Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bio511: Assignment 1: Aabbcc X Aabbcc. Assume That You Are Working With A Species That Produces Large
Uploaded by
FAtma HAnysOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio511: Assignment 1: Aabbcc X Aabbcc. Assume That You Are Working With A Species That Produces Large
Uploaded by
FAtma HAnysCopyright:
Available Formats
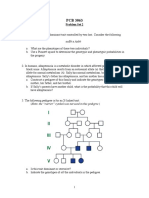
BIO511: ASSIGNMENT 1
1) Assume that eye colour in humans is controlled by a single pair of genes of which the
effect of that for brown (B) is dominant over the effect of that for blue (b).
a) What is the genotype of a brown-eyed individual who marries a blue-eyed individual
and produces a first offspring that is blue-eyed?
b) For the same mating in (a), what proportions of the two eye colours are expected
among further offspring?
c) What are the expected proportions of eye colours among the offspring of a mating
between two brown-eyed individuals who each had one parent that was blue-eyed?
2) In dogs dark coat colour is dominant over albino and short hair is dominant over long
hair. If these effects are caused by two independently segregating gene pairs, write the
most probable genotypes for the parents of each of the following crosses, using the
symbols C and c for the dark and albino coat colour alleles, and S and s for the short
and long-hair alleles, respectively.
Phenotypes of Offspring
Parental Phenotypes Dark Dark Albino Albino
Short Long Short Long
a) Dark short x dark short 89 31 29 11
b) Dark short x dark long 18 19 0 0
c) Dark short x albino short 20 0 21 0
d) Albino short x albino short 0 0 28 9
e) Dark long x dark long 0 32 0 10
f) Dark short x dark short 46 16 0 0
g) Dark short x dark long 29 31 9 11
3) A cross made between two plants differing in three independently assorting gene pairs,
AaBBcc x AaBbCc. Assume that you are working with a species that produces large
numbers of progeny. Use the forked line method to arrive at the answers to the
following questions:
a) What fraction of the progeny will be heterozygous for all three genes?
b) What fraction of the progeny will be heterozygous for gene A?
c) What fraction of the progeny will express the dominant phenotypes for genes A and
C, and recessive for gene B?
4) Phenylketonuria, a metabolic disease in humans, is caused by a recessive allele, k. Two
heterozygous carriers of the allele marry and plan a family of five children. Determine the
probability for the following combinations of offspring:
a) All their children will be unaffected.
b) Four children will be unaffected and one affected with Phenylketonuria.
c) At least three children will be unaffected.
d) First child will be an unaffected girl.
You might also like
- Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test BankDocument12 pagesConcepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test Bankhutaq100% (1)
- LABORATORY ACTIVITY 6 - GENETIC LINKAGE AND RECOMBINATIONDocument3 pagesLABORATORY ACTIVITY 6 - GENETIC LINKAGE AND RECOMBINATIONNorsaidin TungkagNo ratings yet
- Genetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFDocument10 pagesGenetics Ch04 Test Bank PDFejanlindsay50% (2)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Genetics 10th Edition William S KlugDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Genetics 10th Edition William S Klugashleyhaaswxcbmagsde100% (28)
- Population Genetics: Tutorial 5Document8 pagesPopulation Genetics: Tutorial 5minaNo ratings yet
- 2009 MidtermI Form1Document12 pages2009 MidtermI Form1svNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 Question (Chapter 4) (Periodic Table) : HAAH/2013Document2 pagesCHM 420 Question (Chapter 4) (Periodic Table) : HAAH/2013FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Beginning Chi Manipulation TechniqueDocument3 pagesBeginning Chi Manipulation Techniqueellemistery100% (1)
- Lumko Ntuli Student No 221015440 Genetic 240 Tutorial 2 20Document4 pagesLumko Ntuli Student No 221015440 Genetic 240 Tutorial 2 20Mthetheleli NxeleNo ratings yet
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadDocument27 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6th Edition Pierce Test Bank DownloadMax Martinez100% (21)
- Gene Mapping PracticeDocument4 pagesGene Mapping PracticeBobbyWhite100% (1)
- Genetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesGenetics A Conceptual Approach 6Th Edition Pierce Test Bank Full Chapter PDFsoojeebeautied9gz3h100% (10)
- Learning Genetics with Punnett Squares & PedigreesDocument9 pagesLearning Genetics with Punnett Squares & PedigreesSir100% (1)
- Lab 9 ProtocolDocument7 pagesLab 9 ProtocolKareem HassanNo ratings yet
- Genetics Problem Set on Linkage, Inheritance PatternsDocument5 pagesGenetics Problem Set on Linkage, Inheritance PatternskristalNo ratings yet
- QP Pbi Bio Xii 2022-23Document10 pagesQP Pbi Bio Xii 2022-23Hetasvi SabhayaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Worksheet # 2 12th GradeDocument4 pagesGenetics Worksheet # 2 12th GradeCRISTINA MARTINEZ OLANONo ratings yet
- Genetics Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesGenetics Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsVenakadalakshmi Kannappan100% (1)
- Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test BankDocument25 pagesConcepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test BankChristinaHaleexngm100% (49)
- Genetics Discussion 3Document4 pagesGenetics Discussion 3nightowl721No ratings yet
- Genetics PracticeDocument4 pagesGenetics PracticeYanaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Exam 1Document8 pagesGenetics Exam 1Tanweer Kumar100% (1)
- Mendelian Principles - Work Sheet 1Document8 pagesMendelian Principles - Work Sheet 1Carlos FrancoNo ratings yet
- Assignment For MSC Animal Breeding and Genetics Students Final 2020Document8 pagesAssignment For MSC Animal Breeding and Genetics Students Final 2020Hundeessaa OliiqaaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Report on Dihybrid InheritanceDocument12 pagesGenetics Lab Report on Dihybrid InheritanceTime NextNo ratings yet
- Questions and Problems 3Document8 pagesQuestions and Problems 3Arnytha VebrianiNo ratings yet
- Prac Ex 01Document11 pagesPrac Ex 01Jinal PatelNo ratings yet
- Genetics WorkbookDocument57 pagesGenetics WorkbookLauren WinnettNo ratings yet
- Heredity Practice Exam KEYDocument4 pagesHeredity Practice Exam KEYjacky qianNo ratings yet
- Agron/Gen 309 Genetics PROBLEM THREE - Mendelian GeneticsDocument5 pagesAgron/Gen 309 Genetics PROBLEM THREE - Mendelian GeneticsMar GomezNo ratings yet
- Genetics and Heredity Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument32 pagesGenetics and Heredity Multiple Choice QuestionsMensah Vilas FrancisNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering Pros & Cons AssessmentDocument13 pagesGenetic Engineering Pros & Cons AssessmentAlvin PaboresNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-Genetics SASE ReviewerDocument2 pagesBIOLOGY-Genetics SASE ReviewerSarah HendrixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document15 pagesChapter 15nfnf otupyooorefnNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument2 pagesProblem SetKentKawashimaNo ratings yet
- Nicart, Jeric-Vincent C. - Genetics LaboratoryDocument3 pagesNicart, Jeric-Vincent C. - Genetics Laboratoryebenicart0No ratings yet
- Chapter 03 Exercices(4)Document9 pagesChapter 03 Exercices(4)Radwan BourjiNo ratings yet
- BIO SET B - WatermarkDocument8 pagesBIO SET B - Watermarkbtkusuma01No ratings yet
- Full Download Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test BankDocument21 pagesFull Download Genetics Canadian 2nd Edition Hartwell Test Bankbeliechopper05srz100% (31)
- Quiz - Simple Mendelian CrossDocument4 pagesQuiz - Simple Mendelian CrossShaden MasriNo ratings yet
- Mendelian Genetics 2Document6 pagesMendelian Genetics 2Joonie JoonNo ratings yet
- 103期末Document7 pages103期末Rose FuNo ratings yet
- Genetics FinalDocument11 pagesGenetics Finalmrx2312.rxNo ratings yet
- Genetic ProblemsDocument20 pagesGenetic Problemsatik0% (2)
- Question Bank GeneticsDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank GeneticsTapajyoti RouthNo ratings yet
- Taller 1, Genética MendelianaDocument3 pagesTaller 1, Genética MendelianaalesssssNo ratings yet
- Neet Pedigree Questions Worksheet 5ef6eb6eca031Document8 pagesNeet Pedigree Questions Worksheet 5ef6eb6eca031sarudarshinij.s123No ratings yet
- Cbjescpu 08Document10 pagesCbjescpu 08Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - Period: - AP Biology Genetics Problems PracticeDocument5 pagesName: - Date: - Period: - AP Biology Genetics Problems PracticesandsphilipNo ratings yet
- Genetic Cross Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageGenetic Cross Practice QuestionsJOEL VIVIANNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Concepts of Genetics 10th Edition Klug Test Bank PDFmaryjomacklemus100% (13)
- Problems From Patterns of Inheritance (Ch. 10)Document9 pagesProblems From Patterns of Inheritance (Ch. 10)Rathil MadihalliNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1 2018-19 SolutionsDocument4 pagesSeminar 1 2018-19 SolutionsAna Rodriguez PedrouzoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Long QuizDocument4 pagesGenetics Long QuizPaul Stephen SorianoNo ratings yet
- Final Genetics 31Document11 pagesFinal Genetics 31mrx2312.rxNo ratings yet
- Selina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Genetics Some Basic FundamentalsDocument9 pagesSelina Solutions For Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Genetics Some Basic FundamentalsMysterious SinghNo ratings yet
- Lingkages ProblemsDocument7 pagesLingkages ProblemsAnthony HugillNo ratings yet
- BSP 502 ExercisesDocument8 pagesBSP 502 ExercisesTemitope Oluwakemi OlaNo ratings yet
- Biology MCQDocument5 pagesBiology MCQSungdeok MinNo ratings yet
- 50 Great Myths of Human Evolution: Understanding Misconceptions about Our OriginsFrom Everand50 Great Myths of Human Evolution: Understanding Misconceptions about Our OriginsNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Stoichiometry and Theoretical YieldDocument8 pagesExperiment 4 Stoichiometry and Theoretical YieldFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 Compound Identification Lab ReportDocument6 pagesCHM 420 Compound Identification Lab ReportFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Standardizing Potassium Permanganate by Redox TitrationDocument7 pagesStandardizing Potassium Permanganate by Redox TitrationFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- War Crimes: Established by ?Document2 pagesWar Crimes: Established by ?FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- PDJ 2Document6 pagesPDJ 2FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective and Learning OutcomeDocument17 pagesLearning Objective and Learning OutcomeFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- PRESENTATION SCE No BGDocument62 pagesPRESENTATION SCE No BGFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Types of Chemical ReactionDocument8 pagesExperiment 3 Types of Chemical ReactionFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document11 pagesLecture 5FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- PDJ 1Document3 pagesPDJ 1FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- The Muscular System: How Nerves Control ContractionDocument22 pagesThe Muscular System: How Nerves Control ContractionFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- CHM420 - b1 Syllabus 210313 (EDITED)Document6 pagesCHM420 - b1 Syllabus 210313 (EDITED)FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal SystemDocument30 pagesThe Skeletal SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Presentation SceDocument53 pagesPresentation SceFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions Falling ObjectDocument14 pagesMisconceptions Falling ObjectFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument15 pagesCellular RespirationFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Cell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemDocument22 pagesCell, Tissue, Organ and Organ SystemFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 STOICHIOMETRY QUESTIONSDocument2 pagesCHM 420 STOICHIOMETRY QUESTIONSFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 Questions (Chapter 1) Measurement Matter: HAAH/2013Document2 pagesCHM 420 Questions (Chapter 1) Measurement Matter: HAAH/2013FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Educational in Malaysia (Group)Document31 pagesEducational in Malaysia (Group)FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Education in Ancient Rome: A Concise HistoryDocument16 pagesEducation in Ancient Rome: A Concise HistoryFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Q Chap 5 CHM420Document2 pagesQ Chap 5 CHM420FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 Question (Chapter 3) Atomic Structure & Quantum Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesCHM 420 Question (Chapter 3) Atomic Structure & Quantum Electromagnetic WavesFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Ancient Rome (Individual)Document7 pagesAncient Rome (Individual)FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of Transition Metal CationsDocument5 pagesSpectrophotometric Analysis of Transition Metal CationsFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Determining Ligand Percentages in Coordination CompoundsDocument11 pagesDetermining Ligand Percentages in Coordination CompoundsFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Experiment on ComplexesDocument6 pagesInorganic Chemistry Experiment on ComplexesFAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- CHM 420 Tentative Schedul Sep14Document2 pagesCHM 420 Tentative Schedul Sep14FAtma HAnysNo ratings yet
- Printed Quiz Primary Schools General Knowledge For Class Use (4) 1Document8 pagesPrinted Quiz Primary Schools General Knowledge For Class Use (4) 1anon_727234579No ratings yet
- Activity Worksheet in English 6 #1Document20 pagesActivity Worksheet in English 6 #1Angelica BuquiranNo ratings yet
- CBLM Cookery Uc 6Document187 pagesCBLM Cookery Uc 6mary ann coperNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument2 pagesSubarachnoid HemorrhageJethro Bacayo Zamora100% (1)
- Clare E James: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesClare E James: ObjectiveAnas KabarNo ratings yet
- Tle Agriculture AnimalsDocument2 pagesTle Agriculture AnimalsRonel Sayaboc AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Joints: Mr. Saihou SannehDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Joints: Mr. Saihou Sannehflex gyNo ratings yet
- CondomsDocument4 pagesCondomsSandeep SoniNo ratings yet
- Devario in Bangladesh: Species DiversityDocument37 pagesDevario in Bangladesh: Species DiversitySubhadra LaimayumNo ratings yet
- Speaking and listening – Superlatives conversation cardsDocument2 pagesSpeaking and listening – Superlatives conversation cardsEirini Stypsianou0% (1)
- Module 1Document25 pagesModule 1princess mae paredesNo ratings yet
- Ailments RemediesDocument219 pagesAilments RemediesSubramanya RaoNo ratings yet
- Surgery 421Document218 pagesSurgery 421AshNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo 4TH Grade Anna and The DolphinDocument9 pagesCuadernillo 4TH Grade Anna and The DolphinMaria Belen SalaNo ratings yet
- P-3 - A Tiger in The Zoo - Ques.-Ans.Document1 pageP-3 - A Tiger in The Zoo - Ques.-Ans.bindragunroopNo ratings yet
- The Switch by ItsakyoDocument151 pagesThe Switch by ItsakyolordzuqiNo ratings yet
- Mixed Level TeachingDocument14 pagesMixed Level TeachingTaraprasad PaudyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 17 - Respiratory SystemXyla HapatingaNo ratings yet
- A Case Report On Scabies in A GoatDocument4 pagesA Case Report On Scabies in A Goatalifnaufaliyanto100% (1)
- Ant and CocoonDocument4 pagesAnt and CocoonDian ikaNo ratings yet
- BX Essentials - Cleric and Magic-User SpellsDocument37 pagesBX Essentials - Cleric and Magic-User SpellsArda Emirgeloğlu100% (2)
- SemanticsDocument69 pagesSemanticsYusuf Iro Husodo100% (2)
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiDocument1 pageInv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanNo ratings yet
- Pemantapan Kota 2019 - C 01 (ENG)Document16 pagesPemantapan Kota 2019 - C 01 (ENG)yeni indraNo ratings yet
- Gape, Lestlie 1bse-A C5 Semantics L1Document6 pagesGape, Lestlie 1bse-A C5 Semantics L1LESTLIE GAPENo ratings yet
- Aptis ReadingDocument26 pagesAptis ReadingCẩm Chi LêNo ratings yet
- Soal UKK Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2 SD-MIDocument1 pageSoal UKK Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2 SD-MIDian Indah LestariNo ratings yet
- The Toy PoodleDocument2 pagesThe Toy Poodlebudi domisolNo ratings yet
- Sex Limited TraitsDocument9 pagesSex Limited TraitsCHRISTOFER CORONADONo ratings yet