Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Forms
Types of Forms
Uploaded by
Carljohn MasucolOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Forms
Types of Forms
Uploaded by
Carljohn MasucolCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of forms
1. Point: A point form allows you to drop a point on a map which creates a feature/data point on
the map. Creating new forms for the location of new potholes in your city or the location of
animal sightings in your area are examples of use cases of a point form.
2. Polygon: A polygon form allows you to draw a polygon on a map which created a new
feature/data area on a map. This is useful for when you want to draw the area to represent a plot of land,
building, or area on a map.
3. Line: A line form allows you to draw a line on a map that creates a new feature/data on a map.
When you would like to track a line or distance on a map, a line form would be useful in representing
that. Examples of a line form would be when you want to show on a map how long a sandbag barrier is to
prevent flooding.
4. Repeatable Section: Repeatable forms are a type of form that doesn't have it's own geometry, but
can be nested within forms that do have geometries or used on it's own. Repeatable Sections allow users
to create a set of form questions that can be repeated an infinite amount of times within the form that is
being filled out. An example of when a repeatable form might be used is in housing inspection forms. In a
section where it asks how many appliances the house has, there might be multiple types and amounts of
appliances, so inside the form you can add as many entries as necessary that apply to that situation.
5. Data Form: Data forms allow you to input data into Lightship without having it's own geometry.
An example of a data form would be if you want to keep track of your clients information (name, address,
phone number etc.) through Lightship.
6. Form Linked to an Existing Layer: A linked form contains tabular data that has no geometry, but
is instead associated, or linked, to a layer with geometry. One use case for linked tables is inspections and
maintenance on assets. For example, you can create a linked form for your inspections data and attach it
to a unique ID for each individual asset in the dataset. This enables you to attach inspections to assets
without altering the original data.
A form is a document with spaces (also named fields or placeholders) in which to write or
select, for a series of documents with similar contents. The documents usually have the printed
parts in common, except, possibly, for a serial number.
Forms, when completed, may be a statement, a request, an order, etc.; a check may be a form.
Also there are forms for taxes; filling one in is a duty to have determined how much tax one
owes, and/or the form is a request for a refund. See also Tax return.
Forms may be filled out in duplicate (or triplicate, meaning three times) when the information
gathered on the form needs to be distributed to several departments within an organization. This
can be done using carbon paper.
History
Forms have existed for a significant amount of time, with historians of law having discovered
preprinted legal forms from the early 19th century that greatly simplified the task of
drafting complaints and various other legal pleadings.
Advantages[
Advantages of forms include the following:
One has to write less (while the printing is almost universally done in some automatic
way)
One is told or reminded what information has to be supplied
There is uniformity, for convenience in processing
Information is collected in writing and so can be re-examined later (the form can also
include a signature field to allow someone to take responsibility for the accuracy of the
information provided).
Simpler tasks, such as collecting or distributing data, can be separated in
the workflow from more skilled processes, such as making decisions. Issuing and processing
the forms may then be done by less skilled staff, or by a computer. The de-skilled task
becomes issuing or completing the appropriate form for the circumstances, and then passing
it on to the next step in the workflow. This might reduce costs and increase the volume of
work that can be handled.
A form on a computer allows for conveniently typing in the variable parts (the input data).
Form structure
A blank form is like a usual document, with some outlined parts with spaces. Blank forms are
generally not copyrightable in the US.
Frame and fixed content
Part of the document that never changes. Usually a frame with title and textual instructions.
Placeholders
Boxes or spaces where the user can write or type to fill in the form.
You might also like
- Intro Clustering in RDocument346 pagesIntro Clustering in RAmelia Sánchez ReyesNo ratings yet
- ch05 Accounting Systems Solution ManualDocument12 pagesch05 Accounting Systems Solution ManualLindsey Clair Royal100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - FEMDocument34 pagesChapter 7 - FEMpaivensolidsnake100% (1)
- Form (Document) - WikipediaDocument9 pagesForm (Document) - WikipediaAtep RakalNo ratings yet
- Unit 16Document14 pagesUnit 16vivekbhartiofficial11No ratings yet
- Term Paper OF System Analysis AND Design Theory Topic:-Indentification OF Computer Output S Submitted ToDocument21 pagesTerm Paper OF System Analysis AND Design Theory Topic:-Indentification OF Computer Output S Submitted Toshailesh singhNo ratings yet
- PresentDocument4 pagesPresentnguyenphuoclhp2508No ratings yet
- Written Report in AISDocument14 pagesWritten Report in AISRobert MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ict Database CourseworkDocument5 pagesIct Database Courseworkf5dq3ch5100% (2)
- Microsoft Office Infopath 2007Document50 pagesMicrosoft Office Infopath 2007George MoonNo ratings yet
- Understanding 19 - 11Document10 pagesUnderstanding 19 - 11arunNo ratings yet
- Haroon Fainal AssessmentDocument41 pagesHaroon Fainal AssessmentIdrees AhmadNo ratings yet
- SSS2 Computer Studies 2ndT 222 23Document84 pagesSSS2 Computer Studies 2ndT 222 23TahmidNo ratings yet
- Spread Sheet FeatureDocument7 pagesSpread Sheet FeatureErick AloyceNo ratings yet
- jss3 NotesDocument33 pagesjss3 NotesQueen TochiNo ratings yet
- 92 Impl 14 CustomTools UserDefinedFieldsDocument28 pages92 Impl 14 CustomTools UserDefinedFieldssparsh upadhyayNo ratings yet
- Lotus Notes R8 Developer Training Session3Document105 pagesLotus Notes R8 Developer Training Session3Swapan Singh100% (1)
- 28-Point Cambria 28-Point Calibri: Bold Italic Underline Bold Italic UnderlineDocument3 pages28-Point Cambria 28-Point Calibri: Bold Italic Underline Bold Italic UnderlineCj SernaNo ratings yet
- Access Form DesignDocument18 pagesAccess Form Designijunoella28No ratings yet
- Dbms Practical FileDocument15 pagesDbms Practical FileSaurav Maddy0% (1)
- Database Management SystemsDocument7 pagesDatabase Management SystemsLavinia LaviaNo ratings yet
- Access Form Design: Technical Support ServicesDocument51 pagesAccess Form Design: Technical Support ServicesSunday Paul100% (1)
- ABAP Adobe Forms DevelopmentDocument19 pagesABAP Adobe Forms Developmentkrishna reddyNo ratings yet
- Tableau Terminology - Learn Tableau GlossaryDocument5 pagesTableau Terminology - Learn Tableau GlossaryGiri RajNo ratings yet
- Zoho Creator - Mis SurveyDocument13 pagesZoho Creator - Mis SurveyJosephin Dyna0% (1)
- Final Test Handout - ProgrammingDocument24 pagesFinal Test Handout - ProgrammingGhala AlholiNo ratings yet
- Inventory Data NeedsDocument5 pagesInventory Data Needsم. فضل محمد الفرحNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter G9Document14 pages3RD Quarter G9FlareNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and Design: Fall 2021Document4 pagesSystem Analysis and Design: Fall 2021Ngọc TrâmNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis PresentationDocument5 pagesData Analysis PresentationHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter No 8Document4 pagesChapter No 8Kashaf AmreenNo ratings yet
- Oda Lo 4 PPT 2013Document7 pagesOda Lo 4 PPT 2013Kinfe BeregaNo ratings yet
- Database 2 PDFDocument33 pagesDatabase 2 PDFSpyderbit SpyderNo ratings yet
- ch3 Queries, Forms and ReportsDocument3 pagesch3 Queries, Forms and Reportspragunjain2010No ratings yet
- Objective 2: Explain The Functions and Uses of The Major Types of Software ToolsDocument7 pagesObjective 2: Explain The Functions and Uses of The Major Types of Software Toolsrenell simonNo ratings yet
- MSAccess Database Management SystemDocument13 pagesMSAccess Database Management SystemtekleyNo ratings yet
- Ism Lab FileDocument63 pagesIsm Lab FileAshwin K NNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheets Vs DatabaseDocument11 pagesSpreadsheets Vs DatabaseMarietta Fragata RamiterreNo ratings yet
- Automatic Recognition of Tables in Construction Tender Documents Yang CaoDocument12 pagesAutomatic Recognition of Tables in Construction Tender Documents Yang Caopujiati sri rejekiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Topic On User-Defined Fields and User-Defined TablesDocument38 pagesWelcome To The Topic On User-Defined Fields and User-Defined Tablesoctavio pazNo ratings yet
- MS Access 2003 Forms DesignDocument24 pagesMS Access 2003 Forms Designkannunn100% (8)
- Create FormsDocument7 pagesCreate Formsbiruk mollaNo ratings yet
- Electronic MailDocument6 pagesElectronic MailRichard L PachuauNo ratings yet
- G S I P 2007: Etting Tarted With NFO ATHDocument13 pagesG S I P 2007: Etting Tarted With NFO ATHqwerty12348No ratings yet
- UnderstandingDocs 18 - 11Document6 pagesUnderstandingDocs 18 - 11arunNo ratings yet
- Bethany Labrador Bsit-A1: 1. What Are The Advantages of Using Flowchart?Document9 pagesBethany Labrador Bsit-A1: 1. What Are The Advantages of Using Flowchart?BETHANY LABRADORNo ratings yet
- Ict Coursework DatabaseDocument6 pagesIct Coursework Databasexmufyevcf100% (2)
- Information Technology ToolsDocument17 pagesInformation Technology Toolstarrant HighNo ratings yet
- Assessment 4 PDFDocument1 pageAssessment 4 PDFyamkelaNo ratings yet
- Report Specification Guide: Section 1 - RequestDocument6 pagesReport Specification Guide: Section 1 - RequestMuna AtyafNo ratings yet
- DocumentsDocument3 pagesDocumentsminor brisketNo ratings yet
- 1) Define: Database-: Foreign KeyDocument43 pages1) Define: Database-: Foreign KeyAbhimanyu Suresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Designing Efficient Web Forms - On Structure, Inputs, Labels and Actions - Smashing MagazineDocument20 pagesDesigning Efficient Web Forms - On Structure, Inputs, Labels and Actions - Smashing MagazineMinahel Noor FatimaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document54 pagesUnit 4pvedant861No ratings yet
- Databases (Ms Access) NotesDocument11 pagesDatabases (Ms Access) NotesDavid B MwathyNo ratings yet
- A Spreadsheet Is A Computer Application For OrganizingDocument9 pagesA Spreadsheet Is A Computer Application For Organizingritukatiyar02No ratings yet
- Project MS AccessDocument16 pagesProject MS Accessayeshajamilafridi100% (2)
- Creating Reports and Forms in Access PDFDocument25 pagesCreating Reports and Forms in Access PDFAlbert NgiruwonsangaNo ratings yet
- 3 Tips For Building Better ReportsDocument2 pages3 Tips For Building Better ReportsJose GuerraNo ratings yet
- It PortfolioDocument11 pagesIt Portfoliocordelia0255No ratings yet
- How To Develop A Performance Reporting Tool with MS Excel and MS SharePointFrom EverandHow To Develop A Performance Reporting Tool with MS Excel and MS SharePointNo ratings yet
- Geometric Primitive: Exploring Foundations and Applications in Computer VisionFrom EverandGeometric Primitive: Exploring Foundations and Applications in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Phrases Vocabulary Meaning Usage SentenceDocument26 pagesPhrases Vocabulary Meaning Usage SentenceCarljohn MasucolNo ratings yet
- Enhance Professional PracticeDocument7 pagesEnhance Professional PracticeCarljohn MasucolNo ratings yet
- ProfessionalismDocument20 pagesProfessionalismCarljohn MasucolNo ratings yet
- Competency Development of The Learner As A Result of The Training. Can Actually Do Outcomes Knowledge, Skills and AttitudeDocument10 pagesCompetency Development of The Learner As A Result of The Training. Can Actually Do Outcomes Knowledge, Skills and AttitudeCarljohn MasucolNo ratings yet
- Fake Talent Release FormDocument1 pageFake Talent Release FormValiant VNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Sheetmetal DesignDocument153 pagesWelcome To Sheetmetal Designjd4uNo ratings yet
- C ProgrammingDocument148 pagesC Programmingapi-20009988100% (1)
- Color Video Formation and PerceptionDocument20 pagesColor Video Formation and PerceptiontehazharrNo ratings yet
- Mom Shayri Images - Google Search PDFDocument1 pageMom Shayri Images - Google Search PDFMuskan JasNo ratings yet
- Data Privacy Act RA10173Document106 pagesData Privacy Act RA10173MikhailFAbzNo ratings yet
- Botvinnik-Keres WCC FIDE Tournament (Hague & Moscow 1948)Document3 pagesBotvinnik-Keres WCC FIDE Tournament (Hague & Moscow 1948)navaro kastigiasNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Notes BetzDocument547 pagesPower Electronics Notes BetzRobert BetzNo ratings yet
- ENPM667: Control of Robotic Systems Final Project: University of Maryland, College ParkDocument18 pagesENPM667: Control of Robotic Systems Final Project: University of Maryland, College ParkSandeep Kota100% (1)
- Six Sigma Green Belt 2009Document3 pagesSix Sigma Green Belt 2009pawan kumar dubeyNo ratings yet
- Saas Sales Models PDFDocument15 pagesSaas Sales Models PDFgsrrs100% (1)
- B.N.N College, Bhiwandi Department of Information Technology Subject: Business Intelligence Questions BankDocument49 pagesB.N.N College, Bhiwandi Department of Information Technology Subject: Business Intelligence Questions BankYohan MalshikaNo ratings yet
- Vulkan11 Reference GuideDocument16 pagesVulkan11 Reference GuideDebjit ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Regul R500. System Manual (DPA-311 v2.24) en v2Document220 pagesRegul R500. System Manual (DPA-311 v2.24) en v2Moises PerezNo ratings yet
- The School of The Future)Document2 pagesThe School of The Future)Diaconescu Cristian AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Form DesignDocument43 pagesForm DesignMinahel Noor FatimaNo ratings yet
- TZ Series: Dual PID Control Temperature ControllerDocument2 pagesTZ Series: Dual PID Control Temperature Controllerwaqasasad408No ratings yet
- YL80C ManualDocument25 pagesYL80C Manualmrperik0% (1)
- DLookup Function - Access - Microsoft OfficeDocument2 pagesDLookup Function - Access - Microsoft OfficevinahackNo ratings yet
- ME162 Technical Description v11Document14 pagesME162 Technical Description v11elemenatNo ratings yet
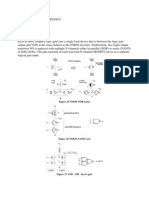
- Logic GatesDocument8 pagesLogic GatesNikunj ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Bloomberg Businessweek Europe 18 July 24 July 2016Document76 pagesBloomberg Businessweek Europe 18 July 24 July 2016Βασίλης ΣίνοςNo ratings yet
- Internet Bullying Circle - An Adaption of Dr. Dan Olweus and Barbara Coloroso's Bullying CircleDocument1 pageInternet Bullying Circle - An Adaption of Dr. Dan Olweus and Barbara Coloroso's Bullying CircleJeff PelichNo ratings yet
- MPC2550 SMDocument1,169 pagesMPC2550 SMCristian TempyNo ratings yet
- Shaft Encoder ComplianceDocument1 pageShaft Encoder ComplianceBASHAMOHUDDIN SHEIKNo ratings yet
- Metsec Framing Detail sf445 PDFDocument1 pageMetsec Framing Detail sf445 PDFBanditAkosNo ratings yet
- Get Ready!: Issues? ImportantDocument2 pagesGet Ready!: Issues? ImportantDionelio MorenoNo ratings yet
- EC462 Mixed Signal Circuit DesignDocument2 pagesEC462 Mixed Signal Circuit Designamruth lal.v.No ratings yet