Professional Documents
Culture Documents
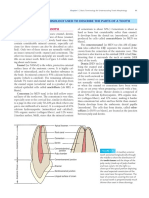
4 Cementum PDL
Uploaded by
Tanairi EspinaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4 Cementum PDL
Uploaded by
Tanairi EspinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ankylosis - Immobility
Cementum & Alveolar Bone fuse
PDL obliterated
Guided Tissue Regeneration
Block gingival/epithelial cell growth
Allow PDL & Bone to regenerate
(1) Aging
Decrease fibroblasts
PDL Decrease organic matrix/cells
Decrease width of PDL
Decrease Decrease repair/regeneration
Increase elastic fibres
Irregular structure
(1) Children
Increase (2) Occlusal Loading
Clinical Implications
Cementicle (Hang Around)
Result of trauma
Can be free in PDL
Masses of cementum
Cementum grows over Enamel (60%)
Dentinal Hypersensitivity
Cementum meets Enamel (30%)
Cementum does not meet Enamel (10%)
Hypercementosis
Cementum Harder to extract
(1) Tooth Grinding
(2) Functional position
(3) Age
Increase Becomes less permeable
Increase width
Increase resorption bays
Decrease
Structure:
Hourglass shape
Narrowest at mid root
Between root & lamina dura
Week 4: Stomatodeum (Primitive Oral Cavity)
Cells Types : Top: Frontal Prominence (Brain)
Ectomesenchymal cells Bottom: Developing Heart
Epithelial cell rests of Malassez Side: 1st Arch
Fibroblasts (Synthesize & Degrade)
Osteoblasts/Odontoblast/Cementoblasts Week 6: Tooth Formation
Osteoclasts/Odontoclast/Cemetoclast
Macrophage/Monocyte Oral epithelium (Gives rise to enamel epithelium)
Mesenchymal cells
Sharpey Fibres (A-H-O-A-I)
1) Placode
Alveolar Crest (Vert)
Downward growth of epithelium
Horizontal (Hori)
Oblique (Vert); Develop first
Apical (Vert) 2) Bud
Inter-radicular (Only in multi rooted; Both) Downward growth of epithelium
Components: Determines tooth morphology
Stages
PDL 3) Cap
Unequal epithelium growth
ECM
Collagen (Develop from tooth side)
Reticulin (Type 3)
(4) Cementum & PDL 4) Bell
Unequal epithelium growth
Oxytalan / Elastin Determines position/height of cusps
GAG/GP Early stage: Histodifferentiation
Advanced stage: Morphodifferentiation
Sensory Undifferentiated: Dental Follicle
Nociception Located bottom of enamel organ; Surrounds entire organ
Myeliated & Unmyelinated Nerves Cementum
PDL
Autonomic Alveolar Bone
Periodontal blood vessels
Unmyelinated Supportive: Differentiated:
Nerves Cementoblast
Blood Vessels Vessels Cementocyte
Mesenchyme Fibroblast
Lingual Artery Lingual & Palatine arteries Cementum
Palatine Artery
Undifferentiated: Dental Papilla
Dentin
Functions: Pulp
(1) Sensory Development Components
(2) Attachment Differentiated:
(3) Nutritive Odontoblast
(4) Absorb Shock Fibroblast
(5) Regenerative Macrophages/Dendritic/Lymphocytes
Undifferentiated Mesenchyme
S-A-N-A-R Enamel Organ
Undifferentiated:
IEE (Columnar) into ameloblasts
Enamel OEE (Cuboidal)
Structure Stellate Reticulum (GAGs)
Thickest at apex/root Oral Epithelium
Thinnest at cervical area Differentiated :
Continuous deposition throughout life Ameloblasts
Cementocyte will degenerate (Avascular) unlike bone
Supporting
Hertwig's Epithelial Root Sheath
NO blood vessels
NO nerves Located at cervical root of enamel organ
NO lymph Fusion of IEE & OEE
SUPPORT FROM PDL Function (1): Guides root formation
Function (2): IEE causes papilla differentiation into odontoblast
Function (3): Secretes Hyaline Layer of Hopewell Smith (Binds cementum to dentin)
Extrinsic Fibre : Fate (1): Apoptosis
Fibres operating outside Fate (2): Become Cementum
Perpendicular to root surface Fate (3): Become PDL
Fate (4): Become Epithelial cell rests of Malassez (Induce undifferentiated cells to differentiate)
Intrinsic Fibre : Cementum Fate (5): Become Cementoblasts
Fibres operating inside
Parallel to root surface
Types
Acellular Extrinsic Fibre
First formed
Mainly for Attachment
Common Type
Cellular Intrinsic Fibre
Found near root
Cementogenesis
Collagen/ECM
Cementoblast entomed
Matrix vesicles (like dentinogenesis)
Heterogeneous nucleation
Incremental lines of (Salter)
Acellular vs Cellular
LOSER
FRCS
DPH
Location: Apical/Cervical
First: First/Second
Rate: Fast/Slow (Lines)
Calcification: More/Less
Sharpey: More/Less
Demarcation(Dentin): Clear/Unclear
Precementum: Yes/No
Housing: Lacunae/Canaliculi
L-F-R-C-S-D-P-H
You might also like
- (Asce) MT 1943-5533 0000446Document6 pages(Asce) MT 1943-5533 0000446NilsimhaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Connective Tissue: Desmosomes Tight Junctions Gap JunctionsDocument1 pageEpithelial Tissue Connective Tissue: Desmosomes Tight Junctions Gap JunctionsJalen GalvezNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Connective Tissue: Desmosome S Tight Junctions Gap JunctionsDocument1 pageEpithelial Tissue Connective Tissue: Desmosome S Tight Junctions Gap JunctionsJalen GalvezNo ratings yet
- Week 15 - Sports InjuryDocument5 pagesWeek 15 - Sports InjuryJanselle H ArmaNo ratings yet
- Cement UmDocument8 pagesCement UmHannasa R JNo ratings yet
- Influence of Cellulose Filaments On Cement Paste and ConcreteDocument14 pagesInfluence of Cellulose Filaments On Cement Paste and ConcreteDhiren SagarNo ratings yet
- Section Iii: A. Four Tissues of A ToothDocument2 pagesSection Iii: A. Four Tissues of A ToothYoshe Kartika SentosaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Concept MapDocument1 pageSkeletal System Concept MapkacchanNo ratings yet
- Adhesive Resin Cements For Bonding Esthetic Restorations - A Review PDFDocument28 pagesAdhesive Resin Cements For Bonding Esthetic Restorations - A Review PDFKarla Alanis100% (1)
- Grossman's Endodontic Practice 13 Ed-59-66Document8 pagesGrossman's Endodontic Practice 13 Ed-59-66Karma YogaNo ratings yet
- Composite PDFDocument5 pagesComposite PDFruchikaNo ratings yet
- Dental Thermoplastics: The Evolution and Advancement ofDocument3 pagesDental Thermoplastics: The Evolution and Advancement ofAhmed HamzaNo ratings yet
- Estresse de ContraçãoDocument8 pagesEstresse de Contraçãobrunaflage1No ratings yet
- 6 CementumDocument81 pages6 CementumYousef ZaiterNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- Dental Cements For Luting20190521 59257 189ohxw With Cover Page v2Document15 pagesDental Cements For Luting20190521 59257 189ohxw With Cover Page v2Oke Soe MoeNo ratings yet
- Unusual Application - FSADocument4 pagesUnusual Application - FSASulaiman Kadher KNo ratings yet
- Dentin-Bonded All-Ceramic: Crowns: Current StatusDocument6 pagesDentin-Bonded All-Ceramic: Crowns: Current StatusDr Sai Govind GavaraNo ratings yet
- Bonded Amalgams and Their Use in Clinical Practice: Dentistry DentalDocument7 pagesBonded Amalgams and Their Use in Clinical Practice: Dentistry DentalAsmita SonawneNo ratings yet
- Polymerization Shrinkage and Contraction Stress of Dental Resin CompositesDocument8 pagesPolymerization Shrinkage and Contraction Stress of Dental Resin CompositesStephanie MonzonNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDocument1 pageTuberculosis: Mycobacterium BacilliDeni Marie GomonidNo ratings yet
- Silhouette Enhanced The Contours of My Face and Put A Smile Upon ItDocument20 pagesSilhouette Enhanced The Contours of My Face and Put A Smile Upon Iteidwisam100% (1)
- 95 731 01 SilanesSelectorGuideDocument4 pages95 731 01 SilanesSelectorGuideAelya SanNo ratings yet
- Composite Resins: A Review of The Types, Properties and Restoration TechniquesDocument8 pagesComposite Resins: A Review of The Types, Properties and Restoration TechniquesAdam HusniNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Lesson4 CMBIODocument3 pagesModule 1-Lesson4 CMBIODeanille Antoine TurbanosNo ratings yet
- Adhesion (Enamel and Dentin)Document31 pagesAdhesion (Enamel and Dentin)umairNo ratings yet
- Adhesives - Part 1 Inside DentDocument4 pagesAdhesives - Part 1 Inside DentVanessa MordiNo ratings yet
- Kelteks - EDGE PROTECTOR 2020 - FLYER - ENDocument6 pagesKelteks - EDGE PROTECTOR 2020 - FLYER - ENghariharan95No ratings yet
- Principles of Tooth PreparationDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Tooth PreparationNoor HaiderNo ratings yet
- J Esthet Restor Dent - 2006 - MAGNE - Immediate Dentin Sealing A Fundamental Procedure For Indirect Bonded RestorationsDocument11 pagesJ Esthet Restor Dent - 2006 - MAGNE - Immediate Dentin Sealing A Fundamental Procedure For Indirect Bonded RestorationsAlfred OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Unit VII PowerpointDocument24 pagesUnit VII PowerpointSteve SullivanNo ratings yet
- Composite ResinDocument26 pagesComposite ResinKhylle Camron LuzzieNo ratings yet
- For Dental Implants: The Very Best ReasonDocument12 pagesFor Dental Implants: The Very Best ReasonMukul PatilNo ratings yet
- Infographic Plant SafetyDocument1 pageInfographic Plant SafetySri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Cementos Dentales para Restauraciones de Cementación y Unión Cementos de Resina Autoadhesivos PDFDocument14 pagesCementos Dentales para Restauraciones de Cementación y Unión Cementos de Resina Autoadhesivos PDFgerson fabian arangoNo ratings yet
- Biomimetic Remineralization of Resin-Bonded Acid-Etched DentinDocument6 pagesBiomimetic Remineralization of Resin-Bonded Acid-Etched DentinCynthia LlangaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Different Ceramic and Composite Materials On Stress Distribution in Inlay and Onlay Cavities: 3-D Finite Element AnalysisDocument10 pagesEffects of Different Ceramic and Composite Materials On Stress Distribution in Inlay and Onlay Cavities: 3-D Finite Element AnalysisAndrei VasileNo ratings yet
- ContentServer Asp-8 PDFDocument13 pagesContentServer Asp-8 PDFLeandra TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Geofoam5006 - Revised January 2019Document1 pageGeofoam5006 - Revised January 2019iced velonzaNo ratings yet
- FSA-1 Fines Stabilization AgentDocument1 pageFSA-1 Fines Stabilization Agentpedro taquichiriNo ratings yet
- MechanicalDocument13 pagesMechanicalAngelNo ratings yet
- Belli 2005Document4 pagesBelli 2005Luciano ESENARRONo ratings yet
- The Influence of Elastic Modulus of Base Material On The Marginal Adaptation of Direct Composite RestorationDocument7 pagesThe Influence of Elastic Modulus of Base Material On The Marginal Adaptation of Direct Composite Restorationbackupwa040No ratings yet
- Principles of AdhesionDocument44 pagesPrinciples of AdhesionOmar Hesham SalahNo ratings yet
- TrueDocument12 pagesTrueThree AuNo ratings yet
- 8 CoDocument11 pages8 CoSaad LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Simplifying The Cementation Protocol: e Uca IonDocument4 pagesSimplifying The Cementation Protocol: e Uca IonMario Zúñiga GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Effect of Polyethylene FiberDocument5 pagesEffect of Polyethylene FiberfelipeNo ratings yet
- EUV DevelopmentsDocument38 pagesEUV DevelopmentsGabriel DonovanNo ratings yet
- Concept Map (Cells: Sci Bio)Document1 pageConcept Map (Cells: Sci Bio)lu.justina100% (8)
- Composites Used With Ribbond Fibers: (Not An Exclusive List)Document1 pageComposites Used With Ribbond Fibers: (Not An Exclusive List)grisellaNo ratings yet
- Cementoenamel Junction An InsightDocument6 pagesCementoenamel Junction An InsightJessica ChenNo ratings yet
- List of Existing Power Plants List of Existing Power Plants (Grid-Connected) As of June 2020Document4 pagesList of Existing Power Plants List of Existing Power Plants (Grid-Connected) As of June 2020Pedro GojoNo ratings yet
- Thermopress 400: One System For Five Thermoplastic MaterialsDocument16 pagesThermopress 400: One System For Five Thermoplastic MaterialsMilan BojovicNo ratings yet
- Deliperi2017 PDFDocument11 pagesDeliperi2017 PDFDrAditya BansalNo ratings yet
- Proses Pmma CadDocument7 pagesProses Pmma CadferaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of A "Resin Coating" On The Interfacial Adaptation of Composite InlaysDocument8 pagesThe Effect of A "Resin Coating" On The Interfacial Adaptation of Composite InlaysAli Al-QaysiNo ratings yet
- 2 Obstacle Avoiding Robot PDFDocument7 pages2 Obstacle Avoiding Robot PDFRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- D D D D D D P P P D: Procedure For Calculating Apparent-Pressure Diagram From Measured Strut LoadsDocument1 pageD D D D D D P P P D: Procedure For Calculating Apparent-Pressure Diagram From Measured Strut LoadsjcvalenciaNo ratings yet
- 1 Manalo Vs Sistoza DigestDocument2 pages1 Manalo Vs Sistoza DigestRowell Ian Gana-an0% (1)
- Finned Surfaces: Name:Mohamed Hassan Soliman ID:190513 DR - Mohamed HassanDocument7 pagesFinned Surfaces: Name:Mohamed Hassan Soliman ID:190513 DR - Mohamed HassanMohamed HassanNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of World Health OrganisationDocument26 pagesA Case Study of World Health OrganisationFarNo ratings yet
- Kaitlyn Duron ResumeDocument2 pagesKaitlyn Duron Resumeapi-453866596No ratings yet
- Sadza: ChickenDocument13 pagesSadza: ChickenTsitsi Ngara SibandaNo ratings yet
- ACAINvs CADocument2 pagesACAINvs CAabogada1226No ratings yet
- Oktoberfest ReportDocument28 pagesOktoberfest ReportUvin RanaweeraNo ratings yet
- Ukraine - A History PDFDocument887 pagesUkraine - A History PDFFidel Trejo Orozco100% (9)
- FPGA and PLD SurveyDocument29 pagesFPGA and PLD SurveykavitaNo ratings yet
- Rules and Reminders For Online Classes 2Document14 pagesRules and Reminders For Online Classes 2api-220703221No ratings yet
- Best of Mexican CookingDocument154 pagesBest of Mexican CookingJuanNo ratings yet
- Company Profile Ariandra Media Ardhana Web UploadDocument26 pagesCompany Profile Ariandra Media Ardhana Web UploadMrKanghasanNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 First Periodical Test in EPPDocument6 pagesGrade 6 First Periodical Test in EPPPrecilla Halago88% (8)
- Assignment On Rules of InferenceDocument1 pageAssignment On Rules of InferenceAlone100% (1)
- The Invention of The Internet Connecting The WorldDocument14 pagesThe Invention of The Internet Connecting The WorldSolomia Sushko100% (1)
- Desert RoseDocument2 pagesDesert RoseGADAANKITNo ratings yet
- Mitchell - Heidegger and Terrorism (2005)Document38 pagesMitchell - Heidegger and Terrorism (2005)William Cheung100% (2)
- Senate - Community Projects 2009-10Document98 pagesSenate - Community Projects 2009-10Elizabeth Benjamin100% (3)
- Topic 5 - Market Forces - SupplyDocument5 pagesTopic 5 - Market Forces - Supplysherryl caoNo ratings yet
- 2023 WARN Notice ListingsDocument15 pages2023 WARN Notice ListingsMasonNo ratings yet
- Jimmy Lim 2Document33 pagesJimmy Lim 2Ramsraj100% (1)
- Mckenzie Ross Resume 3 12 15Document1 pageMckenzie Ross Resume 3 12 15api-281264881No ratings yet
- Dhilp ProjectDocument53 pagesDhilp ProjectSowmiya karunanithiNo ratings yet
- My Mother at SixtysixDocument18 pagesMy Mother at SixtysixAnoushka RaiNo ratings yet
- Construction Method Statement SafetyDocument4 pagesConstruction Method Statement SafetyRaiZaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Two CartoonsDocument3 pagesAssignment Two CartoonsAbraham Kang100% (1)
- Othello JourneyDocument38 pagesOthello Journeyapi-270897909No ratings yet
- Verbyla Et Al. - 2013Document6 pagesVerbyla Et Al. - 2013Johnny Jala QuirozNo ratings yet