100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views1 pageUnderstanding Structural Isomers
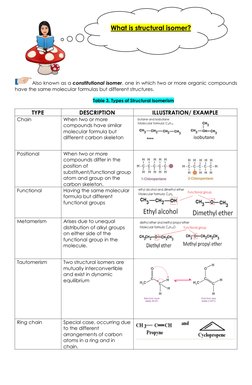
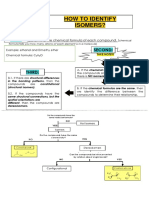
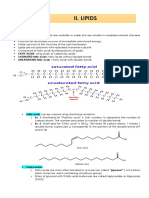
Structural isomers, also known as constitutional isomers, are organic compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures. There are several types of structural isomerism including chain, positional, functional, metamerism, tautomerism, and ring-chain isomers which differ based on variations in carbon skeleton arrangements, positions of substituents, and functional groups.
Uploaded by
Jam AicaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
6K views1 pageUnderstanding Structural Isomers
Structural isomers, also known as constitutional isomers, are organic compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structures. There are several types of structural isomerism including chain, positional, functional, metamerism, tautomerism, and ring-chain isomers which differ based on variations in carbon skeleton arrangements, positions of substituents, and functional groups.
Uploaded by
Jam AicaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Structural Isomers: Describes structural isomers, their different types, and provides examples of each type to illustrate the concept.