Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ans. Xanthelasma Answer Peripheral Cyanosis
Uploaded by
Jordan Abosama Mamalumpong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Quiz-3-Anatomy-of-the-heart (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesAns. Xanthelasma Answer Peripheral Cyanosis
Uploaded by
Jordan Abosama MamalumpongCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
SA node preload
Systole afterload
Murmurs xanthelasma
Depolarization Central cyanosis
Whooshing sound Peripheral cyanosis
Working cells sympathetic
Myometrium parasympathetic
Repolarization Gallop
Endometrium Wheeze
International normalized ratio
Baroreceptors
AV node
Automaticity
Myocardial ischemia
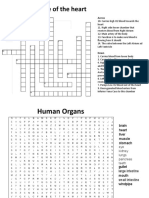
1.Period of ventricular contraction resulting in ejection of blood from the ventricles
into the pulmonary artery and aorta.
2.Primary pacemaker in the heart, located in the right atrium.
3.Muscle layer of the heart responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
4.Condition in which heart muscle cells receive less oxygen than needed.
5.Sounds created by abnormal, turbulent flow of blood in the heart
6.Ability to initiate an electrical impulse
7.Cardiac myocytes
8.A standard method for reporting prothrombin levels, eliminating the variation in
test results from laboratory to laboratory.
9.Return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry of potassium into the cell
while sodium exists the cell.
10.Nerve fibers located in the aortic arch & carotid arteries that are responsible for
reflex control of the BP
11. Degree of stretch of cardiac muscle fibers at the end of diastole Ans. Preload
12. a soft, yellowish, fatty deposit that forms under your skin.
Ans. Xanthelasma
13. Blue hands or feet Answer peripheral cyanosis
14. Releases two hormones within the body in response to stress, resulting in an
"adrenaline rush", or a sense of urgency that occurs during stressful conditions. Ans.
The sympathetic nervous system
15. An abnormal heart sound Ans. Gallop
Answers 1 to 10 of test I
1. Systole
2. SA node
3. Myometrium
4. Myocardial ischemia
5. Murmurs
6. Automaticity
7. Working cells
8. International normalized ratio
9. Repolarization
10. Baroreceptors
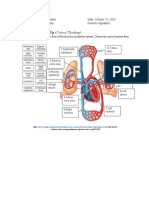
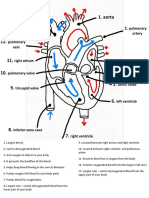
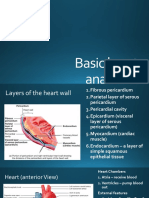
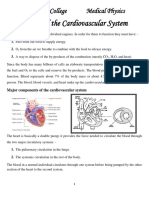
1. ntricleInferioe vena cava
2. Right atrium
3. Tricuspid valve or right
atrioventricular valve
4. Right ventricle
5. Pulmonary artery
6. Pulmonary vein
7. Left atrium
8. Bicuspid valve
9. Left ventricle
10. aorta
You might also like
- The Cardiovascular System ReviewDocument18 pagesThe Cardiovascular System ReviewDanisha Reeves100% (1)
- Quintinitarosalyn Module 1-Wk1respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesQuintinitarosalyn Module 1-Wk1respiratory Systemrosalyn quintinita60% (5)
- Cardiovascular Clinical ExaminationDocument27 pagesCardiovascular Clinical ExaminationAshiniNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular TestDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Testglai RamosNo ratings yet
- NAGA COLLEGE FOUNDATION ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORYDocument4 pagesNAGA COLLEGE FOUNDATION ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LABORATORYPado100% (1)
- PRELIM EXAM-SY 2020-2021 NCM-117: Fides Et ServitiumDocument6 pagesPRELIM EXAM-SY 2020-2021 NCM-117: Fides Et ServitiumJordan Abosama Mamalumpong100% (4)
- Lab Technologist 5Document42 pagesLab Technologist 5AHAMED SHIFAANNo ratings yet
- Cara Membaca CT ThoraxDocument43 pagesCara Membaca CT Thoraxeliana100% (3)
- DR Clarke Medicine Book 2020Document88 pagesDR Clarke Medicine Book 2020JJ100% (1)
- Firsr Periodical Test in Science - Grade VIDocument7 pagesFirsr Periodical Test in Science - Grade VIDennis Reyes83% (6)
- Past Years SNQ Answer by RCSIDocument47 pagesPast Years SNQ Answer by RCSIhelamahjoubmounirdmo100% (1)
- Brokenshire College Socsksargen, Inc.: Dandy C. Valin, RN, MN Clinical InstructorDocument19 pagesBrokenshire College Socsksargen, Inc.: Dandy C. Valin, RN, MN Clinical InstructorJordan Abosama Mamalumpong50% (2)
- Foramen of WinslowDocument3 pagesForamen of Winslowprinzzzy5No ratings yet
- Laboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesLaboratory Worksheet 12 Heart Structure and FunctionAndrea SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Sced 3204B LDocument5 pagesSced 3204B LEllen Grace Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Radley Miguel Adarlo - Module 1 Activities Lesson 4-6Document5 pagesRadley Miguel Adarlo - Module 1 Activities Lesson 4-6JK De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document9 pagesChapter 12Charlie AbagonNo ratings yet
- What To Do (Page 7)Document1 pageWhat To Do (Page 7)Victor Glenn SantosNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Bio400Document21 pages7.2 Bio400SHUHADA NURNo ratings yet
- 1020 Prac 4Document16 pages1020 Prac 4j.baldiNo ratings yet
- NKJD AnswersHeart and Mediastinum Images-1Document27 pagesNKJD AnswersHeart and Mediastinum Images-1intarebatinya32No ratings yet
- 2402 Model KeysDocument90 pages2402 Model KeysThrexsia SandeNo ratings yet
- Axia College Material: Identifying Anatomical Structures Ch. 3, 4, & 5Document3 pagesAxia College Material: Identifying Anatomical Structures Ch. 3, 4, & 5Robin PawleyNo ratings yet
- Local Media6090474202173155980Document2 pagesLocal Media609047420217315598013PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Laboratory 11Document8 pagesLaboratory 11Jc JardinicoNo ratings yet
- FiSIOLOGI JANTUNG ONI Pertemuan 4Document48 pagesFiSIOLOGI JANTUNG ONI Pertemuan 4Ria Fauziah SiswadiNo ratings yet
- 2Document9 pages2Oscar Angelo Jr.No ratings yet
- Axia College Material: Identifying Anatomical Structures Ch. 3, 4, & 5Document4 pagesAxia College Material: Identifying Anatomical Structures Ch. 3, 4, & 5jhall2924No ratings yet
- 2023 DEFIBRILLATOR 2PDocument58 pages2023 DEFIBRILLATOR 2Ptsarayuth1.2017No ratings yet
- BLOODDocument2 pagesBLOODNorhainaNo ratings yet
- Basic Ecg PP Tall SlidesDocument15 pagesBasic Ecg PP Tall SlidesAmmuNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Embryology - DR Radit PDFDocument37 pagesCardiac Embryology - DR Radit PDFCandice Lavigne100% (1)
- Structure of The Heart: AcrossDocument2 pagesStructure of The Heart: AcrossJessica PilamungaNo ratings yet
- HyayDocument4 pagesHyaySri nurjannah RifalNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Conduction System Power Point PresentationDocument30 pagesCardiac Conduction System Power Point PresentationAaya AdelNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY-Cardiovascular SystemDocument1 pageBIOLOGY-Cardiovascular SystemSilverNo ratings yet
- Exploring the Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesExploring the Circulatory SystemJamaica M DanguecanNo ratings yet
- Angiology: (Circulatory System)Document40 pagesAngiology: (Circulatory System)api-19641337100% (1)
- Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology Lab ActivitiesDocument1 pageNervous System Anatomy and Physiology Lab ActivitiesHowen AlejanNo ratings yet
- Heart Anatomy Exam 3Document4 pagesHeart Anatomy Exam 3Amar AlkhafajiNo ratings yet
- Pollen to Stigma, Circulatory Pathway, & RespirationDocument3 pagesPollen to Stigma, Circulatory Pathway, & RespirationCharlene Mae LazoNo ratings yet
- Subject 1 (Clock-Wise) Eye Movement Observation Subject 2 (Counterclockwise) Eye Movement Observation Subject 3 (Eyes Close) Eye Movement ObservationDocument6 pagesSubject 1 (Clock-Wise) Eye Movement Observation Subject 2 (Counterclockwise) Eye Movement Observation Subject 3 (Eyes Close) Eye Movement ObservationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- LAMPIRAN Embrio AyamDocument3 pagesLAMPIRAN Embrio AyamdidinNo ratings yet
- CV 2 PHDocument22 pagesCV 2 PHaya najemNo ratings yet
- 235 2024S U1 Circulatory VOCDocument52 pages235 2024S U1 Circulatory VOCNguyễn HùngNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System in ActionDocument28 pagesThe Cardiovascular System in ActionCharmen Evangelio Pabilona-FloresNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Laboratory Moving Exam Anatomical ModelsDocument14 pagesAnaPhy Laboratory Moving Exam Anatomical ModelsimmajinbuxoxoNo ratings yet
- Microscopic HSB ReviewDocument92 pagesMicroscopic HSB ReviewVictoria Tan100% (1)
- Practice Test: Biology: Body Fluids & Circulation For Live Session On 17-Nov-2018 On Neetprep Youtube ChannelDocument4 pagesPractice Test: Biology: Body Fluids & Circulation For Live Session On 17-Nov-2018 On Neetprep Youtube ChannelSamprita DuttaNo ratings yet
- Surface Marking-1Document4 pagesSurface Marking-1Sandip SatpathiNo ratings yet
- Check-List Praktikum Anatomi Blok 8 Cardiovaskular: Meja 1 - Bagian Luar JantungDocument5 pagesCheck-List Praktikum Anatomi Blok 8 Cardiovaskular: Meja 1 - Bagian Luar JantungMarthaLhtNo ratings yet
- Ontogeni Cor: Abd. Razak Datu Department of Anatomy Fac. of Medicine UnhasDocument43 pagesOntogeni Cor: Abd. Razak Datu Department of Anatomy Fac. of Medicine UnhasStefan CandraNo ratings yet
- Bowser DocumentDocument10 pagesBowser Documentأ. علي محمدNo ratings yet
- Organs of chickens, pigeons, male and female catfish, and male tilapiaDocument6 pagesOrgans of chickens, pigeons, male and female catfish, and male tilapiaAlfiah Sahraeni Julianti SalamNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System LectureDocument83 pagesCardiovascular System LectureJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- Essential anatomy for dissection assessmentsDocument3 pagesEssential anatomy for dissection assessmentsbnvjNo ratings yet
- EwanDocument1 pageEwanJamie Lynn Lee AbanillaNo ratings yet
- DMLT - 2023 Answer KeysDocument6 pagesDMLT - 2023 Answer KeysNishaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument58 pagesCardiovascular Systemsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For 2013-2014 Systematic Anatomy Final ExamDocument2 pagesAnswer Key For 2013-2014 Systematic Anatomy Final ExamsammyNo ratings yet
- Diah Ummul Nafisa - Pratikum IDKDocument10 pagesDiah Ummul Nafisa - Pratikum IDKDiah NafisaaNo ratings yet
- All-1Document388 pagesAll-1Natalie MuslehNo ratings yet
- 1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood VesselsDocument9 pages1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood Vessels13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnaphy ReviewerSamantha Joy VidalNo ratings yet
- Practical Applications of Cardiovascular AnatomyDocument5 pagesPractical Applications of Cardiovascular AnatomyJohn JanuaryNo ratings yet
- Pre Reading Cardio Vascular System AssessmentDocument10 pagesPre Reading Cardio Vascular System AssessmentShahbaz aliNo ratings yet
- Lab Exam 1Document184 pagesLab Exam 1Alana BolloneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Assistants of Physiology Physiology Department Medical Faculty, Moeslem Indonesia of UniversityDocument22 pagesCardiovascular System: Assistants of Physiology Physiology Department Medical Faculty, Moeslem Indonesia of UniversityAyu Yunita Jaury HRNo ratings yet
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideFrom EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideNo ratings yet
- Jordan Mamalumpong - NCM 116 Prelim Assignment 01Document1 pageJordan Mamalumpong - NCM 116 Prelim Assignment 01Jordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Mamalumpong Jordan A. Bsn-Iii Assignment: Date Published: November 6, 2020 Source: The Francis Crick InstituteDocument2 pagesMamalumpong Jordan A. Bsn-Iii Assignment: Date Published: November 6, 2020 Source: The Francis Crick InstituteJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Application of ParabolaDocument13 pagesApplication of ParabolaJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Families of ParabolaDocument12 pagesFamilies of ParabolaJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Assessing Older Adults' Health and FunctioningDocument11 pagesAssessing Older Adults' Health and FunctioningJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Jordan Mamalumpong - NCM 116 Prelim Assignment 01Document1 pageJordan Mamalumpong - NCM 116 Prelim Assignment 01Jordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Midterm Assignment 01Document1 pageNCM 116 Midterm Assignment 01Jordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Assessing Older Adults' Health and FunctioningDocument11 pagesAssessing Older Adults' Health and FunctioningJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Final Version of HIV ResearchDocument29 pagesFinal Version of HIV ResearchJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Case Study .Document2 pagesCase Study .Jordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Prelim Examination SECOND SEMESTER S.Y 2020-2021: Brokenshire College SOCSKSARGEN, IncDocument2 pagesPrelim Examination SECOND SEMESTER S.Y 2020-2021: Brokenshire College SOCSKSARGEN, IncJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Assignment ncm112 Oct 21Document3 pagesAssignment ncm112 Oct 21Jordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Brokenshire College Socsksargen, Inc.: Ced Avenue, Lagao, General Santos CityDocument2 pagesBrokenshire College Socsksargen, Inc.: Ced Avenue, Lagao, General Santos CityJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 RLE ASSIGNMENT SOLVINGDocument2 pagesNCM 112 RLE ASSIGNMENT SOLVINGJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Jordan A.Mamalumpong Bsn-3Document4 pagesJordan A.Mamalumpong Bsn-3Jordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: List of Enrolled PupilsDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: List of Enrolled PupilsJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Case Study .Document2 pagesCase Study .Jordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- AtenololDocument2 pagesAtenololJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Jordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryDocument11 pagesJordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Jordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryDocument11 pagesJordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- MAMALUMPONG JORDAN A. BSN-3 Literature ReviewDocument3 pagesMAMALUMPONG JORDAN A. BSN-3 Literature ReviewJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Jordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryDocument11 pagesJordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Jordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryDocument11 pagesJordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 RLE ASSIGNMENT SOLVINGDocument2 pagesNCM 112 RLE ASSIGNMENT SOLVINGJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Jordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryDocument11 pagesJordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Care For Adult AssessmentDocument5 pagesCare For Adult AssessmentJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 RLE ASSIGNMENT SOLVINGDocument2 pagesNCM 112 RLE ASSIGNMENT SOLVINGJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Somatom Volume Access Special Va40!04!00209670Document74 pagesSomatom Volume Access Special Va40!04!00209670carlosvladNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology Test PaperDocument3 pagesAnimal Physiology Test PaperRenjith Moorikkaran MNo ratings yet
- KP 1.3.2.1 Aktivitas Mekanik Jantung (2 Jam)Document68 pagesKP 1.3.2.1 Aktivitas Mekanik Jantung (2 Jam)Try MutiaraNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Question Paper Maharashtra HSC Class 12 Board Exam March 2019 PDFDocument3 pagesBIOLOGY Question Paper Maharashtra HSC Class 12 Board Exam March 2019 PDFBhavaniNo ratings yet
- Mitral Annular CalcificationDocument8 pagesMitral Annular CalcificationJiawei ZhouNo ratings yet
- 0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument10 pages0610 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachershiNo ratings yet
- TURTLE DISSECTION LAB Provides Insights Into Reptile AnatomyDocument7 pagesTURTLE DISSECTION LAB Provides Insights Into Reptile AnatomyDemetra AlbescuNo ratings yet
- Angina PostprandialDocument10 pagesAngina PostprandialJoaquín SosaNo ratings yet
- Ehac237 Supplementary DataDocument112 pagesEhac237 Supplementary DataGeoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ExplainedDocument3 pagesCirculatory System ExplainedJjongNo ratings yet
- Left Vs Right: Heart FailureDocument3 pagesLeft Vs Right: Heart FailureRosalinda PerigoNo ratings yet
- NCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionDocument128 pagesNCM103 - 2016 - Lecture2 - Response To Altered Respiratory FunctionrimeoznekNo ratings yet
- IAS AneurysmDocument13 pagesIAS AneurysmE'len HamidahNo ratings yet
- 2023 Super Mock Int. Science 1Document5 pages2023 Super Mock Int. Science 1Maame AgyeiwaaNo ratings yet
- Failure of Weaning:: According To The European Respiratory Society (ERS) Task ForceDocument12 pagesFailure of Weaning:: According To The European Respiratory Society (ERS) Task ForceAmr El Taher0% (1)
- Types of ShocksDocument33 pagesTypes of Shocksmark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsDocument5 pagesPhysiology of The Normal Heart: Key PointsGustavo TejerinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document17 pagesChapter 27Jessica nonyeNo ratings yet
- Mathematical and Physical Models of A Total Artificial HeartDocument6 pagesMathematical and Physical Models of A Total Artificial HeartBishal UchilNo ratings yet
- Through The Human HeartDocument14 pagesThrough The Human HeartAsemed AsemedNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Cardiovascular System: Dentistry College Medical PhysicsDocument10 pagesPhysics of The Cardiovascular System: Dentistry College Medical PhysicsMustafa MustafaNo ratings yet
- Brief History of High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) HistoryDocument4 pagesBrief History of High Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) Historybacharelado2010No ratings yet
- 9700 s13 QP 13Document16 pages9700 s13 QP 13Muhammad ShahzebNo ratings yet