Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EM - 2a Série - 2018-1b-2b - Apostila - Passado Simples - Diversity
Uploaded by
Carolina CordeiroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EM - 2a Série - 2018-1b-2b - Apostila - Passado Simples - Diversity
Uploaded by
Carolina CordeiroCopyright:
Available Formats
CEd GISNO - NOTURNO - ENSINO MÉDIO - 1º e 2º BIMESTRES - INGLÊS Prof.
: ANDRÉ DA MATA
Nome: ________________________________________________________________
2ª Série Data: _____ / _____ / 2018
PASSADO SIMPLES – FORMA AFIRMATIVA
(SIMPLE PAST – AFFIRMATIVE FORM)
Examplos: VERBO
INFINITIVO
PASSADO PARTICÍPIO
TRADUÇÃO
PRINCIPAL SIMPLES PASSADO
1) He watched TV last Sunday. REGULAR to watch watched watched assistir
2) They went to the club yesterday.
IRREGULAR to go went gone ir
ESTRUTURA Usa-se a FORMA DE PASSADO SIMPLES DO VERBO
PRINCIPAL.
Os VERBOS REGULARES fazem o passado simples
acrescentado-se “ED” ao final do verbo.
PASSADO SIMPLES DO Os VERBOS IRREGULARES não seguem nenhuma
SUJEITO +
VERBO PRINCIPAL regra, isto é, cada um tem uma FORMA PRÓPRIA DE
PASSADO. Consultar lista de verbos irregulares no fim da
apostila ou usar um dicionário.
VERBO PRINCIPAL – VERBO REGULAR VERBO PRINCIPAL - VERBO IRREGULAR
PASSADO PARTICÍPIO PASSADO PARTICÍPIO
INFINITIVO TRADUÇÃO INFINITIVO TRADUÇÃO
SIMPLES PASSADO SIMPLES PASSADO
to watch watched watched assistir to go went gone ir
I watched I went
You watched You went
He watched He went
She watched She went
It watched It went
We watched We went
You watched You went
They watched They went
ATENÇÃO: AGUARDAR AS ORIENTAÇÕES DO PROFESSOR EM SALA PARA RESPONDER OS EXERCÍCIOS.
EXERCÍCIO A: Complete as frases abaixo com o passado simples do verbo principal entre parênteses:
1) I _______________ a car yesterday. (to buy – bought – bought) NO DICIONÁRIO
rain [rein]: n. chuva // v.
chover
2) He _____________ by plane last year. (to travel – traveled – traveled)
Quando não há informação
alguma da forma de passado
3) You _____________ a pretty girl yesterday. (to know – knew – known) na definição, o verbo é
regular, basta acrescentar
ED no final.
4) It _______________ a lot last week. (to rain – rained – rained)
buy [bai]: n. compra // v. (p.
e p.p. bought) comprar
5) They _____________ for 12 hours last night. (to sleep – slept – slept) Observe que na definição da
palavra, há a informação da
6) We _______________ a lot last year. (to work – worked – worked) forma de passado (v. (p. e
p.p. bought)), portanto, a
palavra é um verbo
7) She _______________ the exercises last class. (to do – did – done) irregular*.
* consultar lista de verbos
8) You ____________ at the club last weekend. (to be – was/were - been) irregulares na página 5.
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -1- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 1º Bimestre - 2ª Série -2- Inglês - Passado Simples
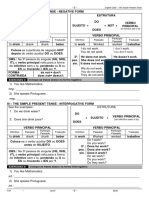
II) PASSADO SIMPLES – FORMA NEGATIVA (SIMPLE PAST – NEGATIVE FORM)
Examplos: VERBO
INFINITIVO
PASSADO PARTICÍPIO
TRADUÇÃO
PRINCIPAL SIMPLES PASSADO
1) He did not watch TV last Sunday.
REGULAR to watch watched watched assistir
2) They did not go to the club yesterday.
IRREGULAR to go went gone ir
ESTRUTURA
Coloca-se verbo auxiliar “DID”, sem tradução, mais a
VERBO
partícula de negação “NOT” antes do INFINITIVO
SUJEITO + DID + NOT + PRINCIPAL
(NO INFINITIVO DO VERBO PRINCIPAL sem o “TO”.
SEM O “TO”)
1. He didn’t watch TV last Sunday.
FORMA
did not = didn’t Ex.:
CONTRAÍDA 2. They didn’t go to the club yesterday.
VERBO PRINCIPAL – VERBO REGULAR VERBO PRINCIPAL - VERBO IRREGULAR
PASSADO PARTICÍPIO PASSADO PARTICÍPIO
INFINITIVO TRADUÇÃO INFINITIVO TRADUÇÃO
SIMPLES PASSADO SIMPLES PASSADO
to watch watched watched assistir to go went gone ir
CONJUGAÇÃO NORMAL FORMA CONTRAÍDA CONJUGAÇÃO NORMAL FORMA CONTRAÍDA
I did not watch I didn’t watch I did not go I didn’t go
You did not watch You didn’t watch You did not go You didn’t go
He did not watch He didn’t watch He did not go He didn’t go
She did not watch She didn’t watch She did not go She didn’t go
It did not watch It didn’t watch It did not go It didn’t go
We did not watch We didn’t watch We did not go We didn’t go
You did not watch You didn’t watch You did not go You didn’t go
They did not watch They didn’t watch They did not go They didn’t go
EXERCÍCIO B: Reescreva as frases abaixo na forma negativa. O verbo principal está entre parênteses.
1) We saw the movie last weekend. (to see - saw - seen)
neg.: __________________________________________________________________________
2) He worked until 9 o’ clock pm yesterday. (to work - worked - worked)
neg.: __________________________________________________________________________
3) They had a dinner party yesterday. (to have – had – had)
neg.: __________________________________________________________________________
4) She watched the movie last week. (to watch – watched – watched)
neg.: __________________________________________________________________________
5) You learned English last year. (to learn – learned – learned) / (usar forma contraída)
neg.: __________________________________________________________________________
6) I told my girlfriend the truth yesterday. (to tell – told – told) / (usar forma contraída)
neg.: __________________________________________________________________________
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -2- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 1º Bimestre - 2ª Série -3- Inglês - Passado Simples
III – PASSADO SIMPLES – FORMA INTERROGATIVA (SIMPLE PAST – INTERROGATIVE FORM)
Examplos: VERBO
INFINITIVO
PASSA DO PARTICÍPIO
TRADUÇÃO
PRINCIPAL SIMPLES PASSADO
1) Did he watch TV last Sunday?
REGULAR to watch watched watched assistir
2) Did they go to the club yesterday?
IRREGULAR to go went gone ir
ESTRUTURA Coloca-se verbo auxiliar “DID”, sem tradução,
ANTES DO SUJEITO. O VERBO PRINCIPAL fica no
VERBO PRINCIPAL
DID + SUJEITO + (NO INFINIVO SEM O “TO”) INFINITIVO sem a partícula “TO”.
VERBO PRINCIPAL – VERBO REGULAR VERBO PRINCIPAL - VERBO IRREGULAR
PASSADO PARTICÍPIO PASSADO PARTICÍPIO
INFINITIVO TRADUÇÃO INFINITIVO TRADUÇÃO
SIMPLES PASSADO SIMPLES PASSADO
to watch watched watched assistir to go went gone ir
Did I watch? Did I go?
Did you watch? Did you go?
Did he watch? Did he go?
Did she watch? Did she go?
Did it watch? Did it go?
Did we watch? Did we go?
Did you watch? Did you go?
Did they watch? Did they go?
EXERCÍCIO C: Reescreva as frases abaixo na forma interrogativa. O verbo principal está entre parênteses.
1) We saw the movie last weekend. (to see - saw - seen)
int.: ____________________________________________________________________________
2) He worked until 9 o’ clock pm yesterday. (to work - worked - worked)
int.: ____________________________________________________________________________
3) They had a dinner party yesterday. (to have – had – had)
int.: ____________________________________________________________________________
4) She watched the movie last week. (to watch – watched – watched)
int.: ____________________________________________________________________________
5) You learned English last year. (to learn – learned – learned)
int.: ____________________________________________________________________________
6) I told my girlfriend the truth yesterday. (to tell – told – told)
int.: ____________________________________________________________________________
IMPORTANTE: A forma “DID”, além de funcionar como verbo auxiliar do passando simples em frases interrogativas e
negativas, pode ser usado em frases afirmativas desse tempo verbal. Neste caso, o verbo auxiliar “DID”, além de indicar
que a frase está no passado, apesar do verbo principal manter sua forma de infinitivo sem o “TO”, funciona como
elemento enfático, com o significado de REALMENTE, DE FATO.
Ex.: They did like the movie yesterday.
Eles realmente gostaram do filme ontem.
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -3- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 1º Bimestre - 2ª Série -4- Inglês - Passado Simples
EXERCÍCIO D: Complete as frases abaixo com o PASSADO SIMPLES do verbo principal entre parênteses:
1) They ______________ to do the homework. (to try – tried – tried) ADVÉRBIOS DE TEMPO
2) He _____________ the homework correctly. (to do – did – done) yesterday = ontem
the day before yesterday =
anteontem
3) She ______________ a letter yesterday. (to write – wrote – written) last week (month, year) =
semana (mês, ano) passada
4) They ______________ late last night. (to arrive – arrived – arrived) … ago = atrás, há tempo
EXERCÍCIO E: Reescreva as frases abaixo na forma negativa. O verbo principal está entre parênteses.
1) We went to the movies last weekend. (to go – went – gone) ATENÇÃO
Observe que, com o
n.: ______________________________________________________________ uso do verbo auxiliar
“DID” para fazer a
2) She traveled by plane last year. (to travel – traveled – traveled) forma negativa, o
verbo principal volta
n.: ______________________________________________________________ para sua forma de
infinitivo sem a
3) I did the exercises last class. (to do - did - done) partícula “TO”.
n.: ______________________________________________________________
EXERCÍCIO F: Reescreva as frases abaixo na forma interrogativa. O verbo principal está entre parênteses.
1) We went to the movies last weekend. (to go – went – gone) ATENÇÃO
Observe que, com o
i.: ______________________________________________________________ uso do verbo auxiliar
“DID” para fazer a
2) She traveled by plane last year. (to travel – traveled – traveled) forma Interrogativas,
o verbo principal
i.: ______________________________________________________________ volta para sua forma
de infinitivo sem a
3) I did the exercises last class. (to do - did - done) partícula “TO”.
i.: ______________________________________________________________
EXERCÍCIO G: Traduza as frases abaixo para o PORTUGUÊS.
1) He went to the school yesterday.
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
2) I played soccer two hours ago.
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
3) We did not answer the English exercise correctly.
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
4) Did it rain hard last month?
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
EXERCÍCIO H: Traduza as frases abaixo para o INGLÊS usando o PASSADO SIMPLES.
1) Choveu forte anteontem.
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
2) Vocês responderam o exercício de inglês ontem.
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
3) Eu não joguei futebol domingo passado.
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
4) Eles foram ao clube mês passado?
res.: ___________________________________________________________________________
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -4- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 1º Bimestre - 2ª Série -5- Inglês - Passado Simples
EXERCÍCIO I: Marque apenas uma opção nas questões abaixo:
1) Sabendo que “to play – played – played” é o verbo 3) (GV-SP) A: When did she ___?
“jogar”, marque a opção que completa a seguinte
B: She left yesterday.
frase com o passado simples desse verbo:
a) left
“We ____ soccer last weekend.”
b) live
a) to play c) lived
b) play d) leaves
c) played e) leave
d) will play
e) would play
4) (UFMA) “I did the test all over again” means I:
2) Marque a opção com a forma negativa da seguinte
frase: “You went to the disco a week ago.” a) destroyed it
b) redid it
a) You went to the disco a week ago?
c) undid it
b) Did you go to the disco a week ago?
d) did it repeatedly
c) Did You went to the disco a week ago?
d) Do you go to the disco a week ago?
LISTA DE VERBOS IRREGULARES
REF. INFINITIVO PASSADO SIMPLES PASSADO PARTICÍPIO TRADUÇÃO
1 to be was / were been ser estar
2 to become became become tornar-se
3 to bring brought brought trazer
4 to buy bought bought comprar
5 to do did done fazer
6 to find found found achar
7 to get got got conseguir
8 to get up got up got up levantar, acordar
9 to go went gone ir
10 to have had had ter
11 to hit hit hit bater, acertar
12 to hold held held segurar
13 to know knew known conhecer, saber
14 to leave left left sair, partir
15 to meet met met encontrar-se
16 to put put put colocar
17 to run ran run corer
18 to see saw seen ver
19 to sleep slept slept dormir
20 to speak spoke spoke Falar
21 to spend spent spent gastar, passer
22 to swim swam swum nadar
23 to take took taken pegar,tomar
24 to teach taught taught ensinar
25 to tell told told falar, contra
26 to write wrote written escrever
ATENÇÃO: O verbo “TO BE” – apesar de constar na lista de verbos irregulares, pois to be – was/were – been
possui as formas “WAS” e “WERE” de passado simples – não aceita o verbo auxiliar
afir.: I was late. afir.: They were busy.
“DID” para formar as estruturas negativas e interrogativas. Com esse verbo, a negativa é
Ex.: neg.: I was not late. neg.: They were not busy.
feita com a própria forma de passado simples mais a partícula “NOT”, enquanto que na
int.: Was I late? int.: Were they busy?
interrogativa, basta colocar a própria forma de passado simples antes do sujeito.
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -5- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 2º Bimestre - 2ª Série -6- Inglês - Vocabulário, Compreensão e Interpretação de Texto
2º BIMESTRE | Nome: ____________________________________________________________
ENEM 2013 ✓ Leia o texto abaixo e responda as questões A a F (com adaptações).
Do one thing for diversity and inclusion GLOSSÁRIO
1 The United Nations Alliance of Civilizations 1. about = sobre
(UNAOC) is launching a campaign aimed at engaging 2. action = ação
3. aimed at = destinada a
3 people around the world to Do One Thing to support 4. all = todos
Cultural Diversity and Inclusion. Every one of us can 5. around = em todo o,ao redor, pelo
6. art = arte, de arte
5 do ONE thing for diversity and inclusion; even one 7. become = tornar-se
very little thing can become a global action if we all 8. campaign = campanha
9. can = pode, poder
take part in it.
10. celebrate = comemorar, celebrar
8 Simple things YOU can do to celebrate the 11. celebration = celebração
12. cultures = culturas
World Day for Cultural Diversity for Dialogue and
13. dedicated = dedicado
Development on May 21: 14. development = desenvolvimento
11 1. Visit an art exhibit or a museum dedicated to other 15. dialogue = diálogo
16. different = diferente, diferentes
cultures. 17. diversity = diversidade
2. Read about the great thinkers of other cultures. 18. even = até mesmo
19. every = cada
14 3. Visit a place of worship different than yours and
20. exhibit = exposição
participate in the celebration. 21. great = grandes
22. If = se
4. Spread your own culture around the world and learn
23. inclusion = inclusão
17 about other cultures. 24. learn = aprenda, aprender
5. Explore music of a different culture. 25. little = pequeno, pequena
26. May 21 = 21 de maio
19 There are thousands of things that you can do, 27. museum = museu
are you taking part in it? 28. of us = de nós
29. one = um, uma
30. own = próprio, própria
UNITED NATIONS ALLIANCE OF CIVILIZATIONS. Disponível em:
31. participate = participe, participar
www.unaoc.org. Acesso em: 16 fev. 2013 (adaptado).
32. people = pessoas
33. spread = espalhe, espalhar
34. support (to support) = apoiar
35. take part in = participar de, fazer parte
de
36. taking part in = participando de
37. The United Nations Alliance of
Civilizations (UNAOC) = Aliança das
Organizações das Nações Unidas
38. thousands = milhares
39. very = muito
40. visit = visite, visitar
41. world = mundo, do mundo, mundial
42. yours = do seu
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -6- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 2º Bimestre - 2ª Série -7- Inglês - Vocabulário, Compreensão e Interpretação de Texto
ATENÇÃO: AGUARDAR AS ORIENTAÇÕES DO PROFESSOR EM SALA PARA RESPONDER OS EXERCÍCIOS.
A) Combine as colunas com base no significado das palavras do texto da página anterior:
( 1 ) do ( ) coisa, coisas
( 2 ) engaging (engage) ( ) culto (religioso), de culto
( 3 ) launching (launch) ( ) envolver
( 4 ) other ( ) fazer, faça
( 5 ) place ( ) há
( 6 ) read ( ) lançando
( 7 ) there are (there is) ( ) leia, ler
( 8 ) thing, things ( ) lugar
( 9 ) thinkers ( ) outro, outra, outros, outras
( 10 ) worship ( ) pensadores
✓ Na questão B, escreva V (verdadeiro) ou F (falso) em cada item.
B) De acordo com o texto da página anterior:
1. ( ) Trata-se de uma campanha da Organização das Nações Unidas para a Educação, a
Ciência e a Cultura.
2. ( ) Para participar da campanha, você deve, por exemplo, ler sobre os grandes pensadores da
cultura de outros países.
✓ Na questão C, escreva V (verdadeiro) ou F (falso) em cada item.
C) De acordo com o texto da página anterior:
1. ( ) You must listen to music of other cultures to take part in the campaign.
2. ( ) There is only one thing that you can do to take part in the campaign.
✓ Na questão D, responda EM PORTUGUÊS de acordo com o texto da página anterior.
D) Quais locais, por exemplo, você pode visitar para participar da campanha?
✓ Na questão E, responda EM INGLÊS de acordo com o texto da página anterior.
E) What is the UNAOC launching?
✓ Na questão F, MARQUE apenas UM item de acordo com o texto da página anterior.
F) (ENEM 2013) Internautas costumam manifestar suas opiniões sobre artigos on-line por
meio da postagem de comentários. O comentário que exemplifica o engajamento proposto
na quarta dica da campanha apresentada no texto é:
1. ( ) “Lá na minha escola, aprendi a jogar capoeira para uma apresentação no Dia da
Consciência Negra.”
2. ( ) “Outro dia assisti na TV uma reportagem sobre respeito à diversidade. Gente de todos os
tipos, várias tribos. Curti bastante.”
3. ( ) “Eu me inscrevi no Programa Jovens Embaixadores para mostrar o que tem de bom em
meu país e conhecer outras formas de ser.”
4. ( ) “Curto muito bater papo na internet. Meus amigos estrangeiros me ajudam a aperfeiçoar
minha proficiência em língua estrangeira.”
5. ( ) “Pesquisei em sites de culinária e preparei uma festa árabe para uns amigos da escola.
Eles adoraram, principalmente, os doces!”
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -7- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 2º Bimestre - 2ª Série -8- Inglês - Vocabulário, Compreensão e Interpretação de Texto
CESPE/UnB – 1º VEST. 2005 ✓ Leia o texto abaixo e responda as questões de A a F (com adaptações).
PLATO: IDEAS AND CONTRIBUTIONS A) Combine as colunas de acordo com o texto:
1 Plato was born into a wealthy (1) appetite ( ) crenças
Athenian family and planned to become a (2) beliefs ( ) desejo, prazer
politician. As he grew older, he became (3) death ( ) razão
4 repulsed by the brutal and unethical (4) reason ( ) morte
practices of Athenian dictators. In 399 B.C. (5) soul ( ) vontade
he left Athens when his friend Socrates was (6) will ( ) alma
7 sentenced to death. Twelve years later, he
B) Escreva V (verdadeiro) ou F (falso) de acordo o texto.
founded a school of philosophy and science 1 . Platão ficou famoso por seus diálogos escritos.
called the Academy, the first university. 2 . O passado de Platão como uma criança pobre lhe deu
10 Plato is famous for his written dialogues, uma forte motivação para fundar a Academia.
conversations between two or more 3 . Platão se tornou um político extraordinário.
characters debating philosophical issues. 4 . Platão dividiu a alma em três partes: razão, vontade e
13 His earliest dialogues utilize Socrates as the desejo.
main character who questions others on
their beliefs and ideas. C) Escreva V (verdadeiro) ou F (falso) de acordo o texto.
16 Plato’s philosophy was based on 1 . Plato argued that the parts of the soul work independently
his theory of a soul divided into three from each other.
components, reason, will and appetite. He 2 . During Plato’s days, Athenian dictators lacked moral
19 contended that one can identify the parts of principles.
the soul because they sometimes clash with 3 . Plato used dialogs as a way to put his ideas across.
each other. A person may crave or have an 4 . Plato became an Athenian dictator.
appetite for something, yet resist the
23 craving with willpower. A correctly operating MARQUE a ÚNICA alternativa CORRETA de acordo com o texto:
soul requires the highest part, reason, to D) Sobre a filosofia de Platão:
1 . A razão é a parte mais vil, mais baixa.
control the lowest part, appetite, with
2 . O desejo é a parte mais elevada, mais alta.
assistance from the will.
3 . A razão, com assistência da vontade, controla o desejo.
Fonte: Cespe/UnB – 1º vest. 2005 (com adaptações)
4 . Nos diálogos escritos de Platão, os personagens
GLOSSARY
as = à medida que, como based on = baseadas no
discutem assuntos religiosos.
called = chamada, denominada became = tornou-se
characters = personagens because = porque, pois
contended = argumentou, become = tornar-se E) Responda EM PORTUGUÊS de acordo com o texto:
contendeu between = entre Como foi chamada e o que foi a primeira universidade?
crave = almejar, desejar clash = entrar em conflito
debating = debatendo craving = desejo
____________________________________________________
earliest = mais recentes founded = fundou ____________________________________________________
later = mais tarde, depois friend = amigo
left = abandonou, saiu da issues = assuntos ____________________________________________________
operating soul = alma ativa main = principal
the highest = a mais elevada older = mais velho
the lowest = a mais vil, baixa others = os outros F) Responda EM INGLÊS de acordo com o texto:
unethical = antiético planned = planejou
willpower = força de vontade questions = questiona What does a correctly operating soul require?
with each other = umas com school = escola ____________________________________________________
as outras someone = qualquer um
written dialogues = diálogos was born = nasceu ____________________________________________________
escritos wealthy = rica
yet = portanto
____________________________________________________
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -8- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 2º Bimestre - 2ª Série -9- Inglês - Música
Ouça o áudio da música em inglês abaixo (coluna da esquerda), responda os exercícios (coluna
MÚSICA:
da direita) e complete os espaços em branco da letra da música (coluna da esquerda):
JUST THE WAY YOU ARE EXERCISES
1 Oh, her eyes, her eyes ✓ Ouça o áudio, marque uma opção e complete
corretamente os espaços em branco da música à esquerda:
Make the stars look like they're not shining
3 Her __________1, her __________1 1) Na linha 3, o substantivo (nome) “cabelo:”
Falls perfectly without her trying a) here
b) hair
5 She's so _______________2
2) Na linha 5, o adjetivo “bonita”:
And I tell her every day
a) wonderful
7 Yeah, I know, I know b) beautiful
__________3 I compliment her 3) Na linha 8, o advérbio “quando”:
She won't believe me a) when
10 And it's so, it's so b) where
Sad to think that she don't see what I see 4) Na linha 12, o presente simples do verbo
12 4
But every time she __________ me "Do I look okay?" “perguntar” (to ask – asked – asked):
a) ask
I say
b) asks
14 When I see your face
5) Na linha 15, a condicional simples do verbo
There's not a thing that I ______________5 “mudar” (to change – changed – changed):
'Cause you're amazing a) will change
17 Just the way you are b) would change
And when you _____________6,
6) Na linha 18, o presente simples do verbo
The whole world stops and stares for a while “sorrir” (to smile – smiled – smiled):
20 'Cause girl you__________7 amazing a) to smile
Just the way you are b) smile
22 Her __________8, her __________8 7) Na linha 20, o presente simples do verbo “ser
9
I could __________ them all day if she let me ou estar” (to be – was/were – been):
a) ‘s
24 Her laugh, her laugh
b) ‘re
She hates but I __________10 it's so sexy
8) Na linha 22, o substantivo (nome) “lábios”:
26 She's so _______________2 a) lips
And I tell her every day b) tips
28 Oh, you know, you know, you know 9) Na linha 23, o verbo “beijar”:
I'd never ask you to change a) kiss
30 If perfect is what you______________11 for b) miss
Then just stay the same 10) Na linha 25, o presente simples do verbo
“pensar, achar” (to think – thought – thought):
32 So don't even bother asking
a) think
If you look okay
b) thought
You know I____________12
11) Na linha 30, o presente contínuo do verbo
35 The way you are “buscar” (to search – searched – searched):
The way you are a) ‘re searching
37 Girl you're amazing b) ‘d search
Just the way you are 12) Na linha 34, o futuro simples do verbo “dizer”
(to say – said – said)
Just The Way You Are – Bruno Mars a) is saying
Source: www.vagalume.com.br/bruno-mars/just-the-way-you-are.html b) ‘ll say
"Se você quer ser bem sucedido, precisa ter dedicação total, buscar seu último limite e dar o melhor de si mesmo." (Ayrton Senna)
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br -9- E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
GISNO - Noturno - 2018 - Ensino Médio - 1º e 2º Bimestres - 2ª Série - 10 - Inglês - Referências
REFERÊNCIAS
ALENCAR, João Carlos de Pinho. English Basic Structures. 2. ed. Teresina: Produção
Independente.
AMOS, Eduardo, PRESCHER, Elizabeth. Aquarius - Simplified Grammar Book. São Paulo:
Moderna, 1995.
DICIONÁRIO ONLINE PARA 28 IDIOMAS. In: Bab.la. Disponível em: <http://pt.bab.la/>. Acesso em:
5 mai. 2017.
DIXSON, Robert J. Essential Idioms in English for the Foreign Born: With Exercises for Practice
and Tests. Rio de Janeiro: Ao Livro Técnico, 1967.
FERRARI, Mariza, RUBIN, Sarah G. Inglês - Ensino Médio - Volume Único. São Paulo: Scipione,
2000. Coleção Novos Tempos.
FRANÇA, Milton Brito de. Inglês no vestibular. São Paulo: FTD, 1994.
GOOGLE TRADUTOR. In: Google Tradutor. Disponível em: <https://translate.google.com.br/>.
Acesso em: 5 mai. 2017.
GRAMÁTICA DA LÍNGUA INGLESA - ENGLISH GRAMMAR. In: Só Língua Inglesa!. Disponível
em: <http://www.solinguainglesa.com.br/>. Acesso em 5 mai. 2017.
HADDAD, Clara et al. Linguagens e culturas. São Paulo: Global, 2013. Coleção Viver, Aprender -
Linguagens e Códigos (Ensino Médio).
HEWINGS, Martin. Advanced Grammar in Use: A self-study reference and practice book for
advanced learners of English. Cambridge University Press, 1999.
HOLLAENDER, Arnon, SANDERS, Sidney. New Keyword: A Complete English Course. 2. Ed. São
Paulo: Moderna, 2001.
LIBERATO, Wilson. Compact English Book: Inglês - Ensino Médio - Volume Único. São Paulo:
FTD, 1998.
PAS - Programa de Avaliação Seriada. In: CESPE/UnB (Cebraspe). Disponível em:
<http://www.cespe.unb.br/pas/>. Acesso em: 22 jan. 2017.
PRESCHER, Elisabeth, PASQUALIN, Ernesto, AMOS, Eduardo. Graded English: Inglês - Volume
Único. São Paulo: Moderna, 2000.
PROVAS E GABARITOS. In: Enem. Disponível em: <http://portal.inep.gov.br/web/guest/provas-e-
gabaritos>. Acesso em: 22 jan. 2017.
TAVARES, Kátia Cristina do Amaral, FRANCO, Cláudio de Paiva. Way To Go!. Língua Estrangeira
Moderna - Inglês 1 - Ensino Médio. São Paulo: Ática, 2014.
VALLANDRO, Leonel. Dicionário inglês-português, português-inglês. 23. ed. São Paulo: Globo,
1998.
VELLOSO, Mônica Soares. Inglês para Concursos. 5. ed. Brasília: VESTCON, 1999.
VESTIBULARES ANTIGOS. In: CESPE/UnB (Cebraspe). Disponível em:
<http://www.cespe.unb.br/vestibular/antigos.asp>. Acesso em: 22 jan. 2017.
BLOG: andrematta.blogspot.com.br - 10 - E-MAIL: andre.mata@outlook.com
You might also like
- English For Staff - HotelsDocument312 pagesEnglish For Staff - HotelsCora María Olmos Gómez92% (13)
- Consolations of Philosophy - Alain de BottonDocument198 pagesConsolations of Philosophy - Alain de BottonAlbert Gar100% (2)
- Preterite Irregular Verbs ClassworkDocument2 pagesPreterite Irregular Verbs ClassworkMY DONo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument17 pagesPast SimpleVeni UN0% (1)
- Schopenhauer, Arthur Singh, R. Raj Death, Contemplation and Schopenhauer PDFDocument141 pagesSchopenhauer, Arthur Singh, R. Raj Death, Contemplation and Schopenhauer PDFNegru Corneliu100% (1)
- Philosophy in A New Key - Susanne LangerDocument470 pagesPhilosophy in A New Key - Susanne LangerDaniel Henriques Lourenço100% (1)
- Understanding Philosophy Through Key ConceptsDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Philosophy Through Key ConceptsMaria Virginia Fernandez100% (7)
- PAST SIMPLE TENSEDocument17 pagesPAST SIMPLE TENSENerma AgovicNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be LessonDocument12 pagesVerb To Be LessonMercy Dioselina Torres SantamariaNo ratings yet
- I.E.P. Santo Domingo Savio Simple PastDocument4 pagesI.E.P. Santo Domingo Savio Simple PastSC JulioNo ratings yet
- How to use simple past tense verbsDocument3 pagesHow to use simple past tense verbs71010 Fahri Arya MaulanaNo ratings yet
- WORKBOOK KIDS LEVEL 7Document7 pagesWORKBOOK KIDS LEVEL 7karenr.melgarlazaroNo ratings yet
- Learn key verb tenses and parts of speechDocument4 pagesLearn key verb tenses and parts of speechRhea RonuloNo ratings yet
- Simple Past-Group 4Document12 pagesSimple Past-Group 4Cristhian Michael Curillo MiteNo ratings yet
- We Use The Past Simple To Talk About Finished Actions in The PastDocument3 pagesWe Use The Past Simple To Talk About Finished Actions in The PastJulia aNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR. The Past Tense of Be: Review: Unit 2 - On Vacation LESSON 1 - Greet Someone Arriving From A TripDocument5 pagesGRAMMAR. The Past Tense of Be: Review: Unit 2 - On Vacation LESSON 1 - Greet Someone Arriving From A TripCARLOSNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Tense in Movies: Form, Meaning and ExamplesDocument17 pagesPast Simple Tense in Movies: Form, Meaning and ExamplesRoberto PitaNo ratings yet
- John Cabot Sailed To America in 1498. My Father Died Last Year. He Lived in Fiji in 1976. We Crossed The Channel YesterdayDocument11 pagesJohn Cabot Sailed To America in 1498. My Father Died Last Year. He Lived in Fiji in 1976. We Crossed The Channel YesterdayEduardo Chávez DuránNo ratings yet
- Modulo 03-IV 2doDocument2 pagesModulo 03-IV 2doGael Augusto Prado PaucarNo ratings yet
- Le Futur ProcheDocument2 pagesLe Futur ProcheRohaan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Let'S Live in The Past: For A WhileDocument15 pagesLet'S Live in The Past: For A WhilePayal Is LearningNo ratings yet
- 2nd W1 Sept20th Sept24thDocument3 pages2nd W1 Sept20th Sept24thMaricruz Cruz PérezNo ratings yet
- 1a Sec - Present Perfect Tense - PracticeDocument2 pages1a Sec - Present Perfect Tense - PracticeAngi Quincho YaulliNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument1 pagePast Simplex1andresgbNo ratings yet
- Educación: Affirmative WorkedDocument2 pagesEducación: Affirmative WorkedAntonio Beltrán SalasNo ratings yet
- (May.3rd-7th2021) Workshop Week 1Document6 pages(May.3rd-7th2021) Workshop Week 1Gabriel Duarte RodriguezNo ratings yet
- VerbDocument3 pagesVerbK11Ega SiyamtoNo ratings yet
- WORKBOOK KIDS LEVEL 6Document8 pagesWORKBOOK KIDS LEVEL 6karenr.melgarlazaroNo ratings yet
- 7 AnoDocument2 pages7 AnoGenilson SantosNo ratings yet
- English Booklet (5th Year) 2021Document54 pagesEnglish Booklet (5th Year) 2021Debora AzcurraNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Did You Father: Let'S Revise Past Simple!Document3 pagesTeacher: Did You Father: Let'S Revise Past Simple!salihNo ratings yet
- G1 - S2 - U4 - W14 - P5.6 - Simple PastDocument30 pagesG1 - S2 - U4 - W14 - P5.6 - Simple PastHồng NhungNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense Grammar RulesDocument5 pagesSimple Past Tense Grammar RulesXavier GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument9 pagesPast SimpleSimiciuc SilviuNo ratings yet
- The Simple Past TenseDocument8 pagesThe Simple Past Tensejana bojaNo ratings yet
- Past SimpleDocument5 pagesPast SimpleMariam KobakhidzeNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument14 pagesSimple Present Tensekasana7398No ratings yet
- Simple Past ADocument15 pagesSimple Past AAbdulrazakAlsagheerNo ratings yet
- Passive - Present Simple Grammar Summary - BrainPOP ELLDocument7 pagesPassive - Present Simple Grammar Summary - BrainPOP ELLimran hamliNo ratings yet
- (2°medio) Reading Comprehension and Practice 'Past Continuous & Past Simple'Document4 pages(2°medio) Reading Comprehension and Practice 'Past Continuous & Past Simple'Yoni Kííng SanchezNo ratings yet
- Learn English Plan Week 5/6Document20 pagesLearn English Plan Week 5/6小籠包LildragonbunNo ratings yet
- Articles: Kinds of AdjectivesDocument29 pagesArticles: Kinds of AdjectivesKostis SNo ratings yet
- Ketting Formulier Past Simple, Shortened ProgramDocument16 pagesKetting Formulier Past Simple, Shortened ProgramYohanan Moraes IsbellNo ratings yet
- 8a Sc3a9rie One Day The Simple Future TenseDocument5 pages8a Sc3a9rie One Day The Simple Future TenseFernanda MotaNo ratings yet
- 8a Sc3a9rie One Day The Simple Future Tense PDFDocument5 pages8a Sc3a9rie One Day The Simple Future Tense PDFFernanda Mota0% (1)
- VERB TO BE (Ser o Estar) : He Is A Doctor (Singular)Document9 pagesVERB TO BE (Ser o Estar) : He Is A Doctor (Singular)Briones rockNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Simple Past TenseDocument4 pagesGrammar - Simple Past TenseOscarNo ratings yet
- Institucion Tecnologica Colegio Mayor de Bolivar Itcmb: The Past TenseDocument9 pagesInstitucion Tecnologica Colegio Mayor de Bolivar Itcmb: The Past TenseAusencia SentimentalNo ratings yet
- W - Verbos Regulares e IrregularesDocument10 pagesW - Verbos Regulares e IrregularesDeogracio Possiano JaimeNo ratings yet
- Simple Past - Gramática Inglesa - EFDocument1 pageSimple Past - Gramática Inglesa - EFSoniaClaudiaTeixeiraNo ratings yet
- GUIA DE SEPTIEMBRE DE 3 AñoDocument11 pagesGUIA DE SEPTIEMBRE DE 3 Añobelen PereiraNo ratings yet
- Tiempo Verbal Pasado Simple Tiempo Verbal Pasado Simple: DID Regular E IrregularDocument18 pagesTiempo Verbal Pasado Simple Tiempo Verbal Pasado Simple: DID Regular E IrregularEliana Zurita TorresNo ratings yet
- English Tenses TableDocument1 pageEnglish Tenses Tableパス•クシメナ100% (1)
- Learn Simple Past Tense VerbsDocument14 pagesLearn Simple Past Tense VerbsAna Belen ZuritaNo ratings yet
- SimplePast N-QDocument20 pagesSimplePast N-QFiryal MagdiNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Expressing Past Time: The Simple PastDocument8 pages2-1 Expressing Past Time: The Simple PastNur Uswatun HasanahNo ratings yet
- INPHOGRAPHIC Pasado SimpleDocument1 pageINPHOGRAPHIC Pasado Simplerosario dzulNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 B3-ADocument1 pageHomework 1 B3-AKING DEMON 777No ratings yet
- English Worksheet #1: Colegio San Ignacio Concepción English Department 2020 11th Grade - Ms Verónica OrmeñoDocument9 pagesEnglish Worksheet #1: Colegio San Ignacio Concepción English Department 2020 11th Grade - Ms Verónica OrmeñoNdt ElearningNo ratings yet
- Funciones Del "Simple Past": EjemplosDocument4 pagesFunciones Del "Simple Past": EjemplosCrasec ArtNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense ExplainedDocument15 pagesSimple Past Tense ExplainedMary Murias100% (1)
- Past Simple - Affirmative Form Irregular VerbsDocument1 pagePast Simple - Affirmative Form Irregular VerbsEglys AnayaNo ratings yet
- Tiempos verbales activos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #1From EverandTiempos verbales activos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #1No ratings yet
- Common Irregular Verb ListDocument4 pagesCommon Irregular Verb Listapi-27488371100% (1)
- Childhood 101 Christmas Charades CardsDocument12 pagesChildhood 101 Christmas Charades CardsAtta2112No ratings yet
- Q Tip Shapes PDFDocument6 pagesQ Tip Shapes PDFAF00No ratings yet
- 6 Thinking Hats Speaking RolesDocument1 page6 Thinking Hats Speaking RolesCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Advanced Conversational English extracts and analysisDocument82 pagesAdvanced Conversational English extracts and analysisCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Gavea 12-14 PDFDocument165 pagesGavea 12-14 PDFCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- How To Talk To Your Customers: Help ScoutDocument31 pagesHow To Talk To Your Customers: Help ScoutCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Do Does in Yes No Questions 1 PDFDocument1 pageDo Does in Yes No Questions 1 PDFadamNo ratings yet
- EM - 2a Série - 2018-1b-2b - Apostila - Passado Simples - DiversityDocument10 pagesEM - 2a Série - 2018-1b-2b - Apostila - Passado Simples - DiversityCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- 2 Simple-Present PDFDocument6 pages2 Simple-Present PDFAnnie AzNo ratings yet
- EM - 2a Série - 2018-1b-2b - Apostila - Passado Simples - DiversityDocument10 pagesEM - 2a Série - 2018-1b-2b - Apostila - Passado Simples - DiversityCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Taxonic Enterprise Vocabulary Management A Lexicographic ViewDocument30 pagesTaxonic Enterprise Vocabulary Management A Lexicographic ViewCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Taxonic Enterprise Vocabulary Management A Lexicographic ViewDocument30 pagesTaxonic Enterprise Vocabulary Management A Lexicographic ViewCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Form and UseDocument13 pagesPast Continuous Form and UseCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- English conditional sentencesDocument10 pagesEnglish conditional sentencesCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Past Simple - Irregular Verbs - 7th GradeDocument6 pagesPast Simple - Irregular Verbs - 7th GradeCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Have Got - 7th GradeDocument6 pagesHave Got - 7th GradeCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative of Adjectives - 7th GradeDocument23 pagesComparative and Superlative of Adjectives - 7th GradeCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Past Simple - To Be and Regular - 7th GradeDocument17 pagesPast Simple - To Be and Regular - 7th GradeCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocument5 pagesAdverbs of FrequencyCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- DigitalstorytellingDocument4 pagesDigitalstorytellingapi-278240286No ratings yet
- Eli 08167 BDocument23 pagesEli 08167 BDana DobreNo ratings yet
- How To Digital StorytellingDocument16 pagesHow To Digital StorytellingCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Digital StorytellingDocument14 pagesDigital StorytellinggjeaksNo ratings yet
- Emotions Word List PDFDocument7 pagesEmotions Word List PDFCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Comparative and Superlative of AdjectivesDocument23 pagesComparative and Superlative of AdjectivesCarolina CordeiroNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Tutorial ExercisesDocument14 pagesVerb Tenses Tutorial ExercisesYenTranNo ratings yet
- Complete Irregular VerbsDocument32 pagesComplete Irregular VerbsCarolina Cordeiro0% (1)
- Western Philosophies of Man ExplainedDocument12 pagesWestern Philosophies of Man ExplainedSophia EspañolNo ratings yet
- Robin Waterfield - Protagoras and The Challenge of Relativism Plato's Subtlest Enemy. by Ugo Zilioli (Article)Document2 pagesRobin Waterfield - Protagoras and The Challenge of Relativism Plato's Subtlest Enemy. by Ugo Zilioli (Article)DonaldNo ratings yet
- Book ReviewsDocument2 pagesBook ReviewsDaniel NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Gec 01 - UtsmoduleDocument249 pagesGec 01 - UtsmoduleJhoana PabillareNo ratings yet
- Plato's Views on Marriage, Family and Gender RolesDocument7 pagesPlato's Views on Marriage, Family and Gender RolesAkanksha JogaleNo ratings yet
- SocratesDocument3 pagesSocratesBenitez Gherold0% (1)
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1Anisa Febriani Puspa KiranaNo ratings yet
- Political philosophy notes provide insight into Plato's ideal state and the role of philosophers as rulersDocument6 pagesPolitical philosophy notes provide insight into Plato's ideal state and the role of philosophers as rulerstoobaziNo ratings yet
- Misery Loves Company: The Inescapable Unhappiness in The Good LifeDocument7 pagesMisery Loves Company: The Inescapable Unhappiness in The Good LifeGauri BahugunaNo ratings yet
- Allen. Anamnesis in Plato's Meno and PhaedoDocument11 pagesAllen. Anamnesis in Plato's Meno and PhaedoLucasDoneganaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Study Guide on Ancient Greek History, Culture, and MythologyDocument2 pagesChapter 5 Study Guide on Ancient Greek History, Culture, and Mythologyjanet_tranNo ratings yet
- Miller - The Philosopher in Plato's Statesman PDFDocument221 pagesMiller - The Philosopher in Plato's Statesman PDFAlejandro H. Sánchez100% (3)
- Tantric Practice of PlatonismDocument8 pagesTantric Practice of Platonismgoforitandgetit007No ratings yet
- Views of Plato and Nietzsche On Love, Sex and Marriage FINALDocument29 pagesViews of Plato and Nietzsche On Love, Sex and Marriage FINALMudit BabelNo ratings yet
- Was Gorgias A SophistDocument11 pagesWas Gorgias A SophistAbeonaNo ratings yet
- Oxford University, Classics Mods (Course IIA) 2000 PlatoDocument5 pagesOxford University, Classics Mods (Course IIA) 2000 PlatotoobaziNo ratings yet
- Plato's Apology Insights on WisdomDocument2 pagesPlato's Apology Insights on WisdomParisNo ratings yet
- 1.1philosophical Theories On The Self Intro Socrates Plato ST AugustineDocument46 pages1.1philosophical Theories On The Self Intro Socrates Plato ST AugustineArvin Rodriguez100% (1)
- ( (Biblioteca Clasica Gredos) (Spanish Edition) ) Homero - La Odisea (1982, Gredos)Document25 pages( (Biblioteca Clasica Gredos) (Spanish Edition) ) Homero - La Odisea (1982, Gredos)Delton Luiz CavalliNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: The Self From Various Perspective. From The Perspective of PhilosophyDocument25 pagesUNIT 1: The Self From Various Perspective. From The Perspective of PhilosophyAngel TesoreroNo ratings yet
- Doing Philosophy: Understanding its Meaning and ValueDocument12 pagesDoing Philosophy: Understanding its Meaning and ValueJoross Sibal PacturanNo ratings yet
- (Trends in Classics) Beatriz Bossi-Plato's - Sophist - Revisited-De Gruyter (2013)Document315 pages(Trends in Classics) Beatriz Bossi-Plato's - Sophist - Revisited-De Gruyter (2013)jimtsok100% (1)
- Business Ethics and Good GovernanceDocument53 pagesBusiness Ethics and Good GovernanceGuray RoseanneNo ratings yet
- Parmenides to Kant: Key Thinkers in Metaphysics, Ethics, Logic and EpistemologyDocument2 pagesParmenides to Kant: Key Thinkers in Metaphysics, Ethics, Logic and EpistemologyMarissa Asim100% (1)
- SuicideDocument27 pagesSuicideJoaquin GalindoNo ratings yet
- 301Document324 pages301Ashwini SahooNo ratings yet