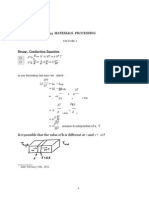
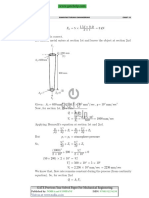
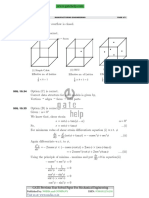
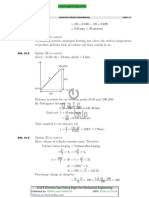
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
θ t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t
θ t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
θ t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t
θ t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t t
Uploaded by
SameerChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
www.gatehelp.
com
PAGE 342 HEAT TRANSFER CHAP 7
(th1 − tC2) − (th2 − tC1) (t − t ) − (th2 − th1) 2 (th1 − th2)
θmc = = h1 h2 = ...(i)
ln :th1 − tC2 D ln :th1 − th2 D ln :th1 − th2 D
th2 − tC1 t h2 − t h1 t h2 − t h1
(B) For parallel flow given : th1 = tC 2 , th 2 = tC 1
LMTD , θmp = θ1 − θ2
ln b θ1 l
θ2
(t − t ) − (th2 − tC2) (t − t ) − (th2 − th1) 2 (th1 − th2)
θmp = h1 C1 = h1 h2 = ...(ii)
t − t
ln : h1 C1 D t − t
ln : h1 h2 D ln :th1 − th2 D
th2 − tC2 t h2 − t h1 t h2 − t h1
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
θmc = θmp
SOL 7.47 Option (D) is correct.
Given : F13 = 0.17
Applying summation rule :
F11 + F12 + F13 = 1
The flat surface cannot see itself.
So, F11 = 0
This gives, F12 = 1 − F11 − F13 = 1 − 0 − 0.17 = 0.83
SOL 7.48 Option (C) is correct.
S. No. Materials Thermal Conductivity (W/m − K)
1. Aluminum 237
2. Pure Iron 80.2
3. Liquid Water 0.607
4. Saturated Water Vapour 0.026
**********
GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical Engineering
Published by: NODIA and COMPANY ISBN: 9788192276250
Visit us at: www.nodia.co.in
You might also like
- Heat Transfer-23Document1 pageHeat Transfer-23SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer-15 PDFDocument1 pageHeat Transfer-15 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer-15 PDFDocument1 pageHeat Transfer-15 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- P Q y T X T P y Q X y T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument2 pagesP Q y T X T P y Q X y T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- θ θ θ θ θ θ θ θ x θ θ θ θ x θ θ θ x θ θ x θ: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument1 pageθ θ θ θ θ θ θ θ x θ θ θ θ x θ θ θ x θ θ x θ: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment 1 - Ersa Berliana - 04211941000041Document6 pagesHome Assignment 1 - Ersa Berliana - 04211941000041roberto luckyNo ratings yet
- F A A d rl π π d rl: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument3 pagesF A A d rl π π d rl: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document6 pagesAssignment 2Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems Laboratory: ECE131L/B5/4Q1920Document7 pagesFeedback and Control Systems Laboratory: ECE131L/B5/4Q1920Brandon Malabanan100% (1)
- 2019-ME-127 Exp.4 HMT LabDocument11 pages2019-ME-127 Exp.4 HMT LabZeeshan AliNo ratings yet
- Fouriour SeriesDocument39 pagesFouriour SeriesHerberTNo ratings yet
- CLL261-Dynamic Characteristics of More Complicated Process: Hariprasad Kodamana Iit DelhiDocument24 pagesCLL261-Dynamic Characteristics of More Complicated Process: Hariprasad Kodamana Iit DelhiGARGI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Signals Approximation, 2 NfcietDocument7 pagesSignals Approximation, 2 Nfcietapi-19788618No ratings yet
- Ee4501f18 HW 7Document3 pagesEe4501f18 HW 7al-muntheral-mairikiNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas of Two-State AtomsDocument4 pagesIdeal Gas of Two-State AtomsrujintoNo ratings yet
- Control Systems: Module No.: 01Document13 pagesControl Systems: Module No.: 01Tetsuya OkazakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Mathematical Modeling of ProcessDocument10 pagesChapter Three Mathematical Modeling of ProcessNaeemo IraqiNo ratings yet
- Dsa S8Document11 pagesDsa S8ergrehgeNo ratings yet
- Taller Cuatro Análisis de SistemasDocument5 pagesTaller Cuatro Análisis de SistemasCarlosNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment1 PDFVuyoNo ratings yet
- Conduction-Convection Systems: HPDX (T T)Document8 pagesConduction-Convection Systems: HPDX (T T)Nihad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Digital PID For DC Motor ControlDocument7 pagesDigital PID For DC Motor ControlMohsensorNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Two Wheel Balancing RobotDocument7 pagesModeling of Two Wheel Balancing RobotAbdullah AhmedNo ratings yet
- Finite Differerence Temp 2DDocument6 pagesFinite Differerence Temp 2DOkan EryilmazNo ratings yet
- Polytropic EfficienciesDocument4 pagesPolytropic EfficiencieshamidNo ratings yet
- E T σ Q A A A T T ε ε ε ε σ: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument1 pageE T σ Q A A A T T ε ε ε ε σ: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note About Non Harmonic MotionDocument6 pagesLecture Note About Non Harmonic MotionYasir LoneNo ratings yet
- X T K Q: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument2 pagesX T K Q: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Lezione11 - MoltiplicazioneMatrici - Teoremi GeneraliDocument24 pagesLezione11 - MoltiplicazioneMatrici - Teoremi GeneralismegmusNo ratings yet
- Option Valuation Methods (2017-04-20)Document2 pagesOption Valuation Methods (2017-04-20)Andrew JohnNo ratings yet
- Nda (Maths) Mock Test - 62 (Solution)Document7 pagesNda (Maths) Mock Test - 62 (Solution)Gurpreet GabaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For John e Freunds Mathematical Statistics With Applications 8 e Miller MillerDocument11 pagesSolution Manual For John e Freunds Mathematical Statistics With Applications 8 e Miller MillerStevenRobertsonideo100% (36)
- Chapter2 2Document39 pagesChapter2 2hailegebreselassie24No ratings yet
- TD Analyse 2Document31 pagesTD Analyse 2عالم السعادة- World HappinessNo ratings yet
- Assign 8 SolnDocument5 pagesAssign 8 SolnabaytekinovicNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Algorithms: Prof. Shafi GoldwasserDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Algorithms: Prof. Shafi GoldwasserUtsav BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument30 pagesChapter 4 PDFAram Nasih MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chap4 CourseDocument24 pagesChap4 CourseAbdul rahman WahidNo ratings yet
- Dsa Q8Document7 pagesDsa Q8sanskritiNo ratings yet
- Fem 3Document14 pagesFem 3tilahun yeshiyeNo ratings yet
- Mugi Maula Muttaqin - 3334190034 - METFISB - TUGASPENURUNANFIKS2Document4 pagesMugi Maula Muttaqin - 3334190034 - METFISB - TUGASPENURUNANFIKS2Mugi MaulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 1Document38 pagesChapter2 1hassen miberNo ratings yet
- Known Closed Forms For QuantsDocument12 pagesKnown Closed Forms For Quantsapi-3729160100% (1)
- 28 July Shift I PhysicsDocument4 pages28 July Shift I PhysicsVortexLolNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer - SolutionDocument27 pagesHeat Transfer - SolutionNeeleshNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Algorithms (SET: 2) SolutionsDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Algorithms (SET: 2) SolutionsergrehgeNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument46 pagesAttachmentaaaNo ratings yet
- Fluctuation-Dissipation TheoremDocument2 pagesFluctuation-Dissipation TheoremGunnar CalvertNo ratings yet
- CS 141 Homework 1: Problem 1Document5 pagesCS 141 Homework 1: Problem 1tilahunNo ratings yet
- ACS132 ACS1321 Instructions and Data Sheet 2020-21Document6 pagesACS132 ACS1321 Instructions and Data Sheet 2020-21EJAZ AHMADNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document9 pagesChapter 9Nagamani NunavathNo ratings yet
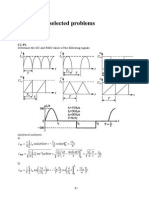
- Solutions To Selected Problems C1-C3Document12 pagesSolutions To Selected Problems C1-C3Prichindel MorocanosNo ratings yet
- P Q y T X T P y Q X y T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageP Q y T X T P y Q X y T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Soluzionea 010915Document3 pagesSoluzionea 010915Pietro TestaNo ratings yet
- MCQ 18ce310 Fourier Series and Partial Differential EquationsDocument8 pagesMCQ 18ce310 Fourier Series and Partial Differential EquationsGnanarajNo ratings yet
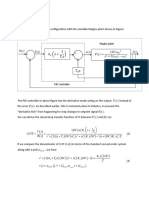
- Theory: Maglev PlantDocument3 pagesTheory: Maglev PlantPraveen RathodNo ratings yet
- 4 Recurrence and Master TheoremDocument37 pages4 Recurrence and Master TheoremHarshit RoyNo ratings yet
- 3.044 Materials Processing: ρ c T ρ c kDocument8 pages3.044 Materials Processing: ρ c T ρ c kAlejandroNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-55Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-55SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-54Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-54SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- F D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageF D T D T: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Processes Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4Document1 pageProcesses Associated State of Stress P. 3. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 4SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-46Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-46SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-53Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-53SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- α 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1Document1 pageα 12c t t φ r r α α t φ φ: Machining process Mechanism of material removal P. 2. Q. 3. R. 4. S. 1SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- For Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageFor Metal: Atomic Weight Valency The Metal Removal Rate: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-52Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-52SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-51Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-51SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-48Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-48SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- ADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inDocument1 pageADE Δ θ DE x x θ x x Z d x: Visit us at: www.nodia.co.inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Column I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageColumn I Column II P. 4. Q. 1. R. 2. S. 3.: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- A N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 pageA N B N VT A VT B VT: Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-45Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-45SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-40Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-40SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-38Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-38SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Solution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveDocument1 pageSolution: Metal Forming Process Types of Stress 1. S. Compressive 2. P. Tensile 3. Q. Shear 4. R. Tensile and CompressiveSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-28 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-28 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringDocument1 pageVisit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - In: GATE Previous Year Solved Paper For Mechanical EngineeringSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- 175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inDocument1 page175 MM 200 MM 200 MM 10 MM 10 / Ms : Visit Us At: WWW - Nodia.co - inSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-34Document1 pageManufacturing Engineering-34SameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-30 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-30 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-31 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-31 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-29 PDFDocument1 pageManufacturing Engineering-29 PDFSameerChauhanNo ratings yet