Professional Documents
Culture Documents
74F85 4-Bit Magnitude Comparator: Features Pin Configuration
Uploaded by
Maykerr MontoyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
74F85 4-Bit Magnitude Comparator: Features Pin Configuration
Uploaded by
Maykerr MontoyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4-bit magnitude comparator 74F85
FEATURES PIN CONFIGURATION
• High-impedance NPN base inputs for reduced loading
(20µA in High and Low states) B3 1 16 VCC
• Magnitude comparison of any binary words IA<B 2 15 A3
• Serial or parallel expansion without extra gating IA=B 3 14 B2
IA>B 4 13 A2
A>B 5 12 A1
DESCRIPTION
The 74F85 is a 4-bit magnitude comparator that can be expanded to A=B 6 11 B1
almost any length. It compares two 4-bit binary, BCD, or other A<B 7 10 A0
monotonic codes and presents the three possible magnitude results
at the outputs. The 4-bit inputs are weighted (A0–A3) and (B0–B3) GND 8 9 B0
where A3 and B3 are the most significant bits. The operation of the
74F85 is described in the Function Table, showing all possible logic SF00075
conditions. The upper part of the table describes the normal
operation under all conditions that will occur in a single device or in
a series expansion scheme. In the upper part of the table the three TYPE TYPICAL TYPICAL
outputs are mutually exclusive. In the lower part of the table, the PROPAGATION SUPPLY CURRENT
outputs reflect the feed-forward conditions that exist in the parallel DELAY (TOTAL)
expansion scheme. The expansion inputs IA>B, and IA=B and IA<B 74F85 7.0ns 40mA
are the least significant bit positions. When used for series
expansion, the A>B, A=B and A<B outputs of the lease significant
word are connected to the corresponding IA>B, IA=B and IA<B inputs
ORDERING INFORMATION
of the next higher stage. Stages can be added in this manner to any COMMERCIAL RANGE
length, but a propagation delay penalty of about 15ns is added with DESCRIPTION VCC = 5V ±10%, PKG DWG #
each additional stage. For proper operation, the expansion inputs of Tamb = 0°C to +70°C
the least significant word should be tied as follows: IA>B = Low, 16-pin plastic DIP N74F85N SOT38-4
IA=B = High, and IA<B = Low.
16-pin plastic SO N74F85D SOT162-1
INPUT AND OUTPUT LOADING AND FAN OUT TABLE
PINS DESCRIPTION 74F (U.L.) HIGH/LOW LOAD VALUE HIGH/LOW
A0–A3 Comparing inputs 1.0/0.033 20µA/20µA
B0–B3 Comparing inputs 1.0/0.033 20µA/20µA
IA<B, IA=B, IA>B Expansion inputs (active High) 1.0/0.033 20µA/20µA
A<B, A=B, A>B Data outputs (active High) 50/33 1.0mA/20mA
NOTE: One (1.0) FAST unit load is defined as: 20µA in the High state and 0.6mA in the Low state.
LOGIC SYMBOL IEC/IEEE SYMBOL
10 12 13 15 9 11 14 1 10 COMP
0
12
13 P
A0 A1 A2 A3 B0 B1 B2 B3 15
3
2 IA<B 9 7
0 P<Q
11 6
P=Q
3 IA=B
14 Q 5
P>Q
4 IA>B 1
3
A>B A=B A<B 2
<
3
=
4
VCC = Pin 16 >
GND = Pin 8 5 6 7
SF00076 SF00077
September 27, 1994 2 853–0055 13903
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4-bit magnitude comparator 74F85
LOGIC DIAGRAM
15
A3
1
B3
5
A>B
13
A2
14
B2
2
IA<B
3 6
IA=B A=B
4
IA>B
12
A1
11
B1
7
A<B
10
A0
9
B0
VCC = Pin 16
GND = Pin 8
SF00078
FUNCTION TABLE
COMPARING INPUTS EXPANSION INPUTS OUTPUTS
A3,B3 A2,B2 A1,B1 A0,B0 IA>B IA<B IA=B A>B A<B A=B
A3>B3 X X X X X X H L L
A3<B3 X X X X X X L H L
A3=B3 A2>B2 X X X X X H L L
A3=B3 A2<B2 X X X X X L H L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1>B1 X X X X H L L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1<B1 X X X X L H L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0>B0 X X X H L L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0<B0 X X X L H L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0=B0 H L L H L L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0=B0 L H L L H L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0=B0 L L H L L H
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0=B0 X X H L L H
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0=B0 H H L L L L
A3=B3 A2=B2 A1=B1 A0=B0 L L L H H L
H = High voltage level
L = Low voltage level
X = Don’t care
September 27, 1994 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
4-bit magnitude comparator 74F85
APPLICATION
The parallel expansion scheme shown in Figure 1 demonstrates the
INPUTS most efficient general use of these comparators. The expansion
inputs can be used as a fifth input bit position except on the least
(LSB) B23 B3
significant device, which must be connected as in the serial scheme.
A23 A3
B22 B2
The expansion inputs used by labeling IA>B as an “A” input, IA<B as
A22 A2 a “B” input and setting IA=B = Low. The 74F85 can be used as a 5-bit
B21 B1 A<B comparator only when the outputs are used to drive the (A0–A3) and
A21 A1 A=B NC (B0–B3) inputs of another 74F85 device. The parallel technique can
B20 B0 A>B be expanded to any number of bits as shown in Table 1.
A20 A0
B19 IA<B
L IA=B
Table 1.
A19 IA>B NUMBER OF TYPICAL SPEEDS
WORD LENGTH
PACKAGES 74F
B18 B3
A18 A3 1–4 bits 1 12ns
B17 B2
5–24 bits 2–6 22ns
A17 A2
B16 B1 A<B 25–120 bits 8–31 34ns
A16 A1 A=B NC
B15 B0 A>B
A15 A0
B14 IA<B
L IA=B
A14 IA>B
B13 B3 B3
A13 A3 A3
B12 B2 B2
A12 A2 A2 OUTPUTS
B11 B1 A<B B1 A<B
A11 A1 A=B NC A1 A=B
B10 B0 A>B B0 A>B
A10 A0 A0
B9 IA<B A<B
L IA=B A=B
A9 IA>B A>B
B8 B3
A8 A3
B7 B2
A7 A2
B6 B1 A<B
A6 A1 A=B NC
B5 B0 A>B
A5 A0
B4 IA<B
L IA=B
A4 IA>B
B3 B3
A3 A3
B2 B2
A2 A2
B1 B1 A<B
A1 A1 A=B
(LSB) B0 B0 A>B
A0 A0
L IA<B
H IA=B
L IA>B
SF00079
Figure 1. Comparison of Two 24-Bit Words
September 27, 1994 4
You might also like
- 4-Bit Magnitude Comparator: Philips SemiconductorsDocument10 pages4-Bit Magnitude Comparator: Philips SemiconductorsSridhar KandlaguntaNo ratings yet
- 74LS85 (On) PDFDocument9 pages74LS85 (On) PDFJuanDiegoNo ratings yet
- 74LS85Document4 pages74LS85jaja558No ratings yet
- 4-Bit Magnitude Comparator SN54/74LS85: Low Power SchottkyDocument4 pages4-Bit Magnitude Comparator SN54/74LS85: Low Power SchottkyRenjan SolisNo ratings yet
- 4-Bit Magnitude Comparator SN54/74LS85: Low Power SchottkyDocument4 pages4-Bit Magnitude Comparator SN54/74LS85: Low Power SchottkySon HungleNo ratings yet
- HCF4063B: 4-Bit Magnitude ComparatorDocument9 pagesHCF4063B: 4-Bit Magnitude ComparatorHarish YadavNo ratings yet
- 74245_PHILLIPSDocument10 pages74245_PHILLIPSandrycastNo ratings yet
- 74HCHCT85Document9 pages74HCHCT85Edison Abado AnccoNo ratings yet
- Digital Techniques Lab - 4-bit Magnitude ComparatorDocument8 pagesDigital Techniques Lab - 4-bit Magnitude ComparatorARSLAN IJAZNo ratings yet
- DLD LAB Experiment 3 2014Document5 pagesDLD LAB Experiment 3 2014Dinh LâmNo ratings yet
- High-Performance Silicon-Gate CMOS: Semiconductor Technical DataDocument6 pagesHigh-Performance Silicon-Gate CMOS: Semiconductor Technical DataJosé AdelinoNo ratings yet
- 74LS85 PDFDocument4 pages74LS85 PDFDeni KhanNo ratings yet
- TC7MB3251FK: 1-Of-8 FET Multiplexer/DemultiplexerDocument7 pagesTC7MB3251FK: 1-Of-8 FET Multiplexer/DemultiplexerKush SethiNo ratings yet
- vc33 Kopl Kurzba eDocument1 pagevc33 Kopl Kurzba eSafetyjoe2No ratings yet
- Lab 4Document6 pagesLab 4JohnNo ratings yet
- Digital System Lab 6Document5 pagesDigital System Lab 6Abdul Hafiz ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Caring Beyond Our Technical DocumentationDocument4 pagesCaring Beyond Our Technical DocumentationBarbara SilvaNo ratings yet
- SN74LS85 4-Bit Magnitude Comparator: LOW Power SchottkyDocument9 pagesSN74LS85 4-Bit Magnitude Comparator: LOW Power SchottkygbrsylarNo ratings yet
- 4-B It Binary Full Adder: VCC Pin 16 GND Pin 8Document4 pages4-B It Binary Full Adder: VCC Pin 16 GND Pin 8Norberto Delgado del AngelNo ratings yet
- I/O Connector Quick Reference GuideDocument8 pagesI/O Connector Quick Reference GuidethehanhctmNo ratings yet
- 74ABT245 Octal Transceiver With Direction Pin (3-State) : Features DescriptionDocument6 pages74ABT245 Octal Transceiver With Direction Pin (3-State) : Features DescriptionBontha RajuNo ratings yet
- 7485 Comparador DatasheetDocument9 pages7485 Comparador DatasheetJuan Ramírez SNo ratings yet
- MC74AC245, MC74ACT245 Octal Bidirectional Transceiver With 3 State Inputs/OutputsDocument10 pagesMC74AC245, MC74ACT245 Octal Bidirectional Transceiver With 3 State Inputs/OutputsPanagiotis PanagosNo ratings yet
- TLC1542C, TLC1542I, TLC1542M, TLC1542Q, TLC1543C, TLC1543I, TLC1543Q 10-Bit Analog-To-Digital Converters With Serial Control and 11 Analog InputsDocument27 pagesTLC1542C, TLC1542I, TLC1542M, TLC1542Q, TLC1543C, TLC1543I, TLC1543Q 10-Bit Analog-To-Digital Converters With Serial Control and 11 Analog InputsCarlos Alberto de Andrade Freitas JuniorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Digital ComparatorsDocument2 pagesChapter 7 - Digital ComparatorsJugurtha MeddourNo ratings yet
- T67CB T67CBWDocument3 pagesT67CB T67CBWEdgard ChancayauriNo ratings yet
- Data-HD74LS245 Octal Bus TransceiversDocument6 pagesData-HD74LS245 Octal Bus TransceiversGallego OrtizNo ratings yet
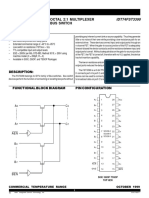
- IDT74FST3390 OCTAL 2:1 MULTIPLEXER BUS SWITCHDocument5 pagesIDT74FST3390 OCTAL 2:1 MULTIPLEXER BUS SWITCHspotNo ratings yet
- sp5055 PDFDocument9 pagessp5055 PDFami oreverNo ratings yet
- Dual 4-Line To 1-Line Multiplexer: Integrated CircuitsDocument9 pagesDual 4-Line To 1-Line Multiplexer: Integrated Circuitspriyasumbria46No ratings yet
- 64-Bit TTL Bipolar RAM, Inverting (3-State) : Integrated CircuitsDocument10 pages64-Bit TTL Bipolar RAM, Inverting (3-State) : Integrated CircuitsEdher Hugo Morales EscobedoNo ratings yet
- 74HC245 Octal 3 State Noninverting Bus Transceiver: High Performance Silicon Gate CMOSDocument9 pages74HC245 Octal 3 State Noninverting Bus Transceiver: High Performance Silicon Gate CMOSsdsNo ratings yet
- 74HC245 Octal 3 State Noninverting Bus Transceiver: High Performance Silicon Gate CMOSDocument8 pages74HC245 Octal 3 State Noninverting Bus Transceiver: High Performance Silicon Gate CMOSAmit BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Sy8105 Tsot23-6 Mark NyxyzDocument11 pagesSy8105 Tsot23-6 Mark NyxyzrammerDankovNo ratings yet
- Unit 7Document12 pagesUnit 7Suresh MeesalaNo ratings yet
- 74HCT245 Octal 3-State Noninverting Bus Transceiver With LSTTL-Compatible InputsDocument8 pages74HCT245 Octal 3-State Noninverting Bus Transceiver With LSTTL-Compatible InputsadilNo ratings yet
- 8-Bit Bidirectional Binary Counter (3-State) : Integrated CircuitsDocument12 pages8-Bit Bidirectional Binary Counter (3-State) : Integrated CircuitsShadowHollow333No ratings yet
- Am29f400bb 90si Amd Datasheet 72825Document5 pagesAm29f400bb 90si Amd Datasheet 72825Joel AgbekponouNo ratings yet
- Siemens VC DefaultDocument1 pageSiemens VC DefaultFida HussainNo ratings yet
- D3FC-UK ParkerDocument8 pagesD3FC-UK ParkerFernando BorgesNo ratings yet
- SN 74 Ls 245Document19 pagesSN 74 Ls 245Luisdceo LggNo ratings yet
- SN74LS245Document6 pagesSN74LS245api-3825669No ratings yet
- Description/ordering Information: SN54AC245, SN74AC245 Octal Bus Transceivers With 3-State OutputsDocument22 pagesDescription/ordering Information: SN54AC245, SN74AC245 Octal Bus Transceivers With 3-State OutputsStuxnetNo ratings yet
- ls245 PDFDocument18 pagesls245 PDFEL Picasesos TE VA PicarNo ratings yet
- MC 14510B Contador Ascendente Descendente BCDDocument10 pagesMC 14510B Contador Ascendente Descendente BCDmenu1973No ratings yet
- Window Discriminator TCA 965 B: Preliminary Bipolar ICDocument18 pagesWindow Discriminator TCA 965 B: Preliminary Bipolar ICMasli DarNo ratings yet
- DM74LS90/DM74LS93 Decade and Binary Counters: General DescriptionDocument10 pagesDM74LS90/DM74LS93 Decade and Binary Counters: General DescriptionThế giới điện tửNo ratings yet
- Eee 342 PpiDocument71 pagesEee 342 PpiHafiz Adil AsrarNo ratings yet
- VU Meter A Led, KA2284Document3 pagesVU Meter A Led, KA2284hamed sazegaranNo ratings yet
- DAC-HP Series: High-Performance, 16-Bit Digital-to-Analog ConvertersDocument4 pagesDAC-HP Series: High-Performance, 16-Bit Digital-to-Analog ConvertersStephan BaltzerNo ratings yet
- 24VDCDocument6 pages24VDCAB-S ELECTRO MECHANICAL INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATIONNo ratings yet
- SN74LS245 Octal Bus Transceiver: LOW Power SchottkyDocument4 pagesSN74LS245 Octal Bus Transceiver: LOW Power Schottky4909151No ratings yet
- DSD QB Sol.Document22 pagesDSD QB Sol.Erana RanaNo ratings yet
- HCF4033B: Decade Counter/Divider With Decoded 7-Segment Display Output and Ripple BlankingDocument11 pagesHCF4033B: Decade Counter/Divider With Decoded 7-Segment Display Output and Ripple BlankingtimNo ratings yet
- SN74LS47 BCD To 7-Segment Decoder/Driver: LOW Power SchottkyDocument8 pagesSN74LS47 BCD To 7-Segment Decoder/Driver: LOW Power SchottkyJesus AntonioNo ratings yet
- DIGI-260 - Lab 08 - Digital-to-Analog Conversion - Rev 04Document15 pagesDIGI-260 - Lab 08 - Digital-to-Analog Conversion - Rev 04KirkNo ratings yet
- Dac & Adc SCDocument4 pagesDac & Adc SCsameer rajNo ratings yet
- Arduino MusicaDocument393 pagesArduino Musicampison100% (11)
- Tutorial 04 - Processing Introduction2Document22 pagesTutorial 04 - Processing Introduction2Maykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- SG90 TowerProDocument6 pagesSG90 TowerProImanuel YosuaNo ratings yet
- Wonderware Intouch Users: Wonderware Programming - Tank Filling Example With Complete ScriptDocument11 pagesWonderware Intouch Users: Wonderware Programming - Tank Filling Example With Complete ScriptMaykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- 74HC HCT595 PDFDocument24 pages74HC HCT595 PDFseanz001No ratings yet
- TT2170LS PDFDocument4 pagesTT2170LS PDFJosé BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Wonderware Intouch Users: Wonderware Programming - Tank Filling Example With Complete ScriptDocument11 pagesWonderware Intouch Users: Wonderware Programming - Tank Filling Example With Complete ScriptMaykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer - Oscillator TutorialDocument26 pages555 Timer - Oscillator TutorialAnonymous 8bbVmLtQNo ratings yet
- Respaldo 3Document5 pagesRespaldo 3Maykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- ITScripts and LogicDocument202 pagesITScripts and LogicvaldecirpacheosouzaNo ratings yet
- Respaldo 2Document4 pagesRespaldo 2Maykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- 74163Document12 pages74163Obenelia MartinezNo ratings yet
- LCD Fvx4i5lhpg4n6z8 PDFDocument1 pageLCD Fvx4i5lhpg4n6z8 PDFMaykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- 74F148 8-Line to 3-Line Priority EncoderDocument6 pages74F148 8-Line to 3-Line Priority EncodersaralabitmNo ratings yet
- 54F/74F138 1-Of-8 Decoder/Demultiplexer: General Description FeaturesDocument11 pages54F/74F138 1-Of-8 Decoder/Demultiplexer: General Description FeaturesMaykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Dual 2-To-4 Line Decoder/demultiplexer 74HC/HCT139: Philips Semiconductors Product SpecificationDocument3 pagesDual 2-To-4 Line Decoder/demultiplexer 74HC/HCT139: Philips Semiconductors Product SpecificationMaykerr MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Costas Loop For BPSK DemodulatorDocument5 pagesDesign and Implementation of Costas Loop For BPSK DemodulatorBushra AnsariNo ratings yet
- Rockford Fosgate 1100a2 Review: Powerful 2-Channel AmpDocument2 pagesRockford Fosgate 1100a2 Review: Powerful 2-Channel Ampfloyd21No ratings yet
- 07 Registers and CountersDocument28 pages07 Registers and CountersChandravadhana NarayananNo ratings yet
- Active Band Pass Filter DesignDocument11 pagesActive Band Pass Filter DesignFarhan NitrateNo ratings yet
- Digital Principles and System Design Lecture PlanDocument3 pagesDigital Principles and System Design Lecture PlanaddssdfaNo ratings yet
- K7400 K7500 MONITOR block diagramDocument1 pageK7400 K7500 MONITOR block diagramcomzNo ratings yet
- PIC18F248Document402 pagesPIC18F248Ioannis PerperisNo ratings yet
- Experiment: Design of Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters Design of Mod-5 Synchronous CounterDocument3 pagesExperiment: Design of Synchronous and Asynchronous Counters Design of Mod-5 Synchronous CounterVrushali patilNo ratings yet
- Analog Integrated CircuitDocument19 pagesAnalog Integrated CircuitmanishaNo ratings yet
- Am Radio Receiver With Single Ic Mk484Document3 pagesAm Radio Receiver With Single Ic Mk484Tio Sam Drexler100% (1)
- Frequency Bands and Applications: International Telecommunication UnionDocument7 pagesFrequency Bands and Applications: International Telecommunication UniongezahegnNo ratings yet
- Advanced VLSI Design Lab (EC17203) : Experiment No. 7Document4 pagesAdvanced VLSI Design Lab (EC17203) : Experiment No. 7Huzaifa AhmedNo ratings yet
- TK-3202 3206-K.K2.M.M2 M.M3 PDFDocument45 pagesTK-3202 3206-K.K2.M.M2 M.M3 PDFengelalex2014No ratings yet
- Digital Circuits Demultiplexer QuestionsDocument75 pagesDigital Circuits Demultiplexer QuestionsJai RajeshNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Home Theater Circuit Diagram Using Ic Tda2030Document3 pages5.1 Home Theater Circuit Diagram Using Ic Tda2030jose luis rodriguez caberos60% (5)
- NOR Gate ExplainedDocument3 pagesNOR Gate ExplainedRahul Kumar MinaNo ratings yet
- CMOSIC For Current-Mode PWM Power Supply: Hiroshi MaruyamaDocument6 pagesCMOSIC For Current-Mode PWM Power Supply: Hiroshi MaruyamaMalfo10No ratings yet
- M29F800DT M29F800DB: 8 Mbit (1Mb x8 or 512Kb x16, Boot Block) 5V Supply Flash MemoryDocument40 pagesM29F800DT M29F800DB: 8 Mbit (1Mb x8 or 512Kb x16, Boot Block) 5V Supply Flash MemoryAn as akrasNo ratings yet
- Design 2-digit BCD display using 7447 decoder & 7490 counterDocument23 pagesDesign 2-digit BCD display using 7447 decoder & 7490 counterrowmanNo ratings yet
- Features Description: 4-Ampere Dual Low-Side Ultrafast MOSFET DriversDocument13 pagesFeatures Description: 4-Ampere Dual Low-Side Ultrafast MOSFET DriversBabajide AdedapoNo ratings yet
- DLC Previous Questions PapersDocument12 pagesDLC Previous Questions PapersSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- M12l64164a (2y) PDFDocument45 pagesM12l64164a (2y) PDFTeddy KhantNo ratings yet
- Introductory PagesDocument15 pagesIntroductory PagesTejeswari polaki0% (1)
- Multisimm Report 301 Final ProjectDocument3 pagesMultisimm Report 301 Final Projectapi-296881750No ratings yet
- HazardsDocument58 pagesHazardsAshutosh Verma100% (1)
- Chapter09 - Advanced Techniques in CMOS Logic CircuitsDocument25 pagesChapter09 - Advanced Techniques in CMOS Logic CircuitsMalvika Diddee100% (1)
- Lecture 100 (Instrumentation Amplifier)Document3 pagesLecture 100 (Instrumentation Amplifier)ShubamNo ratings yet
- SEO-optimized title for digital logic gates documentDocument5 pagesSEO-optimized title for digital logic gates documentAtta Ur Rahman AfridiNo ratings yet
- Notes On Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps)Document16 pagesNotes On Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps)Venu Gopal Rao AggressNo ratings yet
- Monostable MultivibratorDocument15 pagesMonostable MultivibratorHema SundarNo ratings yet