Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assessing Educators' Digital Competence
Uploaded by
Nina Bitskinashvili0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pagesOriginal Title
digcompedu_leaflet_final.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
44 views2 pagesAssessing Educators' Digital Competence
Uploaded by
Nina BitskinashviliCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
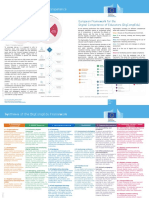
Assessing Educators' Digital Competence
To encourage take-up, it is proposed to refer to
proficiency levels using motivating role descriptors.
Enthusiasts (B1) experiment with digital tools for a
range of purposes, trying to understand which digital Proposal for a European Framework for the
These can, however, be mapped onto the proficiency strategies work best in which contexts.
levels used by the Common European Framework of
Professionals (B2) use a range of digital tools Digital Competence of Educators (DigCompEdu)
Reference for Languages (CEFR), ranging from A1
confidently, creatively and critically to enhance their
(Newcomer) to C2 (Pioneer). In general, the following March 2017
professional activities. They continuously expand their
characterisations apply:
repertoire of practices.
Newcomers (A1) have had very little contact with digital As the teaching professions face rapidly changing DigCompEdu considers six different competences
Experts (C1) rely on a broad repertoire of flexible,
tools and need guidance to expand their repertoire. demands, educators require an increasingly broad areas with a total of 23 competences.
comprehensive and effective digital strategies. They are
Explorers (A2) have started using digital tools without, a source of inspiration for others. set of competences. In particular the ubiquity of Area 1 focuses on the professional environment;
however, following a comprehensive or consistent digital devices and the duty to help students
Pioneers (C2) question the adequacy of contemporary become digitally competent requires educators to Area 2 on sourcing, creating and sharing digital
approach. Explorers need insight and inspiration to
digital and pedagogical practices, of which they resources;
expand their competences. develop their own digital competence.
themselves are experts. They lead innovation and are a
role model for younger teachers. The DigCompEdu framework aims to capture these Area 3 on managing and orchestrating the use of
educator-specific digital competences. digital tools in teaching and learning;
The framework is directed towards educators at all Area 4 on digital tools and strategies to enhance
levels of education, from early childhood to higher assessment;
and adult education, including general and Area 5 on the use of digital tools to empower
vocational training, special needs education, and learners;
non-formal learning contexts. It aims to provide a
general reference frame for developers of Digital Area 6 on facilitating learners' digital competence.
Competence models, i.e. Member States, regional Areas 2 to 5 form the pedagogic core of the
governments, national and regional agencies, framework. They detail the competences educators
educational organisations themselves, and public or need to possess to foster effective, inclusive and
private professional training providers. innovative learning strategies, using digital tools.
Figure 3: Key words used in the proficiency progression
Online Stakeholder consultation
From March to May 2017 all stakeholders and interested parties are invited to contribute to refining the
framework: https://ec.europa.eu/eusurvey/runner/DigCompEduConsultation
and its accompanying self-assessment questionnaire:
https://ec.europa.eu/eusurvey/runner/DigCompEduSAQ
For more information, please contact:
Yves.Punie@ec.europa.eu
Christine.Redecker@ec.europa.eu
https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/digcompedu
Figure 1: Overview of the DigCompEdu framework
Synthesis of the DigCompEdu Proposal
Figure 2: Synthesis of the DigCompEdu competence descriptors
6. Facilitating Learners' Digital
1. Professional engagement 2. Digital Resources 3. Digital Pedagogy 4. Digital Assessment 5. Empowering Learners
Competence
6.1 Information and media
3.1 Instruction 5.1 Accessibility and inclusion
literacy
1.1 Data management To implement digital devices and To ensure accessibility to learning
To incorporate learning activities,
To use digital tools to effectively resources into the teaching resources and activities, for all
2.1 Selecting digital resources 4.1 Assessment formats assignments and assessments which
and safely store, retrieve, analyse process, so as to enhance the learners, including those with
To identify, assess and select digital To use digital tools for formative require learners to articulate
and share administrative and effectiveness of instructional special needs. To consider and
resources for teaching and and summative assessment. To information needs; to find
student-related data. To contribute practices. To appropriately scaffold, respond to learners' (digital)
learning, understanding applicable enhance the diversity and information and resources in digital
to discussing and critically manage and orchestrate digital expectations, abilities, uses and
copyright and accessibility suitability of assessment formats environments; to organise, process,
reflecting on data management teaching interventions. To misconceptions, as well as
requirements. and approaches. analyse and interpret information;
strategies and policies at the experiment with and develop new contextual, physical or cognitive
and to compare and critically
organisational level. formats and pedagogical methods constraints to their use of digital
evaluate the credibility and reliability
for instruction. tools.
of information and their sources.
2.2 Organising, sharing and
publishing digital resources
3.2 Teacher-learner interaction 5.2 Differentiation and
1.2 Organisational To organise digital resources for
To use digital tools and services to personalisation
communication one's own current and future use 6.2 Digital communication &
enhance the interaction with To use digital tools to address
To use digital technologies to and re-use, as well as for sharing 4.2 Analysing evidence collaboration
learners, individually and learners diverse learning needs,
enhance organisational them with others. To digitally To generate, select, critically To incorporate learning activities,
collectively, within and outside the e.g. by allowing them to follow
communication with learners, publish learning resources and analyse and interpret digital assignments and assessments which
learning session. To use digital different learning pathways and
parents and third parties. To share them with learners, parents evidence on learner activity, require learners to effectively and
technologies to offer timely and goals, by offering alternative
contribute to collaboratively and other educators, respecting the performance and progress, in view responsibly use digital tools for
targeted guidance and assistance. approaches and tools, and allowing
developing and improving rules of copyright. To understand of informing teaching and learning. communication, collaboration and
To experiment with and develop learners to proceed at different
organisational communication the use and creation of open civic participation.
new forms and formats for offering speeds towards individual learning
strategies. licences and open educational
guidance and support. goals.
resources, including their proper
attribution.
2.3 Creating and modifying 4.3 Feedback and Planning
1.3 Professional collaboration digital resources To use digital tools to provide 6.3 Digital content creation
To use digital technologies to To modify and build on existing 3.3 Learner collaboration targeted and timely feedback to To incorporate assignments and
engage in collaboration with other openly licensed resources and other To use digital technologies to foster learners. To adapt teaching learning activities which require
educators, sharing and exchanging resources where this is permitted. and enhance collaborative learning strategies accordingly and to 5.3 Actively engaging learners learners to express themselves
knowledge and experience and To create or co-create new digital strategies, e.g. as a basis for the provide targeted support, based on To use digital tools to foster through digital means, and to modify
collaboratively innovating educational resources. To consider collaborative exchange in the the evidence generated by the learners' active and creative and create digital content in different
pedagogic practices. To use the specific learning objective, group, as a tool for conducting a digital tools used. To enable engagement with a subject matter. formats. To teach learners how
professional collaborative networks context, pedagogical approach, and collaborative assignment, or as a learners and parents to understand copyright and licences apply to digital
as a source for one's own learner group, when designing means of presenting results. the evidence provided by digital content, how to reference sources
professional development. digital resources and planning their tools and use it for decision- and attribute licenses.
use. making.
6.4. Wellbeing
3.4 Self-directed learning
To take measures to ensure learners'
To use digital technologies to
physical, psychological and social
1.4 Reflective practice support self-directed learning
well-being while using digital
To individually reflect on, critically processes, i.e. to enable learners to
technologies. To empower learners to
assess and actively develop one's plan, monitor and reflect on their
manage risks and make use of digital
digital pedagogical practice. own learning, evidence progress,
technologies to support their own
share insights and come up with
social, psychological and physical
creative solutions.
wellbeing.
6.5 Digital problem solving
1.5 Digital Continuous
To incorporate learning and
Professional Development
assessment activities which require
(CPD)
learners to identify and solve
To use digital sources and
technical problems or to transfer
resources for continuous
technological knowledge creatively to
professional development.
new situations.
You might also like
- Digcompedu Leaflet En-2017!10!09Document2 pagesDigcompedu Leaflet En-2017!10!09angieNo ratings yet
- European Framework For The Digital Competence of Educators (Digcompedu)Document2 pagesEuropean Framework For The Digital Competence of Educators (Digcompedu)Catalin TurcuNo ratings yet
- Dccs Newsletter No 2 - enDocument4 pagesDccs Newsletter No 2 - enapi-457427318No ratings yet
- CPD Plan TemplateDocument6 pagesCPD Plan TemplateGia KhanhNo ratings yet
- LD Upskilling of SHS Teachers of Empowering Technology and Media Information Literacy RepairedDocument15 pagesLD Upskilling of SHS Teachers of Empowering Technology and Media Information Literacy RepairedChris Marlowe YambaoNo ratings yet
- Educ 6Document9 pagesEduc 6Regine QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Technology For Teaching and Learning KissieDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Technology For Teaching and Learning KissieAndrew C. BrazaNo ratings yet
- ICT Competency Standards For Philippine Pre-Service Teacher EducationDocument8 pagesICT Competency Standards For Philippine Pre-Service Teacher EducationDominique TacangNo ratings yet
- Handouts Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument3 pagesHandouts Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningKhemme Lapor Chu Ubial100% (3)
- Computing Curriculum Class 5 - Part ADocument11 pagesComputing Curriculum Class 5 - Part Ashazea shafiqNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Ed 107 Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument14 pagesReviewer in Ed 107 Technology For Teaching and LearningJesille May Hidalgo Bañez100% (1)
- Part Iv: Development Plans: 1.Kindergarten-Janice G. ParedesDocument7 pagesPart Iv: Development Plans: 1.Kindergarten-Janice G. ParedesRodnel MonceraNo ratings yet
- Educational Media and Technology: Faculty of EducationDocument7 pagesEducational Media and Technology: Faculty of EducationDS SEUTLOADINo ratings yet
- Reviewer Ed107Document16 pagesReviewer Ed107Margareth De VillaNo ratings yet
- New LD Proposal Template EditableDocument16 pagesNew LD Proposal Template Editableneilmarc tomas100% (1)
- 061Paper-S - Stefanova Application of Trialogical DesignDocument5 pages061Paper-S - Stefanova Application of Trialogical DesignAizeeNo ratings yet
- TTL 2 NotesDocument8 pagesTTL 2 Noteskristelannantong3No ratings yet
- Research Proposal1Document16 pagesResearch Proposal1Lovely Grace Dasig ArconNo ratings yet
- Digital Higher Education in The EU: Christine Redecker, PH.DDocument28 pagesDigital Higher Education in The EU: Christine Redecker, PH.DAdelina SilvaNo ratings yet
- Activity Lesson 1Document3 pagesActivity Lesson 1RAIZEN LANIPA OBODNo ratings yet
- G12 E Tech - SyllabusDocument10 pagesG12 E Tech - Syllabusvagidiy697No ratings yet
- Running Head: TECHNOLOGY IN WGPCS1Document19 pagesRunning Head: TECHNOLOGY IN WGPCS1api-569408899No ratings yet
- TTL Module 2 1Document31 pagesTTL Module 2 1Je Ann CandelarioNo ratings yet
- The Indicators For The Research-1Document6 pagesThe Indicators For The Research-1SYIFA FADHILAH HAMIDNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1Wowie MarianoNo ratings yet
- ttl1 MidtermDocument62 pagesttl1 MidtermJo Michael Flores Agarma100% (1)
- TTL ReviewerDocument3 pagesTTL ReviewerAeverly V. QuetuaNo ratings yet
- Digital Literacy: Lesson Plan On Social Media Unit OverviewDocument13 pagesDigital Literacy: Lesson Plan On Social Media Unit OverviewEsplana Martinez Mae AngelNo ratings yet
- Emerging Trends in 21st Century EducationDocument70 pagesEmerging Trends in 21st Century EducationLiezl Valiente100% (2)
- Ict Teacher Prof Dev Prog Course Outline April 2019Document28 pagesIct Teacher Prof Dev Prog Course Outline April 2019api-464043271No ratings yet
- Developing Physics Digital Literacy Skill Diagnostic Test Assisted by Google Form For Senior High School StudentsDocument7 pagesDeveloping Physics Digital Literacy Skill Diagnostic Test Assisted by Google Form For Senior High School StudentsA SNo ratings yet
- ACCO 018 - Business Management Accounting - BSBAMM 2 2Document9 pagesACCO 018 - Business Management Accounting - BSBAMM 2 2easiroy23No ratings yet
- Milestone AccomplishmentDocument2 pagesMilestone AccomplishmenthendrixNo ratings yet
- Sde Icts 2017Document13 pagesSde Icts 2017Syed Rahmath AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Technology For Teaching and LearningDocument3 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction To Technology For Teaching and Learninglisa75% (4)
- WhatDocument5 pagesWhatrachelle& allaineNo ratings yet
- Cipres ProposalDocument22 pagesCipres ProposalLouie GerenteNo ratings yet
- Euro J of Education - 2019 - Caena - Aligning Teacher Competence Frameworks To 21st Century Challenges The Case For TheDocument14 pagesEuro J of Education - 2019 - Caena - Aligning Teacher Competence Frameworks To 21st Century Challenges The Case For TheMillet SantosNo ratings yet
- EDUC206-MODULES ReviewerDocument48 pagesEDUC206-MODULES ReviewerIvy Novero SibuloNo ratings yet
- TTL KleinDocument2 pagesTTL KleinKleinNo ratings yet
- Ed 207 - TTL 1 Unit 4Document12 pagesEd 207 - TTL 1 Unit 4kimpeterjohnlebunaNo ratings yet
- Edu 20231203 14Document6 pagesEdu 20231203 14annisah nainggolanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Teachnology and LearningDocument62 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Teachnology and LearningAngela MarcosNo ratings yet
- University Teachers Digital CompetenceDocument18 pagesUniversity Teachers Digital CompetenceDeyanira ChavezNo ratings yet
- UNIT I: Teaching and Learning With Technology - An IntroductionDocument3 pagesUNIT I: Teaching and Learning With Technology - An IntroductionJhon Carlo DelmonteNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1Document10 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1Angela Rose BanastasNo ratings yet
- 2.01 EAEC - PPT - ERASMUS+ Overview-Makrides PDFDocument85 pages2.01 EAEC - PPT - ERASMUS+ Overview-Makrides PDFtishamadalinaNo ratings yet
- J Mateo Presentation - DepED ICT Competency Standards PDFDocument8 pagesJ Mateo Presentation - DepED ICT Competency Standards PDFRafael LavillaNo ratings yet
- MarcoProFuturo Resumen-Ejecutivo ENG-onlineDocument24 pagesMarcoProFuturo Resumen-Ejecutivo ENG-onlineSimón VelandiaNo ratings yet
- Training On The Use of Teaching Technology in Online Setting Class I. Proposal Brief II. Program Background and RationaleDocument12 pagesTraining On The Use of Teaching Technology in Online Setting Class I. Proposal Brief II. Program Background and RationaleAngelo Aniag UnayNo ratings yet
- ICT Competency Standards (CHED-UNESCO), Policy, Standards and Guidelines (PSG) For Pre-Service Teacher EducationDocument5 pagesICT Competency Standards (CHED-UNESCO), Policy, Standards and Guidelines (PSG) For Pre-Service Teacher EducationPrincess Veah IlaoNo ratings yet
- Learning and Development PackageDocument10 pagesLearning and Development PackageSonny Matias100% (7)
- SC TTL Reviewer MidtermDocument2 pagesSC TTL Reviewer MidtermGenevie ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Esbb3 Seagul 2023Document14 pagesEsbb3 Seagul 2023RODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- Batch 1 STEM Education Master Course For Teachers 2022 - PrimerDocument10 pagesBatch 1 STEM Education Master Course For Teachers 2022 - PrimerJane GanadoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1-Task 1Document5 pagesMODULE 1-Task 1Relan MortaNo ratings yet
- PoliciesDocument20 pagesPoliciesapi-411978564No ratings yet
- Module 1 Technology For Teaching and Learning 1Document12 pagesModule 1 Technology For Teaching and Learning 1Monica Benitez RicoNo ratings yet
- Course Pack Prof Ed. 10 Module 1Document12 pagesCourse Pack Prof Ed. 10 Module 1Ever Shekhaina-XavierNo ratings yet
- Digital Competence in Teacher Education: March 2019Document50 pagesDigital Competence in Teacher Education: March 2019Nina BitskinashviliNo ratings yet
- 2017 - 1024 Common Digital Competence Framework For Teachers PDFDocument83 pages2017 - 1024 Common Digital Competence Framework For Teachers PDFNina BitskinashviliNo ratings yet
- Construct Validation of A Questionnaire To Measure Teachers Digital Competence CDD PDFDocument30 pagesConstruct Validation of A Questionnaire To Measure Teachers Digital Competence CDD PDFNina BitskinashviliNo ratings yet
- Unesco ICT Competency Framework For TeachersDocument66 pagesUnesco ICT Competency Framework For TeachersNina BitskinashviliNo ratings yet
- Design 6 SyllabusDocument2 pagesDesign 6 SyllabusLikhit GrandhiNo ratings yet
- Unit Title: Inquiry: Establishing The Purpose of The UnitDocument3 pagesUnit Title: Inquiry: Establishing The Purpose of The UnitNina BitskinashviliNo ratings yet
- Steps To Planning Your InfographicDocument4 pagesSteps To Planning Your InfographicNina BitskinashviliNo ratings yet
- A Mathematical Question and Answer Revision Booklet ProposalDocument14 pagesA Mathematical Question and Answer Revision Booklet ProposalJob Makori OmbuiNo ratings yet
- Brilliant Study Centre, Pala: 14658 292543 SANA MDocument1 pageBrilliant Study Centre, Pala: 14658 292543 SANA MMINNAH FATHIMANo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesMon Eric LomedaNo ratings yet
- MATH GR9 QTR4-M2 24pagesDocument24 pagesMATH GR9 QTR4-M2 24pageschrxtine hernandoNo ratings yet
- GES 101 General English and Communication Skills-1Document247 pagesGES 101 General English and Communication Skills-1Nwabundo VictoryNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Q4 LT 1Document4 pagesMath 10 Q4 LT 1Samantha agarinNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Portfolio: Course 1Document49 pagesTeacher's Portfolio: Course 1CaidreeNo ratings yet
- Irene Adhiambo-ResumeDocument3 pagesIrene Adhiambo-ResumeNabhan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Vap 2017 MbaDocument36 pagesVap 2017 MbaVasthadu Vasu Kannah DLNo ratings yet
- Communication LettersDocument4 pagesCommunication LetterssyraNo ratings yet
- CATCHUP FRIDAYS - MONITORING Tool - February OnwardsDocument2 pagesCATCHUP FRIDAYS - MONITORING Tool - February OnwardsAnita Fabillar100% (2)
- Schedule - ATAL FDP IIT BHUDocument3 pagesSchedule - ATAL FDP IIT BHUdivya8955No ratings yet
- Activity Proposal 2024 National Womens Month Celebration SY 2022 2023Document9 pagesActivity Proposal 2024 National Womens Month Celebration SY 2022 2023Nimrod Cabrera100% (3)
- Office Performance Commitment and Review Form (Opcrf)Document14 pagesOffice Performance Commitment and Review Form (Opcrf)JEREMIAS SARENO100% (1)
- Chapter 3 PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 3 PDFtanisha ravalNo ratings yet
- Sample of Recomondation LetterDocument4 pagesSample of Recomondation LetterAtiqullah sherzadNo ratings yet
- CITY STAR March 2024 EditionDocument16 pagesCITY STAR March 2024 Editioncitystar newsNo ratings yet
- Unofficial TranscriptDocument6 pagesUnofficial Transcriptapi-337689519No ratings yet
- Q4 Week 1 Math 7Document4 pagesQ4 Week 1 Math 7Meralyn Puaque BustamanteNo ratings yet
- 2 Scrub 1 CircuDocument3 pages2 Scrub 1 CircuKatrina CaveNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and Employability Skills Training - Day IDocument37 pagesEntrepreneurship and Employability Skills Training - Day IAhmed Adem100% (1)
- E Tills Slides 16Document29 pagesE Tills Slides 16Johanna Steffie Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Resume A4 Ver 1Document1 pageResume A4 Ver 1api-515415242No ratings yet
- RT Ntegrated Earning: VerviewDocument42 pagesRT Ntegrated Earning: VerviewMukesh MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Final Programme InvitationDocument6 pagesFinal Programme InvitationYatharth KohliNo ratings yet
- Happy Campers Level 5 TE Unit2Document9 pagesHappy Campers Level 5 TE Unit2fernando sanchezNo ratings yet
- Muslim University of MorogoroDocument3 pagesMuslim University of MorogorosaidimtolaNo ratings yet
- Tibagan High School Supreme Student Government Brigada Eskwela Narrative ReportDocument8 pagesTibagan High School Supreme Student Government Brigada Eskwela Narrative ReportBeejay Taguinod100% (1)
- Swim.: Learning Center Use of English Partial Evaluation Level: Jb4 / Ab4 Teacher's Name: José David Rodríguez TarangoDocument6 pagesSwim.: Learning Center Use of English Partial Evaluation Level: Jb4 / Ab4 Teacher's Name: José David Rodríguez TarangoEdgar GallardoNo ratings yet
- Abdul Rahman Nani CVDocument5 pagesAbdul Rahman Nani CVKelvin NanyNo ratings yet