Professional Documents
Culture Documents
BS Part 11
Uploaded by
ebc07Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
BS Part 11
Uploaded by
ebc07Copyright:
Available Formats
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.
com/
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE Part 11
1.To whom is the formulation of the cell theory attributed?
I. Theodor Schwann
II. Matthias Schleiden
III. Rudulph Virchow
A. I only
B. I and II
C. II only
D. only and III
Ans: B. I and II
- credit for developing cell theory is usually given to two scientist: Theodor Schwann and
Matthias Jakob Schleiden. While Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory, he is not as
credited for his attribution toward it. In 1855, he added the third component of the theory
proposing that cells come from pre-existing cells.
2. What are the cell tenets of the cell theory?
I. All living organism are composed of one or more cells
II. Cell is the basic un of structure and organization in organisms
III. Cells arise from pre-existing cells
IV. Cells need nourishment to divide.
A. I, II and III
B. II and III
C. I and II
D. I and III
Ans: A. I, II and III
- The cell theory states:
· All living organism are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicellular
· The cell is the basic unit of life.
· Cells arise from pre-existing cells.(They are not derived from spontaneous
generation.)
3. Which is NOT a part occurs within cells
A. Energy flow occurs within cells
B. Living organisms may unicellular or multicellular
C. All cells have the same basic chemical compistion
D. Heredity information (DNA) is passes on from cell to cell
Ans: B. Living organisms may unicellular or multicellular
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
- The modern version of the Cell theory includes the ideas that:
· Energy flow occurs within cells
· Heredity information (DNA) is passed on from cell to cell
· All cells have the same basic chemical composition
4. With statements is TRUE of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
A. Eukaryotes have a nucleus, while Prokaryotes do not have
B. Prokaryotes have a nucleus while eukaryotes do not have
C. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have no nucleus
D. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes have nucleus
Ans: A. Eukaryotes have a nucleus, while Prokaryotes do not have
- The biggest difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is that eukaryotes have
nucleus. Eukaryotes organize different functions within specialized membrane-bound
compartments called organelle. These structures do not exist in Prokaryotes.
5. Which of the following is an example of prokaryotic cell?
A. Animal cell
B. Bacterial cell
C. Eukaryote
D. Plant cell
Ans: B. Bacterial cell
-Bacteria are an example of prokaryotes. Prokaroytes cells do not contain a nucleus or
any other membrane-bound organelle. Prokaryotes include two groups: bacteria and
another group called archaea.
6. Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A. Prokaryotic cells came before Eukaryotes cells
B. Prokaryotic cells are bigger than Eukaryotic cells
C. Eukaryotic cells are simple, Prokaryotic cells are complex
D. Eukaryotic cells do not have nucleus, prokaryotic cells do.
Ans: A. Prokaryotic cells came before Eukaryotes cells
- Prokaryotic cells are often thought to be the first life on the planet. Evidence supports
the idea that eukaryotes cells are actually the descendants of separate prokaryotic cells
that joined together in a symbolic.
7. A cells has nucleus is complex and large and has membrane organelles. What type
of cell is this?
A. Bacteria
B. Eukaryotic
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
C. Prokaryotic
D. Not enough information is given
Ans: B. Eukaryotic
- See the explanation on item 64
8. Which cellular part/s is/are found in plants but NOT in animals
I. Chloroplasts
II. Plastids
III. Centrioles
A. I only
B. I and II
C. I and III
D. II and III
Ans: B. I and II
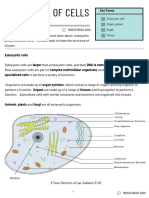
- Plant and animal cells have several difference and similarities. For example anima;
cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplast but plants cells do. Animal cells are rounded
and irregular in shape while plants cells are both eukaryotic cells so they have several
features in common, such as the presence of a cell oraganelles like the nucleus,
mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
Animal Cell versus Plant
Cell comparison chart
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Cell wall Absent Present (formed of
cellulose)
Shape Round Rectangular (fixed shape)
Vacuole One more small vacuoles One, large central vacuole
(much smaller than plants taking up 90% of cell
cells) volume
Centrioles Present in all animal cell Only present in lower plant
forms
Chloroplast Animal cell don’t have Plant cells have chloroplast
chloroplasts because they make their
own food
Cytoplasm Present Present
Ribosomes Present Present
Mitochondria Present Present
Plastids Present Present
Endoplasmic Present Present
Reticulum(smooth and
Rough)
Golgi Apparatus Present Present
Plasma Membrane Only cell membrane Cell wall and a cell
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
membrane
Microtubules/ Present Present
Microfilaments
Flagella May be found in some May be found in some cells
Lysosomes Lysosomes occur in Lysosomes usually not
cytoplasm evident
Nucleus Present Present
Cilia Present Most plants cell do not
contain cilia
9. Which cellular part is NOT found in animal cells but found in plants?
A. Cell membrane
B. Cell wall
C. Centiole
D. Vacuoles
Ans: B. Cell wall
- See explanation
10. Which applies to animal cells but NOT to plants cells?
A. Irregular shapes
B. Plastids
C. Rectangular shapes
D. Cell wall
Ans: A. Irregular shapes
- See explanation on item 68
11. If placed in a hypertonic solution a plant cell will __________.
A. burst
B. swell
C. shrink in size
D. remain constant in size
Ans: C. shrink in size
- When a plant cell is placed in a hypertonic solution the water inside the cell (highest
concentration) moves out of the cell (lowest concentration) causing the pant cell to
shrink and the plant wilts because there is a loss of turgor pressure.
12. The cell membrane of the red blood cell will allow water, oxygen carbon dioxide
glucose and glucose to pass through. Because other substance are blocked from
entering this membrane is called ______.
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
A. non-conductive
B. permeable
C. perforated
D. semi-permeable
Ans: D. semi-permeable
- A semi-permeable membrane is a type of biological or synthetic, polymeric membrane
that will allow certain molecules or ions pass through it by diffusion –or occasionally
transport. Semi-permeable membrane describes a membrane that allows some
particles to pass through (by size), whereas the selectively permeable membrane
“chosen” what passes through (size is not a factor).
13. Which is/are TRUE of passive transport cells?
I. requires no energy from the cell
II. Requires energy from the cell
III. Examples of passive transport are the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide and
osmosis of water.
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II
D. II and III
Ans: C. I and II
- Passive transport doesn’t require energy (ATP),active transport does require energy.
Passive transport moves molecules against the concentration gradient (high to low)
while active transport. Moves molecules against the concentration gradient (low to
high). There are multiples forms of passive transport :simple diffusion, facilitated
diffusion filtration and osmosis. Passive transport occurs because of the entropy of the
system, so additional energy isn’t required for it t occur.
14. Which is/are TRUE of active transport in cells?
I. Requires no energy from cell
II. Requires energy from the cell usually in the form of ATP
III. Examples include transport of large molecules (non-lipid soluble) and the sodium
potassium pump
A. II only
B. III only
C. I and III
D. II and III
Ans: D. II and III
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
- Active transport requires the cell to spend energy, usually in the form of ATP.
Examples include transport of large molecules (non-lipids solube) and the sodium
potassium pump passive transport requires no energy from the cell. Examples include
the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide, osmosis of water and facilitated diffusion.
15. Which is responsible for the movement of amino acids, glucose and fatty acids into
the blood stream?
A. Facilitated diffusion
B. Filtration
C. Osmosis
D. Simple diffusion
Ans: A. Facilitated diffusion
- In simple diffusion, solutes move from a region of higher concentration to lower
concentration. In facilitated diffusion, solutes move across a membrane from higher to
lower concentration with the aid of trans membrane proteins. In filtration, solute and
solvent molecules and ions cross a membrane because of hydrostatic pressure.
Molecules small to pass through the filter may pass. In osmosis, solvent molecule move
from lower to higher solute concentration across a semi-permeable membrane. Note
this make the solute molecules more dilute.
16. Which error/s or mutation/s in DNA has/have no impact on the DNA sequence?
A. Missense Mutation
B. Silent mutation
C. Runaway mutation
D. Silent mutation
Ans: B. Silent mutation
- Silent mutation are mutations in DNA that do not significantly alter the phenotype of
the organism in which they occur.
17. Which of describe/s misense mutation?
I. Alter amino acid sequence
II. May multiply overtime that leads to cycle disruption and the formation of tumors
III. Does not alter amino acids sequences
A. I only
B. II only
C. III only
D. I and II only
Ans: D. I and II only
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
- Missense mutations occur when the DNA change alters a single amino acid in the
polypeptide chain. Chemical mutagens have been shown to cause missense ,mutations
leading leading to cancer
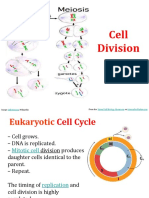
18. Which of the following stages of mitosis occur?
I. Interphase
II. Prophase
III. Prometaphase
IV. Metaphase
V. Anaphase
VI. Telophase
A. I-II-III-IV-V-VI
B. III-I-IIIV-V-VI
C. II-III-IV-I-V-VI
D. I-III-II-V-IV-VI
Ans:
- Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle which a typical cell spends most of its life.
During this phase, the cell copies ist DNA in preparation for mitosis. Mitosis is a nucleus
division plus cytokinesis and produce two identical daughter cells during prophase,
prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
19. Which one contains the hereditary materials?
A. ADP
B. ATP
C. DNA
D. RNA
Ans: C. DNA
- DNA, sometimes called a genetic blue print contains the hereditary material in nearly
all organism. This improper copying of DNA produce two types of error, or mutations.
Silent mutations have impact on DNA sequence, but missense mutations which alter
amino acid sequence often impact the association function. Missense mutations can
multiply over time, leading to cell cycle disruption and the formation of tumors. Which
are the product of runaway cell reproduction. Cancer occurs when mutated cells ignore
or override the normal “check points” regulating mitosis and begin to reproduce
uncontrollably.
20. Meiosis involves ____ successive cell division and results in_____ daughter cells
A. 2:4
B. 2:6
C. 3:6
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
D. 2:8
Ans: A. 2:4
- Meiosis begins with a parent cell that is diploid, meaning it has two copies of each
chromosomes. The parent cell undergoes one round of DNA replication followed by two
separate cycles of nuclear division. The process results in four daughter cells that are
haploid , which means they contain half the number of chromosomes of the diploid
parent cell.
Download more reviewers here: https://letqa.blogspot.com/
You might also like
- 2 ChE Program - October 2021Document3 pages2 ChE Program - October 2021ebc07No ratings yet
- IPHO Accomplishment Report For May 2018Document12 pagesIPHO Accomplishment Report For May 2018ebc07No ratings yet
- IPHO Accomplishment Report For May 2018Document12 pagesIPHO Accomplishment Report For May 2018ebc07No ratings yet
- PRC Cover LetterDocument1 pagePRC Cover Letterebc07No ratings yet
- C A L A B A R Z o N: D I L GDocument54 pagesC A L A B A R Z o N: D I L Gebc07No ratings yet
- Validity and ReliabilityDocument2 pagesValidity and Reliabilityebc07No ratings yet
- Science Unit Plan: Mendelian Genetics and Genetic TechnologiesDocument44 pagesScience Unit Plan: Mendelian Genetics and Genetic Technologiesebc07No ratings yet
- HRMPSB Form 2 - OmnibusDocument1 pageHRMPSB Form 2 - Omnibusebc07No ratings yet
- Name: Score: Grade & Section: DateDocument1 pageName: Score: Grade & Section: Dateebc07No ratings yet
- 6.1 Women - and - ChildrenDocument15 pages6.1 Women - and - Childrenebc07No ratings yet
- TESDA Circular No. 051-2019 PDFDocument60 pagesTESDA Circular No. 051-2019 PDFebc07No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles - PhoneDocument46 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Life Cycles - PhoneKavindu MunasingheNo ratings yet
- Gummy Worm Meiosis LabDocument4 pagesGummy Worm Meiosis Labtheograph361No ratings yet
- GENBIO1 - Q1 - MOD8 OF 8 - Mitosis.Document25 pagesGENBIO1 - Q1 - MOD8 OF 8 - Mitosis.Warlin FernandezNo ratings yet
- Meiosis-FoldableDocument7 pagesMeiosis-Foldableapi-267309851No ratings yet
- Concepts of Biology - Lab ManualDocument43 pagesConcepts of Biology - Lab ManualUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMNo ratings yet
- ICAR Animal Science Short NotesDocument252 pagesICAR Animal Science Short NotesDr AMEER SUHAIL LOYOLITENo ratings yet
- Practice Test For Botany Class 11Document4 pagesPractice Test For Botany Class 11Debangsu Ghosh100% (1)
- CELLSDocument21 pagesCELLSPhia LhiceraNo ratings yet
- The Final Ultimate CML Case Pres Final 1 1Document113 pagesThe Final Ultimate CML Case Pres Final 1 1Levy Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 2 Notes (Grade 11)Document5 pagesBiology Chapter 2 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (6)
- SLRPDocument8 pagesSLRPAirene Mae SupilarNo ratings yet
- 2 MODULE CHAPTER 3&4 AnaPhy 2020-2021 PDFDocument51 pages2 MODULE CHAPTER 3&4 AnaPhy 2020-2021 PDFJosh MagatNo ratings yet
- G 6 Scintbk 2Document275 pagesG 6 Scintbk 2Bullet Rubia100% (1)
- Meiosis in Grasshopper TestisDocument7 pagesMeiosis in Grasshopper TestisRonisa100% (3)
- Cell Growth & Reproduction and Protein Synthesis Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCell Growth & Reproduction and Protein Synthesis Cheat SheetNajib AyoubNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument20 pagesMeiosisRosalina ColetoNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Structure and Function of Living ThingsDocument82 pagesUnit 7 Structure and Function of Living ThingsSUMMER JORDAN CARLUENNo ratings yet
- Genetics Learning Materials Bsa 2 1Document34 pagesGenetics Learning Materials Bsa 2 1Khy Renz Bajaj100% (1)
- Unit: Genetics and Biotechnology: NYCTA Unit Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesUnit: Genetics and Biotechnology: NYCTA Unit Plan Templateapi-466659492No ratings yet
- Topic 2Document49 pagesTopic 2Charmi PATELNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 2nd Edition by BeeryDocument9 pagesTest Bank For Genetics and Genomics in Nursing and Health Care 2nd Edition by BeeryFranklin Roberts100% (39)
- GenBio SMILE LP4 Q1 WEEK4Document16 pagesGenBio SMILE LP4 Q1 WEEK4bobby carsonNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Study Guide KEYDocument8 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Study Guide KEYrodneyperuNo ratings yet
- Botany 102 Notes Section 1 To 8 0 PDFDocument24 pagesBotany 102 Notes Section 1 To 8 0 PDFJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCDocument31 pagesCell Division Mitosis Biology Lecture PowerPoint VCBCAzilani Bin Ishak100% (1)
- Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Divisioncandice swanepoel100% (2)
- ELS ReviewerDocument9 pagesELS ReviewerMia TorettoNo ratings yet
- Answer Key-Biotech 8 2nd Periodical Test January 23,2024Document5 pagesAnswer Key-Biotech 8 2nd Periodical Test January 23,2024Lucky LaguraNo ratings yet
- Mitosis-And-Meiosis-Ppt 7781Document30 pagesMitosis-And-Meiosis-Ppt 7781zhao YingingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsDocument53 pagesLesson 3-Cell Cycle and CheckpointsHonleth Jheney MamarilNo ratings yet