0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views4 pagesEnglish Grammar Guide for Serbs
This document provides a grammar handbook covering:
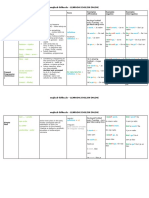
1) Time expressions like when, then, by, by the time, already, and before.
2) The past perfect tense which is used to refer to actions that occurred before other past actions.
3) The past perfect continuous tense which emphasizes that a past action was ongoing.
4) Various ways to express the future in English including the future simple with will, be going to, the present continuous, future continuous, and future perfect.
Uploaded by
SerpanaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
77 views4 pagesEnglish Grammar Guide for Serbs
This document provides a grammar handbook covering:
1) Time expressions like when, then, by, by the time, already, and before.
2) The past perfect tense which is used to refer to actions that occurred before other past actions.
3) The past perfect continuous tense which emphasizes that a past action was ongoing.
4) Various ways to express the future in English including the future simple with will, be going to, the present continuous, future continuous, and future perfect.
Uploaded by
SerpanaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd