Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fetal Development
Uploaded by
Mohammed Abd0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views27 pagesFetal development occurs in three stages - preembryonic, embryonic, and fetal - from fertilization through birth. During the embryonic stage from weeks 2-8, the placenta forms to support fetal growth and development. The fetal stage from weeks 9 until birth sees continued development of organs and systems as the fetus grows and moves in preparation for life outside the womb.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFetal development occurs in three stages - preembryonic, embryonic, and fetal - from fertilization through birth. During the embryonic stage from weeks 2-8, the placenta forms to support fetal growth and development. The fetal stage from weeks 9 until birth sees continued development of organs and systems as the fetus grows and moves in preparation for life outside the womb.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views27 pagesFetal Development
Uploaded by
Mohammed AbdFetal development occurs in three stages - preembryonic, embryonic, and fetal - from fertilization through birth. During the embryonic stage from weeks 2-8, the placenta forms to support fetal growth and development. The fetal stage from weeks 9 until birth sees continued development of organs and systems as the fetus grows and moves in preparation for life outside the womb.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Fetal development
Dr. Thabat J. Al-Maiahy
MBCHB, DOG, CAOG
objectives
• Define fertilization
• Describe the site of fertilization and
implantation
• Identify the stages of fetal
development
Fetal Development
• Measured in the number of weeks
after fertilization
• Average pregnancy lasts 280 days
or 40 weeks from the date of the
last menstrual period (LMP)
• Fertilization usually occurs 14 days
after the LMP
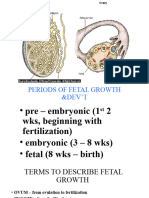
Three Stages of
Fetal Development
• Preembryonic stage: fertilization
through the second week
• Embryonic stage: end of second
week through the eighth week
• Fetal stage: ninth week until birth
Preembryonic Stage
(Stage 1)
• Fertilization - union of the ovum and
sperm in the outer 3rd of the fallopian
tube creating a zygote
• The union restores the diploid number of
46 chromosomes
Preembryonic Stage
(Stage 1)
• Zygote undergoes cleavages
(mitosis) as it is transported to the
uterine cavity in 72⁰
• Cleavages create a ball of 16 cells
called a morula, which divides into
cells that form fetal structures
Preembryonic Stage
(Stage 1)
• Blastocysts - inner cells form the
embryo and the amnion
• Trophoblasts - outer cells form the
embryonic membranes, Chorion and
placenta
• Implantation in the endometrium
occurs between the 7th to 10th day.
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
• A placenta is an organ of round or oval shape
• It is about 20 cm in length, weight of 600g
• It is composed of two different surfaces,
the maternal surface,
fetal surface,
• the umbilical cord, the link between the placenta and
the fetus.
Embryonic Stage
Fetal surface (Stage 2)
• is covered by a structure called the amnion, or amniotic
membrane. Underlying the amnion is the chorion, a
thicker membrane. This structure of the
• placenta is continuous with the lining of the uterine wall.
• Emerging from the chorion are the villi where lies a
system of fetal capillaries (blood vessels) to allow
maximum contact area with the maternal blood (also
known as the intervillous space
• Also visible on the fetal surface of the placenta are the
umbilical veins and arteries that spread out from where
is situated the umbilical cord, near the center of the
organ
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
Maternal surface
• is composed of the decidua,
• There are different portions to the decidua
that have specific names according to
where they are located and what their
function is:
• •Decidua capsularis, decidua basalis,
decidua placentalis, decidua vera, decidua
parietalis
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
Maternal surface
• Also visible on the maternal surface are lobules,
approximately 15 to 20 called cotyledons. They are divided
by deep channels more commonly known as sulci. Each
individual lobule is divided into smaller sections containing
one villi. These villi are the same ones emerging from the
chorion, containing fetal capillaries, which bathe in the
intervillous space (it is important to note that fetal and
maternal blood never mix).
• Embeded in the decidua are maternal veins and arteries
that end in the intervillous space. They are also in
continuous with the maternal circulation.
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
Placenta
• Functioning by end of the 3rd wk.
• Produces hormones that control the
basic physiology of the mother and near
term mature fetal organs for life outside
of the uterus
• Protects the fetus from immune attack
by the mother
• Removes waste produced by the fetus
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
• Placental barrier prevents the mix of
maternal blood with fetal blood
Placental Hormones
• Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
• Human placental lactogen (hPL)
• Estrogen, progesterone
• Relaxin
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
Amniotic Fluid
• Surrounds embryo,
• Helps maintain a constant body
temperature for the fetus
• Permits symmetric growth and
development
• Cushions the fetus from trauma
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
Amniotic Fluid Function
• Allows the umbilical cord to be relatively
free of compression
• Promotes fetal movement to enhance
musculoskeletal development
Embryonic Stage
(Stage 2)
Umbilical cord
• Life line between mother and embryo
• 1 large vein & 2 small arteries (AVA)
• Wharton’s jelly surrounds the blood
vessels preventing compression
• Term length 22 in. / 1 in. wide
• Central insertion site on the placenta
Embryonic stage 3rd to 8th wk.
• Neural tube forms
• Brain waves detectable
• Heart development completed and beats
• Arms and legs move
• Resembles a human being
• Weight 1gram
Fetal Stage
(Stage 3)
9Th week to Birth
• 12 wks.- heart beat heard with Doppler,
sex is distinguishable, placenta
formation completed
• 13-16 wks.- fetal movement (quickening)
felt by mother
• 17-20 wks.- heart beat can be heard
with a stethoscope
Fetal Stage
(Stage 3)
• 21-24 wks.- lungs produce surfactant
• 24-32 wks.- alveoli begin to mature,
eyelids can open and close, increase in
subcutaneous fat
• 32-40 wks.- fetus kicks actively, lanugo
decrease, weight 7-8 lb’s
Length 17.3-19.2 in
Fetal Circulation
• Needed to sustain the fetus
• Must develop quickly and accurately
since the fetal nutrient needs Increase
as the embryo advances to a fetus
• Oxygen received from the placenta
• Placenta functions for the fetal lungs
and liver
You might also like
- Obstetric Physical ExaminationDocument17 pagesObstetric Physical ExaminationYusnida Rahmawati100% (1)
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument18 pagesFertilization & ImplantationReshma AjayNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Embryology LectureDocument57 pagesYear 2 Embryology LectureIjeoma Doris100% (1)
- The Growing FetusDocument68 pagesThe Growing Fetusjean thereseNo ratings yet
- Last Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsFrom EverandLast Minute Embryology: Human embryology made easy and digestible for medical and nursing studentsNo ratings yet
- Fertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyDocument8 pagesFertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyNikki M. Arapol100% (1)
- History of Past IllnessDocument4 pagesHistory of Past IllnesspachichoyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embryology 1Document72 pagesIntroduction To Embryology 1Sam MumoNo ratings yet
- Sri Ramachandra University Department of Obg Dissertation Topics - 2012-2015 Batch PG Name Topic GuideDocument4 pagesSri Ramachandra University Department of Obg Dissertation Topics - 2012-2015 Batch PG Name Topic GuideGunaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusDocument5 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- 2 Introduction To Embryology and FetalDocument55 pages2 Introduction To Embryology and Fetaldemeke andebetNo ratings yet
- Genetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentDocument54 pagesGenetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentBiraito TakanaNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument43 pagesFetal DevelopmentRob N Michelle50% (2)
- Fertilization and Fetal Development Abd CirculiationDocument54 pagesFertilization and Fetal Development Abd CirculiationMohnnad Hmood AlgaraybhNo ratings yet
- Q1 Animal Production (Swine) NC II 9-12 - Module 2Document20 pagesQ1 Animal Production (Swine) NC II 9-12 - Module 2dominador man-onNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan FisiologiDocument60 pagesAnatomi Dan FisiologiBimantoro SaputroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Labor and Delivery Stages of Labor Diagnosis Intervention Rationale IndependentDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan For Labor and Delivery Stages of Labor Diagnosis Intervention Rationale IndependentCLARISSE GEMROSE CUÑADANo ratings yet
- Neonatal Assessment FormDocument3 pagesNeonatal Assessment FormLeen ShweikiNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System PDFDocument111 pagesFemale Reproductive System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument22 pagesConception and Fetal DevelopmentChari RivoNo ratings yet
- The Growing Fetus For CPDocument19 pagesThe Growing Fetus For CPyzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1A Genetics Conception Fall 2015 Student'sDocument49 pagesLecture 1A Genetics Conception Fall 2015 Student'sDurgaNo ratings yet
- Conception Fetal Development & Genetics: Mary L. Dunlap MSN, Fall 2015Document49 pagesConception Fetal Development & Genetics: Mary L. Dunlap MSN, Fall 2015DurgaNo ratings yet
- Normal PregnancyDocument86 pagesNormal PregnancygayleesinfuegoNo ratings yet
- Ana&Physio 16 - Human DevelopmentDocument37 pagesAna&Physio 16 - Human DevelopmentShery Han Bint HindawiNo ratings yet
- The Placenta BDocument48 pagesThe Placenta BLulano MbasuNo ratings yet
- Placenta & Fetal CirculationDocument32 pagesPlacenta & Fetal CirculationFarxan Da Napolian BwoyNo ratings yet
- Placenta UpdatedDocument49 pagesPlacenta UpdatedSaad HasanNo ratings yet
- File 2Document104 pagesFile 2Djo RamNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument42 pagesStages of Fetal DevelopmentKara Ashleigh0% (1)
- 3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessDocument83 pages3 Fertilization and Implantation ProcessMarie Cecille Soliven VarillaNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdDocument18 pagesPerkembangan Plasenta (Autosaved) .En - IdFATIMAHNo ratings yet
- Parturition, Foetal Membranes and Multiple PregnanciesDocument38 pagesParturition, Foetal Membranes and Multiple PregnanciesGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- 10 Placenta DR - GosaiDocument29 pages10 Placenta DR - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument23 pagesPrenatal Developmentmooncrescent908006No ratings yet
- Embryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesDocument13 pagesEmbryology, Pathophysiology, and Ultrasound Characteristics of The Placenta ObjectivesAudrey100% (5)
- Ace Achievers: Embryologic Development of Human Fetus With Special Reference To FaceDocument10 pagesAce Achievers: Embryologic Development of Human Fetus With Special Reference To FaceaditryjeeNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument15 pagesFetal DevelopmentAna Cristina MontillanoNo ratings yet
- Fetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2Document40 pagesFetus Development From Conception To Birth Part2jeremyzucker321No ratings yet
- 3rd LecDocument8 pages3rd Lecنشط عقلكNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development Part 1 by Lea CortezDocument26 pagesPrenatal Development Part 1 by Lea CortezLea Cabillo CortezNo ratings yet
- Care of The Mother and The FetusDocument99 pagesCare of The Mother and The FetusBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development FinalDocument49 pagesPrenatal Development FinalAndreah PelingonNo ratings yet
- Sexual Response Fertiliztion ImplantationembryoDocument38 pagesSexual Response Fertiliztion ImplantationembryoHana-Lou TaquiquiNo ratings yet
- Development of Foetus and PlacentaDocument35 pagesDevelopment of Foetus and Placentaboragam.saisharanyaNo ratings yet
- NMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentDocument49 pagesNMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentYorgos TheodosiadisNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document37 pagesLec 2ibrahim.21hm32No ratings yet
- THE FETUS and PLACENTADocument50 pagesTHE FETUS and PLACENTAKyla CalsoNo ratings yet
- Fertilization & ImplantationDocument18 pagesFertilization & ImplantationArunashree ajayNo ratings yet
- 1-Prenatal & Fetal Development-93666Document45 pages1-Prenatal & Fetal Development-93666Izziddin YassineNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument37 pagesEmbryologySHOWMAN DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument34 pagesFetal Developmentanimemaster2kNo ratings yet
- Embryological Developemnt PDTCDocument14 pagesEmbryological Developemnt PDTCJoy JoycNo ratings yet
- Prenatal GrowthDocument26 pagesPrenatal GrowthKar InNo ratings yet
- FertilizationDocument63 pagesFertilizationDheressaaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesStages of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentGrant KhangabNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusDocument15 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusLuna Sang-an100% (1)
- Fetal Growth and DevelopmentDocument45 pagesFetal Growth and DevelopmentKrystel Anne MilanNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument24 pagesPlacentaNibedita 2015No ratings yet
- Week 3 (2) - Developmental Anatomy 1Document35 pagesWeek 3 (2) - Developmental Anatomy 1kittyrose 1No ratings yet
- ch.8 Embryo PDFDocument22 pagesch.8 Embryo PDFMohammad GhannamNo ratings yet
- Human Development and Menstrual CycleDocument34 pagesHuman Development and Menstrual CycleCharmaine FernandezNo ratings yet
- Abhinav 3 Obg TeachingDocument22 pagesAbhinav 3 Obg TeachingEkta RajputNo ratings yet
- 10 Kuliah PLACENTADocument33 pages10 Kuliah PLACENTAAya KamajayaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1yunjung0518100% (7)
- Introduction To EmbryologyDocument49 pagesIntroduction To EmbryologyTofik MohammedNo ratings yet
- The Female Pelvis and Fetal Skull PDFDocument9 pagesThe Female Pelvis and Fetal Skull PDFMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- Heart Disease in Pregnancy VoiceoverDocument30 pagesHeart Disease in Pregnancy VoiceoverMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- UTI in Pregnancy VoiceoverDocument10 pagesUTI in Pregnancy VoiceoverMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes MellitusDocument42 pagesGestational Diabetes MellitusMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy PDFDocument9 pagesHypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy PDFMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- Antepartum HemorrhageDocument12 pagesAntepartum HemorrhageMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument16 pagesPuerperiumMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- PuerperiumDocument16 pagesPuerperiumMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- Complication & Minor Ailments of PuerperiumDocument61 pagesComplication & Minor Ailments of PuerperiumMohammed AbdNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Tungkol Sa Teenage PregnancyDocument4 pagesTerm Paper Tungkol Sa Teenage Pregnancyea726gej100% (1)
- Practical Research 1 MODULE 7Document5 pagesPractical Research 1 MODULE 7Jimboy MaglonNo ratings yet
- (A) Zygote: (C) Fish 3Document2 pages(A) Zygote: (C) Fish 3UGC GAMERNo ratings yet
- Menopause - RajonivrittiDocument13 pagesMenopause - RajonivrittiSivaram Shanmugha VilasNo ratings yet
- A Endometriotic Lesions Occur in 1-20% of All Women, The Majority of Which Present Symptomatically and Are Diagnosed With The ConditionDocument7 pagesA Endometriotic Lesions Occur in 1-20% of All Women, The Majority of Which Present Symptomatically and Are Diagnosed With The ConditionNikhil TyagiNo ratings yet
- Instruments in Endometrial BiopsyDocument13 pagesInstruments in Endometrial BiopsySiddhant DNo ratings yet
- MenstruationDocument3 pagesMenstruationcoco yomieNo ratings yet
- Learner: Lord Mvoula: Test Name Completion Date Score Timespent ResultDocument3 pagesLearner: Lord Mvoula: Test Name Completion Date Score Timespent ResultLord M.No ratings yet
- Literature Review On Legalization of AbortionDocument6 pagesLiterature Review On Legalization of Abortiontkpmzasif100% (1)
- Herbal MedicineDocument5 pagesHerbal MedicineParth RathodNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kebidanan: Volume 10 Nomor 1 (2020) 48-53Document6 pagesJurnal Kebidanan: Volume 10 Nomor 1 (2020) 48-53Hariyanto DuriNo ratings yet
- Hot Topic Sex Education Abstinence OnlyDocument10 pagesHot Topic Sex Education Abstinence Onlyapi-432991579No ratings yet
- Movie Analysis - Sarah Mae S ObisDocument5 pagesMovie Analysis - Sarah Mae S ObisSarah Mae ObisNo ratings yet
- MAPEH (Health) : Quarter 1 - Module 6: Teenage Issues and Concerns: Pre-Marital Sex and Teenage PregnancyDocument11 pagesMAPEH (Health) : Quarter 1 - Module 6: Teenage Issues and Concerns: Pre-Marital Sex and Teenage PregnancyAlbert Ian Casuga100% (1)
- Population Class 9 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 6 PDFDocument7 pagesPopulation Class 9 Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 6 PDFpushkar162519No ratings yet
- 3-Psychological Factors of Menarche, Sexual and Reproductive DevelopmentDocument19 pages3-Psychological Factors of Menarche, Sexual and Reproductive DevelopmentIzzah KhurramNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Formatted (Last)Document4 pagesNeonatal Formatted (Last)Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Exam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersDocument118 pagesExam MCQ عين شمس + AnswersIsmail Ahmed0% (1)
- Vaginal Infection 160505210023Document41 pagesVaginal Infection 160505210023Supekshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of AdenomyosisDocument3 pagesDiagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment of AdenomyosisAndres MahechaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health AssignmentDocument12 pagesReproductive Health AssignmentRmanojkumar OmanNo ratings yet
- Obstetri Dan Ginekologi: NO Diagnosa Kode Icd 10Document32 pagesObstetri Dan Ginekologi: NO Diagnosa Kode Icd 10hubus syahidahNo ratings yet
- Prom Pprom DiagnosisDocument9 pagesProm Pprom DiagnosisTiAs TiAriyahNo ratings yet
- Breastfeeding in Hiv Positive MothersDocument13 pagesBreastfeeding in Hiv Positive MothersBeverly MenendezNo ratings yet