Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peripherally Acting Analgesics
Uploaded by
sharenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peripherally Acting Analgesics
Uploaded by
sharenCopyright:
Available Formats
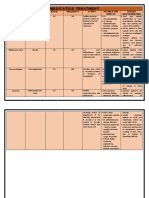
Peripherally Acting Analgesics (non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs : NSAID)
Drugs Therapeutic effects Therapeutics uses Adverse effects
Salicyclates a. Anti-inflammatory actions: Due to inhibition a. Na salicyclate, choline salicyclate, choline Mg a. GI: epigastric distress, nausea, vomiting, microscopic GI bleeding
(Aspirin, of CO activity and PG synthesis (neither arrest salicyclate and aspirin : anti-pyretics and b.Blood: reduce level of platelet TXA2 leads to inhibition of platelet aggregation
Choline Mg progression nor induce remission of inflamm) analgesics in treatment of gout, rheumaric (prolonged bleeding time, thus shouldn’t be taken 1 week before surgery)
Salicyclates, b.Analgesic actions: PGE2 sensibilize nerve fever, rheumatoid arthritis and to inhibit c. Respiration: in toxic dose: respiratory depression with uncompensated respiratory
Diflunisal) endings to the action of bradykinin and platelet aggregation (headache, arthralgia, and metabolic acidosis
histamine released during inflamm, thus myalgia) d.Metabolic processes: in toxic dose cause uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation
inhibit PG inhibit sensation of pain b.Salicyclic acid: treat corns, calluses and leads to E wasting as heat (pyretic effects)
c. Antipyretic action: inhibits PGE2 synthesis epidermophytosis (eruption caused by fungi) e. Hypersensitivity: urticaria, bronchoconstriction, angioneurotic edema
and release by thermoregulatory centers of ant c. Salicylamide: analgesic and sedative f. Reye’s syndrome (if given during viral infection): is an fatal fulminating hepatitis
hypothalamus, also increase heat dissipation preparations with cerebral edema
by vasodilation action d.Methyl salicyclate: cutaneous counterirritant g.Drug’s interaction: produce undesirable side effects
d.Respiratory actions: act on resp centers cause in liniments h.Salicylism (salicyclate intoxication) includes
hyperventilation and resp alkalosis e. Diflunisal: 4x more potent than aspirin as i. Nausea
e. GI effects: PGI2 inhibits gastric secretion and analgesic and anti-inflammatory agents (but ii. Vomiting
PGE2 and PGF2 stimulate synthesis of has no antipyretic effects and thus cannot relief iii. Marked hyperventilation
protective mucus, thus inhibition of PG fever) iv. Headache
increased acid secretion and diminished mucus f. Low dose aspirin: transient ischemic attack v. Mental confusion
protection leads to epigastric distress, and unstable angina vi. Dizziness
ulceration and hemorrhage vii. Tinnitus (ringing in ears)
f. Effects on platelets: i. In severe salicylism
g.Effects on kidney: PGE2 and PGI2 maintain i. All listed above (i-vii)
renal blood flow, thus inhibition of PG result ii. Restlessness
in water and Na retention leads to edema and iii. Delirium
hyperkalemia. (interstitial nephritis may iv. Hallucination
occurs with all NSAIDs except aspirin) v. Convulsions
vi. Coma
vii. Resp and metabolic acidosis
viii. Death due to resp failures
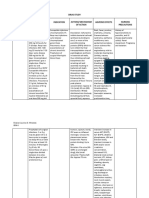
Phenylbutazone a. Powerful anti-inflammatory effect a. Short-term therapy of acute gout and acute a. Poorly tolerated (thus should be given for short period of time)
b.Weak analgesic and antipyretic effects rheumatoid arthritis when other NSAID agents b.Nausea, vomiting, skin rashes and epigastric distress
have failed c. Fluid and electrolyte retention with edema and increased urine volume
d.Diarrhea, vertigo, insomnia, blurred vision, euphoria, nervousness and hematuria
e. Reduce uptake of I2 by thyroid gland result in goiter and myxedema
f. Agranulocytosis and aplastic edema
Indomethacin a. Anti-inflammatory effects (more potent than a. Control pain associated with uveitis and a. GI: nausea, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea, abdominal pain, ulceration of upper GI tract
aspirin) postoperative ophthalmic pain with perforation and hemorrhage
b.Antipyretic effects b.Antipyretic for Hodgkin disease b.CNS: frontal headache, dizziness, vertigo, light headache, mental confusion
c. Analgesics effects c. Effective anti-inflammatory agents in acute c. Acute pancreatitis, hepatitis and jaundice
gouty arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and d.Hematopoietic reactions: neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia
osteoarthritis of the hip) e. Hypersensitivity reactions: rashes, urticaria, itching, acute attack of asthma, 100%
cross reactivity with aspirin
Sulindac a. Analgesic effects a. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing Similar to other NSAIDs but less severe
b.Anti-inflammatory effects (but less potent spondylitis, osteoarthritis, acute gout
than indomethacin)
Ibuprofen a. Analgesic effects Hypersensitivity reaction
(related drugs: b.Anti-inflammatory effects (same potency as GI disturbances (but better tolerated than aspirin)
naproxen, aspirin)
ketoprofen and c. Antipyretic effects
fenoprofen)
Piroxicam Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosis GI disturbances
(t1/2 : 45hrs, spondylitis and osteoarthritis)
thus admin
once per day)
Ketorolac
Non-Narcotic Analgesics
Acetaminophen a. Antipyretic and analgesic effects (due to a. Substitute for analgesic and antipyretic effects a. Do not cause physical dependent or tolerance
Phenacetin inhibition of PG synthesis in CNS) of aspirin in patients with gastric complaints, b.Skin rash and minor allergic reaction (rare)
b.Weak anti-inflammatory effects (due to less prolongation of bleeding time or those do not c. Minor alteration in leukocyte counts
effect on cyclooxygenase in peripheral tissue) require anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin d.Transient renal tubular necrosis and hypoglycemic coma (in prolonged large-dose
c. Do not affect platelet fx, do not increase b.Choice for children with viral infection or therapy)
blood clotting time chicken pox (coz aspirin enhance Reye e. In overdose may cause hepatic necrosis (treatment: admin N-acetylcysteine which
syndrome) toxic metabolite can bind) [in normal doses, toxic metabolites are bind to glutathione
c. Can be used in patient with gout coz don’t forming non-toxic substances]
antagonize urisonic agent (e.g probenecid)
You might also like
- DISC-GO-DEVIL ManualDocument10 pagesDISC-GO-DEVIL Manualpeterl@discgotech.com100% (2)
- Horse Riding Manual - Kings FarmDocument40 pagesHorse Riding Manual - Kings FarmRihanna JNo ratings yet
- Shaking and Stiffness in The Extremities, More Present On The Left SideDocument20 pagesShaking and Stiffness in The Extremities, More Present On The Left SidesharenNo ratings yet
- A Feasibility Study On Flappy Eggs in Barangay MesaoyDocument49 pagesA Feasibility Study On Flappy Eggs in Barangay Mesaoydantoy86100% (1)
- 2nd Test Drugs FinalDocument23 pages2nd Test Drugs FinalWissam DadiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJIESEL ACEBEDONo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetaminophen: Generic NameDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Acetaminophen: Generic Namebobo gamingNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- Patient'S Name: Chris Jhon Ruz Bed No: 155 DX: PneumoniaDocument5 pagesPatient'S Name: Chris Jhon Ruz Bed No: 155 DX: Pneumoniatanene08No ratings yet
- DrugstudyDocument2 pagesDrugstudyacissej_o3No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesMrLarry DolorNo ratings yet
- Prctmol OkDocument1 pagePrctmol OkSethlyn_Gomez_5337No ratings yet
- Paracetamol (Alvedon) Acetylcysteine Fluimucil KCL (Kalium Durule)Document1 pageParacetamol (Alvedon) Acetylcysteine Fluimucil KCL (Kalium Durule)Jesse James Advincula EdjecNo ratings yet
- Antiviral and Antitubercular Student'sDocument38 pagesAntiviral and Antitubercular Student'sapril jholynna garroNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyLorelyn FabrigarasNo ratings yet
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocument3 pagesDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- 4 AutacoidsDocument9 pages4 AutacoidsAli EllaffiNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Drugs Study - 3rdrotationDocument15 pagesDrugs Study - 3rdrotationDette CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ParacetamolDocument4 pagesDrug Study - ParacetamolMary Grace VillegasNo ratings yet
- XtendaDocument2 pagesXtendaAlexis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Cotrimoxazole, AllopurinolDocument6 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Cotrimoxazole, Allopurinolpaupaulala89% (9)
- Group Work FeliciaDocument3 pagesGroup Work FeliciaFELICIA KASIMUNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - Para, Plasil, CiprofloxacinDocument5 pagesDRUG STUDY - Para, Plasil, CiprofloxacinrhegellNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument1 pageParacetamoljennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesDrug Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Adverse Effect Indication Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesJoshua Davantes100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studylilac_jasminNo ratings yet
- IX. Drug StudyDocument1 pageIX. Drug StudykingpinNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyDocument6 pagesNeonatal Sespsis - Drug StudyAlvincent D. BinwagNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyUzziah Dharambai GurbuxaniNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study. PTB. DMDocument5 pagesDrugs Study. PTB. DMsowkieNo ratings yet
- Medication TreatmentDocument2 pagesMedication TreatmentCute AkoNo ratings yet
- CNS: Siezures (High Doses) GI: Pseudomembranous,: Helicobacter PyloriDocument5 pagesCNS: Siezures (High Doses) GI: Pseudomembranous,: Helicobacter Pylorir_cyrusNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyKarl KiwisNo ratings yet
- AtherosclerosisDocument5 pagesAtherosclerosisLance SilvaNo ratings yet
- B. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsDocument12 pagesB. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsSienaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyTheresa Reyes De JesusNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NRMFDocument3 pagesDrug Study NRMFandreaNo ratings yet
- Fluimucil TabletDocument21 pagesFluimucil TabletJammilaKateDakayNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication /contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument10 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication /contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJohnmark PascuaNo ratings yet
- Name Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Generic: Captopril MIDocument4 pagesName Classificatio N Action Indication Contraindicati ON Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities Generic: Captopril MIHarvey BanagNo ratings yet
- GoutDocument4 pagesGoutapi-3822433100% (1)
- Anti Inflammatory Revised VersionDocument12 pagesAnti Inflammatory Revised VersionVictor Joshua De LeonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Study TramadolKersey Adricula RicaldeNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument1 pageParacetamolcen janber cabrillos100% (1)
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology LectureDocument18 pagesPharmacology LectureChloe MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Indomethacin: By: Hedy Mae Bautista and Ana Francesca JacintoDocument10 pagesIndomethacin: By: Hedy Mae Bautista and Ana Francesca JacintoAna FrancescaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/ Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesJohnrick VenturaNo ratings yet
- Significant: BullousDocument6 pagesSignificant: BullousMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Drud Study Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesDrud Study Skin IntegrityVimae TayaoNo ratings yet
- Treatment/Medications: By: Nadine M. Mico & Michael Christian DionisioDocument9 pagesTreatment/Medications: By: Nadine M. Mico & Michael Christian DionisioMikes CastroNo ratings yet
- DIPHENHYDRAMINEDocument4 pagesDIPHENHYDRAMINEJoevence Gazo CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument9 pagesGeneric Name Dosage / Frequency Action Side Effects Nursing Responsibilityorhocelo6908No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudymalindaNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancreatitis DKA HHNSDocument4 pagesAcute Pancreatitis DKA HHNSAna Rose Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MARCOS, ARIAN MAY S. DRUG STUDY BSN 2faDocument10 pagesMARCOS, ARIAN MAY S. DRUG STUDY BSN 2faArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification & Indication Dose, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesDrug Classification & Indication Dose, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiestristanpaulNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyasthenia Gravis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nonunion of FracturesDocument43 pagesNonunion of FracturessharenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument31 pagesUntitledsharenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledsharenNo ratings yet
- Case Scenario: - HistoryDocument35 pagesCase Scenario: - HistorysharenNo ratings yet
- Medical Faculty: Division For Foreign Student With Instruction Conduct in EnglishDocument17 pagesMedical Faculty: Division For Foreign Student With Instruction Conduct in EnglishsharenNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Aneurysm: Mohamed Mamdouh Al-BannaDocument31 pagesCerebral Aneurysm: Mohamed Mamdouh Al-BannasharenNo ratings yet
- Case Stydy Angina PectorisDocument46 pagesCase Stydy Angina PectorissharenNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Spine Disease. Back Pain Syndrome. Special Features of Diagnostic and TreatmentDocument150 pagesDegenerative Spine Disease. Back Pain Syndrome. Special Features of Diagnostic and TreatmentsharenNo ratings yet
- Meninggococcal InfDocument14 pagesMeninggococcal InfsharenNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis Osteoarthrosis Degenerative Joint Disease: Prof. Dr. Ülkü AkarırmakDocument53 pagesOsteoarthritis Osteoarthrosis Degenerative Joint Disease: Prof. Dr. Ülkü AkarırmaksharenNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion 2 - TB in Children: Picture of CPG CoverDocument46 pagesCase Discussion 2 - TB in Children: Picture of CPG CoversharenNo ratings yet
- Management of Severe Respiratory Failure in Complex Trauma PatientsDocument9 pagesManagement of Severe Respiratory Failure in Complex Trauma PatientssharenNo ratings yet
- Mied Study Loan Application Form: Student Name: Institution Course Type: DiplomaDocument9 pagesMied Study Loan Application Form: Student Name: Institution Course Type: DiplomasharenNo ratings yet
- Multifetal Pregnancy: Amr Nadim, MDDocument36 pagesMultifetal Pregnancy: Amr Nadim, MDsharenNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Spine Disease. Back Pain Syndrome. Special Features of Diagnostic and TreatmentDocument150 pagesDegenerative Spine Disease. Back Pain Syndrome. Special Features of Diagnostic and TreatmentsharenNo ratings yet
- Case HistoryDocument10 pagesCase HistorysharenNo ratings yet
- Final Project - A STUDY OF GROWTH PROSPECTS OF ONLINE REATAILORS AND E-COMMERCE IN INDIADocument94 pagesFinal Project - A STUDY OF GROWTH PROSPECTS OF ONLINE REATAILORS AND E-COMMERCE IN INDIAhariiNo ratings yet
- 22.examradar Com Data Communication Transmission Mode Simplex Half Duplex Full Duplex McqsDocument5 pages22.examradar Com Data Communication Transmission Mode Simplex Half Duplex Full Duplex McqsTushar SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Select The Best Earthing SystemDocument7 pagesHow To Select The Best Earthing SystemdedeerlandNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Tankvision NXA820, NXA821, NXA822Document16 pagesTechnical Information Tankvision NXA820, NXA821, NXA822Jhon Anderson Arango Rodriguez100% (1)
- BUFFALO MiniStation HD-PCU2 Manual DiskformatterDocument90 pagesBUFFALO MiniStation HD-PCU2 Manual DiskformatterfrankmdNo ratings yet
- Industry Report Blockchain Real Estate: Fibree 2021Document164 pagesIndustry Report Blockchain Real Estate: Fibree 2021chen mlNo ratings yet
- Marketing Seg PosDocument17 pagesMarketing Seg PosRameshKatakeNo ratings yet
- Epic AP Calculus Formul Sheet AB Derivatives Limits IntegralsDocument2 pagesEpic AP Calculus Formul Sheet AB Derivatives Limits IntegralsZacharyNo ratings yet
- Alhawity 2019Document6 pagesAlhawity 2019Briant TSNo ratings yet
- CRRP ProposalDocument28 pagesCRRP ProposalDennis MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Ancient Civilizations ProjectDocument3 pagesAncient Civilizations Projectapi-263663934No ratings yet
- HDS AMS2500 - Getting Started GuideDocument36 pagesHDS AMS2500 - Getting Started GuidejemonterrosaNo ratings yet
- 25 Cerpen Bahasa InggrisDocument26 pages25 Cerpen Bahasa InggristhukulfotocopydanprintingNo ratings yet
- Technological University (Mandalay) Department of Electrical Power EngineeringDocument24 pagesTechnological University (Mandalay) Department of Electrical Power EngineeringThankyou ThankyouNo ratings yet
- Understanding Blockchain Technology: August 2018Document8 pagesUnderstanding Blockchain Technology: August 2018Dhana SekarNo ratings yet
- Resit Coursework Assignment Brief MKT744 June 2022Document2 pagesResit Coursework Assignment Brief MKT744 June 2022Aryjeet K.No ratings yet
- Venn Diagram: Walk The Extra Smile (Answers)Document3 pagesVenn Diagram: Walk The Extra Smile (Answers)Antony Cortes100% (4)
- Topic 4 - Implementing HRD ProgrammeDocument20 pagesTopic 4 - Implementing HRD ProgrammeHassan SallehNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Practice 3. Observation and Comparison of Cells Under A Light Microscope.Document9 pagesLaboratory Practice 3. Observation and Comparison of Cells Under A Light Microscope.Andrea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Term 2 - Grade - VI - Science - P1 2018Document16 pagesTerm 2 - Grade - VI - Science - P1 2018Bhawana SinghNo ratings yet
- Numerical Metods Chapter 1 & 2Document35 pagesNumerical Metods Chapter 1 & 2Naren Sundararajan100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of ComputersDocument4 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Computerschris ayumaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer From Finned SurfacesDocument12 pagesHeat Transfer From Finned SurfacesandersonNo ratings yet
- Business Research Methods: Fourth EditionDocument39 pagesBusiness Research Methods: Fourth EditionMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Novozymes Bioprep® Fusion: Easy and Reliable Pre-Treatment of Cotton KnitsDocument2 pagesNovozymes Bioprep® Fusion: Easy and Reliable Pre-Treatment of Cotton KnitsSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- English8 q2 Mod3of5 Comparingandcontrasting-Multimodal-Texts v2Document26 pagesEnglish8 q2 Mod3of5 Comparingandcontrasting-Multimodal-Texts v2Kimberly Marie Aban PaderaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Precious Metal Refineries v4Document12 pagesLaboratory and Precious Metal Refineries v4Amb B. R. PersadNo ratings yet