Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kinematically Indeterminate Structures Slope Deflection Method
Uploaded by
mujeeb0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageThis document discusses kinematically indeterminate structures and the slope deflection method of analysis. A structure is kinematically indeterminate if the unknown joint deflections caused by loading cannot be determined through compatibility conditions alone. The slope deflection method can be used to analyze statically determinate and indeterminate beams/frames by assuming deformations are due only to bending. For kinematically indeterminate structures, additional unknowns like sway must be considered, requiring more equations to solve for member end moments and joint rotations.
Original Description:
Original Title
sa mod 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses kinematically indeterminate structures and the slope deflection method of analysis. A structure is kinematically indeterminate if the unknown joint deflections caused by loading cannot be determined through compatibility conditions alone. The slope deflection method can be used to analyze statically determinate and indeterminate beams/frames by assuming deformations are due only to bending. For kinematically indeterminate structures, additional unknowns like sway must be considered, requiring more equations to solve for member end moments and joint rotations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageKinematically Indeterminate Structures Slope Deflection Method
Uploaded by
mujeebThis document discusses kinematically indeterminate structures and the slope deflection method of analysis. A structure is kinematically indeterminate if the unknown joint deflections caused by loading cannot be determined through compatibility conditions alone. The slope deflection method can be used to analyze statically determinate and indeterminate beams/frames by assuming deformations are due only to bending. For kinematically indeterminate structures, additional unknowns like sway must be considered, requiring more equations to solve for member end moments and joint rotations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
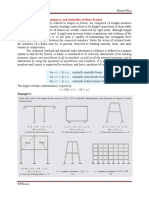
Kinematically inDeterminate structure.
When a structure is loaded, it undergoes deflection at
the joints i.e. translation and rotation. In slope deflection method of analysis, these deflections
are treated as unknown quantities. If these unknown quantities can be found by applying
compatibility conditions alone then the structure is Kinematically Determinate. However, if these
unknown deflections cannot be found by compatibility conditions then the structure is
Kinematically Indeterminate (KI), the Indeterminacy being the number of unknown deflections
which cannot be found by compatibility conditions. This will be clear by giving a few examples.
In these examples axial deformation is neglected.eg propped cantilever.advtge of slop
deflection- a.It can be used to analyze statically determinate and indeterminate beams and
frames. b. In this method it is assumed that all deformations are due to bending only. c. In other
words deformations due to axial forces are neglected. d. The slope-deflection equations are not
that lengthy in comparison.behaviour of portal frame with sway- In sway frames there is a in-
plane displacement due to horizontal force (or) asymmetrical loading (or) different moment of
inertia (or) unequal legs in Portal frame. An unsymmetrical portal frame is that which either
frames are not symmetrical or the loading symmetrical. In such cases, the rigid joints between
the columns and the beams will have a motion of translation called sway. The sway of the
columns will become additional unknown quantity and additional equations are required to
analyse the structure. 1Unsymmetrical loading (eccentric loading2Different end conditions of
the columns of the frame3Non uniform sections of the members4Horizontal loading on column
of the frameSettlement of the supports of the frame.procedure of slope deflection
md•Determine the fixed-end moments for the members of the beam.•Determine the
rotations of the chord if there is any support settlement.•Write the slope-deflection
equation for the members’ end moments in terms of unknown rotations.•Write the
equilibrium equations at each joint that is free to rotate in terms of the end moments of
members connected at that joint.•Solve the system of equations obtained simultaneously to
determine the unknown joint rotations.•Substitute the computed joint rotations into the
equations obtained in step 3 to determine the members’ end moments•Draw a free-body
diagram of the indeterminate beams indicating the end moments at the joint.•Draw the
shearing force diagrams of the beam by considering the freebody diagram of each span of
the beam in the case of a multi-span structure.-degree of freedom- The number of
independent ways by which a dynamic system can move, without violating any constraint imposed
on it, is called number of degrees of freedom. In other words, the number of degrees of freedom can
be defined as the minimum number of independent coordinates that can specify the position of the
system completely.
You might also like
- Beams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsFrom EverandBeams and Framed Structures: Structures and Solid Body MechanicsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Lecture 1428730889Document53 pagesLecture 1428730889Govind Gaurav100% (2)
- Non-Linear Structures: Matrix Methods of Analysis and Design by ComputersFrom EverandNon-Linear Structures: Matrix Methods of Analysis and Design by ComputersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Structural Analysis 2Document52 pagesStructural Analysis 2Srinivas EnamandramNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument54 pagesSlope Deflection Methodsuhademir100% (2)
- Structural Analysis PDFDocument52 pagesStructural Analysis PDFShamran KhanNo ratings yet
- 05a - ASTT-2015 Metode Defleksi-Sudut KemiringanDocument39 pages05a - ASTT-2015 Metode Defleksi-Sudut Kemiringandwi sakNo ratings yet
- Wk6L16 18Document21 pagesWk6L16 18lengs SimzNo ratings yet
- 05-ASTT-2015 Metode Defleksi-Sudut KemiringanDocument39 pages05-ASTT-2015 Metode Defleksi-Sudut KemiringankatonNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis-IIDocument10 pagesStructural Analysis-IIRitwik PaulNo ratings yet
- Hari KrishanDocument6 pagesHari KrishanharikrishanNo ratings yet
- Determinate beams and frames analysisDocument35 pagesDeterminate beams and frames analysisColin MacDougallNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection Method ExplainedDocument33 pagesSlope Deflection Method ExplainedBari FayzulNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection MethodDocument21 pagesSlope Deflection MethodDivya Ramdev100% (1)
- Unit 4 PDFDocument55 pagesUnit 4 PDFHAyath KNo ratings yet
- Civil Iii Year 2017-2018Document109 pagesCivil Iii Year 2017-2018Frank JohnNo ratings yet
- Force Methods - Consistent DeformationDocument41 pagesForce Methods - Consistent DeformationShakira100% (4)
- ST 1 MarksDocument15 pagesST 1 Marksashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Beam Examples02Document114 pagesBeam Examples02pitamberNo ratings yet
- CE5101 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS-II Lecture NotesDocument25 pagesCE5101 STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS-II Lecture Notesधीरज कुमारNo ratings yet
- Displacement Method Analysis of Indeterminate StructuresDocument118 pagesDisplacement Method Analysis of Indeterminate StructuresRennee Son BancudNo ratings yet
- Module 5, Week 5, CE-301, Dr. Bashir AlamDocument51 pagesModule 5, Week 5, CE-301, Dr. Bashir AlamMohd IdreesNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis (FINALS) PDFDocument45 pagesStructural Analysis (FINALS) PDFJunel Torrejos100% (1)
- Sample Seismic Analysis ReportDocument14 pagesSample Seismic Analysis ReportricardobonillaNo ratings yet
- CH2 Analysis of Statically Determinate StructureDocument37 pagesCH2 Analysis of Statically Determinate StructureKong VisalNo ratings yet
- CIVIL III YEAR 2 Marks 16 Marks PDFDocument116 pagesCIVIL III YEAR 2 Marks 16 Marks PDFELEVATED KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- The SlopeDocument2 pagesThe SlopeIkechukwu OkekeNo ratings yet
- L6 Deflection and StiffnessDocument21 pagesL6 Deflection and StiffnessBabila JosephNo ratings yet
- L29 - Beam DeflectionsDocument13 pagesL29 - Beam DeflectionsVince CabugNo ratings yet
- Eas Unit IiDocument260 pagesEas Unit IiRekha ManideepNo ratings yet
- Structural Engg. Lecture 1Document34 pagesStructural Engg. Lecture 1Mr. Danish SaeedNo ratings yet
- Self EvaluationDocument19 pagesSelf EvaluationRheanna SalutanNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis NotesDocument166 pagesStructural Analysis NotesdunyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Stiffness Method For FrmesDocument26 pagesLesson 5 Stiffness Method For Frmescriscab12345No ratings yet
- C-SA2-Three Moment Equations MethodDocument34 pagesC-SA2-Three Moment Equations Methodeid ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Rigid Body Equilibrium and Structural AnalysisDocument26 pagesRigid Body Equilibrium and Structural AnalysisAnkur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Statically Determinate Plane TrussDocument56 pagesStatically Determinate Plane Trussஅருண்ராஜ் கிருஷ்ணன்சாமிNo ratings yet
- Junior Design Engineer PresentationDocument67 pagesJunior Design Engineer Presentationyedida viswanadhNo ratings yet
- Slope Deflection Method Statically Indeterminate Beams and Frames Week 6: Lessons 16-18Document21 pagesSlope Deflection Method Statically Indeterminate Beams and Frames Week 6: Lessons 16-18lengs SimzNo ratings yet
- Shear ForceDocument9 pagesShear ForceMuhamed ZaimNo ratings yet
- Static Determinacy of Plane FramesDocument9 pagesStatic Determinacy of Plane FramesCHA CHANo ratings yet
- Analysis and Drift of Multi-Storey Rigid FramesDocument68 pagesAnalysis and Drift of Multi-Storey Rigid FramesPijuddin BhaniNo ratings yet
- 2022-04-20 Topic5 Stiffness Method TrussDocument47 pages2022-04-20 Topic5 Stiffness Method TrussMary Joanne AninonNo ratings yet
- 12 5-12 7Document25 pages12 5-12 7WawanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Twelve: Analysis of Indeterminate Beams and Frames by The Slope-Deflection MethodDocument15 pagesChapter Twelve: Analysis of Indeterminate Beams and Frames by The Slope-Deflection MethodAhmed MandorNo ratings yet
- Structure AnaylsisDocument13 pagesStructure AnaylsisHassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Force (Flexibility) Method of Structural AnalysisDocument48 pagesForce (Flexibility) Method of Structural AnalysisthareendaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Buildings For Gravity LoadsDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Buildings For Gravity LoadsPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Methods of Design of Arch Dams: Commonly Used Methods AreDocument20 pagesMethods of Design of Arch Dams: Commonly Used Methods Areefa bayisaNo ratings yet
- I. Ii. Iii. Iv. VDocument1 pageI. Ii. Iii. Iv. VJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Cie 136Document151 pagesCie 136Sancho BilogNo ratings yet
- Rigid Frames: Ajeesh K Nikitha M2-CaseDocument44 pagesRigid Frames: Ajeesh K Nikitha M2-CasedeepuspNo ratings yet
- Junior Design Engineer Methods AnalysisDocument46 pagesJunior Design Engineer Methods Analysisyedida viswanadhNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Symmetric LoadsDocument13 pagesAircraft Symmetric LoadsNavish KotwalNo ratings yet
- Structure report PDFDocument14 pagesStructure report PDFRawaz KanabieNo ratings yet
- CE 3132 Module 05 - Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures (Part 1)Document8 pagesCE 3132 Module 05 - Analysis of Statically Determinate Structures (Part 1)FedieTabaquiraoNo ratings yet
- Chapter One ColumnsDocument26 pagesChapter One Columnsmintesinot sisayNo ratings yet
- Theory of StructuresDocument35 pagesTheory of StructurespjNo ratings yet
- Strength of Mat I 01Document5 pagesStrength of Mat I 01Vlad ManoloiuNo ratings yet
- AIRCRAFT STRUCTURES REVIEWDocument150 pagesAIRCRAFT STRUCTURES REVIEWJuly Tade100% (1)
- Study Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 3-MODULE - 35Document16 pagesStudy Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 3-MODULE - 35mujeebNo ratings yet
- Arup Kumar Kundu-Bedside Clinics in Medicine, Part 1-Academic Publishers (2010)Document562 pagesArup Kumar Kundu-Bedside Clinics in Medicine, Part 1-Academic Publishers (2010)Sharat Chandra75% (8)
- Computer PartsDocument2 pagesComputer PartsmujeebNo ratings yet
- Automated Highway Systems An Intelligent Transportation System For The Next Century'Document4 pagesAutomated Highway Systems An Intelligent Transportation System For The Next Century'mujeebNo ratings yet
- Bio-Vision - SSLC Chemistry SmileDocument19 pagesBio-Vision - SSLC Chemistry SmilemujeebNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 5-MODULE - 55Document20 pagesStudy Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 5-MODULE - 55mujeebNo ratings yet
- Ipv4 Vs Ipv6: What Is Ip?Document6 pagesIpv4 Vs Ipv6: What Is Ip?mujeebNo ratings yet
- Proportioning Guidelines for Extradosed Prestressed BridgesDocument14 pagesProportioning Guidelines for Extradosed Prestressed BridgesRadek SekNo ratings yet
- Department of Ethnography CollectionsDocument13 pagesDepartment of Ethnography CollectionsmujeebNo ratings yet
- Soil Nailing For Slope Stabilization An OverviewDocument6 pagesSoil Nailing For Slope Stabilization An OverviewmujeebNo ratings yet
- NullDocument21 pagesNullmujeebNo ratings yet
- Jute Geotextiles-Srtabilisation of SlopesDocument70 pagesJute Geotextiles-Srtabilisation of Slopesnimm1962No ratings yet
- Study Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 6-MODULE - 64Document11 pagesStudy Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 6-MODULE - 64mujeebNo ratings yet
- NullDocument22 pagesNullmujeebNo ratings yet
- M2-Cs304-Compiler DesignDocument12 pagesM2-Cs304-Compiler DesignmujeebNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 2-MODULE - 2Document25 pagesStudy Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 2-MODULE - 2mujeebNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument182 pagesEnglishJothy50% (2)
- Ktu Students: For More Study Materials WWW - Ktustudents.inDocument8 pagesKtu Students: For More Study Materials WWW - Ktustudents.inmujeebNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 1-MODULE - 1Document39 pagesStudy Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 1-MODULE - 1mujeebNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 6-MODULE - 64Document11 pagesStudy Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 6-MODULE - 64mujeebNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 5-MODULE - 55Document20 pagesStudy Material - Heat and Mass Transfer MODULE 5-MODULE - 55mujeebNo ratings yet
- Causa ProximaDocument13 pagesCausa ProximamujeebNo ratings yet
- Ktunotes - In: To Get More Study Materails Visit WWW - Ktunotes.inDocument32 pagesKtunotes - In: To Get More Study Materails Visit WWW - Ktunotes.inmujeebNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Part 1Document268 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Part 1Navin kumarNo ratings yet
- Intersection of Solids: Session 8Document7 pagesIntersection of Solids: Session 8mujeebNo ratings yet
- Informal Design Guidelines for Relational DatabasesDocument4 pagesInformal Design Guidelines for Relational DatabasesmujeebNo ratings yet
- Dhs M2 Ktunotes - inDocument18 pagesDhs M2 Ktunotes - insyamakNo ratings yet
- Impact of Advances in Mobile Technology On Higher Education in Developing CountriesDocument5 pagesImpact of Advances in Mobile Technology On Higher Education in Developing CountriesmujeebNo ratings yet
- Main Pro Report CompleteDocument21 pagesMain Pro Report CompletemujeebNo ratings yet
- Reportonsafetyfeatureincar 170618080647Document28 pagesReportonsafetyfeatureincar 170618080647mujeebNo ratings yet
- ECB 3143 - Example 2Document3 pagesECB 3143 - Example 2Mohamad ZulfikrieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To General Relativity Solutions 31-35Document5 pagesIntroduction To General Relativity Solutions 31-35daveNo ratings yet
- Book - Python - Hands-On Simulation Model PythonDocument347 pagesBook - Python - Hands-On Simulation Model PythonKiều Nhi Nguyễn100% (3)
- Welsh Brown Modules 1 2 PDFDocument38 pagesWelsh Brown Modules 1 2 PDFGarrison GerardNo ratings yet
- Classical Ciphers: Cryptography - CS 411 / 507 Erkay Savas Sabancı UniversityDocument52 pagesClassical Ciphers: Cryptography - CS 411 / 507 Erkay Savas Sabancı UniversityBEYZA ÇAVUŞOĞLUNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Phase 1 ReportDocument25 pagesFinal Year Project Phase 1 ReportAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Gravity Gradient TorqueDocument7 pagesGravity Gradient TorquePomPhongsatornSaisutjaritNo ratings yet
- PrenovaDocument17 pagesPrenovaErmitañoDelValleNo ratings yet
- GEOMETRY BOARD QUESTION PAPER FROM OCTOBER 2014Document3 pagesGEOMETRY BOARD QUESTION PAPER FROM OCTOBER 2014Latif Ismail ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Cretest 1Document34 pagesCretest 1ajith_cvaNo ratings yet
- TransportationDocument155 pagesTransportationAnand100% (3)
- MGT 221: Business Research MethodsDocument2 pagesMGT 221: Business Research MethodsShreya BhetuwalNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee All India Test Series: Concept Recapitulation Test - IiDocument15 pagesFiitjee All India Test Series: Concept Recapitulation Test - IiAryan AroraNo ratings yet
- Twisting Momentsin Two-Way SlabsDocument6 pagesTwisting Momentsin Two-Way SlabsProfessor Dr. Nabeel Al-Bayati-Consultant Engineer100% (2)
- Formula SheetDocument16 pagesFormula SheetgwerNo ratings yet
- Seacom Skills University: B.Tech 2 Year 4 Semester Theory Paper Sl. No. Paper Paper Code Credit PointDocument11 pagesSeacom Skills University: B.Tech 2 Year 4 Semester Theory Paper Sl. No. Paper Paper Code Credit PointM RoyNo ratings yet
- Fisika Teknik Bab 4 PDFDocument31 pagesFisika Teknik Bab 4 PDFedo saputraNo ratings yet
- Database Mba NOTESDocument35 pagesDatabase Mba NOTESWasim Ahamad KhanNo ratings yet
- Exam3 Fin370 B KeyDocument22 pagesExam3 Fin370 B KeyNick GuidryNo ratings yet
- Ved V. DatarDocument3 pagesVed V. DatarJoseph ChavoyaNo ratings yet
- 21 MAT41 Set 1Document8 pages21 MAT41 Set 1Sushant KNo ratings yet
- Math g5 m4 Lessons 1 12Document168 pagesMath g5 m4 Lessons 1 12Viktoria AlekseyevaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Ability Practice Test Set 5 Answers RevisedDocument2 pagesAnalytical Ability Practice Test Set 5 Answers RevisedKylaNo ratings yet
- 10 1 1 465 2066 PDFDocument236 pages10 1 1 465 2066 PDFShahid Rashid100% (1)
- GQB Ece PDFDocument561 pagesGQB Ece PDFckvirtualize95% (43)
- EA-4-02 REV01 - Expression of The Uncertainty of Measurement in CalibrationDocument29 pagesEA-4-02 REV01 - Expression of The Uncertainty of Measurement in CalibrationTiago Guimarães100% (1)
- CVSB 371Document8 pagesCVSB 371Long NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Introduction to FORTRANDocument114 pagesIntroduction to FORTRANKalpesh KarkeliNo ratings yet
- Fluent Chp07-Defining Physical PropertiesDocument74 pagesFluent Chp07-Defining Physical PropertiesPiyush SandujaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 PDFDocument212 pagesChapter 16 PDFGabriela Sequeira60% (5)
- Digital SAT Reading and Writing Practice Questions: Test Prep SeriesFrom EverandDigital SAT Reading and Writing Practice Questions: Test Prep SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- GMAT Prep 2024/2025 For Dummies with Online Practice (GMAT Focus Edition)From EverandGMAT Prep 2024/2025 For Dummies with Online Practice (GMAT Focus Edition)No ratings yet
- AP World History: Modern Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review with 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionFrom EverandAP World History: Modern Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review with 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus Premium, 2024: 12 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Calculus Premium, 2024: 12 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- Digital SAT Preview: What to Expect + Tips and StrategiesFrom EverandDigital SAT Preview: What to Expect + Tips and StrategiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The LSAT Law School Admission Test Study Guide Volume I - Reading Comprehension, Logical Reasoning, Writing Sample, and Analytical Reasoning Review Proven Methods for Passing the LSAT Exam With ConfidenceFrom EverandThe LSAT Law School Admission Test Study Guide Volume I - Reading Comprehension, Logical Reasoning, Writing Sample, and Analytical Reasoning Review Proven Methods for Passing the LSAT Exam With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Medical English Dialogues: Clear & Simple Medical English Vocabulary for ESL/EFL LearnersFrom EverandMedical English Dialogues: Clear & Simple Medical English Vocabulary for ESL/EFL LearnersNo ratings yet
- AP English Language and Composition Premium, 2024: 8 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP English Language and Composition Premium, 2024: 8 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Digital SAT Prep 2024 For Dummies: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatFrom EverandDigital SAT Prep 2024 For Dummies: Book + 4 Practice Tests Online, Updated for the NEW Digital FormatNo ratings yet
- MCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsFrom EverandMCAT Biology & Biochemistry Practice Questions: High Yield MCAT QuestionsNo ratings yet
- Finish What You Start: The Art of Following Through, Taking Action, Executing, & Self-DisciplineFrom EverandFinish What You Start: The Art of Following Through, Taking Action, Executing, & Self-DisciplineRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (94)
- AP European History Premium, 2024: 5 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP European History Premium, 2024: 5 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- GMAT Foundations of Verbal: Practice Problems in Book and OnlineFrom EverandGMAT Foundations of Verbal: Practice Problems in Book and OnlineNo ratings yet
- AP Q&A Psychology, Second Edition: 600 Questions and AnswersFrom EverandAP Q&A Psychology, Second Edition: 600 Questions and AnswersNo ratings yet
- LSAT For Dummies (with Free Online Practice Tests)From EverandLSAT For Dummies (with Free Online Practice Tests)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- AP Biology Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review With 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionFrom EverandAP Biology Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review With 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionNo ratings yet
- AP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Microeconomics/Macroeconomics Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- AP Computer Science A Premium, 2024: 6 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Computer Science A Premium, 2024: 6 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Exercises With Answers Part 5: Your Quest Towards C2From EverandEnglish Grammar Exercises With Answers Part 5: Your Quest Towards C2No ratings yet
- AP Environmental Science Premium, 2024: 5 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Environmental Science Premium, 2024: 5 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet
- Digital PSAT/NMSQT Study Guide Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandDigital PSAT/NMSQT Study Guide Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet