Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3a 3c 4 Dopamine, A Neurotransmitter Located Primarily in The
Uploaded by
알파Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3a 3c 4 Dopamine, A Neurotransmitter Located Primarily in The
Uploaded by
알파Copyright:
Available Formats
20 UNIT 1 • CURRENT THEORIES AND PRACTICE
Presynaptic Major neurotransmitters have been found to play a role
neuron in psychiatric illnesses as well as in the actions and side
effects of psychotropic drugs. Table 2.1 lists the major neu-
rotransmitters and their actions and effects. Dopamine and
serotonin have received the most attention in terms of the
study and treatment of psychiatric disorders (Tecott &
Presynaptic Smart, 2005). The following sections discuss the major
receptor neurotransmitters associated with mental disorders.
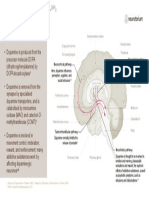
Dopamine
4
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter located primarily in the
Metabolite Enzy 3a brain stem, has been found to be involved in the control of
m Reuptake
3b e
complex movements, motivation, cognition, and regula-
1 T 3c tion of emotional responses. It is generally excitatory and
2 is synthesized from tyrosine, a dietary amino acid. Dop-
amine is implicated in schizophrenia and other psychoses
Postsynaptic
as well as in movement disorders such as Parkinson’s dis-
neuron Postsynaptic
ease. Antipsychotic medications work by blocking dop-
receptor
amine receptors and reducing dopamine activity.
Figure 2.3. Schematic illustration of (1) neurotransmitter
(T) release; (2) binding of transmitter to postsynaptic
receptor; termination of transmitter action by (3a) reuptake
Norepinephrine and Epinephrine
of transmitter into the presynaptic terminal, (3b) enzymatic Norepinephrine, the most prevalent neurotransmitter in
degradation, or (3c) diffusion away from the synapse; and the nervous system, is located primarily in the brain stem
(4) binding of transmitter to presynaptic receptors for and plays a role in changes in attention, learning and
feedback regulation of transmitter release.
memory, sleep and wakefulness, and mood regulation.
Norepinephrine and its derivative, epinephrine, are also
metabolized and inactivated by enzymes, primarily mono- known as noradrenaline and adrenaline, respectively.
amine oxidase (MAO) (Figure 2.3). Excess norepinephrine has been implicated in several anx-
These neurotransmitters are necessary in just the right iety disorders; deficits may contribute to memory loss,
proportions to relay messages across the synapses. Studies social withdrawal, and depression. Some antidepressants
are beginning to show differences in the amount of some block the reuptake of norepinephrine, whereas others
neurotransmitters available in the brains of people with inhibit MAO from metabolizing it. Epinephrine has lim-
certain mental disorders compared with people who have ited distribution in the brain but controls the fight-or-
no signs of mental illness (Figure 2.4). flight response in the peripheral nervous system.
Dopamine Dopamine
receptor
A Deficient neurotransmitter C Excess neurotransmitter
B Deficient receptors D Excess receptors
Figure 2.4. Abnormal neurotransmission causing some mental disorders because of excess transmission or excess
responsiveness of receptors.
78616_02_ch02_p017-042.indd 20 11/12/09 6:35:45 PM
You might also like
- Introduction to Biology and Psychology Chapter 2Document8 pagesIntroduction to Biology and Psychology Chapter 2MIKAELA YENG MERCADONo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology Study GuideDocument171 pagesPsychopharmacology Study GuideVaib NigamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Brain and BehaviourDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Brain and Behaviour038 Suri HananNo ratings yet
- Revisi SOHO Slide Quetiapine XR For Bipolar & SchizophreniaDocument25 pagesRevisi SOHO Slide Quetiapine XR For Bipolar & Schizophreniaayesha devinaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer of A PsychologyDocument55 pagesReviewer of A PsychologyCAMMILLE EDZ FERRAS SELONGNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Bio Asmuni CutDocument40 pagesWeek 3 Bio Asmuni CutNavanisha SekarNo ratings yet
- 02 NeurotransmittersDocument51 pages02 NeurotransmittersPasha GhazalNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Finals For PrintingDocument13 pagesNCM 106 Finals For PrintingJULIANNAH ATHENA MERCADONo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia DiseaseDocument6 pagesSchizophrenia DiseasemarkNo ratings yet
- FINALS NCM 106 Lesson 1 Part 1 Drugs Acting in The Central and Peripheral Nervous System Week 1Document4 pagesFINALS NCM 106 Lesson 1 Part 1 Drugs Acting in The Central and Peripheral Nervous System Week 1Rayanna MaligaNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument37 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourDecode MusicNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmission Notes 3Document4 pagesNeurotransmission Notes 3api-188978784No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AntidepressantsDocument28 pagesPharmacology of Antidepressantsحيدر كريم سعيد حمزهNo ratings yet
- Describing An Atypical Antipsychotic: Receptor Binding and Its Role in PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesDescribing An Atypical Antipsychotic: Receptor Binding and Its Role in PathophysiologyZulay BohorquezNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Behaviour: Brain, Neurons, NeurotransmittersDocument28 pagesBiological Bases of Behaviour: Brain, Neurons, NeurotransmittersRAJ KUMAR YADAVNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Physiology I: 11.10.2020 Dr. Ahmed ThabetDocument3 pagesVeterinary Physiology I: 11.10.2020 Dr. Ahmed ThabetMayar HasanNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia: Presented By: Seng, Shena H. Siocon, Jewrich G. Ubag, Jazzyleene M. Vesagas, Christian Jay BDocument23 pagesSchizophrenia: Presented By: Seng, Shena H. Siocon, Jewrich G. Ubag, Jazzyleene M. Vesagas, Christian Jay BFatima Medriza DuranNo ratings yet
- Dopamin: Nur Fadhillah Khalid (P062181024) Mata Kuliah: NeurontrasmitterDocument27 pagesDopamin: Nur Fadhillah Khalid (P062181024) Mata Kuliah: Neurontrasmitternur fadhillah khalidNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioDocument65 pagesPsychotropic Drugs: Bryan Mae H. DegorioBryan Mae H. Degorio100% (2)
- Chapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainDocument9 pagesChapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainciaraNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Neurobiology and Aetiology (Slide 14)Document1 pageSchizophrenia Neurobiology and Aetiology (Slide 14)AldrinNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS MECHANISMS OF ACTION AND GENERIC/BRAND NAMESDocument16 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICS MECHANISMS OF ACTION AND GENERIC/BRAND NAMESGelah DacanayNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Behavior: Neuro Hormones. GABA, Glycine Peptides (Opiates)Document35 pagesBiological Bases of Behavior: Neuro Hormones. GABA, Glycine Peptides (Opiates)Adeel AizadNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Antidepressants: PHCL411Document76 pagesPharmacology of Antidepressants: PHCL411Mustapha ImadudeenNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Introduction To Psychopharmacology and The Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesPowerPoint Introduction To Psychopharmacology and The Nervous SystemRaeika GanjiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 NeurotransmittersDocument40 pagesModule 5 NeurotransmittersRAZZLE LOLONGNo ratings yet
- Regular Medications at WorkDocument2 pagesRegular Medications at Workdhw24162No ratings yet
- NeuropsychologyDocument76 pagesNeuropsychologybushra231100% (1)
- NeurotransmittersDocument12 pagesNeurotransmittersEya BaldostamonNo ratings yet
- How Drugs Affect the Nervous SystemDocument30 pagesHow Drugs Affect the Nervous SystemGwen De CastroNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemsDocument19 pagesPharmacology: Drugs Acting On The Central and Peripheral Nervous SystemsShun Reigh SumilangNo ratings yet
- Notes Pathophysio Serotonin: Basal GangliaDocument3 pagesNotes Pathophysio Serotonin: Basal GangliaSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Chemical Transmission in the Synapse: Neurotransmitters and ReceptorsDocument24 pagesChemical Transmission in the Synapse: Neurotransmitters and ReceptorslibreizanNo ratings yet
- نسخة ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC 2Document28 pagesنسخة ANTI-ARRHYTHMIC 2ManWol JangNo ratings yet
- CNS Stimulants PDFDocument7 pagesCNS Stimulants PDFZehra AmirNo ratings yet
- SCTL NeurotransmitterDocument32 pagesSCTL Neurotransmitternur qistina humaira zulkarshamsiNo ratings yet
- Describing Noradrenergic TransmissionDocument5 pagesDescribing Noradrenergic TransmissionKwadwo OwoaheneNo ratings yet
- L 2 Anatomy and Physiology of AddictionDocument62 pagesL 2 Anatomy and Physiology of AddictionSemeeeJunior100% (1)
- Neurobiological Theories of Mental DisordersDocument12 pagesNeurobiological Theories of Mental DisordersNovelyn Kaye Ramos CalanogaNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmitterDocument4 pagesNeurotransmitterVincent Lau Bi ShengNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants DrugsDocument2 pagesAntidepressants DrugsSony Montaño CañeteNo ratings yet
- Paychiatric NursingDocument7 pagesPaychiatric NursingJe Carmel Marie ElentorioNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Science Lecture 2Document34 pagesBehavioral Science Lecture 2Natia BadridzeNo ratings yet
- Dopaminergic Pathways - LAGDocument30 pagesDopaminergic Pathways - LAGalvinbb100% (1)
- NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageNeurotransmittersSai SubuNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument2 pagesDocxEvanNo ratings yet
- Current Treatment of Schizoaffective Disorder According To A Neuralnetwork 2157 7099 1000441Document5 pagesCurrent Treatment of Schizoaffective Disorder According To A Neuralnetwork 2157 7099 1000441Akhsay ChandraNo ratings yet
- Biological Treatments: Drug Treatment ChemotherapyDocument6 pagesBiological Treatments: Drug Treatment ChemotherapyAw AdivaraNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument5 pagesAnxiolyticsRawan AlshammaNo ratings yet
- Synapses and Neurotransmitters ExplainedDocument3 pagesSynapses and Neurotransmitters ExplainedYcky RheyNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters Implicated in Psychiatry: MENTOR-Dr. Lokesh Shekhawat Sir. PRESENTOR - Dr. Vibha TomarDocument79 pagesNeurotransmitters Implicated in Psychiatry: MENTOR-Dr. Lokesh Shekhawat Sir. PRESENTOR - Dr. Vibha Tomaranon_870875350100% (1)
- 2.1 Theories-and-Treatment-Biological ApproachDocument6 pages2.1 Theories-and-Treatment-Biological ApproachRogelle Fiehl ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Clinical ToxicologyDocument6 pagesClinical ToxicologyGrace MarinoNo ratings yet
- Neurotranssmitter Dan Efek Pada Organ ManusiaDocument3 pagesNeurotranssmitter Dan Efek Pada Organ ManusiaPANI78No ratings yet
- Major Neurotransmitters and Their FunctionsDocument29 pagesMajor Neurotransmitters and Their FunctionsashupathakaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Midterms Review UwuDocument11 pagesPharma Midterms Review UwuAJ BayNo ratings yet
- Kasus 3 No 4Document10 pagesKasus 3 No 4syahdanNo ratings yet
- Neurobiochemical Basis of Psychiatric DisorderDocument2 pagesNeurobiochemical Basis of Psychiatric DisorderMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Chemical Transmission at the SynapseDocument3 pagesChemical Transmission at the SynapseSJNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of FractureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Fracturemyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- Analogy Test With Answers PDFDocument13 pagesAnalogy Test With Answers PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- CUES CholeDocument9 pagesCUES Chole알파No ratings yet
- Analogy Test With Answers PDFDocument13 pagesAnalogy Test With Answers PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- Analogy Test With Answers PDFDocument13 pagesAnalogy Test With Answers PDFsaiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Therapy in Suspected Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument10 pagesOxygen Therapy in Suspected Acute Myocardial InfarctionPutri YunandaNo ratings yet
- Solving Radical Equations Step-by-StepDocument3 pagesSolving Radical Equations Step-by-StepJewel PottNo ratings yet
- Gordon's 11 Functional Health PatternsDocument1 pageGordon's 11 Functional Health PatternsTracy100% (37)
- Triage in Emergency DepartmentDocument25 pagesTriage in Emergency Departmenthatem alsrour91% (11)
- BP TakingDocument4 pagesBP Taking알파No ratings yet
- Measuring MatterDocument3 pagesMeasuring Matter알파No ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument25 pagesHealth AssessmentGovindaraju Subramani100% (1)
- The Impact of The Tax System On Health Insurance CoverageDocument2 pagesThe Impact of The Tax System On Health Insurance Coverage알파No ratings yet
- Docslide - Us - Drug Study FormatDocument2 pagesDocslide - Us - Drug Study Format알파No ratings yet
- LMV 014Document5 pagesLMV 014알파No ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Oncology PatientsDocument35 pagesNursing Care for Oncology Patients알파No ratings yet
- Nursing Care for Oncology PatientsDocument35 pagesNursing Care for Oncology Patients알파No ratings yet
- Approaching Disaster Management Through Social Learning 2010Document14 pagesApproaching Disaster Management Through Social Learning 2010알파No ratings yet
- PPP BCCDocument1 pagePPP BCC알파No ratings yet
- Pulmonary Mass Left Upper LobeDocument8 pagesPulmonary Mass Left Upper Lobe알파No ratings yet
- Oncology Nursing Management for Cancer Cell GrowthDocument3 pagesOncology Nursing Management for Cancer Cell Growth알파No ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction and Management in The PhilippinesDocument32 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction and Management in The PhilippinesErnan BaldomeroNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Maintenance of Patent AirwayDocument13 pagesFluids and Electrolytes: Maintenance of Patent Airway알파No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tuberculosis: PathogenesisDocument1 pageGastrointestinal Tuberculosis: Pathogenesis알파No ratings yet
- PPP - CholelithiasisDocument1 pagePPP - Cholelithiasis알파No ratings yet
- Filariasis 140310130022 Phpapp02Document18 pagesFilariasis 140310130022 Phpapp02알파No ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration MBA BrochureDocument7 pagesMaster of Business Administration MBA BrochureAnmol SadwalNo ratings yet
- Statistical PhysicsDocument4 pagesStatistical PhysicsRenan ZortéaNo ratings yet
- 2 The Crypt of Elder Hallow 2ndDocument13 pages2 The Crypt of Elder Hallow 2ndmike roulette100% (1)
- 0611CT1001net PDFDocument272 pages0611CT1001net PDFAdrian M FahriNo ratings yet
- Magh Bihu or Maghar DomahiDocument8 pagesMagh Bihu or Maghar Domahihackdarenot4No ratings yet
- Value-Added ProductsDocument7 pagesValue-Added ProductsTendai MutisiNo ratings yet
- Micro-Finance: 16 Principles of Grameen BankDocument5 pagesMicro-Finance: 16 Principles of Grameen BankHomiyar TalatiNo ratings yet
- BS 07579-1992 (1999) Iso 2194-1991Document10 pagesBS 07579-1992 (1999) Iso 2194-1991matteo_1234No ratings yet
- Teaching Profession: Lesson 2: General Domains of Teaching CompetenceDocument11 pagesTeaching Profession: Lesson 2: General Domains of Teaching CompetenceKris MontesNo ratings yet
- Press Release-HandoverDocument2 pagesPress Release-HandovermoblogNo ratings yet
- Technical Lead with 9 years' experience in .NET, Angular and AzureDocument2 pagesTechnical Lead with 9 years' experience in .NET, Angular and AzureModi SandeepNo ratings yet
- Igbe Religion's 21st Century Syncretic Response to ChristianityDocument30 pagesIgbe Religion's 21st Century Syncretic Response to ChristianityFortune AFATAKPANo ratings yet
- Document PDFDocument16 pagesDocument PDFnelson_herreraNo ratings yet
- Explosive Ordnance Disposal & Canine Group Regional Explosive Ordnance Disposal and Canine Unit 3Document1 pageExplosive Ordnance Disposal & Canine Group Regional Explosive Ordnance Disposal and Canine Unit 3regional eodk9 unit3No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 (Introductory Class)Document23 pagesLecture 1 (Introductory Class)Amara SoOmroNo ratings yet
- How To Install Elastix On Cloud or VPS EnviornmentDocument4 pagesHow To Install Elastix On Cloud or VPS EnviornmentSammy DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Quiz Microeconomics BECO201 Date 30/10/2017 Name: IDDocument5 pagesQuiz Microeconomics BECO201 Date 30/10/2017 Name: IDAA BB MMNo ratings yet
- Speidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.Document11 pagesSpeidel, M. O. (1981) - Stress Corrosion Cracking of Stainless Steels in NaCl Solutions.oozdemirNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Prevent Food SpoilageDocument30 pagesTechniques To Prevent Food SpoilageCourtney GrahamNo ratings yet
- CatalogueDocument36 pagesCataloguehgwlin100% (1)
- 03 IoT Technical Sales Training Industrial Wireless Deep DiveDocument35 pages03 IoT Technical Sales Training Industrial Wireless Deep Divechindi.comNo ratings yet
- Exam On Multiculturalism: - Acculturation Process of Immigrants From Central and Eastern Europe in SwedenDocument60 pagesExam On Multiculturalism: - Acculturation Process of Immigrants From Central and Eastern Europe in SwedenMarta santosNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Religious Beliefs Cosmology FilipinoDocument7 pagesIndigenous Religious Beliefs Cosmology FilipinoRegz GasparNo ratings yet
- Chem 6AL Syllabus Winter 2021Document5 pagesChem 6AL Syllabus Winter 2021John SmithNo ratings yet
- Calculating parameters for a basic modern transistor amplifierDocument189 pagesCalculating parameters for a basic modern transistor amplifierionioni2000No ratings yet
- StanadyneDocument1 pageStanadyneJunior IungNo ratings yet
- Awards and Honors 2018Document79 pagesAwards and Honors 2018rajinder345No ratings yet
- Exercise For FitnessDocument44 pagesExercise For FitnessSheena Mae Sube PoNo ratings yet
- Alat Studio Dan KomunikasiDocument14 pagesAlat Studio Dan Komunikasiraymon akbarNo ratings yet
- Annual Report-2018-19 (English)Document242 pagesAnnual Report-2018-19 (English)Alle de BeusNo ratings yet