Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UT Useful Formulas: Feature Formula Remarks
Uploaded by
SANJAY AKASH BOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UT Useful Formulas: Feature Formula Remarks
Uploaded by
SANJAY AKASH BCopyright:
Available Formats
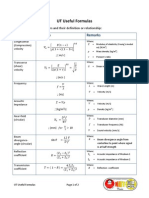
UT Useful Formulas
Main ultrasonic parameters and their definition or relationship:
Feature Formula Remarks
Longitudinal Where:
(Compression) = Modulus of elasticity (Young’s modul
us) [N/m2]
velocity
= Mass density [kg/m3]
; [ m/s ]
= Poisson’s ratio
Transverse Where:
(shear) = Shear modulus [N/m2]
velocity
; [m/s ]
Frequency Where:
= Wave Length [m]
= Velocity [m/s]
; [Hz]
Acoustic Where:
impedance = Velocity [m/s]
; [kg/m2s] = Density [kg/m3 ]
Near‐field Where:
= Transduser diameter [mm]
(circular)
= Transduser frequency [Hz]
; [mm]
= Sound velocity [mm/s]
Beam Where:
divergence‐ = Beam divergence angle from
angle (circular) centerline to point where signal
is at half strength
Reflection Where:
coefficient = Acoustic impedance of Medium 1
= Acoustic impedance of Medium 2
Transmission Where:
coefficient = Reflection coefficient
UT Useful Formulas Page 1 of 2
Snell’s law Where:
= the longitudinal wave velocities
in the first and second materials,
respectively
= the shear wave velocities in the
first and second materials,
respectively
= the angles of incident and
refracted longitudinal waves,
respectively
= the angles of the converted
reflected and refracted shear
waves, respectively
Amplitude Where:
attenuation = Initial (unattenuated) amplitude
= Attenuation coefficient [dB/m]
= Traveled distance [m]
Sound amplitude Where:
; [dB] = Amblitude of the first pulse
gain (or loss) in
= Amblitude of the second pulse
Decibel
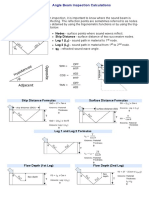
Distance to Where:
= Sound velocity (longitudinal or
reflector or
shear) [m/s]
discontinuity = Time difference [s]
(normal or angle
beam)
Surface Distance
& Depth (1st
Leg)
Surface Distance
& Depth (2nd
Leg)
Skip Distance for
weld inspection
UT Useful Formulas Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- UT Equations 1Document2 pagesUT Equations 1NeelakandanNo ratings yet
- Angle Beam Trig Calculations - Ultrasonic TestingDocument3 pagesAngle Beam Trig Calculations - Ultrasonic TestingArjun Rawat100% (3)
- Handout 8 WavesDocument6 pagesHandout 8 WavesMary Grace AcostaNo ratings yet
- NDT-Basic-FormulaeDocument3 pagesNDT-Basic-FormulaeJayeshNo ratings yet
- Clem Waves Lesson02 PresentationDocument29 pagesClem Waves Lesson02 PresentationAldiona DaulleNo ratings yet
- N4 & N5 - Waves and Radiation Summary NotesDocument21 pagesN4 & N5 - Waves and Radiation Summary NotesRana BustamiNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - Rafael DominguezDocument5 pagesPre Task - Rafael DominguezelianaNo ratings yet
- Refraction DispersionDocument74 pagesRefraction DispersionmaribeldeleonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Useful FormulaDocument4 pagesUltrasonic Testing Useful FormulaBaguz SaputraNo ratings yet
- Physics - WavesDocument21 pagesPhysics - WavesMemory SitambuliNo ratings yet
- UT EquationsDocument2 pagesUT EquationsNavneet Singh100% (1)
- Basics of Seismic ProspectingDocument68 pagesBasics of Seismic Prospectingshubham panchalNo ratings yet
- CP4 SummaryDocument2 pagesCP4 SummaryAhmad PatelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 c10Document14 pagesTutorial 1 c10Priyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Physics Fast Revision NotesDocument8 pagesPhysics Fast Revision NotesdivyanshagrawalbsNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - Fraiber ZambranoDocument5 pagesPre Task - Fraiber ZambranoLugar De La Mancha MuñozNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument1 pageWavesJordan ChizickNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Architectural Physics: Dr. Shankha Pratim BhattacharyaDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Architectural Physics: Dr. Shankha Pratim BhattacharyaArchana GavasNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Useful FormulaeDocument4 pagesUltrasonic Testing Useful Formulaerac mediaNo ratings yet
- Pre Task (1) - Brayan Devia - 203058 - 74 - Teoría Electromagnética y OndasDocument3 pagesPre Task (1) - Brayan Devia - 203058 - 74 - Teoría Electromagnética y OndasBrayan Andres Devia HerreraNo ratings yet
- Factsheet Physics: Stationary Waves On Strings and in Air ColumnsDocument3 pagesFactsheet Physics: Stationary Waves On Strings and in Air ColumnsM Abubakar BehgalNo ratings yet
- Sound:: PropagationDocument8 pagesSound:: PropagationDadan HamdaniNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument32 pagesWavesAllan GunawanNo ratings yet
- Midterm Report Instruct: A KRTDocument4 pagesMidterm Report Instruct: A KRTSheril Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- UT-Encyclopedia - FormulaDocument3 pagesUT-Encyclopedia - FormulaAllwynNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument11 pagesWavesdilsharakaviNo ratings yet
- 진동음향실험_조대승Document45 pages진동음향실험_조대승jwpaprk1No ratings yet
- Notes08 Turbulence Flow in Thin FilmsDocument27 pagesNotes08 Turbulence Flow in Thin FilmsYuryNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic PrintDocument2 pagesUltrasonic PrintALNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 Sound Wave and Light: Gelombang Bunyi Dan CahayaDocument51 pagesCHAPTER 1 Sound Wave and Light: Gelombang Bunyi Dan CahayaPuringNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law Impedance Phase Angle Magnetic Permeability: Home - General Resources Eddy Current Inspection FormulaDocument3 pagesOhm's Law Impedance Phase Angle Magnetic Permeability: Home - General Resources Eddy Current Inspection FormulaAllwynNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Light PDFDocument15 pagesThe Nature of Light PDFthinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Chapter 16 Part 1Document19 pagesLecture 1 - Chapter 16 Part 1Mircea PanteaNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic 4 Study GuideDocument8 pagesPhysics Topic 4 Study GuideSai 0235No ratings yet
- FAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000319 Reference Material I 18-Oct-2022 Fundamental of OpticsDocument13 pagesFAL (2022-23) FRESHERS PHY1008 ETH AP2022234000319 Reference Material I 18-Oct-2022 Fundamental of OpticsPritam PatraNo ratings yet
- 3 3 1 Progressive and Stationary WavesDocument3 pages3 3 1 Progressive and Stationary Waves11morganaNo ratings yet
- Wave MechanicsDocument77 pagesWave MechanicsAlbasher SahibuddinNo ratings yet
- Pre-Tarea - Reconocimiento - ANDRES GUEVARADocument5 pagesPre-Tarea - Reconocimiento - ANDRES GUEVARAanfer guegoNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled Documentapi-385992165No ratings yet
- (L2) - Waves - 24th Dec. PDFDocument49 pages(L2) - Waves - 24th Dec. PDFharishNo ratings yet
- Module 11 - Mechanical WavesDocument32 pagesModule 11 - Mechanical WavesJorge Jr DelgadoNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument28 pagesWAVESAbdallah Soud AllyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Waves (PTG)Document30 pagesLesson 10 - Waves (PTG)desiredheavensxNo ratings yet
- PH-X NotesDocument26 pagesPH-X NotesIlyas KhanNo ratings yet
- Oscillations and Waves SLDocument112 pagesOscillations and Waves SLyashitiwari011No ratings yet
- Waves (Physics) ? 2Document3 pagesWaves (Physics) ? 2Hiral KatyalNo ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument4 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskMelanny MenesesNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of WavesDocument12 pagesCharacteristics of WavesGabriela FernandezNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonics Level 3ADocument156 pagesUltrasonics Level 3Anayan vyas100% (2)
- Mechanical Waves2Document29 pagesMechanical Waves2Dennis ANo ratings yet
- Properties of WaveDocument61 pagesProperties of WavePASSAWAT BOONCHITSIRIKULNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes - Waves Part 1Document3 pagesPhysics Notes - Waves Part 1ankur11783officialNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties PosterDocument1 pageWave Properties Posterjaxsonsalminen1302No ratings yet
- My Waves NotesDocument2 pagesMy Waves NotesphydotsiNo ratings yet
- Exercise Tester - Unit 1 - EMWCharacterizationDocument1 pageExercise Tester - Unit 1 - EMWCharacterizationJulio CaceresNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 Principle of SoundDocument44 pagesTopic 9 Principle of SoundSurie AiniezaNo ratings yet
- CfE Waves and Sound NOTES NAT 4 With Answers.Document26 pagesCfE Waves and Sound NOTES NAT 4 With Answers.Ross O'BrienNo ratings yet
- Waves and SuperpositionsDocument19 pagesWaves and SuperpositionsTazrin BibortonNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Science Revision PowerpointDocument45 pages10.3 Science Revision PowerpointJeffreyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Q4 SLM3Document13 pagesPhysical Science Q4 SLM3Winsear VardeNo ratings yet
- 4PH0 1P Que 20160119Document28 pages4PH0 1P Que 20160119naamashirNo ratings yet
- Answer Key & Solutions: ScienceDocument4 pagesAnswer Key & Solutions: ScienceBhanu PurushothamaNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Splicing and Testing NTCDocument122 pagesOptical Fiber Splicing and Testing NTCfmsarwarNo ratings yet
- Expanded Beam White PaperDocument14 pagesExpanded Beam White PaperM. SaadNo ratings yet
- OFC Question BankDocument4 pagesOFC Question BankSaurabh WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/23Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- Applications of Total Internal ReflectionDocument2 pagesApplications of Total Internal ReflectionAbdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Paper 6 NotesDocument9 pagesPaper 6 NotesabdulNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Fiber Optics and Waveguides - SolutionsDocument4 pagesWeek 4 - Fiber Optics and Waveguides - SolutionsSamar PratapNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Module 1Document63 pagesFiber Optics Module 1Ravi Teja AJNo ratings yet
- User Manual Gem Cut StudioDocument61 pagesUser Manual Gem Cut StudioAlvaro GuarinNo ratings yet
- Tomasi Chapter 14 SummaryDocument4 pagesTomasi Chapter 14 SummaryNico RobinNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments: Chapter NineDocument8 pagesRay Optics and Optical Instruments: Chapter NineRohit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Class X - Science - Pre Board I - 2020-21 - Pages-DeletedDocument9 pagesClass X - Science - Pre Board I - 2020-21 - Pages-DeletedRylan DsaNo ratings yet
- Light Prism Pandathe Test2 Question PaperDocument4 pagesLight Prism Pandathe Test2 Question Paperboltu100% (1)
- PH 110 Physics Laboratory Instruction Manual: # (I) Instructions To StudentsDocument38 pagesPH 110 Physics Laboratory Instruction Manual: # (I) Instructions To StudentsKaranpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Sound: 1) Longitudinal Wave Motion and 2) Transverse Wave MotionDocument31 pagesSound: 1) Longitudinal Wave Motion and 2) Transverse Wave MotionVinothNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Oscillations and WavesDocument55 pagesLecture Notes - Oscillations and WavesRashmikaNo ratings yet
- Ten Years Board Problems CBSE 2018Document9 pagesTen Years Board Problems CBSE 2018Adhish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation On Light Emitting Concrete - Translucent ConcreteDocument11 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On Light Emitting Concrete - Translucent ConcreteTECH MACNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument51 pagesLIGHTMaryam ShahidNo ratings yet
- MCE enDocument192 pagesMCE enAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Optics F 1 Ass 1Document11 pagesOptics F 1 Ass 1NikhilPrakashNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 (Science-2020)Document3 pagesExperiment 2 (Science-2020)VivekNo ratings yet
- Refraction Through PrismDocument2 pagesRefraction Through PrismOrbit MBBS PreparationNo ratings yet
- Physics Huygen's Principle and Law of Refraction and Young's Double Slit ExperimentDocument32 pagesPhysics Huygen's Principle and Law of Refraction and Young's Double Slit Experimente.laneNo ratings yet
- Studentinfo HomeworkDocument23 pagesStudentinfo HomeworkTANISHA TANISHANo ratings yet
- Physica B: Keyin Li, Kangxian Guo, Litao LiangDocument5 pagesPhysica B: Keyin Li, Kangxian Guo, Litao LiangMohamed JaawaneNo ratings yet
- Physics Gce o Level Syllabus 2010 2Document44 pagesPhysics Gce o Level Syllabus 2010 2abi_5dec94100% (3)