Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paf-Kiet: Project Proposal
Uploaded by
talha khanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Paf-Kiet: Project Proposal
Uploaded by
talha khanCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Proposal
PAF-KIET
MAIN CAMPUS KARACHI
Computing & Information Sciences Department
Course: Data Communication and Networks
Course Code: NW301
Term: FALL 2020
Program: BS (CS)
Project Title:
C E L LULAR N E TWO R K S
Group Members:
T A L HA KHAN 9651
U S AMA R E HMA N 9894
N O UMA N A L I 9964
(Name) (Student. ID.)
Submission Date
1 5 / 0 9 / 2 0
(Date: DD/MM/YY)
Submitted To:
Dr. Maaz Bin Ahmed
(Course Instructor)
Signature: ________________ Max Marks: _____ Marks Obtained: ___
Project Proposal
Defination:
A cellular network or mobile network is a communication network where the
last link is wireless. The network is distributed over land areas called "cells",
each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, but more normally,
three cell sites or base transceiver stations.
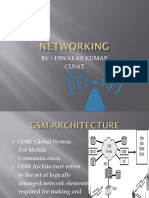
Basic cellular network Archeitecture:
An overall cellular network contains a number of different elements from the
base transceiver station (BTS) itself with its antenna back through a base
station controller (BSC), and a mobile switching centre (MSC) to the location
registers (HLR and VLR) and the link to the public switched telephone
network (PSTN). These all elements are discussed shortly below:-
1. Base transceiver station, BTS:
The base transceiver station or system, BTS consists of a number of different
elements. The first is the electronics section normally located in a container at
the base of the antenna tower. This contains the electronics for
communicating with the mobile handsets and includes radio frequency
amplifiers, radio transceivers, radio frequency combiners, control,
communication links to the BSC, and power supplies with back up.
2. Mobile switching centre (MSC)
The MSC is the control centre for the cellular system, coordinating the actions
of the BSCs, providing overall control, and acting as the switch and
connection into the public telephone network. In view of the importance of
the MSC, it contains many backup and duplicate circuits to ensure that it does
not fail. Obviously backup power systems are an essential element of this to
guard against the possibility of a major power failure, because if the MSC
became inoperative then the whole network would collapse.
Key cellular communications concepts
As the name indicates, cellular telecommunications technology is based
around the concept of using a large number of base stations each covering a
small area or cell. With each base station communicating with a reasonable
number of users, it means that the whole system can accommodate a huge
number of connections, and the levels of frequency use are good.
A cellular communications system has a number of different areas, each of
which performs a different function. The main areas detailed below are the
main ones that are normally referred to when discussing cellular
communications systems. Each of these areas can often be split much further
into different entities.
Project Proposal
Mobile handset or user equipment, UE: The user equipment or
mobile phone is the element of a mobile communications system that the
user sees. It connects to the network and enables the user to access voice
and data services. The user equipment could also be a dongle used for
accessing data on a laptop, or it could also be a modem on another form of
device – for example cellular communications is starting to be used for
Internet of Things, IoT applications and as a result it could be attached to a
smart meter to automatically send meter readings or it could be used for
any one of a host of other applications.
Radio access network, RAN: The radio access network is at the
periphery of the cellular communications system. It provides the link to the
user equipment from the cellular network. It comprises a number of
elements and broadly includes the base station and base station controller.
With cellular communications technology advancing, the terms used and
exactly what they contain is changing, but their basic function remains
essentially the same.
Core network: The core network is the hub of the cellular
communications system. It manages the overall system as well as storing
user data, manages access control, links to the external world and provides
a host of other functions.
HandOff Process in a Cellular Networks:
The process of handoff is used when users moves from cell to cell. A well
planned cell clusters will have a seamless handoff, this is experienced when
traffic is transferred from one BS to another without experiencing a distortion
in call or data transmission process. There are 2 types of handoff as shown in
the figure below namely:
1. Soft Handoff
2. Hard Handoff
Project Proposal
Figures and Diagrams:
Project Proposal
You might also like
- Seminar On Mobile ComputingDocument7 pagesSeminar On Mobile ComputingJack RatanNo ratings yet
- Welcome Home (Sanitarium) (guitarTAB)Document4 pagesWelcome Home (Sanitarium) (guitarTAB)parisfrance89No ratings yet
- Final SRSDocument23 pagesFinal SRSArsalan Ashraf50% (4)
- LM3915Document25 pagesLM3915Ashfak PathanNo ratings yet
- Ventures ArcadeDocument6 pagesVentures ArcadeYeimmy LemusNo ratings yet
- Mobile Communication ComputingDocument11 pagesMobile Communication ComputingvenkateshmukharjiNo ratings yet
- Psna College of Engineering and Technology Dindigul-624 622Document13 pagesPsna College of Engineering and Technology Dindigul-624 622Kíshor VfçNo ratings yet
- Internship Report in PTCL, WLL DepartmentDocument34 pagesInternship Report in PTCL, WLL Departmentansari_86No ratings yet
- Wireless Network Communication: Radiofrequency - Spectrum and BandDocument12 pagesWireless Network Communication: Radiofrequency - Spectrum and BandVamsi KalNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Unit 1 PDFDocument22 pagesMobile Computing Unit 1 PDFVani BaskaranNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Concept of MobileDocument20 pagesEvolution and Concept of Mobilemahfuz.jkkniu13No ratings yet
- LoluDocument10 pagesLoluSunilNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing - Past, Present and FutureDocument17 pagesMobile Computing - Past, Present and FutureApeksha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2Document45 pagesChapter - 2Niharica SohalNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Informatics Department of Information TechnologyDocument8 pagesFaculty of Informatics Department of Information TechnologyyonasNo ratings yet
- Mobile Wireless ComputingDocument10 pagesMobile Wireless ComputingBridget SmithNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing: Sixth Semester Diploma Examination in Engineering/Technology-MARCH, 2014Document17 pagesMobile Computing: Sixth Semester Diploma Examination in Engineering/Technology-MARCH, 2014Midhun CMNo ratings yet
- Wireless and MobileDocument11 pagesWireless and MobilevenkateshmukharjiNo ratings yet
- Human - Computer Interaction ComputerDocument18 pagesHuman - Computer Interaction ComputerVipul VeramNo ratings yet
- WCC VTU Module 2 NotesDocument10 pagesWCC VTU Module 2 NotesSushíl kanikeNo ratings yet
- Mobile COMPUTING NotesDocument50 pagesMobile COMPUTING NotesArchana KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Networks: Past, Present, and Future: Lourens O Walters PS KritzingerDocument15 pagesCellular Networks: Past, Present, and Future: Lourens O Walters PS Kritzingerbenjamin bosireNo ratings yet
- Rahu FinalDocument14 pagesRahu FinalkirankumarikanchanNo ratings yet
- Mobile Wireless ComputingDocument9 pagesMobile Wireless Computinganon_99391795No ratings yet
- Getting To Know Wireless Networks and TechnologyDocument13 pagesGetting To Know Wireless Networks and TechnologyBijay SinghNo ratings yet
- A Presentation byDocument15 pagesA Presentation bymeenonNo ratings yet
- Cellular TechnologyDocument21 pagesCellular TechnologyjolieprincesseishimweNo ratings yet
- Mobile ComputingDocument20 pagesMobile ComputingMohammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- A Presentation By: U.Ajay KumarDocument14 pagesA Presentation By: U.Ajay Kumarapi-19799369No ratings yet
- Cell To Switch AssinmentDocument25 pagesCell To Switch AssinmentBedadipta BainNo ratings yet
- ElysiumDocument61 pagesElysiumRama SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Evolutionary Analysis of GSM, UMTS and LTE Mobile Network ArchitecturesDocument13 pagesEvolutionary Analysis of GSM, UMTS and LTE Mobile Network ArchitecturesConstructif La CritiqueNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Basic Cellular SystemDocument14 pagesUnit-1 Basic Cellular SystemBhuvan VarmaNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemDocument9 pagesCommunication SystemNouman BajwaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsDocument25 pagesLecture 2. Telephone System InstallationsOpilaStephen100% (1)
- B.Swetha: Vignan'S Engineering CollegeDocument15 pagesB.Swetha: Vignan'S Engineering CollegeBridget SmithNo ratings yet
- Bahra University: Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument7 pagesBahra University: Global System For Mobile Communicationajay palsraNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Wireless and Mobile CommunicationDocument24 pagesUnit 1 Wireless and Mobile Communicationshantanupal229No ratings yet
- An Efficient Call Admission Control Scheme For Handling Handoffs in Wireless Mobile NetworksDocument18 pagesAn Efficient Call Admission Control Scheme For Handling Handoffs in Wireless Mobile NetworksijansjournalNo ratings yet
- By - Diwakar Kumar CusatDocument43 pagesBy - Diwakar Kumar CusatDIWAKAR KUMARNo ratings yet
- Department of Computer ScienceDocument7 pagesDepartment of Computer ScienceBESUFEKAD TABORNo ratings yet
- MOB1Document16 pagesMOB1Paterson NguepiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document21 pagesModule 1Shamna100% (1)
- CARLL NETflix ReviewerDocument6 pagesCARLL NETflix ReviewerCarllNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 2021Document26 pagesLec 2 2021Al7asanAmmarNo ratings yet
- P1.L01 1 (61s) Mobile Telecommunication Infrastructures 20131029Document61 pagesP1.L01 1 (61s) Mobile Telecommunication Infrastructures 20131029Bùi Văn TúNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 2Document9 pagesComputer Networks 2eshanpadhiar3No ratings yet
- GSM Cell Site ForensicsDocument15 pagesGSM Cell Site ForensicsAkinpelu OluyemiNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Mobile ComputingDocument23 pagesUNIT-1 Mobile ComputingShobhit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ids Unit 1Document24 pagesIds Unit 1aswinhacker28No ratings yet
- WCN Open Ended Experiment-1Document6 pagesWCN Open Ended Experiment-14025 Kamalika DuttaNo ratings yet
- Hijack & DoS GSMDocument17 pagesHijack & DoS GSMResearch Guy100% (1)
- Ad Hoc and Wireless Sensor Networks: Faculty: R.RajaganapathiDocument318 pagesAd Hoc and Wireless Sensor Networks: Faculty: R.RajaganapathiRajaganapathi RajappanNo ratings yet
- Review Wireless and Global System For Mobile Communication System Through Wireless NetworkDocument6 pagesReview Wireless and Global System For Mobile Communication System Through Wireless NetworkInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- IOSR JournalsDocument8 pagesIOSR JournalsInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- WC Unit 2Document38 pagesWC Unit 2shashi176597No ratings yet
- Lab Manual: IT-602 Wireless & Mobile ComputingDocument19 pagesLab Manual: IT-602 Wireless & Mobile ComputingSanjay kurmiNo ratings yet
- Paf-Kiet: Project ProposalDocument4 pagesPaf-Kiet: Project Proposaltalha khanNo ratings yet
- Lab 04 - EEDDocument10 pagesLab 04 - EEDAhmad MusabNo ratings yet
- Presentation byDocument15 pagesPresentation byapi-19799369No ratings yet
- UMTSDocument4 pagesUMTSalzahradakirNo ratings yet
- Simulation & Performance Study of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Using MATLABDocument8 pagesSimulation & Performance Study of Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Using MATLABescanusNo ratings yet
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesFrom EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Federal Investigation Agency RECRUITMENT PHASE II Arish-1Document1 pageFederal Investigation Agency RECRUITMENT PHASE II Arish-1talha khanNo ratings yet
- Applicant Information : Application FormDocument3 pagesApplicant Information : Application Formtalha khanNo ratings yet
- Order ReceiptDocument2 pagesOrder Receipttalha khanNo ratings yet
- From Containers To Kubernetes With NodejsDocument255 pagesFrom Containers To Kubernetes With NodejsOscar Daza100% (1)
- Advertisement InterneesDocument1 pageAdvertisement Interneestalha khanNo ratings yet
- Welcome LetterDocument1 pageWelcome Lettertalha khanNo ratings yet
- LinkedIn Generated ResumeDocument1 pageLinkedIn Generated Resumetalha khanNo ratings yet
- LinkedIn Generated ResumeDocument1 pageLinkedIn Generated Resumetalha khanNo ratings yet
- CS607 Handouts 1 45 PDFDocument208 pagesCS607 Handouts 1 45 PDFFazle Hannan100% (1)
- SolutionDocument247 pagesSolutiontalha khanNo ratings yet
- Talha's ResumeDocument1 pageTalha's Resumetalha khanNo ratings yet
- Talha's ResumeDocument1 pageTalha's Resumetalha khanNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Television Corporation: Proforma For One Year Paid Internship Photograph (Paste Here)Document2 pagesPakistan Television Corporation: Proforma For One Year Paid Internship Photograph (Paste Here)SyedMohiuddinZiaNo ratings yet
- Arish Khan ResumeDocument1 pageArish Khan Resumetalha khanNo ratings yet
- Talha Khan - 9651 - DCN Final ExamDocument19 pagesTalha Khan - 9651 - DCN Final Examtalha khanNo ratings yet
- Sunnah 51Document22 pagesSunnah 51nasir hussainNo ratings yet
- Anum Anum 1Document3 pagesAnum Anum 1talha khanNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument4 pagesCourse Outlinetalha khanNo ratings yet
- Huda ResumeDocument1 pageHuda Resumetalha khanNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Organizational Work Conditions On Employee Job Satisfaction Evidence From The Ethiopian Airline IndustryDocument7 pagesFactors Affecting Organizational Work Conditions On Employee Job Satisfaction Evidence From The Ethiopian Airline IndustryEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Class Activity - PDF (19 Feb, 2021)Document2 pagesClass Activity - PDF (19 Feb, 2021)talha khanNo ratings yet
- National Computer Education Accreditation Council Nceac: Course Descritption FormDocument5 pagesNational Computer Education Accreditation Council Nceac: Course Descritption Formtalha khanNo ratings yet
- College of Computing and Information Sciences Final Assessment Spring 2020 SemesterDocument27 pagesCollege of Computing and Information Sciences Final Assessment Spring 2020 Semestertalha khanNo ratings yet
- College of Computing and Information Sciences: Mid-Term Assessment Fall 2020 SemesterDocument15 pagesCollege of Computing and Information Sciences: Mid-Term Assessment Fall 2020 Semestertalha khanNo ratings yet
- Paf-Kiet: Project ProposalDocument4 pagesPaf-Kiet: Project Proposaltalha khanNo ratings yet
- Cellular NetworksDocument60 pagesCellular NetworksT FNo ratings yet
- Cellularnetworks 111214093801 Phpapp01Document20 pagesCellularnetworks 111214093801 Phpapp01talha khanNo ratings yet
- Handouts - Data CommDocument244 pagesHandouts - Data CommsaqibcapNo ratings yet
- Talha Khan - 9651 - DCN Final ExamDocument19 pagesTalha Khan - 9651 - DCN Final Examtalha khanNo ratings yet
- Cath Penales Power PointDocument12 pagesCath Penales Power PointjhokenNo ratings yet
- 1.2-Current Differential Relay (RED670)Document32 pages1.2-Current Differential Relay (RED670)JenniferKujanpaa100% (2)
- Triton-Ocean Bottom Seismometer-001Document2 pagesTriton-Ocean Bottom Seismometer-001Furio RuggieroNo ratings yet
- Hopscotch 6 End-Of-Term 1 TestDocument4 pagesHopscotch 6 End-Of-Term 1 Testoradu1395100% (1)
- Most Frequently Cited Books 1970-2014 - Ap LiteratureDocument2 pagesMost Frequently Cited Books 1970-2014 - Ap Literatureapi-311325550No ratings yet
- Mozart and The Guises of Love Author(s) : Hamish Swanston Source: New Blackfriars, May 1991, Vol. 72, No. 849 (May 1991), Pp. 222-230 Published By: WileyDocument10 pagesMozart and The Guises of Love Author(s) : Hamish Swanston Source: New Blackfriars, May 1991, Vol. 72, No. 849 (May 1991), Pp. 222-230 Published By: WileyAndrew BurgmayerNo ratings yet
- Blues BrosDocument14 pagesBlues Brossandrovergara100% (4)
- FTTH Manual Huawei PDFDocument84 pagesFTTH Manual Huawei PDFSatish VermaNo ratings yet
- Realizing Lucier and Stockhausen: Case Studies in Electroacoustic Performance PracticeDocument4 pagesRealizing Lucier and Stockhausen: Case Studies in Electroacoustic Performance PracticescrewscribbedNo ratings yet
- Vocal Jazz SyllabusDocument3 pagesVocal Jazz Syllabusapi-26548742350% (2)
- Optische Uebertragungstechnik Englisch - WebversionDocument68 pagesOptische Uebertragungstechnik Englisch - WebversionLaboriosaNo ratings yet
- Chanakya NeetiDocument27 pagesChanakya NeetiDeepayancNo ratings yet
- Houghton Mifflin Harcourt 2014-2015 Culinary CatalogDocument112 pagesHoughton Mifflin Harcourt 2014-2015 Culinary CatalogHoughton Mifflin Harcourt67% (3)
- Music Vocabulary in Mandarin With English Translations: GeneralDocument6 pagesMusic Vocabulary in Mandarin With English Translations: GeneralrinaselviaNo ratings yet
- Qualcomm Bluetooth Mesh Product Brief 87 Ce928 1Document2 pagesQualcomm Bluetooth Mesh Product Brief 87 Ce928 1Maman BudimanNo ratings yet
- Korea Group 1: Free PPT TemplatesDocument28 pagesKorea Group 1: Free PPT TemplatesKryz ElaizaNo ratings yet
- Clarinet Institute Kuhl Op103Document38 pagesClarinet Institute Kuhl Op103Georgiana MihăilăNo ratings yet
- Studies of Flatness of Lifi Channel For Ieee 802.11BbDocument6 pagesStudies of Flatness of Lifi Channel For Ieee 802.11BbedgarNo ratings yet
- Digital Selective CallingDocument8 pagesDigital Selective CallingAbdel Nasser Al-sheikh Yousef100% (1)
- GD Satcom 3.7M Assembly Manual 4096-225Document32 pagesGD Satcom 3.7M Assembly Manual 4096-225jrdmaNo ratings yet
- Sample Midterm Examination: Ae2 WritingDocument3 pagesSample Midterm Examination: Ae2 WritingYen Tho NguyenNo ratings yet
- FAGERHULT Ljusreglering UKDocument10 pagesFAGERHULT Ljusreglering UKlehongtanNo ratings yet
- Hearing Tsur's "Poetic Mode" The Text Music Relationship From Monody To BjörkDocument191 pagesHearing Tsur's "Poetic Mode" The Text Music Relationship From Monody To BjörkLisa RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Everything We Have Been Afraid To Ask About Amfiteater PDFDocument10 pagesEverything We Have Been Afraid To Ask About Amfiteater PDFtomqzNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Digital MultimeterDocument19 pagesHow To Use A Digital MultimeterSankalp BagwaleNo ratings yet
- Dango Daikazoku Violin Version 1 PDFDocument1 pageDango Daikazoku Violin Version 1 PDFLetty RuedaNo ratings yet