Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1819 Level I Science Exam Related Materials T3 Wk6 PDF
Uploaded by
elena123456elena123456Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1819 Level I Science Exam Related Materials T3 Wk6 PDF
Uploaded by
elena123456elena123456Copyright:
Available Formats
Science Weekly Exam Material
Week: 6 From: May. 12 Till May. 16, 2019
Exam Timetable:
Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday
AMS
Questions in bold are Grid Questions
Questions in italic are Poorly Answered Questions in past exam(s).
AMS Material: 1819-SIM37-WRCC
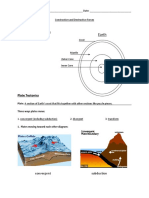
1. The lithosphere, is broken into 8 large “tectonic _________” and many smaller ones that
float on top of the inner mantle.
2. _________ boundaries are locations where two plates that push against each other, and
parts of the denser plate may _________ under the lighter plate and melt in the heat of the
Earth.
3. A _________ is a crack in Earth’s crust from which molten _________ comes to the
surface.
4. Molten rock under the crust is called _________, and once it gets out and runs over the
crust it is called _________.
5. Sometimes so much _________ comes out of undersea volcanoes that _________ form.
Like the Hawaiian Islands.
6. _________ chains usually form when two convergent continental plates push against each
other, neither sliding below the other. Instead, they fold, forming mountains, like the
_________ Mountains.
7. Our Solar System was formed around _________ billion years ago. From a giant cloud of
gases and rocks that gravity pulled together. Most of the matter formed the _________, while
the rest formed _________, _________ and other smaller bodies.
8. The Earth started as a ball of molten _________ which solidified as it cooled, although the
_________ still is largely a hot ball of _________ iron and nickel.
9. The density of the Earth’s material _________ as we go from outside to the inside: Crust
(solid) _________ g/cm3,→ Mantle (soft rock) → Outer core (molten metal) → Inner core
(solid and most dense _________ g/cm3,).
Date 07-05-19 | Level I | 1
10. Convection currents in the lower _________cause the tectonic plates to _________ with
respect to each other (2 cm to 30 cm per year).
11. The _________ consists of 3 layers: the inner and outer _________ (made of molten iron
and nickel ball of radius 3400km), the _________ (consisting of a thickness of 3000 km of
matter), and the _________, (about 40 km thick layer of rock)
12. The Earth behaves like a large magnet with magnetic South Pole near the geographic
_________. This is why the north pole of a magnet is attracted to the _________.
13. A _________ map uses colours or _________ lines to show elevation. A _________ line
joins points with the same elevation to represent mountains and valleys.
14. A _________ is a sphere or with the map of Earth on its _________.
15. The _________ is an imaginary line that _________ Earth and is found midway between
the North and the South Poles.
16. The Northern _________ is the upper half of Earth and extends from the _________ to
the _________. The _________ is the other half of Earth.
17. Lines of _________ are imaginary lines around Earth that are parallel to the _________.
Lines of _________ are imaginary lines around Earth that pass through both poles and cut the
_________ at 90ᵒ.
18. Under continents the crust is called _________ crust, is _________ and in includes
_________, a hard, multicolored rock.
Date 07-05-19 | Level I | 2
1. The lithosphere, is broken into 8 large “tectonic [plates]” and many smaller ones that float
on top of the inner mantle.
2. [Convergent] boundaries are locations where two plates that push against each other, and
parts of the denser plate may [sink] under the lighter plate and melt in the heat of the Earth.
3. A [volcano] is a crack in Earth’s crust from which molten [rock] comes to the surface.
4. Molten rock under the crust is called [magma], and once it gets out and runs over the crust
it is called [lava].
5. Sometimes so much [lava] comes out of undersea volcanoes that [islands] form. Like the
Hawaiian Islands.
6. [Mountain] chains usually form when two convergent continental plates push against each
other, neither sliding below the other. Instead, they fold, forming mountains, like the
[Himalayan] Mountains.
7. Our Solar System was formed around [4.6] billion years ago. From a giant cloud of gases
and rocks that gravity pulled together. Most of the matter formed the [Sun], while the rest
formed [planets], [moons] and other smaller bodies.
8. The Earth started as a ball of molten [rock] which solidified as it cooled, although the
[core] still is largely a hot ball of [liquid] iron and nickel.
9. The density of the Earth’s material [increases] as we go from outside to the inside: Crust
(solid) [2] g/cm3,→ Mantle (soft rock) → Outer core (molten metal) → Inner core (solid and
most dense[10] g/cm3,).
10. Convection currents in the lower [mantle] cause the tectonic plates to [move] with
respect to each other (2 cm to 30 cm per year).
11. The [geosphere] consists of 3 layers: the inner and outer [core] (made of molten iron and
nickel ball of radius 3400km), the [mantle] (consisting of a thickness of 3000 km of matter),
and the [crust], (about 40 km thick layer of rock)
12. The Earth behaves like a large magnet with magnetic South Pole near the geographic
[North Pole]. This is why the north pole of a magnet is attracted to the [north].
13. A [topographic] map uses colours or [contour] lines to show elevation. A [contour] line
joins points with the same elevation to represent mountains and valleys.
14. A [globe] is a sphere or with the map of Earth on its [surface].
15. The [equator] is an imaginary line that [circles] Earth and is found midway between the
North and the South Poles.
16. The Northern [hemisphere] is the upper half of Earth and extends from the [equator] to
the [North Pole]. The [southern hemisphere] is the other half of Earth.
Date 07-05-19 | Level I | 3
17. Lines of [latitude] are imaginary lines around Earth that are parallel to the [equator].
Lines of [longitude] are imaginary lines around Earth that pass through both poles and cut
the [equator] at 90ᵒ.
18. Under continents the crust is called [continental] crust, is [thicker] and in includes
[granite], a hard, multicolored rock.
Date 07-05-19 | Level I | 4
Science Minima of Week 5 (To be tested in Week 6)
Term 3 – 2018-19
Level I
Science Questions and Grid questions of Week 5 (Starting 05-May-2019)
(To be tested starting 12-May-2019)
Sec 6.3 (LP 1-6)
1. G The lithosphere, is broken into 8 large “tectonic [plates]” and many smaller ones
that float on top of the inner mantle.
2. G [Convergent] boundaries are locations where two plates push against each other,
and parts of the denser plate may [sink] under the lighter plate and melt in the heat of
the Earth.
3. G A [volcano] is a crack in Earth’s crust from which molten [rock] comes to the
surface.
4. G Molten rock under the crust is called [magma], and once it gets out and runs over
the crust it is called [lava].
5. G Sometimes so much [lava] comes out of undersea volcanoes that [islands] form.
Like the Hawaiian Islands.
6. G [Mountain] chains usually form when two convergent continental plates push
against each other, neither sliding below the other. Instead, they fold, forming
mountains, like the [Himalayan] Mountains.
Date 07-05-19 | Level I | 5
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To GeologyDocument76 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To GeologyZulaikha KamalNo ratings yet
- Baixar Livro Draw With Jazza Creating Characters de Josiah Broo PDFDocument5 pagesBaixar Livro Draw With Jazza Creating Characters de Josiah Broo PDFCarlos Mendoza25% (4)
- Earth Foldable - Foundation ScienceDocument32 pagesEarth Foldable - Foundation Scienceapi-358472990100% (1)
- Self Authoring SuiteDocument10 pagesSelf Authoring SuiteTanish Arora100% (3)
- PHYS1500 Lecture Notes AstronomyDocument83 pagesPHYS1500 Lecture Notes AstronomyJesse XuNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Nazi Economy - Maxine Yaple SweezyDocument273 pagesThe Structure of The Nazi Economy - Maxine Yaple Sweezygrljadus100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Geology & Soil Science (Safo - 1102)Document31 pagesFundamentals of Geology & Soil Science (Safo - 1102)ShijithNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Grade10 Quarter1 Module1 Week1 PDFDocument15 pagesSCIENCE Grade10 Quarter1 Module1 Week1 PDF알랙스No ratings yet
- Earth Layers Comprehension PDFDocument2 pagesEarth Layers Comprehension PDFEiver Barceló González0% (1)
- Plate Tectonics Web Quest StudentDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics Web Quest Studentapi-33569025579% (24)
- Task Performance Valeros Roeul GDocument6 pagesTask Performance Valeros Roeul GAnthony Gili100% (3)
- Army War College PDFDocument282 pagesArmy War College PDFWill100% (1)
- Harlem Renaissance LiteratureDocument2 pagesHarlem Renaissance LiteratureSylvia Danis100% (1)
- Midterm Earth SciDocument2 pagesMidterm Earth SciPablo Ragay Jr100% (1)
- Tectonic Plates: The Structure of The EarthDocument3 pagesTectonic Plates: The Structure of The EarthbiancanallaNo ratings yet
- Nebulae and Tectonic PlatesDocument4 pagesNebulae and Tectonic PlatesDeeva SethiNo ratings yet
- The Earth SystemDocument7 pagesThe Earth SystemrolandNo ratings yet
- 6th Concept Guide Per 1 Answers1617-Sch101Document5 pages6th Concept Guide Per 1 Answers1617-Sch101api-270387817No ratings yet
- Science 10 1st Grading Module 1Document27 pagesScience 10 1st Grading Module 1vinesseNo ratings yet
- ANSWERS Clickview Video WorksheetDocument3 pagesANSWERS Clickview Video Worksheet李之由No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument26 pagesSciencekhoadragonpro2005No ratings yet
- Engineering GeologyDocument117 pagesEngineering GeologyJoshua Mong'areNo ratings yet
- Physical Geography 2ndDocument21 pagesPhysical Geography 2ndAwais BakshyNo ratings yet
- Geo 151S Lesson Note 2 (The Earth)Document32 pagesGeo 151S Lesson Note 2 (The Earth)Oluseyi AbegundeNo ratings yet
- Geology Chapter 3Document9 pagesGeology Chapter 3Alemkeng BrendaNo ratings yet
- Tectonics PlatesDocument12 pagesTectonics PlatesChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- 40-Research - April Mae CulawayDocument4 pages40-Research - April Mae CulawayAva BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Geomophology PDFDocument20 pagesGeomophology PDFJoel T MbulanjeNo ratings yet
- Lecture12 SolarSystem FormationDocument38 pagesLecture12 SolarSystem FormationRajni TyagiNo ratings yet
- Local Media5988609580861488696Document9 pagesLocal Media5988609580861488696Dise WrightsNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Web Quest StudentDocument9 pagesPlate Tectonics Web Quest Studentapi-330049991No ratings yet
- Tectonic Hazards: Structure of The EarthDocument3 pagesTectonic Hazards: Structure of The EarthHoops Elite UKNo ratings yet
- Subject Grade 10 Earth and Space SCDocument1 pageSubject Grade 10 Earth and Space SCjordan.shapiroNo ratings yet
- Science PeriodicalDocument10 pagesScience PeriodicalduranfredrichinocianNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Web Quest StudentDocument8 pagesPlate Tectonics Web Quest Studentapi-3304629350% (1)
- Liu041 Ring of FireDocument2 pagesLiu041 Ring of FireAurora FanaliNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The Earth Worksheet 1Document7 pagesInternal Structure of The Earth Worksheet 1Ry WannaFlyNo ratings yet
- Formation of EarthDocument54 pagesFormation of Earthniaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document9 pagesScience 10Myca IlustrisimoNo ratings yet
- Earth System and DynamicsDocument7 pagesEarth System and DynamicsJacqui JuanNo ratings yet
- Open Cloze 5Document2 pagesOpen Cloze 5strijelaš MuminovićNo ratings yet
- Liu041 Ring of FireDocument2 pagesLiu041 Ring of Firejohnnorton.academyNo ratings yet
- General Geology: Geology in Civil EngineeringsDocument27 pagesGeneral Geology: Geology in Civil Engineeringshhii aasdasdNo ratings yet
- World Geography Rapid Revision - 6741338Document77 pagesWorld Geography Rapid Revision - 6741338teddyNo ratings yet
- Geology-Notes 1PDocument43 pagesGeology-Notes 1Praul.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q2W3 4Document16 pagesScience 8 - Q2W3 4Kei LocksNo ratings yet
- The Global PerspectiveDocument3 pagesThe Global PerspectivehannaleigmactalNo ratings yet
- Composition of EarthDocument2 pagesComposition of EarthSyed Kumail Abbas ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science For Grade 12 Students: Sally B. Ortega TeacherDocument12 pagesEarth and Life Science For Grade 12 Students: Sally B. Ortega TeacherRaymond DizonNo ratings yet
- Johnathon Bell - Layers of Earth and Earth Magnetism PPT StudentDocument47 pagesJohnathon Bell - Layers of Earth and Earth Magnetism PPT StudentJohnathon BellNo ratings yet
- Earths InteriorDocument1 pageEarths InteriorJosh QuinanolaNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Earth and CompositionDocument12 pagesStructure of The Earth and CompositionFay Valerio AlabaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 3Document4 pagesLesson Plan 3api-331896872No ratings yet
- Lecture 01 - The Earth - Formation and CompositionDocument2 pagesLecture 01 - The Earth - Formation and CompositionZohaib IqbalNo ratings yet
- Tructure of The Arth: and Its Origin and FateDocument23 pagesTructure of The Arth: and Its Origin and FateKent Jasser DuriasNo ratings yet
- Science For TheDocument2 pagesScience For The학년JuNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Activity PDFDocument6 pagesTectonic Activity PDFmark smithNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Science Day 1Document7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Science Day 1CINDYNo ratings yet
- Geology AssDocument2 pagesGeology AssDenjay CatalanNo ratings yet
- 22-23 Constructive Destructive Study GuideDocument5 pages22-23 Constructive Destructive Study Guideapi-234287636No ratings yet
- Yr8 The World Beneath UsDocument40 pagesYr8 The World Beneath UsMaria JiaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Pt1 - IntroductionDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics Pt1 - IntroductionPrudence RwatireraNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument52 pagesPlate TectonicsTrembletonNo ratings yet
- Theories of Earth FormationDocument3 pagesTheories of Earth FormationRosell De RamaNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plate MovementDocument1 pageTectonic Plate MovementVivian PuentesNo ratings yet
- Backyard Landscape 1cm: 3m: Week 8-AmsDocument7 pagesBackyard Landscape 1cm: 3m: Week 8-Amselena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Properties - of - Matter 2Document13 pagesProperties - of - Matter 2elena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Wilhelm Conrad R: Öntgen: A BiographyDocument8 pagesWilhelm Conrad R: Öntgen: A Biographyelena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Adverb Clauses in Sentences PDFDocument2 pagesAdverb Clauses in Sentences PDFelena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Level I Math Term 3 Week 4 Periodic-Sample QuestionsDocument5 pagesLevel I Math Term 3 Week 4 Periodic-Sample Questionselena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Math 1Document6 pagesMath 1elena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- 1819 Level I Science Basic Question CH 6 Sec 2Document5 pages1819 Level I Science Basic Question CH 6 Sec 2elena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- 1819 G-L Final Timetable T2 (Manama) UpdatedDocument2 pages1819 G-L Final Timetable T2 (Manama) Updatedelena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- 1819 Level I Mathematics Periodic Revision T3 Wk4Document1 page1819 Level I Mathematics Periodic Revision T3 Wk4elena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Relative Clauses WhichDocument1 pageRelative Clauses Whichelena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Present Perfect Simple Exercise 2 KeyDocument1 pagePresent Perfect Simple Exercise 2 Keyelena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- 1819 June - August Make-Ups Timetable UpdatedDocument1 page1819 June - August Make-Ups Timetable Updatedelena123456elena123456No ratings yet
- Mbtruck Accessories BrochureDocument69 pagesMbtruck Accessories BrochureJoel AgbekponouNo ratings yet
- Orchestral Tools - The Orchestral Grands ManualDocument12 pagesOrchestral Tools - The Orchestral Grands ManualPiotr Weisthor RóżyckiNo ratings yet
- Alankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONDocument84 pagesAlankit Assignments LTD.: Project Report ONmannuNo ratings yet
- Evolution Epidemiology and Etiology of Temporomandibular Joint DisordersDocument6 pagesEvolution Epidemiology and Etiology of Temporomandibular Joint DisordersCM Panda CedeesNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Inglés.Document14 pagesVocabulary Inglés.Psicoguía LatacungaNo ratings yet
- BUS 301 - Hospitality Industry Vietnam - Nguyễn Thị Thanh Thuý - 1632300205Document55 pagesBUS 301 - Hospitality Industry Vietnam - Nguyễn Thị Thanh Thuý - 1632300205Nguyễn Thị Thanh ThúyNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument48 pagesPeptic Ulcerscribd225No ratings yet
- PDF - Unpacking LRC and LIC Calculations For PC InsurersDocument14 pagesPDF - Unpacking LRC and LIC Calculations For PC Insurersnod32_1206No ratings yet
- Filipino Chicken Cordon BleuDocument7 pagesFilipino Chicken Cordon BleuHazel Castro Valentin-VillamorNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Report GerminationDocument10 pagesBio Lab Report GerminationOli Damaskova100% (4)
- National Healthy Lifestyle ProgramDocument6 pagesNational Healthy Lifestyle Programmale nurseNo ratings yet
- Module 5amp6 Cheerdance PDF FreeDocument27 pagesModule 5amp6 Cheerdance PDF FreeKatNo ratings yet
- Safe Britannia PDFDocument2 pagesSafe Britannia PDFeden4872No ratings yet
- Living in IT Era OutputDocument6 pagesLiving in IT Era OutputDanica Rose SaludarNo ratings yet
- Chap6 Part1Document15 pagesChap6 Part1Francis Renjade Oafallas VinuyaNo ratings yet
- Mae (256F) - HW3 PDFDocument2 pagesMae (256F) - HW3 PDFClaireNo ratings yet
- FFT SlidesDocument11 pagesFFT Slidessafu_117No ratings yet
- Judges Kings ProphetsDocument60 pagesJudges Kings ProphetsKim John BolardeNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Demand ForecastingDocument6 pagesTechniques of Demand Forecastingrealguy789No ratings yet
- Does Social Media Influence Consumer Buying Behavior An Investigation of Recommendations and PurchasesDocument7 pagesDoes Social Media Influence Consumer Buying Behavior An Investigation of Recommendations and Purchasesyash_28No ratings yet
- Appendix I - Plant TissuesDocument24 pagesAppendix I - Plant TissuesAmeera ChaitramNo ratings yet
- Economis Project-MCOM SEM 1Document19 pagesEconomis Project-MCOM SEM 1Salma KhorakiwalaNo ratings yet
- 1907 EMarketer GEN XDocument16 pages1907 EMarketer GEN XRodolfo CampaNo ratings yet
- Byron and The Bulgarian Revival Period - Vitana KostadinovaDocument7 pagesByron and The Bulgarian Revival Period - Vitana KostadinovavitanaNo ratings yet