Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet Potential
Uploaded by
Ruchi ChinfhaChinthaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet Potential
Uploaded by
Ruchi ChinfhaChinthaCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER – 2 REVISION WORKSHEET - 1
Electric Potential and Capacitance
1. (a) Is the electrostatic potential necessarily zero at a point where the electric
field strength is zero? Give an example to illustrate your answer. (CBSE 1990)
(b) Plot a graph showing the variation of V and E due to point charge as a
function of distance R from the point charge.
2. What would be the work done if a point charge +q, is taken from a point A to
the point B on the circumference of a circle with another point charge +q at the
centre . (CBSE 2001)
3. How much work is done in moving a 500μc charge between two points on an
equipotential surface? (CBSE 2002)
4. A and B are two conducting spheres of the same radius. A being solid and B
hollow. Both are charged to the same potential. What will be the relation
between the charges on the two plates? (CBSE 2001)
5. (i) Two point charges 4Q and Q are separated by a distance 1m in air. At what
point on the line joining the charges is the electric field intensity zero?
(ii) Also calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the charge if Q = 2 x 10-7C
(CBSE 2008)
ANS: (i) x = ± 2 (1-x) , If we take (+) sign x = 66.7m , If
we take (-) sign x= 2m
6. Two point charges 10 x 10-8 C and -4 x 10-8C are separated by a distance of
70cm in air.
(i) Find at what distance from point A would the electric potential be zero
(ii) Also calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the system. (CBSE 2008,
2004)
ANS: (i) x = 0.5m (point between two charges) , x= 1.67m ( point on the right side
of negative charge) , (ii) U =5.14 x 10-5 J
7. An electric dipole consists of two opposite charges each of magnitude 1μ C
separated by 2cm. The dipole is placed in an external electric field of 105 N/c. Find
(i) The maximum torque exerted by the field on the dipole (ii) The work which
the external agent will have to do in turning the dipole through 180 0 starting from
the position θ = 0o ANS : (i) τ = 2x10-3Nm (ii) W = 4x10-3J
8. A metal wire is bent in a circle of radius 10cm. It is given a charge of 200μC
which spreads on it uniformly. Calculate the electric potential at its centre. (CBSE
1995) ANS : 18 x 106V
9. Electric field intensity at point B due to point charge Q kept at A is 24N/C and
electric potential at point B due to same charge is 12 J /C. Calculate the distance
AB and also the magnitude of charge Q. (CBSE 2003)
ANS : Distance (AB) = 0.5m , magnitude of charge Q = 0.667 x 10-9C
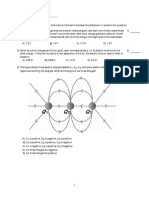
10. Calculate the work done to dissociate the system of three charges placed on
the vertices of a triangle as shown in fig where q = 1.6 x 10-10 C (CBSE 2008)
ANS: W = -U = 2.3 x 10-8 J
11. A charge of 24μC is given to a hollow metallic sphere of radius 0.2m. Find the
potential (a) At the surface of the sphere (b) At a distance 0.1m from the centre
of sphere (CBSE 1995) ANS : (a) 1.08 x 106V (b) 1.08 x 106V
12. (a) Calculate potential at the centre of square side √2m , having charges
100μC, -50μC, 20μC at the four corners of the square. (CBSE 2006) ANS : 9x
104V
(b) A 10µC charge is at the centre of a square of side 10 cm. Find the work done in
moving the charge of 4 C between two diagonally opposite points on the square.
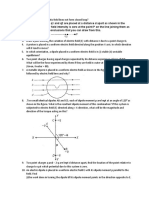
13. A test charge q is moved without acceleration from A to C along path from A
to B and then from B to C in electric field as shown in fig . (i) Calculate the
potential difference between A and C , (ii) At which point is electric potential
more and why ?(CBSE 2012)
ANS: (i) Vc – VA = 4E (ii) Vc > VA , direction of E.F is in decreasing
potential
You might also like
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 2.short Answer Type IIDocument3 pages2.short Answer Type IIJohn WickNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics 1Document2 pages12 Physics 1Aman ShuklaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS (Pyq)Document5 pagesELECTRIC CHARGES AND FIELDS (Pyq)Abhishek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Test1 16FDocument8 pagesTest1 16FJasper LuNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges and Field 01 April 2TESTDocument2 pagesElectric Charges and Field 01 April 2TESTcrawlskullNo ratings yet
- DPP 3 CH 1 ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS THEROMEDocument4 pagesDPP 3 CH 1 ELECTRIC FLUX AND GAUSS THEROMEKanishk kumar NimeshNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 (Electric Charges and Field)Document2 pagesAssignment - 1 (Electric Charges and Field)Pritinanda RayNo ratings yet
- Electrostat-05 - CBSE LevelDocument2 pagesElectrostat-05 - CBSE LevelRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 - Topicwise - Level 2Document6 pagesUnit - 1 - Topicwise - Level 2mokshchawlaNo ratings yet
- Class XII Physics Worksheet (Electrostatic Potential and Potential Energy)Document2 pagesClass XII Physics Worksheet (Electrostatic Potential and Potential Energy)Ayan JunejaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential - WORKSHEET - 18271998 - 2024 - 02 - 27 - 22 - 43Document4 pagesElectric Potential - WORKSHEET - 18271998 - 2024 - 02 - 27 - 22 - 43parasbhardwaj52159No ratings yet
- CBSE Class XII Physics Electrostatics Charges Forces Fields Guess Paper 2012 Set IDocument3 pagesCBSE Class XII Physics Electrostatics Charges Forces Fields Guess Paper 2012 Set Ishubhioo7No ratings yet
- EmfDocument53 pagesEmfNithyananthan Krishnan100% (1)
- One Institute: Type (I) : Very Short Answer Type Questions: (01 Mark Each) 1Document63 pagesOne Institute: Type (I) : Very Short Answer Type Questions: (01 Mark Each) 1saghir merajNo ratings yet
- Jai Gurudev Maharishi Vidya Mandir, Mangadu Physics - Worksheet Electric Fields & ChargesDocument3 pagesJai Gurudev Maharishi Vidya Mandir, Mangadu Physics - Worksheet Electric Fields & ChargesEdge DesignersNo ratings yet
- Force Between Charged SpheresDocument3 pagesForce Between Charged SpheresAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A ForceDocument6 pagesElectric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A ForceTeow JeffNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A ForceDocument6 pagesElectric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A Force加卡内-张进哲No ratings yet
- Chapter 24 SolutionDocument14 pagesChapter 24 SolutionsharathNo ratings yet
- Previous Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesDocument7 pagesPrevious Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapterwise PYQs Shobhit NirwanDocument65 pagesClass 12 Chapterwise PYQs Shobhit NirwanHimanshu92% (13)
- Electromagnetics Assignment Ee /ec: 1.vector Calculas, Coordinate SystemsDocument6 pagesElectromagnetics Assignment Ee /ec: 1.vector Calculas, Coordinate SystemsShubham GoyalNo ratings yet
- 1721740650class 12th HomeworkDocument24 pages1721740650class 12th HomeworkBhupenderYadavNo ratings yet
- Vidhyasagar International Public School: I. Answer All The FollowingDocument2 pagesVidhyasagar International Public School: I. Answer All The FollowingPhysicsNo ratings yet
- NDocument4 pagesNBHAAJI0001No ratings yet
- Guess Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsDocument3 pagesGuess Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsAshish Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Assignment (CHAPTER 1) XIIDocument2 pagesAssignment (CHAPTER 1) XIIsneha guptaNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential AssignDocument8 pagesElectric Potential AssignAditya PanditNo ratings yet
- DR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFDocument50 pagesDR - Hannan Saadeh Solved Problems PDFAbdNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Electric Field, Potential and Coulomb's LawDocument39 pagesElectrostatics: Electric Field, Potential and Coulomb's LawSANCHIT BAWEJA100% (1)
- MCQ Electricity Chapter 1 and 2Document4 pagesMCQ Electricity Chapter 1 and 2qesuzNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics ExerciseDocument20 pagesElectrostatics ExerciseUtkarsh Mittal86% (7)
- Electric Charges and Field 24 MARCH 1TESTDocument2 pagesElectric Charges and Field 24 MARCH 1TESTcrawlskullNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Classroom Assignment 3 With AnswersDocument3 pagesClassroom Assignment 3 With AnswersBishoy EmileNo ratings yet
- Two Small Spheres in MotionDocument12 pagesTwo Small Spheres in MotionharshanauocNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument17 pagesPhysicspaninikumar0000No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Worksheet 2016Document5 pagesElectrostatics Worksheet 2016Rohan ChackoNo ratings yet
- 02 Electrical Tutorial 2Document2 pages02 Electrical Tutorial 2臧华运No ratings yet
- Print Question PaperDocument8 pagesPrint Question PaperSaniya MemonNo ratings yet
- ELECTRIC FIELD POTENTIALDocument8 pagesELECTRIC FIELD POTENTIALPankaj Mishra0% (1)
- 2.short Answer Type IDocument3 pages2.short Answer Type IJohn WickNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TopicwiseDocument19 pagesUnit 1 TopicwiseSimran singhNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields Worksheet SolutionsDocument4 pagesElectric Fields Worksheet Solutionssarcasticb15No ratings yet
- Home Assignment II Las Date of Submission: 26/01/2022Document2 pagesHome Assignment II Las Date of Submission: 26/01/2022Md. Imran AhmedNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICS-3Document2 pagesELECTROSTATICS-3bys628h8skNo ratings yet
- 01 ElectrostaticsDocument14 pages01 ElectrostaticsAarav PatelNo ratings yet
- EM Waves Chapter QuestionsDocument10 pagesEM Waves Chapter QuestionsAnkit VatsaNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesElectrostaticsSharan RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment PDFDocument30 pagesAssignment PDFHương Hà ĐàoNo ratings yet
- FET Online Tutorial Chapter 1: ElectrostaticsDocument6 pagesFET Online Tutorial Chapter 1: Electrostatics胡宇晟No ratings yet
- Chapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument30 pagesChapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldNguyễn Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Previous Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesDocument11 pagesPrevious Exams Questions Ch23-24-With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- Final 2018Document3 pagesFinal 2018Ashraf WaleedNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam IdeaDocument419 pagesPhysics Exam IdeaAditya50% (2)
- Ch. 1 Electric Charges and Fields NCERT & PYQsDocument96 pagesCh. 1 Electric Charges and Fields NCERT & PYQsLakshya Jain100% (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- The University of Melbourne Tuition Fees 2020: Tuition Fee Tables For International StudentsDocument32 pagesThe University of Melbourne Tuition Fees 2020: Tuition Fee Tables For International StudentsRuchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Sci 10Document134 pagesSci 10Pirated VirusNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: RecursionDocument9 pagesComputer Science: RecursionShagun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet PotentialDocument3 pagesWorksheet PotentialRuchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document2 pagesWorksheet 2Ruchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Conference Schedule EMUN@DPSD 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesConference Schedule EMUN@DPSD 2020 PDFRuchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- 5.US Map and Visa Check List Flyer A4Document2 pages5.US Map and Visa Check List Flyer A4Ruchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- WHO - Background Guide - EMUN@DPSD PDFDocument14 pagesWHO - Background Guide - EMUN@DPSD PDFRuchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Conference Schedule EMUN@DPSD 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesConference Schedule EMUN@DPSD 2020 PDFRuchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Conference Schedule 2020 PDFDocument3 pagesConference Schedule 2020 PDFRuchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document2 pagesWorksheet 2Ruchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Delegate HandbookDocument24 pagesDelegate HandbookRuchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- Crash Log 3Document1 pageCrash Log 3Ruchi ChinfhaChinthaNo ratings yet
- HISAMD2019 Program Final 02 PDFDocument12 pagesHISAMD2019 Program Final 02 PDFNguyễnMinhTuấnNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 2-1 - 230521 - 212904 - 230602 - 225042Document8 pagesTutorial - 2-1 - 230521 - 212904 - 230602 - 225042Ajj JajNo ratings yet
- Treumann R.a., Baum Johann W. Advanced Space Plasma Physics (WS, 1997) (ISBN 1860940269) (388s) - PPLDocument388 pagesTreumann R.a., Baum Johann W. Advanced Space Plasma Physics (WS, 1997) (ISBN 1860940269) (388s) - PPLtarwor100% (1)
- Strcteng200 S1 2021Document11 pagesStrcteng200 S1 2021ChengNo ratings yet
- BIT Baroda Institute of Technology: Creo (Pro/ENGINEER) Training atDocument4 pagesBIT Baroda Institute of Technology: Creo (Pro/ENGINEER) Training atNIRALINo ratings yet
- Ieee 1471-2000Document28 pagesIeee 1471-2000Suzanne StewartNo ratings yet
- MATH 4 SLM Week 2Document10 pagesMATH 4 SLM Week 2Dan August A. GalliguezNo ratings yet
- Sump Pump Selection Final ReportDocument19 pagesSump Pump Selection Final ReportEngr Saad Bin SarfrazNo ratings yet
- Songbook EnglishDocument192 pagesSongbook Englishr_c_c_s90% (10)
- Computer Literacy: Hardware & Software ClassificationDocument11 pagesComputer Literacy: Hardware & Software ClassificationAmadoUsla100% (1)
- Electric Field Mapping: Experiment 1Document5 pagesElectric Field Mapping: Experiment 1Pi PoliNo ratings yet
- GEN SPQ RN MSM6280 Based Firmware Release FW2.4.6 v12 F2Document32 pagesGEN SPQ RN MSM6280 Based Firmware Release FW2.4.6 v12 F2djnhh0an100% (1)
- Powder FlowDocument15 pagesPowder FlowSteven SastradiNo ratings yet
- Rules of Categorical Syllogism: Kimjoy S. Auxtero BSTM-3Document5 pagesRules of Categorical Syllogism: Kimjoy S. Auxtero BSTM-3Geviena Pinky Sy SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionDocument63 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 1 - Rate of ReactionSiti Nursyafiqah100% (7)
- Power Control in Ac Isolated Microgrids With Renewable Energy Sources and Energy Storage SystemsDocument1 pagePower Control in Ac Isolated Microgrids With Renewable Energy Sources and Energy Storage SystemssriluNo ratings yet
- JAVA AND JAVAUI HANDSON - Hackerrank Assessments-1 PDFDocument15 pagesJAVA AND JAVAUI HANDSON - Hackerrank Assessments-1 PDFtkkhhaarree0% (1)
- SPSS ImplicationsDocument3 pagesSPSS ImplicationsAnonymous MMNqiyxBUNo ratings yet
- Relational Database: Storing and Manipulating RecordsDocument34 pagesRelational Database: Storing and Manipulating RecordsaNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Power and Delay of CMOS Phase Detector Using Nano TransistorsDocument57 pagesEstimation of Power and Delay of CMOS Phase Detector Using Nano TransistorsViplav SangvaiNo ratings yet
- Chemical and Mechanical Engineering 2300 / Thermodynamics I: Problem 1Document6 pagesChemical and Mechanical Engineering 2300 / Thermodynamics I: Problem 1Takishima N VovoNo ratings yet
- Discussion Sa QualiDocument2 pagesDiscussion Sa QualiAngel Rose SalinasalNo ratings yet
- The Monitoring of Water Quality in An IOT Environment Using MQTT ProtocolDocument4 pagesThe Monitoring of Water Quality in An IOT Environment Using MQTT ProtocolInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Charly ChalkboardDocument9 pagesCharly ChalkboardOscar PachecoNo ratings yet
- BE Information Technology 0Document655 pagesBE Information Technology 0virendra giraseNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Laboratory InstrumentationDocument1 pageMechanical Engineering Laboratory InstrumentationGonzalo LNo ratings yet
- Switched Reluctance MotorDocument52 pagesSwitched Reluctance Motorkoppulabro75% (8)
- Course:: Heating Ventilation & Air-Conditioning (ME 326)Document45 pagesCourse:: Heating Ventilation & Air-Conditioning (ME 326)Muhammad OsamaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of No. of Bolts For Individual Members Bolt DiameterDocument1 pageCalculation of No. of Bolts For Individual Members Bolt DiametercharanNo ratings yet