Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Compito Sett 2013 Eng
Uploaded by
bediangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Compito Sett 2013 Eng
Uploaded by
bediangCopyright:
Available Formats
ACADEMIC YEAR: 2012-2013
DEPARTMENT: N/A CLASS: Meng II
END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION: 1st Semester (First Part)
COURSE TITLE: Physics 2 CODE: PHY215
DATE: September 2013 DURATION: 2 hours
EXAMINER: Prof. Franco Simonetto
INSTRUCTIONS: No books, no notes. Any communication among candidates is strictly forbidden.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
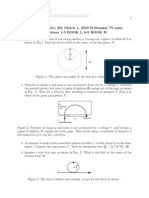
16I Problem Two electric charges are fixed at the points x0=0 and x1=a=-30 cm of the x axis as in the figure. The charge at the
origin is q0 = 10-12 C, the other charge is q1 = -4 q0. y
1) Find the point x0 of the x axis where the electric field is zero, among those listed in the table
2) Find the point x1 along the x axis where the electric potential is minimal.
3) Find the points ym along the y axis where the electric potential is minimal.
4) Is the electric field there equal to zero ? Justify your answer. q q
1 0
a x
II Problem An electric circuit, resistance R=25W, has the shape of a circular ring with radius r=10m. The center of the ring lies in the
origin of the coordinate system. The surrounding space is permeated by a magnetic field B=0.1 T directed along the z axis
(figure). At t=0 the ring lies in the horizontal (xy) plain, then it starts a rotation around the y axis with constant angular velocity,
w=2 rad/s. Neglecting self-induction effects compute:
1. The magnetic energy UB stored inside a sphere centered in the origin of the system and of
radius r=10m.
3
2. The electromagnetic force i acting on the circuit at t 1 = s 4
3. The force per unit length f acting on the point A (see figure) of the circuit in that precise
moment.
4. The force acting on the whole circuit at t2=5 s.
Question Units
I.1 x0 -20 -10 0 10 20
I.2 x1 -20 -10 0 10 20
I.3 ym 0 ±2.3 ±8.1 ±12.5 ±15.6
I.4 E=0 ? yes no
II.1 UB 2.5 6.8 16.7 22.9 35.5
II.2 i 0 28.2 45.5 58.9 62.8
II.3 f 0 0.25 0.75 1.25 2.15
II.4 F 0 0.25 0.75 1.25 2.15
An exercise is correct if, and only if, the right numerical result is found, and the derivation of the result is presented. Therefore the student must :
- mark with a cross the numerical solution in the upper table
- write the units in the last column for the quantity defined in the first column
- write in the booklet provided for this purpose a brief description of the method employed to obtain the result
Each exercise of the first problem is worth a maximum of three points; two points for the exercises of the second problem. Cross missing, or placed on the wrong numerical
value, gives zero points. Description missing, gives also zero point. Units missing costs one point each. Wrong direction cost one point.
Questions
A) In which case a discontinuous magnetic field can be found ?
1) Never
2) When traversing the surface of a solenoid
3) Inside a magnet
B) Which sentence describes the electrostatic screening effect ?
1) The electric field outside a hollow conductor does not depend on the charge placed inside the conductor
2) The electric field inside a hollow conductor does not depend on the charge placed outside the conductor
3) Both the sentences are equally correct
C) Explain why the flux of the magnetic field E across a closed surface, fS(E), must be equal to zero.
1) Because E is a conservative field.
2) That's not true, fS(E) can be different from zero.
3) Because electric charges can only be produced in pairs of opposite sign.
D) Take two identical capacitor, capacitance C0. How should they be arranged to produce a new capacitor with capacitance 1/2 C0 ?
1) make a series.
2) make a parallel.
3) there's no way
E) Faraday's law of induction, E = -dFS(B)/dt, is NOT due to the action of Lorentz's force if:
1) flux variation is due to a change in the geometry, with fixed magnetic field B
2) flux variation is due to a change in the magnetic field B, with fixed geometrical configuration
3) it's always a consequence of the action of the Lorentz force
F) An electric charge is moving in a region permeated by a uniform magnetic field. The charge trajectory is described by:
1) a parabola
2) a spiral
2) an hyperbole
G) The transformer changes the input voltage E1 into the output voltage E2, exploting Faraday's law. This works:
1) only with direct currents
2) only with alternate currents
3) both with direct and with alternate current.
H) A magnetic dipole is placed initially at rest inside a region permeated by a magnetic field
B . The dipole:
1) moves along the same direction and sense of the field
2) moves along the same direction and sense of the field gradient
3) it does not move in any case.
Discussion: operation of the RC circuit
Please, choose your solution drawing a cross above the number of the answer you judge correct.
Each solution, if right, is worth four points (+4). A cross placed in the wrong place costs two points (-2). No cross, zero point (0).
The discussion is worth a maximum of ten (10) points.
You might also like
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Mark It As Positive If Sorting Out of The Sheet, Negative ElseDocument2 pagesMark It As Positive If Sorting Out of The Sheet, Negative ElsebediangNo ratings yet
- February 2014Document3 pagesFebruary 2014bediangNo ratings yet
- Draw An Arrow On The Top Charge To Show Feld Direction and Verse On The Fgure AsideDocument2 pagesDraw An Arrow On The Top Charge To Show Feld Direction and Verse On The Fgure AsidebediangNo ratings yet
- Compito Sett EngDocument2 pagesCompito Sett EngbediangNo ratings yet
- Physics 201 Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesPhysics 201 Midterm Examrosa_elNo ratings yet
- Physics (Theory) : General Instructions: All Questions Are CompulsoryDocument7 pagesPhysics (Theory) : General Instructions: All Questions Are CompulsoryJames RossNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 Selection Test 2Document4 pagesPhase 2 Selection Test 2Marcus PoonNo ratings yet
- C Q V Q CV Q 6× 2.1× 10 × 10 Q 1.26 × 10 F: 1. (A) (I) Define The Term Capacitance'. (1 Mark)Document24 pagesC Q V Q CV Q 6× 2.1× 10 × 10 Q 1.26 × 10 F: 1. (A) (I) Define The Term Capacitance'. (1 Mark)Adam mahabirNo ratings yet
- Trialstpm 2021 KGVP 3 QuestionDocument9 pagesTrialstpm 2021 KGVP 3 QuestionASANAMMAH NACHIAR A/P PAKEER MOHAMED MoeNo ratings yet
- Physics Laboratory Manuals: For B. Tech. II-Semester (Physics-II) Department of Applied SciencesDocument42 pagesPhysics Laboratory Manuals: For B. Tech. II-Semester (Physics-II) Department of Applied SciencesNitish kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Current & B Field LabDocument5 pagesCurrent & B Field LabaaronhwparkNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocument11 pagesNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIYuhua SunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29Document7 pagesChapter 29Gabriel Sortica ReichmannNo ratings yet
- Phys 212 ExamDocument19 pagesPhys 212 ExamJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Hw9aa PDFDocument5 pagesHw9aa PDFhthaier4062No ratings yet
- Phy 208 Final Exam So LNDocument10 pagesPhy 208 Final Exam So LNΧρίστος ΠαπαναστασίουNo ratings yet
- PHYS194 Report 3Document4 pagesPHYS194 Report 3AbdulNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Electromagnetic InductionDocument2 pagesWeek 2 - Electromagnetic InductionShan Armaine CabelaNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics 2007 U2 P2 PDFDocument18 pagesCAPE Physics 2007 U2 P2 PDFJadon ThomasNo ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: JEE (Main+Advanced) : ENTHUSIAST COURSEDocument56 pagesClassroom Contact Programme: JEE (Main+Advanced) : ENTHUSIAST COURSEDiscipleof KarnaNo ratings yet
- Ai TS-3 - 2023-24 - Class XII - 25-9-23Document22 pagesAi TS-3 - 2023-24 - Class XII - 25-9-23Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- UnitTest - D25-Jun-2022 (1) VZSGV CDocument23 pagesUnitTest - D25-Jun-2022 (1) VZSGV CAadil ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 013 Sem-5 Paper 5Document4 pages013 Sem-5 Paper 5Prudhvi Raghu TejaNo ratings yet
- 21 - EEE - EDC NotesDocument156 pages21 - EEE - EDC Notessunil kumar reddyNo ratings yet
- 04 Electric Field Part 2Document6 pages04 Electric Field Part 2kayla888No ratings yet
- Resistor Exam PDFDocument13 pagesResistor Exam PDFRonelAballaSauzaNo ratings yet
- Physics - Board of Studies: W.E.F. 2017-18 ADMITTED BATCHDocument4 pagesPhysics - Board of Studies: W.E.F. 2017-18 ADMITTED BATCHPrudhvi Raghu TejaNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 - TurnerDocument7 pagesMidterm 1 - TurnerAli Abbas SheriffNo ratings yet
- Quesito Unita' I.1 S I.2 II.1 W II.2 S Ii.3 Du III.1 R Iii.2 U III.3 TDocument2 pagesQuesito Unita' I.1 S I.2 II.1 W II.2 S Ii.3 Du III.1 R Iii.2 U III.3 TbediangNo ratings yet
- Mam SaimaDocument8 pagesMam SaimaFaheemNo ratings yet
- Test - 32: Final Test Series (Online) For JEE (Main) - 2021Document10 pagesTest - 32: Final Test Series (Online) For JEE (Main) - 2021Vishal kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Physics 208 Final Exam Dec. 21, 2006Document10 pagesPhysics 208 Final Exam Dec. 21, 2006Χρίστος ΠαπαναστασίουNo ratings yet
- Mid 2020 SDocument11 pagesMid 2020 Samedpv56No ratings yet
- Mesh Analysis and Nodal Analysis: Mapúa UniversityDocument9 pagesMesh Analysis and Nodal Analysis: Mapúa UniversityRick AlvientoNo ratings yet
- Compito2014 1Document3 pagesCompito2014 1bediangNo ratings yet
- Epotential2015 IRSDocument9 pagesEpotential2015 IRS吳俊陞No ratings yet
- AITS 2324 PT III JEEA Paper 2 SolDocument13 pagesAITS 2324 PT III JEEA Paper 2 Solnityapaliwal553No ratings yet
- Examination 3 SolnDocument8 pagesExamination 3 SolnKim Kelley AngNo ratings yet
- PHYS 212 AnswersDocument19 pagesPHYS 212 AnswersJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Entrance Test 2010 Name:: Mechatronics and Sensor Systems TechnologyDocument2 pagesEntrance Test 2010 Name:: Mechatronics and Sensor Systems Technologydangchi_nguyenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - More Applications of Differential EquationsDocument4 pagesLecture 3 - More Applications of Differential EquationsAccio MoraNo ratings yet
- Experiment (4) StasisDocument9 pagesExperiment (4) StasisBabong KobNo ratings yet
- Charge-to-Mass Ratio of An Electron: Phys211LDocument7 pagesCharge-to-Mass Ratio of An Electron: Phys211LElias HannaNo ratings yet
- X X X XXX X X X X X X: SolutionsDocument2 pagesX X X XXX X X X X X X: SolutionsbediangNo ratings yet
- Engineering Admissions Assessment D564/11: Instructions To CandidatesDocument66 pagesEngineering Admissions Assessment D564/11: Instructions To CandidatesxingchenNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam EEE1Document6 pagesMock Exam EEE1nareshchand4ualwaysNo ratings yet
- Name - Solutions To Test 3 November 8, 2017: H E E T e V V MV E Z E NDocument7 pagesName - Solutions To Test 3 November 8, 2017: H E E T e V V MV E Z E NArslan HassanNo ratings yet
- Physics B: Fybnvc07 Electricity and Magnetism: Warning! There Are More Than One Version of The TestDocument7 pagesPhysics B: Fybnvc07 Electricity and Magnetism: Warning! There Are More Than One Version of The TestEpic WinNo ratings yet
- E103 - Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisDocument13 pagesE103 - Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisRick AlvientoNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee: All India Test SeriesDocument17 pagesFiitjee: All India Test SeriesAyush MishraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Brendan J WebNo ratings yet
- FLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsDocument4 pagesFLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsChetanNo ratings yet
- Code Q3 OLABH Qs Ans Solution NEET 2022Document71 pagesCode Q3 OLABH Qs Ans Solution NEET 2022Anantha PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity: Date-TotalDocument3 pagesCurrent Electricity: Date-TotalPranabKumarGoswamiNo ratings yet
- 2Q - Worksheet-3 - Ohms-Law - ASWER KEYDocument2 pages2Q - Worksheet-3 - Ohms-Law - ASWER KEYmissaizcabatinganNo ratings yet
- Answers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2021Document50 pagesAnswers & Solutions: For For For For For NEET (UG) - 2021Rohit PatelNo ratings yet
- Transformador 2.jDocument14 pagesTransformador 2.jjarol zuluaga moralesNo ratings yet
- @bohring - Bot Ai TS2023-24 Class XII @HeyitsyashXDDocument22 pages@bohring - Bot Ai TS2023-24 Class XII @HeyitsyashXDSURYANSH SINGH 12-GNo ratings yet
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Document4 pagesFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanNo ratings yet
- SUST - CONSTRUCTION NAPWs MEng 5Document25 pagesSUST - CONSTRUCTION NAPWs MEng 5bediangNo ratings yet
- Luc Floating Solar - Final - v3 - ABDocument5 pagesLuc Floating Solar - Final - v3 - ABbediangNo ratings yet
- Giu2008 PDFDocument2 pagesGiu2008 PDFbediangNo ratings yet
- Quesito Unita' I.1 R I.2 F - II.1 Q II.2 R III.1 D III.2 I III.3 IDocument2 pagesQuesito Unita' I.1 R I.2 F - II.1 Q II.2 R III.1 D III.2 I III.3 IbediangNo ratings yet
- Irjet V6i5549Document5 pagesIrjet V6i5549bediangNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Design and Material Costs of Tall Wind Turbine Towers in South AfricaDocument10 pagesA Study On The Design and Material Costs of Tall Wind Turbine Towers in South AfricabediangNo ratings yet
- Collected ProblemsDocument2 pagesCollected ProblemsbediangNo ratings yet
- XXXXX XXXXX XXXXX XXX XXX XXX: Quesito Unita' I.1 C I.2 Q I.3 E I.4 Q II.1 I II.2 Verso II.3 V II.4 TDocument2 pagesXXXXX XXXXX XXXXX XXX XXX XXX: Quesito Unita' I.1 C I.2 Q I.3 E I.4 Q II.1 I II.2 Verso II.3 V II.4 TbediangNo ratings yet
- Quesito Unita' I.1 S I.2 II.1 W II.2 S Ii.3 Du III.1 R Iii.2 U III.3 TDocument2 pagesQuesito Unita' I.1 S I.2 II.1 W II.2 S Ii.3 Du III.1 R Iii.2 U III.3 TbediangNo ratings yet
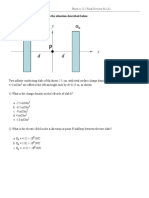
- F F F U: I Problem Two Very Long Parallel Wires Are Displaced by D 20 Cm. On The First Wire Runs A Current IDocument3 pagesF F F U: I Problem Two Very Long Parallel Wires Are Displaced by D 20 Cm. On The First Wire Runs A Current IbediangNo ratings yet
- Soluzioni PrimoDocument1 pageSoluzioni PrimobediangNo ratings yet
- X X X XXX X X X X X X: SolutionsDocument2 pagesX X X XXX X X X X X X: SolutionsbediangNo ratings yet
- CFP LabogenieDocument2 pagesCFP LabogeniebediangNo ratings yet
- Compito2014 1Document3 pagesCompito2014 1bediangNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of An Embankment Dam Case of The Memve'Ele Hydroelectric DamDocument5 pagesStabilization of An Embankment Dam Case of The Memve'Ele Hydroelectric DambediangNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of An Embankment Dam Case of The Memve'Ele Hydroelectric DamDocument5 pagesStabilization of An Embankment Dam Case of The Memve'Ele Hydroelectric DambediangNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No.1Document7 pagesProblem Set No.1floreson 16No ratings yet
- Yahara 2010Document9 pagesYahara 2010Novriza SukurNo ratings yet
- Chapman - Senior Workshop CalculationsDocument252 pagesChapman - Senior Workshop Calculationszementhead100% (3)
- Chapter 15 - Kinetics of Particles MomentumDocument46 pagesChapter 15 - Kinetics of Particles MomentumZizhen JiNo ratings yet
- Physics Year 7: 9.1 Seeing ForcesDocument25 pagesPhysics Year 7: 9.1 Seeing ForcesNurulAinMatAron100% (1)
- Cbiescss 07Document6 pagesCbiescss 07Ayush BeheraNo ratings yet
- 동역학 14 PDFDocument97 pages동역학 14 PDF야옹No ratings yet
- Balloons & Travolta ActivityDocument2 pagesBalloons & Travolta ActivityJACOB SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Center of PressureDocument5 pagesCenter of PressureEdrees Jamal100% (6)
- Physics For Scientists and EngineersDocument20 pagesPhysics For Scientists and EngineersYana IshakNo ratings yet
- Absolute Dependent Motion Analysis of Two ParticlesDocument57 pagesAbsolute Dependent Motion Analysis of Two ParticlesFrancis Philippe Cruzana CariñoNo ratings yet
- Weekly TestDocument12 pagesWeekly Testrossana rondaNo ratings yet
- Part 3 Electric Forces and Electric FieldDocument46 pagesPart 3 Electric Forces and Electric FieldJay Pee Magno NuñezNo ratings yet
- Paper - 2: Full Syllabus Test-1 (Fst-1) - Jee (Advanced)Document21 pagesPaper - 2: Full Syllabus Test-1 (Fst-1) - Jee (Advanced)lol88745No ratings yet
- PhysicsstudypackDocument891 pagesPhysicsstudypackzermina khanNo ratings yet
- Acceleration, Force, Momentum and EnergyDocument46 pagesAcceleration, Force, Momentum and EnergyNorKamilahMakhtarNo ratings yet
- Physics Set D AKDocument1 pagePhysics Set D AKCherry Grace Articulo Dabucon100% (1)
- Dattatray BagulDocument18 pagesDattatray BagulPrathamesh SabaleNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Matter and DensityDocument28 pagesLESSON 2 - Matter and DensityKate OchaveNo ratings yet
- General Let Review Program 2009 - AjdDocument153 pagesGeneral Let Review Program 2009 - AjdKlaribelle Villaceran100% (1)
- Quiz 1 General Physics 1Document2 pagesQuiz 1 General Physics 1Benzene Robi50% (2)
- Lab Act 1Document8 pagesLab Act 1Kenji HiguchiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 General Physics 2 SLM EditedDocument7 pagesLesson 1 General Physics 2 SLM EditedDIANNE PLANANo ratings yet
- Hapter: Conceptual ProblemsDocument52 pagesHapter: Conceptual ProblemsAmeen ShaikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document15 pagesChapter 02Koushik DaharNo ratings yet
- Gis Located Above B)Document10 pagesGis Located Above B)Apple AterradoNo ratings yet
- Decelerometru PDFDocument66 pagesDecelerometru PDFLucianNo ratings yet
- Free-Body Diagram NewDocument26 pagesFree-Body Diagram Newlarsen445No ratings yet
- Kvpy Class 11 Sa Stream Mock Test-2 (Cty P-1 Syllabus)Document7 pagesKvpy Class 11 Sa Stream Mock Test-2 (Cty P-1 Syllabus)TEJA SINGH0% (2)
- Melody Jones - Newton's 2nd Law LabDocument3 pagesMelody Jones - Newton's 2nd Law LabMelody JonesNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (553)
- The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameFrom EverandThe Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (88)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (147)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Step By Step Mixing: How to Create Great Mixes Using Only 5 Plug-insFrom EverandStep By Step Mixing: How to Create Great Mixes Using Only 5 Plug-insRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)