Professional Documents
Culture Documents
12rfbhnnn PDF
Uploaded by
Kelli FloresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
12rfbhnnn PDF
Uploaded by
Kelli FloresCopyright:
Available Formats
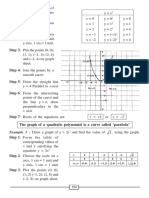
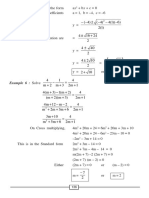
Method II : x 0 1 –1 2 –2
Step 1: Form the table of y –2 –2 0 0 4
corresponding values of (x, y) (0, –2) (1, –2) (–1, 0) (2, 0) (–2, 4)
x and y satisfying
equation y = x2 – x – 2.
Step 2: Choose the scale on x
axis 1 cm = 1 unit and
y axis 1 cm = 1 unit.
Step 3: Plot the points (0, –2);
(1 –2); (–1, 0); (2, 0)
and (–2, 4) on the graph
sheet.
Step 4: Join the points to form
a smooth curve
Step 5: Mark the intersecting
points of the curve and
the x – axis.
Step 6: Roots of the equations are x = –1 or x = 2
Exercise : 5.9
A. 1) Draw the graph of y = x2 and find the value of 7
2) Draw the graph of y = 2x2 and find the value of 3
1 2
3) Draw the graph of y = x and find the value of 10
2
B. 1) Draw the graph of y = x2 and y = 2x + 3 and hence solve the equation
x2 – 2x – 3 = 0
2) Draw the graph of y = 2x2 and y = 3 – x and hence solve the equation
2x2 + x – 3 = 0
3) Draw the graph of y = 2x2 and y = 3 + x and hence solve the equation
2x2 – x – 3 = 0
C. Solve graphically
1) x2 + x – 12 = 0 2) x2 – 5x + 6 = 0 3) x2 + 2x – 8 = 0
4) x2 + x – 6 = 0 5) 2x2 – 3x – 5 = 0 6) 2x2 + 3x – 5 = 0
157
You might also like
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- X 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xDocument4 pagesX 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- X 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xDocument4 pagesX 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- X 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xDocument4 pagesX 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Exercise: 5.8 A. Form The Equation Whose Roots AreDocument5 pagesExercise: 5.8 A. Form The Equation Whose Roots AreKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- X 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xDocument4 pagesX 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- X 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xDocument4 pagesX 0 X 1 X 2 X - 1 X Axis, 1 CM 1 Unit: Example 1: Draw A Graph of y 2xKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- X-Axis.: Example 2: Draw A Graph of y XDocument3 pagesX-Axis.: Example 2: Draw A Graph of y XKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Linear and Quadratic Functions July 23Document4 pagesLinear and Quadratic Functions July 23tatendasigauke05No ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic EquationDocument5 pagesSolving Quadratic EquationMohammad JamilNo ratings yet
- X-Axis X 1 or X - 2: Example 3: Solve The EquationDocument2 pagesX-Axis X 1 or X - 2: Example 3: Solve The EquationKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodDocument4 pagesLesson 2.2 Graphing Linear Functions by The Point Plotting MethodAliah GombioNo ratings yet
- ESS 1001 E Tutorial #5Document3 pagesESS 1001 E Tutorial #5a21217No ratings yet
- If M' and N' Are The Roots Then The Standard Form of The Equation Is - (Sum of The Roots) X + Product of The Roots 0 - (M + N) X + MN 0Document9 pagesIf M' and N' Are The Roots Then The Standard Form of The Equation Is - (Sum of The Roots) X + Product of The Roots 0 - (M + N) X + MN 0Kelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Practice Technology Math Skills 3Document9 pagesPractice Technology Math Skills 3LuisAranaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument19 pagesQuadratic EquationsLoh Chee WeiNo ratings yet
- Example 3: Form The Quadratic Equation Whose Roots Are 3 + 2Document8 pagesExample 3: Form The Quadratic Equation Whose Roots Are 3 + 2Kelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Equations With QuadraticsDocument17 pagesSimultaneous Equations With QuadraticsPetar GeorgievNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Graphs of Functions IIDocument18 pagesChapter 2 - Graphs of Functions IInasir6165No ratings yet
- Example 7: Find The Value of K So That The Equation XDocument6 pagesExample 7: Find The Value of K So That The Equation XKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument18 pagesQuadratic EquationsErwani KamaruddinNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Graphs of Equations and CirclesDocument19 pages1.2 Graphs of Equations and CirclesWEDD FAWAZNo ratings yet
- Math L1Document24 pagesMath L1vexerez1No ratings yet
- Presentation Linear Equation in Two Variables 1516100969 314387Document15 pagesPresentation Linear Equation in Two Variables 1516100969 314387Anmol KhatriNo ratings yet
- DE Lec 1-9Document9 pagesDE Lec 1-9Cheat CodeNo ratings yet
- 9-4 Solving Quadratic Equations by GraphingDocument34 pages9-4 Solving Quadratic Equations by GraphingMisterLemusNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Graphs and PropertiesDocument20 pagesModule 3. Graphs and PropertiesMark Christian dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 2.quadratic EquationsDocument17 pages2.quadratic EquationsHarith HanifNo ratings yet
- Lecture in Math 9 2023 2024 q2 Self StudyDocument38 pagesLecture in Math 9 2023 2024 q2 Self StudyAlyssa Antonette SibalNo ratings yet
- Example 10 Chapter 3 Quadratic InequalitiesDocument3 pagesExample 10 Chapter 3 Quadratic InequalitiesEllington DenhereNo ratings yet
- 5 6179299517544792508Document8 pages5 6179299517544792508Atul JanbandhuNo ratings yet
- S4 Mathematics Homework 7Document4 pagesS4 Mathematics Homework 74A21 SHER WAN YEENo ratings yet
- 11-1 Graphing Linear EquationsDocument10 pages11-1 Graphing Linear Equationsapi-26014607No ratings yet
- Module 2Document30 pagesModule 2Axiel John Ray EscalaNo ratings yet
- Math FT S1 G10 SGS 2023Document7 pagesMath FT S1 G10 SGS 2023noorlailyNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Linear FunctionsDocument28 pages3.3 Linear Functionsm_armoutiNo ratings yet
- revision WorksheetDocument10 pagesrevision WorksheetJumana ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- 7 Las m10 Week 7 Montad Nicanor Jr. S. EditedDocument4 pages7 Las m10 Week 7 Montad Nicanor Jr. S. EditedGemmhainne OrtizNo ratings yet
- Cuts The X-Axis at X - 2 and X 8, Graph 0 (Above X-Axis)Document4 pagesCuts The X-Axis at X - 2 and X 8, Graph 0 (Above X-Axis)Zoe ChoonNo ratings yet
- Graphing TechniquesDocument33 pagesGraphing TechniquesCathy McKayNo ratings yet
- Peta I Think Fizik t4Document18 pagesPeta I Think Fizik t4Yk TayNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Math 9 First Grading 26 50Document18 pagesReviewer in Math 9 First Grading 26 50Ken-Ken BormateNo ratings yet
- Answers Correct To 1 Decimal Place, Where ApplicableDocument2 pagesAnswers Correct To 1 Decimal Place, Where ApplicableBheko NgalonkuluNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet 1 MA2020 Differential Equations (July - November 2016)Document1 pageAssignment Sheet 1 MA2020 Differential Equations (July - November 2016)Siddharth NathanNo ratings yet
- Lessons 5-9 PDFDocument5 pagesLessons 5-9 PDFIbarra KakkiNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Monthly Test March 2016Document10 pagesAdd Maths Monthly Test March 2016Armadaramor ShiNo ratings yet
- Plates-No - 1 1-1 4Document1 pagePlates-No - 1 1-1 4MADELYN QUIMBONo ratings yet
- 2.0 Graphs of Functions 2Document123 pages2.0 Graphs of Functions 2juriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Addmath Form 4Document16 pagesAddmath Form 4Shakti GanesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document25 pagesLecture 8Gia Huy LạiNo ratings yet
- 4.2 SolDocument58 pages4.2 Solsamy gNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Quarter 1Document34 pagesMath 9 Quarter 1Janinne Villa Del Rey100% (1)
- Quadratics Worksheet Sept 2017 QDocument8 pagesQuadratics Worksheet Sept 2017 QnatalieNo ratings yet
- MSM 111 - Quadratic Functions - T3Document2 pagesMSM 111 - Quadratic Functions - T3Chileshe SimonNo ratings yet
- Prelim Problem Set ENGGMATH5Document4 pagesPrelim Problem Set ENGGMATH5Silendrina MishaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 II Graphs of Functions EnrichmentDocument12 pagesChapter 11 II Graphs of Functions EnrichmentksganNo ratings yet
- PRB 2Document2 pagesPRB 2Prosper WabwireNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ODEDocument1 pageTutorial ODENISCHAY VERMANo ratings yet
- 2020 - 2021, Quadratic Function - 071819Document2 pages2020 - 2021, Quadratic Function - 071819Julius ChishikiNo ratings yet
- Graphs RevisionDocument15 pagesGraphs Revisionzylon.d.liteNo ratings yet
- Mach Number (M)Document8 pagesMach Number (M)Kelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Eeuo Part3 Part3Document2 pagesEeuo Part3 Part3Kelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Example 5: If M' and N' Are The Roots of Equation XDocument7 pagesExample 5: If M' and N' Are The Roots of Equation XKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Example 3: Find The Sum and Product of The Roots of Equation 2mDocument1 pageExample 3: Find The Sum and Product of The Roots of Equation 2mKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Example 4: Solve The Equation: A 2 Ac 4) B (B XDocument4 pagesExample 4: Solve The Equation: A 2 Ac 4) B (B XKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- 1 TwgdgfddfgdfgdfgdfvfsDocument2 pages1 TwgdgfddfgdfgdfgdfvfsKelli FloresNo ratings yet