamNo ratings yet
- 20% Off-The-Job Training GuideDocument7 pages20% Off-The-Job Training Guide757rustamNo ratings yet
- Maritime Educators and Trainers - : Knowledge, Skills & AttributesDocument1 pageMaritime Educators and Trainers - : Knowledge, Skills & Attributes757rustamNo ratings yet
- Question OneDocument2 pagesQuestion Onegoodluckpeterson864No ratings yet
- Bord Gáis Energy Gas & Electricity Supplier IrelandDocument1 pageBord Gáis Energy Gas & Electricity Supplier IrelandRomerson AmbrósioNo ratings yet
- Ganya ProjectDocument25 pagesGanya Projectshubham bhondeNo ratings yet
- Perfect Pie Slice Boxes To Protect and Present Your Single Slice at Wholesale RateDocument2 pagesPerfect Pie Slice Boxes To Protect and Present Your Single Slice at Wholesale Ratehafsa rashidNo ratings yet
- 4EC0ec 01 Que 20110606Document24 pages4EC0ec 01 Que 20110606Arif AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Law - MC CorporationDocument26 pagesLaw - MC CorporationJelly Ann AndresNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security: UNIT-1Document5 pagesCryptography and Network Security: UNIT-1atmadeep09No ratings yet
- SBC For Dummies PreviewDocument10 pagesSBC For Dummies PreviewEGX Consultores100% (1)
- Revised - MBA Sem IV - MBOP6013 - Sourcing Management - Reji JohnDocument4 pagesRevised - MBA Sem IV - MBOP6013 - Sourcing Management - Reji JohnHasratNo ratings yet
- Summer Intrnship A Study of AT Brakes India Private LimitedDocument13 pagesSummer Intrnship A Study of AT Brakes India Private LimitedKamalini 97No ratings yet
- Enterprise Risk Management - Beyond TheoryDocument34 pagesEnterprise Risk Management - Beyond Theoryjcl_da_costa6894100% (4)
- JD For Workday HCM Functional ConsultantDocument2 pagesJD For Workday HCM Functional ConsultantDevdutt Singh100% (1)
- Chen PDFDocument23 pagesChen PDFAnonymous N8ktRfrp06No ratings yet
- ESG Explained - Article Series Exploring ESG From The Very Basics - #2 Where Do You Start With ESG ReportingDocument13 pagesESG Explained - Article Series Exploring ESG From The Very Basics - #2 Where Do You Start With ESG Reportingsujaysarkar85No ratings yet
- DNV ST E271 Offshore ContainersDocument107 pagesDNV ST E271 Offshore ContainersWantana RattaneeNo ratings yet
- The New Hire: A Pocket Guide For EmployersDocument10 pagesThe New Hire: A Pocket Guide For Employerskenny_jjjj100% (1)
- PSALM Vs CIRDocument2 pagesPSALM Vs CIRIshNo ratings yet
- Pond's Relaunch StrategyDocument15 pagesPond's Relaunch StrategyAvnit kumarNo ratings yet
- Loyola College (Autonomous), Chennai - 600 034: BC 1502 - Financial AccountingDocument4 pagesLoyola College (Autonomous), Chennai - 600 034: BC 1502 - Financial AccountingIPloboNo ratings yet
- Overview of Multimodal TransportDocument39 pagesOverview of Multimodal TransporthanyimwdmNo ratings yet
- Young2020 KMToolsAndTechniquesManual AsianProductivityOrganizationDocument88 pagesYoung2020 KMToolsAndTechniquesManual AsianProductivityOrganizationGriselda Meza GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Glenn Resume FinalDocument1 pageGlenn Resume FinalRea Angela PurisimaNo ratings yet
- STANDARD FORM OF CONTRACT FOR ENGINEERING CONSULTANCY SERVICES (For Large Projects) TIME BASED ASSIGNMENTSDocument52 pagesSTANDARD FORM OF CONTRACT FOR ENGINEERING CONSULTANCY SERVICES (For Large Projects) TIME BASED ASSIGNMENTSUsman ShahidNo ratings yet
- LM Business Math - Q1 W6 - MELC3 Module 8Document15 pagesLM Business Math - Q1 W6 - MELC3 Module 8Cristina C MarianoNo ratings yet
- PercentageDocument6 pagesPercentageADITYA DESHPANDENo ratings yet
- Mgt420 Introduction Group 4Document9 pagesMgt420 Introduction Group 4Amir HafiyNo ratings yet
- The Military Simulation, Modelling, and Virtual Training Market 2013-2023Document28 pagesThe Military Simulation, Modelling, and Virtual Training Market 2013-2023VisiongainGlobal100% (1)
- Automobile Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesAutomobile Literature Reviewbzknsgvkg100% (1)
- PI-9003520-Mitali Fashions Limited - Self-SGS CTPAT-Announced-Iinitial-AC Fty.Document1 pagePI-9003520-Mitali Fashions Limited - Self-SGS CTPAT-Announced-Iinitial-AC Fty.Faruque UddinNo ratings yet
- Contact Center Template User's Guide PDFDocument217 pagesContact Center Template User's Guide PDFwpduarteNo ratings yet