Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TM Lecture 3 and 4 PDF
TM Lecture 3 and 4 PDF
Uploaded by
Mohammed QuthahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TM Lecture 3 and 4 PDF
TM Lecture 3 and 4 PDF
Uploaded by
Mohammed QuthahCopyright:
Available Formats
The Grashof condition
Theory of Machines
Mechatronics Engineering
Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
Fourbar linkage
• The simplest 1 DOF mechanism is four binary • The Grashof condition is very simple
links. relationship that predicts the rotation
• The fourbar linkage is the most common behavior or rotatability of fourbar linkage’s
device used in machinery. inversions based only on the link length.
• Simplicity is one mark of good design.
• The fourbar linkage should be among the S + L ≤ P + Q
first solutions to motion control problems to
be investigated. S: Length of shortest link
L: Length of longest link
P: Length of one remaining link
Q: Length of other remaining link
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
The Grashof condition
• If S + L ≤ P + Q, the linkage is Grashof and • If S + L > P + Q, the linkage is called non-
at least one link capable of making a full Grashof and no link will be capable of making a
revolution with respect to the ground plane. full revolution with respect to other link.
• This is called a Class I Kinematic chain • This is called a Class II Kinematic chain
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
The Grashof condition
• Class I: S + L < P + Q • If the ground link opposite the shortest link
• If the link connected with ground is the Grashof Double Rocker
shortest Crank Rocker
• If ground link is the shortest Double
Crank
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
The Grashof condition
• Class II: S + L > P + Q
• All inversions will be triple rocker
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
Special case Grashof Linkage
• Class III: S + L = P + Q
• Special case
• All inversions will be
• Double Cranks
• Crank Rockers
• Will have, change point,
twice per revolution when
the links all become collinear.
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
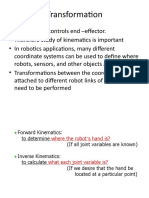
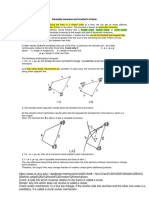
Classification of the fourbar linkage
• Each link is given a letter designation based on type of Coupler link
motion when connected to the other links.
• Crank (C): if link can make full revolution to the
other links
• Rocker (R): if not Output link
• The motion of the assembled linkage based on its Grashof
Driving link
condition and inversion can be given a letter code such as
GCRR. Ground
• The motion designators C and R are always listed in order
of links starting from input linkage to the output linkage.
• The prefix (G) indicates a Grashof linkage.
• The prefix (S) indicates for a special case Grashof
• No prefix means a non-Grashof linkage.
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
Classification of the fourbar linkage
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
Classification of the fourbar linkage 𝑟3
𝑟4
Barker’s classification
𝑟1 𝑟2
𝜆1 =
𝑟2
• In order for four links to be assembled the longest link 𝑟1
must be shorter than the sum of other three links
L< (S+P+Q)
• If L= (S+P+Q) the links can be assembled but will not move
Theory of Machines , Dr. Mohammad Hayajneh
You might also like
- PowerHA 7.2 Configuration Guide - V1.0 PDFDocument37 pagesPowerHA 7.2 Configuration Guide - V1.0 PDFShanm babNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts: ECC309 - Theory of Machines IDocument48 pagesChapter 1: Introduction and Basic Concepts: ECC309 - Theory of Machines IABDULRAHMAN ADAMU MUSANo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Kinematics Fundamentals: Instructor: Weinan Gao, PH.DDocument31 pagesTheory of Machines Kinematics Fundamentals: Instructor: Weinan Gao, PH.DmungutiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 The Grashof ConditionDocument11 pagesLecture 3 The Grashof ConditionKATERENo ratings yet
- MEL3020: Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines: 3 WeekDocument27 pagesMEL3020: Kinematics and Dynamics of Machines: 3 WeekRavi VermaNo ratings yet
- Four LinkDocument19 pagesFour LinkBHAVESH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Four Bar LinkageDocument9 pagesFour Bar LinkageAliceAlormenuNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms Design L 2-4 The Fourbar Linkage and The Grashof ConditionDocument14 pagesMechanisms Design L 2-4 The Fourbar Linkage and The Grashof ConditionaliNo ratings yet
- Tool RetrivelDocument42 pagesTool RetrivelganeshNo ratings yet
- Four Bar MechanismDocument34 pagesFour Bar Mechanismumair rasheed100% (1)
- Grashof's LawDocument3 pagesGrashof's LawSyed Faiz QuadriNo ratings yet
- Summary of Previous LectureDocument24 pagesSummary of Previous LecturebharatNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Fall 2023 (1) ..Document5 pagesTheory of Machines Fall 2023 (1) ..6r7fhxygbmNo ratings yet
- Experiment #3 To Calculate and Draw Velocity, Acceleration Diagram of Four Bar Mechanism. TheoryDocument11 pagesExperiment #3 To Calculate and Draw Velocity, Acceleration Diagram of Four Bar Mechanism. TheoryMuhammad inshalNo ratings yet
- Study On Swing MachineDocument3 pagesStudy On Swing MachineKazi AnisurNo ratings yet
- Lec-4 Kinematic Behaviour of 4R 4bar MechanismsDocument17 pagesLec-4 Kinematic Behaviour of 4R 4bar Mechanismspragathi mudavathNo ratings yet
- Machine DesigningDocument147 pagesMachine DesigningSiddharth VatsNo ratings yet
- Kom Unit 1Document24 pagesKom Unit 1Muthuvel M100% (2)
- Grashof'S Law: (Kinematics and Theory of Machines)Document4 pagesGrashof'S Law: (Kinematics and Theory of Machines)55MESuman sahaNo ratings yet
- All in OneDocument4 pagesAll in Onesahil.s237192101No ratings yet
- Fourbar Linkage 2024Document10 pagesFourbar Linkage 2024ndbira5No ratings yet
- Basics of Mechanisms: Dr.B.Santhosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Amrita School of EngineeringDocument19 pagesBasics of Mechanisms: Dr.B.Santhosh Department of Mechanical Engineering Amrita School of Engineeringkishore sNo ratings yet
- Four Bar ExperimentDocument5 pagesFour Bar ExperimentMohsin IftikharNo ratings yet
- Z - Transform - DSP - Unit-3Document24 pagesZ - Transform - DSP - Unit-3Parth InamdarNo ratings yet
- Kinematic Fundamentals: Theory of Machines, MT 317 Engr. Akhtar KhurshidDocument26 pagesKinematic Fundamentals: Theory of Machines, MT 317 Engr. Akhtar KhurshidHammadMehmoodNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Inversion & Grashof's RiterionDocument10 pagesMechanism Inversion & Grashof's RiterionAHMED ghribiNo ratings yet
- TM Lecture 1 PDFDocument12 pagesTM Lecture 1 PDFMohammed QuthahNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Machines ME-224: Lec Hamza AsifDocument29 pagesMechanics of Machines ME-224: Lec Hamza AsifAsaad WaqarNo ratings yet
- KOM Lect2Document26 pagesKOM Lect2Pranav C PNo ratings yet
- Robotics 7Document17 pagesRobotics 7nadiaNo ratings yet
- GrueblerDocument1 pageGrueblerlatterpolNo ratings yet
- Grashof ConditionDocument23 pagesGrashof ConditionMemeber JNo ratings yet
- Four-Bar Linkage Mechanism PDFDocument4 pagesFour-Bar Linkage Mechanism PDFAhmad AbdNo ratings yet
- Name - Rakesh Majumdar Department - ME Semester - 5 University Roll - 35000720041 Year - 3rd Topic - Grashof's LawDocument7 pagesName - Rakesh Majumdar Department - ME Semester - 5 University Roll - 35000720041 Year - 3rd Topic - Grashof's Law55MESuman sahaNo ratings yet
- Topic4Linkages GWDocument28 pagesTopic4Linkages GWSebas Jimenez MNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine and MechanismsDocument21 pagesTheory of Machine and MechanismssrujanNo ratings yet
- Sewing Machine SolutionDocument7 pagesSewing Machine SolutionRafiaNo ratings yet
- Grashof LawDocument7 pagesGrashof LawPrashant RaturiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Kinematics Fundamentals - Part BDocument37 pagesLecture 3 - Kinematics Fundamentals - Part BSuaid Tariq BalghariNo ratings yet
- Cume213 L2Document80 pagesCume213 L2irvinvongiNo ratings yet
- Lec 8Document12 pagesLec 8nihalsinghNo ratings yet
- Warshall AlgorithmDocument27 pagesWarshall Algorithmmithun karthikNo ratings yet
- Four Bar ChainDocument11 pagesFour Bar ChaindxfdxNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine Student ManualDocument72 pagesTheory of Machine Student ManualWellington LimaNo ratings yet
- Grashof's LawDocument10 pagesGrashof's LawMihir MehanNo ratings yet
- Kom LabDocument15 pagesKom LabNitin KurupNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines: Presentation by Prof. N Mohan Rao Prof. N Mohan Rao JntukDocument47 pagesTheory of Machines: Presentation by Prof. N Mohan Rao Prof. N Mohan Rao JntukDhanu TeotiaNo ratings yet
- Bett Cosmas PDFDocument11 pagesBett Cosmas PDFAnonymous ZJTHro87iNo ratings yet
- Study of Agitated VesselDocument19 pagesStudy of Agitated VesselSander LukeNo ratings yet
- Week 03Document17 pagesWeek 03Muhammad TahaNo ratings yet
- Grashof RRRPDocument11 pagesGrashof RRRPPrathmesh Deshmukh0% (1)
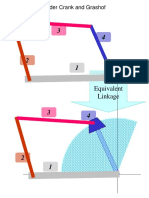
- Equivalent Linkage: Slider Crank and GrashofDocument11 pagesEquivalent Linkage: Slider Crank and GrashofAnshuman TagoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument29 pagesChapter 4 PDFAli Al HadiNo ratings yet
- Z Transform ShortDocument18 pagesZ Transform ShortFozia TabassumNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document35 pagesLecture 3allenkalbo0316No ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Machine Theory - Unit 0 and Unit 1Document28 pagesMechanisms and Machine Theory - Unit 0 and Unit 1Sangamesh ShettarNo ratings yet
- On The Coherence and Weak Dimension of The Rings R (X) and R (X)Document9 pagesOn The Coherence and Weak Dimension of The Rings R (X) and R (X)chhiti.medNo ratings yet
- 21 - 1-Kinematic Inversion and Grashof - S Criteria - Student NoteDocument2 pages21 - 1-Kinematic Inversion and Grashof - S Criteria - Student NoteNishant DeyNo ratings yet
- Introductory Laplace Transform with ApplicationsFrom EverandIntroductory Laplace Transform with ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reactive Programming With Scaal, Lagom, Spark, Akka, PlayDocument31 pagesReactive Programming With Scaal, Lagom, Spark, Akka, PlayRashard Dyess-LaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Circuit Analysis PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 3 - Circuit Analysis PDFAmiera SyuhadhaNo ratings yet
- 4 Bedroom Townhouse: Kitchen 82 FT (7.6 M )Document3 pages4 Bedroom Townhouse: Kitchen 82 FT (7.6 M )FADY_F_F5010No ratings yet
- Vulcan RemovalDocument21 pagesVulcan Removald4rk3No ratings yet
- Katalog Emax2Document306 pagesKatalog Emax2Lidef SellenrofNo ratings yet
- Cibse Guide b2Document159 pagesCibse Guide b2Phil RedmondNo ratings yet
- Hi 1.3 PDFDocument103 pagesHi 1.3 PDFVenkatNo ratings yet
- Electrical Maintenance SparesDocument9 pagesElectrical Maintenance SparesYogendra Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument2 pagesLab ReportLindsey AlexanderNo ratings yet
- DSE890 DSE891 Operators Manual PDFDocument52 pagesDSE890 DSE891 Operators Manual PDFKhaleel KhanNo ratings yet
- Physical Layers:: M. Zaman Ali, Lecturer, CS & ITDocument11 pagesPhysical Layers:: M. Zaman Ali, Lecturer, CS & ITAamir Fayyaz ShahNo ratings yet
- 2-Hydraulic Machines TurbinesDocument50 pages2-Hydraulic Machines TurbinesChris KapendaNo ratings yet
- CCM Info 160915 - Newly Classed VesselsDocument6 pagesCCM Info 160915 - Newly Classed VesselsAMIRNo ratings yet
- BoqDocument2 pagesBoqEngr SwapanNo ratings yet
- Amfi IapDocument6 pagesAmfi IapAshish AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ensure Compliance With Pollution Prevention RequirementsDocument51 pagesEnsure Compliance With Pollution Prevention RequirementsAnton Anton100% (4)
- Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steadystate AnalysisDocument17 pagesChapter 4 Sinusoidal Steadystate AnalysisCraig PeriNo ratings yet
- The Locksmith Journal May-Jun 2013 - Issue 26Document80 pagesThe Locksmith Journal May-Jun 2013 - Issue 26ulfheidner9103No ratings yet
- Webasto Heavy Duty Air Conditioning Accessories CatalogDocument93 pagesWebasto Heavy Duty Air Conditioning Accessories CatalogCarlos Alexandre MendelskiNo ratings yet
- Precast MachineryDocument27 pagesPrecast MachineryHalNo ratings yet
- JCB DELPHI PUMP-9520A500-509S03 - Iss 03Document7 pagesJCB DELPHI PUMP-9520A500-509S03 - Iss 03Ravikant Saini100% (2)
- Project Management Plan - Reconstruction of Runway at JIAP (Electrical)Document12 pagesProject Management Plan - Reconstruction of Runway at JIAP (Electrical)Sabahat HussainNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard Analysis: IP-OPS-066Document9 pagesJob Hazard Analysis: IP-OPS-066ananthu.uNo ratings yet
- MLY OUW HouseCleaningChecklistDocument1 pageMLY OUW HouseCleaningChecklistmulher&mae autista100% (1)
- MGD 2621 P Medical Greyscale Display: Installation & User ManualDocument27 pagesMGD 2621 P Medical Greyscale Display: Installation & User ManualJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Man TGLDocument21 pagesMan TGLViorel RoNo ratings yet
- Welding 10Document64 pagesWelding 10Ammar Izzy0% (1)
- Chapter 9: Electronics: 9. 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionDocument36 pagesChapter 9: Electronics: 9. 1: Uses of The Cathode Ray Oscilloscope (C.R.O) 9.1.1: Thermionic EmissionNurul Afiqah Mohmmad NajibNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Slides (Only Questions) - Internal Forced Convection & Natural ConvectionDocument10 pagesTutorial Slides (Only Questions) - Internal Forced Convection & Natural ConvectionVivaan SharmaNo ratings yet