Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Day's Work PDF
Uploaded by
Mico YogoreOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Day's Work PDF
Uploaded by
Mico YogoreCopyright:
Available Formats
NAVIGATION
Day’s Work
During a day, a number of different courses and distances may be
planned for a trip. We can use the traverse table to quickly find
difference of latitude and departure of each individual leg, so the
total of difference of latitude and departure can be found. These total
difference of latitudes and departures are then applied to the initial
position to find the final position, or DR position.
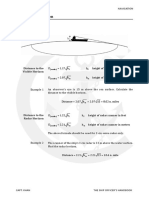
The figure above shows AB, BC, CD and DE are the courses and
distances, where A is the initial position and E is the final position.
AF is difference of latitude made good from initial position A to final
position E, so AF equals the difference of the sum of all difference
of latitudes of each leg that are named north, and the sum of all
difference of latitudes of each leg that are named south. Difference of
latitude AF will be named as the same name with the greatest sum.
In this case, all difference of latitudes are named south except DK,
which is named north.
AF = AH + BC + GD − DK
Similarly, EF is the difference of longitude from the initial position
A to the final position E. Therefore, EF equals the difference of the
sum of all difference of longitudes of each leg that are named west,
and the sum of all difference of longitudes of each leg that are named
east. In this case, difference of longitude of leg AB is named east,
difference of longitude of leg BC is zero, and difference of longitudes
of leg CD and DE are named west
EF = GC + EK − HB
CAPT. KHAN THE SHIP OFFICER’S HANDBOOK
NAVIGATION
Example 1 Using the above method, find the final position when a ship at
position 12°00´N. 110°00´E. steams the following courses and
distances:
Course 120°T 180°T 240°T 280°T
Distance 50 miles 30 miles 40 miles 50 miles
D. Lat. Departure
Course Distance
N S E W
120°T S60°E 50 miles 25.0 43.3
180°T S 30 miles 30.0
240°T S60°W 40 miles 20.0 34.6
280°T N80°W 50 miles 8.7 49.2
8.7 75.0 43.3 83.8
D. Lat. = 75.0′ − 8.7′ = 66.3′(S) = 1° 06.3′ (S)
= 83.8′ − 43.3
Dep. =′ 40.5′ (W)
Initial Latitude 12° 00.0′ N Mean Latitude =11° 26.9′ N
D. Lat. 1° 06.3′(S)
Final Latitude 10°53.7′ N
Dep. 40.5′ ( W )
=
D. Long = = 41.3′ ( W )
cos(Lat m ) cos11° 26.9′
Initial Longitude 110° 00.0′ E
D. Long. 41.3′(W)
Final Longitude 109°18.7′ E
Final position 10°53.7′ N 109°18.7′ E
If a current is setting, it can be treated as another course with the
drift as the distance.
CAPT. KHAN THE SHIP OFFICER’S HANDBOOK
NAVIGATION
Example 2 A ship at position 30°N 60°W steams the following courses and
distances:
Course 150°T 220°T 300°T
Distance 60 miles 30 miles 40 miles
Find the final position if the current is setting 045° with a drift of 12
miles.
D. Lat Departure
Course Distance
N S E W
150°T S 30° E 60 miles 52.0 30.0
220°T S 40° W 30 miles 23.0 19.3
300°T N 60° W 40 miles 20.0 34.6
045°T N 45° E 12 miles 8.5 8.5
28.5 75.0 38.5 53.9
= 75.0′ − 28.5
D. Lat. =′ 46.5′ (S )
= 53.9′ − 38.5
Dep. =′ 15.4′ ( W )
Initial Latitude 30° 00.0′ N Mean Latitude 29°36.8′ N
D. Lat. 46.5′(S)
Final Latitude 29°13.5′ N
Dep. 15.4′ ( W )
=
D. Long. = = 17.7′ W
cos (Lat m ) cos29°36.8′
Initial Longitude 60° 00.0′ W
D. Long. 17.7′( W )
Final Longitude 60°17.7′ W
Final position 29°13.5′ N 060°17.7′ W
CAPT. KHAN THE SHIP OFFICER’S HANDBOOK
You might also like
- 617-NI - 2018-01 Tugs Below 500 GTDocument8 pages617-NI - 2018-01 Tugs Below 500 GTwisnukerNo ratings yet
- Mud Barge Sea ChestDocument1 pageMud Barge Sea ChestAstri NgentNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument395 pagesManualrafael espinosa semperNo ratings yet
- Tugboat material list and drawingsDocument3 pagesTugboat material list and drawingsphankhoa83-1No ratings yet
- Antignano: LNG Terminal / Escort TugDocument3 pagesAntignano: LNG Terminal / Escort TugCovaci EduardNo ratings yet
- Brochure Damen Water Bus Range 04 2017Document4 pagesBrochure Damen Water Bus Range 04 2017Edwin FierroNo ratings yet
- Prediction Using NAVCADDocument2 pagesPrediction Using NAVCADspeedydogNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary ASD Tug 3213-12-2015Document16 pagesExecutive Summary ASD Tug 3213-12-2015Ernesto JuniorNo ratings yet
- Your Propulsion Experts: Nav Schottel NavigatorDocument8 pagesYour Propulsion Experts: Nav Schottel NavigatorMustafa TemelNo ratings yet
- Multipurpose Tug v3 1Document44 pagesMultipurpose Tug v3 1SKEPT.OMENOSNo ratings yet
- Deflection Measuringsystemfor Floating DrydocksDocument6 pagesDeflection Measuringsystemfor Floating DrydocksGermán AguirrezabalaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Paper Shallow Water Effect On Turning Motion of A Pusher Barge System Aphydro 2008Document8 pages3rd Paper Shallow Water Effect On Turning Motion of A Pusher Barge System Aphydro 2008kostas.michaNo ratings yet
- Tank Sounding Manual (MANUAL-T - 4681251 - 1 - A) - 1Document143 pagesTank Sounding Manual (MANUAL-T - 4681251 - 1 - A) - 1Hung LeNo ratings yet
- Naca Rudder HornDocument16 pagesNaca Rudder HornMuhammad Lukman100% (1)
- Stability CriteriaDocument7 pagesStability CriteriaSuperducksNo ratings yet
- SeaBoats ID1127Document14 pagesSeaBoats ID1127nipper7No ratings yet
- Volcanic Alliance Bro 200311 PDFDocument4 pagesVolcanic Alliance Bro 200311 PDFRexx MexxNo ratings yet
- Full Specific at in SD XviiDocument4 pagesFull Specific at in SD XviiLai QuocNo ratings yet
- Damen Year Book No1Document132 pagesDamen Year Book No1minhloc4100% (1)
- RudderDocument33 pagesRuddertribleprinceNo ratings yet
- Test II SM TableDocument9 pagesTest II SM TableMark Lester AndayaNo ratings yet
- Product Sheet Damen Modular Ferry 3710 Yn523024 08 2016Document2 pagesProduct Sheet Damen Modular Ferry 3710 Yn523024 08 2016leoschunckNo ratings yet
- Product Sheet Stan Tug 1606Document2 pagesProduct Sheet Stan Tug 1606Roda NiagaNo ratings yet
- 5 Longitudinal StreghtDocument24 pages5 Longitudinal StreghtSiOlyel Mst 'd-caLm'No ratings yet
- Effect of Resistance & Wake Distribution in Catamaran vs MonohullDocument52 pagesEffect of Resistance & Wake Distribution in Catamaran vs MonohullJEET BANERJEENo ratings yet
- Caisson Production On Floating DockDocument19 pagesCaisson Production On Floating DockThet Naung OoNo ratings yet
- Resistance Prediction of Cruising Motor Catamarans PDFDocument125 pagesResistance Prediction of Cruising Motor Catamarans PDFuchiiha_camiNo ratings yet
- Konstruksi Kapal IIDocument52 pagesKonstruksi Kapal IIVivin Novita Sari SuwaryonoNo ratings yet
- Main Ship Characteristics: Froude Number (FN)Document6 pagesMain Ship Characteristics: Froude Number (FN)Zakiah KartiniNo ratings yet
- MV AzzirDocument106 pagesMV AzzirDominic VillamanteNo ratings yet
- Damen Stan Tender 1504 "H 01"Document2 pagesDamen Stan Tender 1504 "H 01"younes-spiritNo ratings yet
- Anchor Chain Locker Volume CalculationDocument1 pageAnchor Chain Locker Volume Calculationbasant_konatNo ratings yet
- Aplicacion de Helices CicloidalesDocument51 pagesAplicacion de Helices CicloidalesMerrel RossNo ratings yet
- Sotra Anchor and ChainDocument164 pagesSotra Anchor and ChainX-Titan Wan de Pirates100% (2)
- Hiper2010 MelbourneDocument310 pagesHiper2010 MelbournemaciuluNo ratings yet
- 773optimization of Catamaran Demihull Form in Early Stages of The Design Process5-16925-1-Pb - 2Document6 pages773optimization of Catamaran Demihull Form in Early Stages of The Design Process5-16925-1-Pb - 2Muhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- STIX Formula R4Document3 pagesSTIX Formula R4lavrikNo ratings yet
- 800 BHP Twin-Screw Pusher Tug Robert Allan PRESUPUESTODocument38 pages800 BHP Twin-Screw Pusher Tug Robert Allan PRESUPUESTOFederico BabichNo ratings yet
- Du1388 - 2002 - Fire Control and Safety Plan - Rev.3-BvDocument1 pageDu1388 - 2002 - Fire Control and Safety Plan - Rev.3-Bvmohammad atallahNo ratings yet
- Truxor 09 ENG2 PDFDocument16 pagesTruxor 09 ENG2 PDFProjetos TonioloNo ratings yet
- Stability Info BookletDocument15 pagesStability Info BookletShailja ChetanNo ratings yet
- 03 DAMEN SY - High Speed in Severe Waves PDFDocument35 pages03 DAMEN SY - High Speed in Severe Waves PDFjohn kasichNo ratings yet
- Angle Steeldata PDFDocument2 pagesAngle Steeldata PDFRaj P. AbhaleNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0029801817301646 Main PDFDocument15 pages1 s2.0 S0029801817301646 Main PDFOdumoduChigozieUzomaNo ratings yet
- Vibration of Deckhouse StructuresDocument10 pagesVibration of Deckhouse StructuresrthyhtNo ratings yet
- PlaningDocument21 pagesPlaningAmalia CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Bavaria - 30 Cruiser BrochureDocument4 pagesBavaria - 30 Cruiser BrochureJason QuekNo ratings yet
- Ship Wheel PDFDocument18 pagesShip Wheel PDFCarlos LuizNo ratings yet
- SPRID 101.30 Equipment Number CalculationDocument2 pagesSPRID 101.30 Equipment Number CalculationTrường Bửu TrầnNo ratings yet
- Seakeeping LectureDocument30 pagesSeakeeping Lectureknowme73100% (1)
- Naval Architect Briefing on Ship Reference LinesDocument34 pagesNaval Architect Briefing on Ship Reference LinessufianNo ratings yet
- 2.0 - Design and Development of Steering System of ShipDocument24 pages2.0 - Design and Development of Steering System of ShipSandeep MandalNo ratings yet
- Service Floating Dock FacilitiesDocument8 pagesService Floating Dock FacilitiesosamaNo ratings yet
- 6500DWT tanker dimensions and offsets tableDocument2 pages6500DWT tanker dimensions and offsets tableSyafiq SyaridwanNo ratings yet
- An Experimental and Theoritical Study of Planning Surfaces With Trim Flaps PDFDocument63 pagesAn Experimental and Theoritical Study of Planning Surfaces With Trim Flaps PDFGhalih Rasyid Prayogo100% (1)
- CFD Analysis For Improved Hull Performance: Hydrodynamic ServicesDocument2 pagesCFD Analysis For Improved Hull Performance: Hydrodynamic ServicesDavid MestanzaNo ratings yet
- Hrs Rules For Small Craft 2010Document562 pagesHrs Rules For Small Craft 2010XthesinosNo ratings yet
- The Technical University of Norway: Norwegian Ship Model Experiment TankDocument56 pagesThe Technical University of Norway: Norwegian Ship Model Experiment TankDeepak PooranachandranNo ratings yet
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsFrom EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- GBC Quality Manual - Rev 2Document13 pagesGBC Quality Manual - Rev 2Mico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Activity/Area: References: Date:: Item Requirement Reference Findings Obs/NC RemarksDocument1 pageActivity/Area: References: Date:: Item Requirement Reference Findings Obs/NC RemarksMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- CS 2 - On Your BikeDocument1 pageCS 2 - On Your BikeMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Name Section Group Date: Lab/Activity# Nav4: Celestial NavigationDocument2 pagesName Section Group Date: Lab/Activity# Nav4: Celestial NavigationMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- CS - Complaints and Disputes - Rev 5Document3 pagesCS - Complaints and Disputes - Rev 5Mico YogoreNo ratings yet
- How To Extract GHA and DecDocument6 pagesHow To Extract GHA and DecMico Yogore100% (1)
- Internal Audit ReportDocument1 pageInternal Audit ReportMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- CS - Training and Competence - GBC-09Document1 pageCS - Training and Competence - GBC-09Mico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Hour Angle (Time Diagram)Document9 pagesHour Angle (Time Diagram)Mico Yogore100% (1)
- Internal Audit Plan TemplateDocument1 pageInternal Audit Plan TemplateMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Nautical AlmanacDocument7 pagesNautical AlmanacMico Yogore50% (2)
- Mercator Sailing PDFDocument3 pagesMercator Sailing PDFJavier RayleighNo ratings yet
- Equinoxes and Solstices - Micro TeachingDocument8 pagesEquinoxes and Solstices - Micro TeachingMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Latitude by PolarisDocument4 pagesLatitude by PolarisMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Sextant Altitude CorrectionsDocument21 pagesSextant Altitude CorrectionsMico Yogore100% (2)
- Load On DerricksDocument11 pagesLoad On DerricksShoaib hossainNo ratings yet
- Measuring celestial angles with a marine sextantDocument20 pagesMeasuring celestial angles with a marine sextantMico Yogore100% (1)
- Traverse TablesDocument9 pagesTraverse TablesNorris BaguioNo ratings yet
- Seamanship techniques for securing rope endsDocument6 pagesSeamanship techniques for securing rope endsMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Twin ScrewDocument1 pageTwin ScrewPraneel KurhadeNo ratings yet
- Distance of HorizonDocument1 pageDistance of HorizonShoaib hossainNo ratings yet
- Plane Sailing PDFDocument3 pagesPlane Sailing PDFRafael Sanchez Herrera100% (2)
- Ship Handling Principles PDFDocument3 pagesShip Handling Principles PDFClarence PieterszNo ratings yet
- Turning CirclesDocument2 pagesTurning CirclesClarence PieterszNo ratings yet
- Position Lines PDFDocument13 pagesPosition Lines PDFAgung Jr TeamElite ScreatCommunityNo ratings yet
- Chart Projections PDFDocument2 pagesChart Projections PDFMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Seamanship techniques for securing rope endsDocument6 pagesSeamanship techniques for securing rope endsMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Developmental PlansDocument4 pagesDevelopmental PlansMico YogoreNo ratings yet
- Parallel SailingDocument1 pageParallel SailingShoaib hossainNo ratings yet
- Blast Design Guide for Tunnelling ProjectsDocument17 pagesBlast Design Guide for Tunnelling Projectsseba1725No ratings yet
- Graham Cracker Erosion LabDocument6 pagesGraham Cracker Erosion LabbaileyNo ratings yet
- Omechanics Journey in The Western Part of East Java BasinDocument16 pagesOmechanics Journey in The Western Part of East Java BasinHerry SuhartomoNo ratings yet
- Histria 1Document3 pagesHistria 1Hustiuc RomeoNo ratings yet
- South America GK Quiz MCQs and AnswersDocument11 pagesSouth America GK Quiz MCQs and AnswersAbroo MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Pilgrimage To Hell: Death Lands Series Book #01Document335 pagesPilgrimage To Hell: Death Lands Series Book #01ajt9560% (5)
- Hydrocarbon Potential of the Trans Indus RangesDocument28 pagesHydrocarbon Potential of the Trans Indus Rangesjawad khanNo ratings yet
- Active Fault LinesDocument17 pagesActive Fault LinesAriane Blancada CuerquisNo ratings yet
- Landslide Locations and Vulnerability Assessment in Rs/Gis EnvironmentDocument3 pagesLandslide Locations and Vulnerability Assessment in Rs/Gis EnvironmentPushpendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- UB - SutamiDocument12 pagesUB - SutamiakahaaNo ratings yet
- DocDocument77 pagesDocsaopauloNo ratings yet
- Q1 Earth and Life Science 11 - Module 16Document19 pagesQ1 Earth and Life Science 11 - Module 16maricar relatorNo ratings yet
- Geological Investigation For Dams - MiMaEdDocument10 pagesGeological Investigation For Dams - MiMaEdJose Cuadros Loayza100% (1)
- Abbaszadeh Wu LiquefactionofGravellySoils USSD2018 FINALDocument15 pagesAbbaszadeh Wu LiquefactionofGravellySoils USSD2018 FINALMiguel BenítezNo ratings yet
- Block X: An Updated Summary of The Onshore Block in The Talara BasinDocument10 pagesBlock X: An Updated Summary of The Onshore Block in The Talara BasinCristhian Tupac Yupanqui100% (1)
- Lec-01-Anicent History (Stone Age) by JK Exam CrackerDocument8 pagesLec-01-Anicent History (Stone Age) by JK Exam CrackerAbidaah SuheebNo ratings yet
- The Soil and Rock Profiles On SiteDocument3 pagesThe Soil and Rock Profiles On Siteslawek780303No ratings yet
- Introduction To Soil Mechanics and FoundationsDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Soil Mechanics and FoundationsElmer RoseteNo ratings yet
- 1984-1986 Earthquake ReferencesDocument41 pages1984-1986 Earthquake ReferencesSisu StefanNo ratings yet
- 16821574626443af961de58coal Lignite 2021Document30 pages16821574626443af961de58coal Lignite 2021anuNo ratings yet
- VOLADURADocument412 pagesVOLADURAJorge Luis CJviba Vizarres BarrenacheaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Opportunities. Energising Growth.: Annual Report and Accounts For The Year EndedDocument136 pagesExploring Opportunities. Energising Growth.: Annual Report and Accounts For The Year EndedSohini ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Nepal: ArchitectureDocument37 pagesNepal: ArchitectureJoshua BumatayNo ratings yet
- 10 Highest Mountain in The PhilippinesDocument13 pages10 Highest Mountain in The PhilippinesRey MadelosoNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Earth Science SHSDocument19 pagesModule 2 Earth Science SHSJohn Vincent V MagulianoNo ratings yet
- 863 1113 1 PBDocument11 pages863 1113 1 PBAndriNo ratings yet
- Tanzurine, Cherry-Red and Emerald-Green Quartz From TanzaniaDocument9 pagesTanzurine, Cherry-Red and Emerald-Green Quartz From Tanzaniakelompok 3 XI MIPA 1No ratings yet
- LATIHANDocument19 pagesLATIHANNabil Jr.No ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Underground Station in Karstic LimestoneDocument4 pagesDesign and Construction of Underground Station in Karstic Limestonejinwook75No ratings yet