Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Structural Theory Refresher Set PDF
Uploaded by
ezer joseph bacoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Structural Theory Refresher Set PDF
Uploaded by
ezer joseph bacoCopyright:
Available Formats
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
STRUCTURAL THEORY REFRESHER SET
SITUATION 1: A 9 m high retaining wall is laterally supported at the top and fixed at the base. The wall
resists active earth pressure increasing from 0 at the top to 52 kN/m at the base of the per meter length
along the longitudinal axis.
1. Determine the design moment at the base. Apply the fixed end moment equation wL^2/30 at the top
and wL^2/20 at the base. Assume the EI is constant.
a. 315.9 kN m b. 280.8 c. 164.9 d. 204.6
2. The lateral support at the top of the wall was removed, determine the design moment at the base.
a. 567 kN m b. 854 c. 702 d. 66
3. Determine the resulting base shear if the wall is free at the top.
a. 234 kN b. 316 c. 481 d. 607
4. Which of the following that is not described for wind loads?
a. When structures block the flow of wind, its kinetic energy is converted to potential energy of
pressure.
b. The effect of wind on a structure depends upon the density and velocity of the air.
c. For high rise buildings, static approach is used to determine wind loadings.
d. The pressure effects of the wind on the building can be determined from pressure transducers
attached to the model.
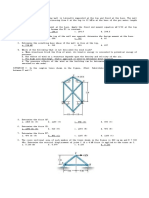
SITUATION 2: In the complex truss shown in the figure, (Hint: Substitute member AD with one placed
between E and C)
5. Determine the force AF.
a. 1428 lb (C) b. 1166 (C) c. 646 (C) d. 580 (C)
6. Determine the force CD.
a. 1593 lb (C) b. 820 (T) c. 1593 (T) d. 473 (T)
7. Determine the force EF.
a. 473 lb (T) b. 473 (C) c. 1166 (T) d. 1166 (C)
8. The cross sectional area of each member of the truss shown in the figure is 400 sq mm and E = 200
GPa. Determine the vertical displacement of joint C if a 4 kN force is applied to the truss at C.
a. 0.205 mm b. 0.079 c. 0.186 d. 0.133
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
SITUATION 3: In this determinate frame shown,
9. Determine the maximum shear of the entire structure.
a. 825 lb b. 750 c. 765 d. 805
10. Determine the maximum shear of member BC.
a. 290 lb b. 320 c. 350 d. 480
11. Find the maximum moment of member AB.
a. 2500 lb ft b. 3000 c. 3100 d. 4400
SITUATION 4: In the given cantilever beam shown,
12. Determine the moment reaction of this beam.
a. 3150 N m b. 2750 c. 3680 d. 2250
13. Determine the slope at point B in N m^2 / EI.
a. 3150 b. 2750 c. 3680 d. 2250
14. Determine the deflection at point B N m^3 / EI.
a. 6437.5 b. 5844.1 c. 6637.5 d. 5478.6
SITUATION 5: Answer the following terms in structural theory.
15. This method relates the moments at the ends of a member to the rotations and displacements of its
ends and the external loads applied to the member.
a. Virtual Work b. Slope Deflection c. Three Moment d. Conjugate Beam
16. It refers to loading that is congruent to an axis in its plane if the deflection of the loading
about the axis is identical to the loading itself.
a. Indeterminate b. Prismatic c. Symmetric d. Unsymmetric
17. These are points that undergo unknown displacements of the structure.
a. Determinancy b. Joints c. Nodes d. Sections\
SITUATION 6: A simply supported beam having a span of 6 m carries a triangular load which varies at 12
kN/m at the center to zero at the supports.
18. Which of the following gives the reaction at B?
a. 24 kN b. 20 c. 36 d. 18
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
19. Which of the following gives the moment at midspan?
a. 24 kN m b. 36 c. 60 d. 72
20. Which of the following gives the deflection at midspan in 1/EI?
a. 130 b. 250 c. 315 d. 95
SITUATION 7: A simply supported beam is supported at both ends. E = 200 GPa, I = 60 x 10^6 mm^4 . It has
a span of 12 m and subjected to a concentrated load of 8 kN at a distance of 3 m from the right support.
21. Which of the following gives the angle of rotation at A in radians.
a. 0.00844 b. 0.00561 c. 0.00284 d. 0.00375
22. Find the location of the maximum deflection.
a. 4.78 m b. 5.17 c. 4.64 d. 6.71
23. Find the maximum deflection of the beam.
a. 16.8 mm b. 11.3 c. 14.9 d. 19.4
SITUATION 8: The bridge truss shown in the figure is to carry a uniform load of 2 kN/m and a concentrated
load of 20 kN. It is required to determine the maximum tensile and compressive force on member BG by
constructing the influence line for axial force on member BG.
24. Determine the coordinate of the reaction if the unit load is at 12 m from the left support.
a. 0 b. 0.25 c. 0.5 d. 0.75
25. Determine the maximum tensile stress on member BG.
a. 8.55 kN b. 9.9 c. 11.8 d. 10.6
26. Determine the maximum tensile stress on member BG.
a. 25.456 kN b. 28.311 c. 35.479 d. 30.144
27. The relative stiffness of a beam or a frame in moment distribution method is the ratio of:
a. Area to moment of inertia c. Modulus of elasticity to area
c. Length to modulus of elasticity d. Moment of inertia to length
28. He proposed the consistent deformation method that involves removing restraints from indeterminate
structures to render the structures determinate.
a. Otto Mohr c. James Maxwell
b. Hardy Cross d. Alberto Castigliano
29. Compute the vertical reaction of this system.
a. 300 kN b. 250 c. 230 d. 175
30. It refers to the representation of the variation of any structural parameters at a specific point
in a member as a concentrated force moves over the member.
a. Shear diagram b. Moment diagram c. Influence lines d. Moment distribution
31. A flexible wire cable weighing 60 N/m over two frictionless pulleys 100 m apart and carrying one
10 kN weight at each end. The weight of the cable is assumed to be uniformly distributed
horizontally. The cable extends 5 m beyond each pulley to the point where they are attached to the
weights. Compute the sag of the flexible wire cable.
a. 7.61 m b. 5.35 c. 8.77 d. 6.84
SITUATION 9: A pin connected circular arch supports a 50 kN vertical load as shown in the figure. Neglect
the weights of the members.
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
32. Compute the bending moment that act on the cross section at 1-1.
a. 17.8 kN m b. 18.4 c. 21.9 d. 22.6
33. What is the shear force that act on the cross section at 1-1?
a. 5.11 kN b. 9.84 c. 6.23 d. 3.66
34. What is the axial force that act on the cross section at 1-1?
a. 13.66 kN b. 14.04 c. 18.47 d. 16.23
SITUATION 10: From the given frame shown, with different moment of inertias, has fixed supports at A and
C. Use three moment equation.
35. Compute the moment at A.
a. 17.89 kN m b. -17.89 c. 14.22 d. -14.22
36. Compute the moment at B.
a. 28.44 kN m b. -28.44 c. 36.16 d. -36.16
37. Compute the moment at C
a. 59.26 kN m b. -59.26 c. 81.80 d. -81.80
SITUATION 11: The three hinged arch shown in the figure is loaded with vertical loads only. Distance H =
12 m and s = 4 m.
38. Determine the horizontal reaction at A.
a. 210 kN b. 170 c. 180 d. 190
39. Determine the vertical reaction at B.
a. 330 kN b. 90 c. 190 d. 240
40. Determine the vertical reaction at C.
a. 0 c. 330 kN c. 240 d. 90
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
SITUATION 12: In the figure shown, a uniform load of 12 kN/m is acting downward and supported by an
upward uniform pressure of q = 48 kN/m.
41. Calculate the maximum shear.
a. 112 kN b. 48 c. 85 d. 96
42. Calculate the maximum moment.
a. 84 kN m b. 75 c. 66 d. 42
43. Determine the distance from the left where the flexural stress is zero.
a. 1.75 m b. 2.25 c. 3.0 d. 3.5
44. From the beam shown in the figure, determine the deflection at D.
a. 55.91/EI b. 46.81/EI c. 42.21/EI d. 39.74/EI
SITUATION 13: The continuous beam A,B, and C have different moment of inertias. BC is twice that of AB.
45. Determine the value of 6A 1 a/I 1 L 1 in kN m^2 due to the contribution of the uniform load acting on
span AB to be used in the three moment equation.
a. 4920 b. 5060 c. 5310 d. 5760
46. Determine the value of 6A 2 b/I 2 L 2 in kN m^2 due to the contribution of the concentrated load acting
on span BC to be used in the three moment equation.
a. 615 b. 525 c. 450 d. 370
47. Find the moment at B.
a. -289.15 kN m b. -261.88 b. -220.16 d. -195.32
SITUATION 14: In the figure shown,
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
48. Compute the maximum tension in the cable.
a. 5.48 kN b. 6.41 kN c. 5.79 d. 3.88
49. Compute the tension at member BC.
a. 2.55 kN b. 1.57 kN c. 1.00 d. 2.33
50. Compute the sag at point B.
a. 2.43 m b. 2.11 c. 1.77 d. 1.59
Visit For more Pdf's Books
Pdfbooksforum.com
You might also like
- College of Engineering Education Achievement Exam CDocument9 pagesCollege of Engineering Education Achievement Exam CJade Paul D. BesanaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Nov Final Preboard MathDocument8 pages2022 Nov Final Preboard MathJOHN CARLO DE GUZMAN AMBAY (JCDGA)No ratings yet
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- Local Media3116916508017834053 2Document7 pagesLocal Media3116916508017834053 2Ben BenbenNo ratings yet
- Spherical Trigonometry Activity ProblemsDocument1 pageSpherical Trigonometry Activity ProblemsEurydiceNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS CIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD NOVEMBER 2003Document3 pagesMATHEMATICS CIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD NOVEMBER 2003Jerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Doubly Reinforced Beams: F F F F C D CDocument17 pagesDoubly Reinforced Beams: F F F F C D CEly ReyesNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Document9 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Battery - 1Michael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Engineering Econ. - ANNUITYDocument35 pagesEngineering Econ. - ANNUITYNikolai VillegasNo ratings yet
- Ucu Trigonometry Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesUcu Trigonometry Practice ProblemsAngie Alcaide BautistaNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 3 – CE4 - 01 Surveying LevelsDocument5 pagesQuiz No. 3 – CE4 - 01 Surveying LevelsGanigan GajoNo ratings yet
- Tos 1Document5 pagesTos 1Allyanna Elise Diam100% (1)
- Mathematics-Surveying-and-Transportation ProblemDocument9 pagesMathematics-Surveying-and-Transportation Problemarnie2295No ratings yet
- Hydrau Geotech Focusproblems3 2019Document7 pagesHydrau Geotech Focusproblems3 2019kimNo ratings yet
- Quiz 12Document6 pagesQuiz 12John Taylor BernasNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument19 pagesUntitledRojane FloraNo ratings yet
- PREBOARD EXAM 1 MATH, SURVEYING AND ECONOMICS REVIEWDocument6 pagesPREBOARD EXAM 1 MATH, SURVEYING AND ECONOMICS REVIEWWinter DeeneNo ratings yet
- Seac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Document6 pagesSeac 2 - Strength of Materials (No Answers)Joshua John Julio100% (1)
- Theory of Structures Review NotesDocument3 pagesTheory of Structures Review NotessadonNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Set - ADocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Set - AAnthony Jay Poraque0% (1)
- Steel Design INSTRUCTION: Read and Understand Each Problem CarefullyDocument3 pagesSteel Design INSTRUCTION: Read and Understand Each Problem CarefullyRoma Raquepo RingorNo ratings yet
- Ce Correl Theory of Structures 2 Situation 1Document5 pagesCe Correl Theory of Structures 2 Situation 1Glenn Frey LayugNo ratings yet
- Inhouse Practice Problems - RCD-Column - Without AnswersDocument1 pageInhouse Practice Problems - RCD-Column - Without AnswersAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNo ratings yet
- 1S1819 Q1 ST1 Set ADocument1 page1S1819 Q1 ST1 Set ALance MendozaNo ratings yet
- Probability CE Review: Combination and Permutation QuestionsDocument3 pagesProbability CE Review: Combination and Permutation QuestionsNaigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- Wala LangDocument3 pagesWala LangEthyl Jean Monday GallarteNo ratings yet
- REVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM MAY 2022 ALVAREZ 1Document3 pagesREVIEW INNOVATIONS CE BOARD EXAM MAY 2022 ALVAREZ 1Mayya BonaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced ConcreteDocument5 pagesReinforced ConcreteLYNSER CORONEL ABANZADO100% (1)
- CEST PRELIM LT 9 2019-2020 SurveyingDocument4 pagesCEST PRELIM LT 9 2019-2020 SurveyingHarold Fritz GumawaNo ratings yet
- Struct Nov2019Document4 pagesStruct Nov2019ryanmikeNo ratings yet
- CEE330 - Influnece Lines PDFDocument9 pagesCEE330 - Influnece Lines PDFAvijit SahaNo ratings yet
- X Tan G : CE Review For Nov 2022 - Hydraulics 7Document1 pageX Tan G : CE Review For Nov 2022 - Hydraulics 7JuDeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document12 pagesLesson 5MIKE ARTHUR DAVID100% (1)
- Soil Lec SoilCompositionDocument4 pagesSoil Lec SoilCompositionMikaela LorescaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mech May 2021Document5 pagesFluid Mech May 2021Naigell SolomonNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsDocument1 pageRefresher Module 16 (GH8) - Geotechnical Engineering and HydraulicsMadelyn OronosNo ratings yet
- 2022 Nov Ce Preboard 1 MathDocument5 pages2022 Nov Ce Preboard 1 Mathrhoge hogeNo ratings yet
- Practice 1 PDFDocument9 pagesPractice 1 PDFJohn Paulo GregorioNo ratings yet
- CIVIL ENGINEERING EXAMDocument7 pagesCIVIL ENGINEERING EXAMAndrew PortugalNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsDocument18 pagesSoil Mechanics Problems and SolutionsBemzar SamsonNo ratings yet
- Week 5 6 Problem SetDocument3 pagesWeek 5 6 Problem SetFidel LansanganNo ratings yet
- Nov 2021 CoachingDocument71 pagesNov 2021 CoachingKenny CaluzaNo ratings yet
- RCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersDocument1 pageRCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersArwin VillegasNo ratings yet
- Feu Hydraulics PreboardDocument2 pagesFeu Hydraulics PreboardEla Macabante100% (1)
- Engineering Correlation Engineering CorrelationDocument8 pagesEngineering Correlation Engineering CorrelationMarbel PerezNo ratings yet
- Refresher Mste Module 031723 PDFDocument5 pagesRefresher Mste Module 031723 PDFRennekien MateoNo ratings yet
- MATH Problem Sets CE Review 2014Document93 pagesMATH Problem Sets CE Review 2014Aj OstiqueNo ratings yet
- Review innovations mechanical engineering exam problemsDocument3 pagesReview innovations mechanical engineering exam problemsKian InductivoNo ratings yet
- Steel 3Document3 pagesSteel 3Mayya Bona100% (1)
- Statics of Rigid Bodies 1: Email AddressDocument15 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies 1: Email AddressKc Kirsten Kimberly MalbunNo ratings yet
- 11 - Design of One-Way Slabs PDFDocument23 pages11 - Design of One-Way Slabs PDFAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNo ratings yet
- Local Media5124777314878222530Document6 pagesLocal Media5124777314878222530Joforce Karl MalanaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis For ShearDocument20 pagesDesign and Analysis For Shearhonesto reynaNo ratings yet
- M05 - SEC 5 Solution (131331) For FB PostingDocument11 pagesM05 - SEC 5 Solution (131331) For FB PostingRimar LiguanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument4 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical EngineeringPhreetzi Ünseen100% (1)
- Design and analysis of laterally supported steel beamsDocument9 pagesDesign and analysis of laterally supported steel beamsCristan RetuermaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyDocument2 pagesHydraulics and Geotechnical Answer KeyAngelica RomeroNo ratings yet
- PEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Document6 pagesPEF 2309 Fundamentos de Mecânica Das Estruturas Timoshenko, S.P.,PWS Publishing Company, 1997, Boston, USA, p.408-410, 580-583. Example 8-4Jc FortNo ratings yet
- STRUCTURAL THEORY REFRESHER SETDocument6 pagesSTRUCTURAL THEORY REFRESHER SETLa BeamNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnDocument2 pagesACFrOgC6RSwXitvNxv5doXAP4XkxEcDPev5JBWgWWpjIm48Kf0i - FaBwWf5y5kx8AAr2V HM5a9QynzxGonhZ - 17VAFd4bS5yAMOvRzRG5YDbIPKku0 YMNrF340S3 D7Kt3Xg8BwvwMGVVSFmnnMark Christian HerreraNo ratings yet
- 8-9 - Sieve AnalysisDocument2 pages8-9 - Sieve Analysisezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- Fine AggregatesDocument22 pagesFine Aggregatesezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- SILT TEST-Data SheetsDocument1 pageSILT TEST-Data Sheetsezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- Concrete Curing GuideDocument27 pagesConcrete Curing Guideezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- WRITTEN REPORT TemplateDocument2 pagesWRITTEN REPORT Templateezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- Blue Icon Charity InfographicDocument1 pageBlue Icon Charity Infographicezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Format SummaryDocument14 pagesBusiness Plan Format Summaryezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- Building Systems ReviewDocument142 pagesBuilding Systems Reviewhanafi100% (8)
- On Writing Book and Article ReviewDocument2 pagesOn Writing Book and Article Reviewezer joseph bacoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - Dynamics (Solutions Manual) PDFDocument2,961 pagesEngineering Mechanics - Dynamics (Solutions Manual) PDFloooooooooolNo ratings yet
- Multiphysics Computational Framework For Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Batteries Under Mechanical Abusive LoadingDocument13 pagesMultiphysics Computational Framework For Cylindrical Lithium-Ion Batteries Under Mechanical Abusive LoadingSravan ChantiNo ratings yet
- Quasi StaticDocument50 pagesQuasi StaticMuhammad Hussain BilalNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test Lab ReportDocument9 pagesTensile Test Lab ReportTan Xuennie0% (1)
- BVBVBVBVBBDocument9 pagesBVBVBVBVBBpspNo ratings yet
- DMM Question BankDocument2 pagesDMM Question Bankzubair ahmedNo ratings yet
- Fortron PPS PDFDocument57 pagesFortron PPS PDFmichaelNo ratings yet
- Deflection of Beam Group 3 PDFDocument11 pagesDeflection of Beam Group 3 PDFdarling youNo ratings yet
- Celanese Corporation Celanex® 1400A Polybutylene TerephthalateDocument2 pagesCelanese Corporation Celanex® 1400A Polybutylene TerephthalateTomGaliciaNo ratings yet
- Kips Flp-4-Mdcat PDFDocument14 pagesKips Flp-4-Mdcat PDFAbdul Salam Baloch100% (1)
- Stress: Engr. Estanislao M. Pialago Jr. PMEDocument16 pagesStress: Engr. Estanislao M. Pialago Jr. PMEBrianNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The NATM Tunnel Load On Concrete Lining Using The Ground Lining Interaction ModelDocument11 pagesEvaluation of The NATM Tunnel Load On Concrete Lining Using The Ground Lining Interaction ModelRAJAT PURWARNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Flexural Strength and Elastic Modulus of Two Different Provisional Restorative Materials Used in Fixed Prosthodontics: An In-Vitro StudyDocument4 pagesComparison of Flexural Strength and Elastic Modulus of Two Different Provisional Restorative Materials Used in Fixed Prosthodontics: An In-Vitro StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Gabrielle Morgan - Experiment #9Document6 pagesGabrielle Morgan - Experiment #9Gabrielle MorganNo ratings yet
- Eurocode Fire Engineering DesignDocument58 pagesEurocode Fire Engineering DesignxangNo ratings yet
- The CST PDFDocument10 pagesThe CST PDFk krishna chaitanya0% (1)
- RADIOSS 2017 Tutorials and ExamplesDocument947 pagesRADIOSS 2017 Tutorials and ExamplesRanjit PatilNo ratings yet
- FRP Product PDFDocument4 pagesFRP Product PDFGowrisankarNo ratings yet
- 01 (Asce) 1090-0241 (1998) 124 4Document13 pages01 (Asce) 1090-0241 (1998) 124 4Милица ДелићNo ratings yet
- Tensile Test - Intro & TheoryDocument8 pagesTensile Test - Intro & TheoryaidasuhanumNo ratings yet
- 497 PDFDocument117 pages497 PDFBakang MolefeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Soil Properties PresentationDocument21 pagesDynamic Soil Properties PresentationMohamedNo ratings yet
- Core Shear Properties of Sandwich Constructions by Beam FlexureDocument8 pagesCore Shear Properties of Sandwich Constructions by Beam FlexureBarang TeknikNo ratings yet
- b2wb6024150170bp261017 Aerofoil System (With Strengthening Bar) - Using 60x24mm Rhs Posts With 170 X 150 Base Plates PDFDocument16 pagesb2wb6024150170bp261017 Aerofoil System (With Strengthening Bar) - Using 60x24mm Rhs Posts With 170 X 150 Base Plates PDFatalayyNo ratings yet
- Astm d695-15 For Compressive Test of PlasticsDocument8 pagesAstm d695-15 For Compressive Test of PlasticsAnvit GadkarNo ratings yet
- 2268 8223 1 PBDocument13 pages2268 8223 1 PBJuanma Macias RosellóNo ratings yet
- Elastomeric Bearing - Full Details PDFDocument11 pagesElastomeric Bearing - Full Details PDFm.ispasNo ratings yet
- FEM Analysis of Landing Gear Strut PDFDocument3 pagesFEM Analysis of Landing Gear Strut PDFRaghu B SNo ratings yet
- 1988, KirbyDocument11 pages1988, KirbyWaibhaw KumarNo ratings yet
- Course FIle Corrective MeasureDocument6 pagesCourse FIle Corrective MeasureMuhammad Waqar NasirNo ratings yet