Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Efferent, or Descending, Nerves Send Impulses Away From The Brain. These Are Also
Efferent, or Descending, Nerves Send Impulses Away From The Brain. These Are Also
Uploaded by
Khate Cassey Paralejas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageOriginal Title
mideterm.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageEfferent, or Descending, Nerves Send Impulses Away From The Brain. These Are Also
Efferent, or Descending, Nerves Send Impulses Away From The Brain. These Are Also
Uploaded by
Khate Cassey ParalejasCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
II.
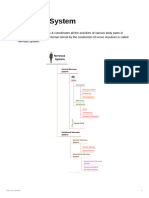
Functions of the nervous system
A. Nervous impulses travel in two directions, and each direction has a separate set of nerves.
1. Efferent, or descending, nerves send impulses away from the brain. These are also
called motor nerves.
2. Sensory impulses that ascend the nerves to the brain are called afferent impulses and
move along afferent nerves.
B. Efferent impulses produce action in distant organs.
C. Afferent impulses deliver information from peripheral nerves to the brain.
D. The integrative function analyzes information input from afferent impulses, files these data, and
stimulates action in response to sensory input.
III. Kinds of nervous tissue and their functions
A. Neurons (”nerve cells”)
1. Neurons initiate and relay electrical nervous impulses toward and away from the brain.
2. Neurons have three basic parts:
I. Cell body.
II. Dendrites (”trees”), which receive incoming messages.
III. Axons, which deliver outgoing messages.
3. Nerves can have any arrangement of dendrites and axons, including one input to many
outputs (divergence), many inputs to one output (convergence) and one input to one
output.
4. Some axons are myelinated (insulated) for rapid impulse delivery. These axons
display saltatory (jumping) conduction.
5. Other axons are unmyelinated.
6. Myelin sheaths develop as a baby grows; disease can interrupt this process.
You might also like
- CH 06 Nervous System (MS)Document63 pagesCH 06 Nervous System (MS)alyssa bananNo ratings yet
- Neuron and Glial CellsDocument25 pagesNeuron and Glial Cellsfakhar aliNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesAnaphy Nervous SystemFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument86 pagesThe Nervous SystemNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- Neural TissueDocument9 pagesNeural TissueJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous SystemYUAN FRANCIS SINGCULANNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue: Saladin 6e Extended OutlineDocument19 pagesNervous Tissue: Saladin 6e Extended Outlineellie marcusNo ratings yet
- Transes Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesTranses Nervous SystemAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument13 pagesUnit 5 The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsIrene Caballero PicazoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesNervous Systemmercaderlorenzo9No ratings yet
- NeuronsDocument9 pagesNeuronsMuhammad Junaid SialNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class X Nervous System NotesDocument20 pagesICSE Class X Nervous System Notesprogrammer.ron.akNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Division of NSDocument12 pagesNervous System - Division of NSshaniaericaNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 pagesOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Fasil Ahmed (MSC) March 2024Document44 pagesNervous System: Fasil Ahmed (MSC) March 2024beletetewodros00No ratings yet
- The NeuronsDocument3 pagesThe NeuronsAsim ZafarNo ratings yet
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument12 pagesNervous System WorksheetLeamae ObinaNo ratings yet
- Nervou S Syste M: Types of NeuronsDocument8 pagesNervou S Syste M: Types of NeuronsMayet BautistaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous Systemnurulainnabila09No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document13 pagesNervous System 1wasim akhtarNo ratings yet
- Analzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Document2 pagesAnalzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Phoebe Sudweste QuitanegNo ratings yet
- Analzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Document2 pagesAnalzying Sensory Somatic Responces - System Reinforcemnt Worksheet1Creative DestinyNo ratings yet
- Wires Really Crossed Teacher 1EDocument5 pagesWires Really Crossed Teacher 1EEllie EllaNo ratings yet
- MC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSDocument7 pagesMC1 REVIEWER (Nervous System) - MIDTERMSFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- 14.1 The Nervous SystemDocument15 pages14.1 The Nervous SystemNathan TeferaNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument8 pagesCoordination and Responsedawn baniNo ratings yet
- Types of NeuronsDocument4 pagesTypes of NeuronsDeirdreNo ratings yet
- Neurology Assignment 1Document9 pagesNeurology Assignment 1workupindia7No ratings yet
- Assignment #1: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesAssignment #1: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesMarvin ParasNo ratings yet
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemAnonymous 3OKQDoiJNo ratings yet
- Ns-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesNs-Elec-4 - Nervous SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.No ratings yet
- Chapter 13: Spinal CordDocument15 pagesChapter 13: Spinal CordDao TranNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesThe Nervous SystemA. MagnoNo ratings yet
- Neurons (Brain Cells) : The Structure of The NeuronDocument2 pagesNeurons (Brain Cells) : The Structure of The NeuronJacques TuckerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Notes - Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Notes - Biological Bases of BehaviorMarina QuaveNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Benign Febrile ConvulsionDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Benign Febrile ConvulsionJan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Nervous SystemUmair BasheerNo ratings yet
- Nervous ControlDocument15 pagesNervous ControlzoeakatNo ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesG-10 Biology, 3.1 The Nervous SystemYohannes NigussieNo ratings yet
- PSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorDocument9 pagesPSY-105 Chapter # 03: Neuro Science and BehaviorSabbir AhammedNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDocument7 pages1.2 Neuroscience and BehaviourDiya MehtaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument43 pagesThe Nervous SystemmalakbasahalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Biology of MindCindy AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument4 pagesClass Notesdaniel holmesNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Care For Clients With Cognitive and Perceptual Disorder 1Document93 pagesModule 1: Care For Clients With Cognitive and Perceptual Disorder 1Woot RootNo ratings yet
- GR 10 07 Control Co Ordination NDocument5 pagesGR 10 07 Control Co Ordination Nrptheashwin0207No ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- Botan's Cns and The Brain 2023Document115 pagesBotan's Cns and The Brain 2023Caamir Dek HaybeNo ratings yet
- Neurons 15032022 022019pmDocument9 pagesNeurons 15032022 022019pmayan khanNo ratings yet
- Neurons ArtycleDocument4 pagesNeurons ArtycleTania PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatDocument37 pagesNervous System: by Dr. K. Sumangala BhatanushkaNo ratings yet
- MARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesMARCH 19, 2024 The Nervous SystemAlmira ZuñigaNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#4 MED3Document3 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#4 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Group of Name: Erfan Efendi (0119017) Hikmayatul Nur S (0119037) Reki Novita Kaesti (0119043)Document6 pagesGroup of Name: Erfan Efendi (0119017) Hikmayatul Nur S (0119037) Reki Novita Kaesti (0119043)AvindaNo ratings yet
- IM AnSci 111 Module 3Document21 pagesIM AnSci 111 Module 3Riza Mae Duran RangasNo ratings yet
- PAS113 Block 2 NotesDocument41 pagesPAS113 Block 2 NotesAngela WuNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients (Protein, Fats, and Carbohydrates)Document4 pagesMacronutrients (Protein, Fats, and Carbohydrates)Khate Cassey ParalejasNo ratings yet
- Macronutrients (Protein, Fats, and Carbohydrates)Document4 pagesMacronutrients (Protein, Fats, and Carbohydrates)Khate Cassey ParalejasNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Anatomy of The BrainDocument3 pagesNervous System - Anatomy of The BrainKhate Cassey ParalejasNo ratings yet
- (Choose) : Flag This QuestionDocument3 pages(Choose) : Flag This QuestionKhate Cassey Paralejas100% (1)
- Examples of Space: Two-Dimensional ArtworksDocument3 pagesExamples of Space: Two-Dimensional ArtworksKhate Cassey ParalejasNo ratings yet
- SpaceoutlinesDocument10 pagesSpaceoutlinesKhate Cassey ParalejasNo ratings yet
- AaaaaaaaDocument29 pagesAaaaaaaaKhate Cassey ParalejasNo ratings yet