Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermo (Sir Javel’s live session
Uploaded by
Ej Parañal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pages1. This document provides definitions and explanations of various thermodynamic concepts and properties.
2. It includes multiple choice questions about intensive and extensive properties, processes like isobaric and isothermal processes, the first law of thermodynamics, and changes in internal energy, entropy, and other thermodynamic quantities.
3. The questions cover a wide range of topics including the gas laws, heat transfer, phase changes, and thermodynamic processes.
Original Description:
Original Title
Thermo Practice test
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. This document provides definitions and explanations of various thermodynamic concepts and properties.
2. It includes multiple choice questions about intensive and extensive properties, processes like isobaric and isothermal processes, the first law of thermodynamics, and changes in internal energy, entropy, and other thermodynamic quantities.
3. The questions cover a wide range of topics including the gas laws, heat transfer, phase changes, and thermodynamic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views4 pagesThermo (Sir Javel’s live session
Uploaded by
Ej Parañal1. This document provides definitions and explanations of various thermodynamic concepts and properties.
2. It includes multiple choice questions about intensive and extensive properties, processes like isobaric and isothermal processes, the first law of thermodynamics, and changes in internal energy, entropy, and other thermodynamic quantities.
3. The questions cover a wide range of topics including the gas laws, heat transfer, phase changes, and thermodynamic processes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
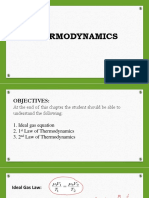
Thermo (Sir Javel’s live session) 12.
Which of the following is an intensive
property?
1. The name thermodynamics stems Temperature
from the Greek words” Therme” and
13. The reciprocal of density is
dynamis” which means. Specific volume
Heat, Power 14. A system is in there is no change in
2. The contact surface shared by both pressure at any point of the system
the system and the surroundings is with time.
called:
Mechanical equilibrium
Boundary 15. Any change that a system undergoes
3. A Closed system is also known as: from one equilibrium state to another
Control mass is called
4. Who coined the term energy in 1807?
Process
Thomas Young – pag may energy 16. A mixture of ice and water that is in
kapa bata kapa equilibrium with air saturated with
5. The boundaries of a control volume vapour at 1 atm pressure is said to be
are called: at Ice point
Control surface
17. What is the density of air under
6. The first thermodynamic textbook standard condition?
was written in 1859 by 1.2kg/m^3
A.William Rankine – most associated 18. What is the freezing point of water in
units the Fahrenheit temperature scale?
7. A water heater, a car radiator, a
32 F
turbine,a car radiator, a turbine, and a 19. During a hearing process the
compressor all involve mass flow and temperature of a system rises by 10 C.
should be analysed as Express the rise in temperature in
a. control mass – closed system Kelvin
b,isolated -
10 K
c. control volume – open system 20. The actual pressure at a given position
d. all of these is called:
8. Any characteristic of a system is called Absolute
Property 21. What pressure is indicated by a
9. The ratio of the density of a substance
barometeter?
to the density of some standard Atmospheric
substance at a specific temperature id 22. The pressure at the bottom of a
called waterpark that has height of 15 m is
Specific gravity or Relative Density
147,15 kPa – sol 9.81kN/m^2 (15m)
10. Propertied that are independent of 23. A vacuum gage connected to a
the size of a system chamber reads 5.8 psi at a location
Intensive – independent where the atmospheric pressure is
Extensive -dependent 14.5. Determine the absolute
11. Extensive propertied per unit mass
pressure in the chamber.
are called 8.7 psi – Sol 14.5-5.8
Specific properties 24. A device consists of a glass or plastic
U-tube containing one or more fluids
such as mercury, water, alcohol, or oil 30. A 2.0 L sample of gas at 0.80 atm
and is commonly used to measure must be compressed to 1.6L at
small and moderate pressure constant temperature. What pressure
differences. must be excerted to bring it to the
Manometer volume?
25. Five moles of water vapour at 100 C 1 atm – sol P1V1 = P2V2
and 1 atm pressure compressed 31. The total pressure of the three gas
isobarically to form liquid at 100 C. components in a certain mixture is 55
the process is reversible, and the ideal kilopascals. If Pa= 20.0 kPa and Pb =
gas laws apply. 7.5 kPa, what is the partial pressure of
153 liter – Sol PV=nRT; V=nRT/P gasa C?
= (5 moles)(0.0821 27.5 kPa – Sol Pa + Pb + Pc = Pf
atm.L/mol.K)(100 + 273) / 1 atm 20kPa + 7.5kPa + Pc = 55kPa
26. A 3.0 lbm of air are contained at a 25 32. A process that is carried out at
psi and 100 F. Given that Rair = 53.35 constant pressure is call:
ft/lbmF, what is the volume of the Isiobaric
container? 33. A fully reversible steady flow adiabatic
24.9 ft^2 – Sol V= mRT/P ; V = process with no work being done:
3lbm(53.54 Throttling
ft/lbm)(100+460)/25psri(12in)^2 34. A process during which, the
27. How many moles of ideally behaving temperature T remains constant is
gas occupy 400 liters at 0.821 atm and called:
200 K? Isothermal process
20 moles – m=PV/Rt = 35. Any process during which, the
0.821atm(400 pressure P remains constant is called:
L)/(0.0821atm.L/mol.K)(200K) Isobaric process
28. What is the pressure in atmospheres 36. A process, during: which, the specific
that a gas exerts if it supports a 380 volume V remains constant is called:
mm column of mercuty? Isovolumic , Isochoric, Isometric
0.500 atm – Sol 37. Which of the following cannot be
(9810N/m^)(13.6)(0.00380m)/(10325Pa) measured by a thermometer?
29. A 700.0 ml-sample of gas at 500.0 torr Latent heat
pressure is compressed “at constant 38. Heat which cause a change in
temperature until its final pressure is temperature of a substance
800.0 torr. What is the Final Volume? Sensible heat
438 ml – Sol P1V1=P2V2 39. The latent heat of vaporization of
Additional mnemonics for gas law water is
formula: 970 BTU
40. A 20 g piece of aluminium (c=0.21
cal/gml C) at 90 C is dropped into a
BT – Boyles (BlueTooth) cavity in a large block of ice at 0 C.
CP – Charle’s (CellPhone) How much ice does the aluminium
GV – Gay lusac’s (GoodVibes) melt?
4.7 g – Sol mal C∆T= mi (hf)
mi = ∆S =
20g(0,21cal/gmC)(90C)/(80cal/g) [5g(540cal/g)(4.2J/1cal)]/(100+273)K
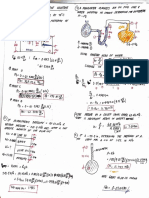
41. Water is being heated by 1500W 47. The first law of thermodynamics is
heater. What is the rate of change in based on which of the following
temperature of a kg of water? principles?
0.357 K/s – Sol 1kg of water = 4.2 Conservation of energy
kJ/kg.K ∆Q = ∆U + ∆W Work done by the
∆T = (1500J/s)/(1kg)(4.2kJ/kg.K) system
42. One kilogram of water = 4,2 kJ/kg,K is ∆Q = ∆U - ∆W Work done on the
heated by 300 BTU of energy. What is system
the change in temperature, in K?
75.4 K – Sol Q = mc∆T 48. If a system absorbs 500 cal of heat at
300BTU(1.055kJ/1BTU)=(1kg)(4.2kJ/k the same time does 400 J of work,
g.k) ∆T Find the change in internal energy of
43. Find the change in internal energy of the system.”
5lbm of oxygen gas when the 1.7kJ - Sol 500cal(4.2J/1cal) = ∆U +
temperature changes from 100 F to 400J
120 F, (Cv = 0.157 BTU/lbm.R) 49. Steam at 1000 lb/ft^2 pressure and
15.7 BTU – Sol ∆U = Q = mc∆T 300R has a specific volume of 6.5
∆F=∆R = ∆T = 120 F – 100 F ft/m^3 and a specific enthalpy of
=20R 9800
Q= lbf.ft/lbm. Find the internal energy
5lbm(0.157BTU/R)(20R) per pound per pound mass of steam.
44. Which of the following is a measure of 3300 lb.ft/lbm – Sol H = U + PV
disorder 9800lbf.ft/lbm = U +
Entropy 1000lb/ft^2 (6.5ft/m^3)
45. Twenty grams of ice at 0 C melts to 50. A gas enclosed in a cylinder with a
water at 0 C. How much does the weighted piston as the top boundary.
entropy of the 0g change in this The gas is heated and expands from a
process? volume of 0.04 m^3 to 0.10 m^3 at a
24.5 J/K - Sol using latent heat ∆S = constant pressure of 200 kPa. Find the
Q/T = mh/T work done on the system.
latent heat of ice to water = 12 kJ/kg – Sol W = P ∆V
80(cal/g) W = (200kPa)(0.10m^3-
∆S = 0.04m^3)
[20g(80cal/g)(4.2J/1cal)]/273K 51. Twenty grams of oxygen gas are
46. Compute the entropy change of a 5g compressed at a constant
of water at 100 C as it changes to temperature of 30 C to 5%of their
steam at 100 C under standard original volume , What work is done
pressure. on the system?
- 30.3 J/K - Sol using latent heat ∆S = 1124 cal –Sol ∆W = PV ln (V2/V1)
Q/T = mhv/T ∆W = mRT ln (V2/V1)
latent heat of vaporization= =20g(0.0619 cal/g.K) ln
540(cal/g) (0.05V1/V1)
=-1123.74 cal
negative because work done ON the type of processes are they?
system. Two isothermal and two isentropic
52. What is the work done for a closed, 59. A simple steam engine receives steam
reversible isometric system? from the boiler at 180 C and exhausrs
ZERO – Sol W=P∆V no change in directly into the air at 200C. What is
volume the upper limit of its efficiency
53. During an adiabatic; internally 17.6% - Sol 𝞰 = [1- (Tcold/Thot) = 1 –
reversible process, what is true. About (100 C + 273)/ (180 C + 273) ] x 100
the change in entropy? 60. Compute the maximum possible
It is always zero efficiency of a heat engine operating
54. A pure substance at absolute zero between the temperature limits of 90
temperature is in perfect order and its C and 300 C
entropy is zero. This is best known as 36.65% - Sol 𝞰 = [1- (Tcold/Thot) = 1 –
The third law of thermodynamics (90 C + 273)/ (300 C + 273) ] x 100
55. Find w and u, for a 6 cm cube of iron 61. A steam engine operating between a
as it is from 20 C to 300 C. For iron, c= boiler temperature of 220 C and a
0.11 cal/g C and the volume condenser temperature of 35 C
coefficient of thermal expansion is delivers 8 hp. If its efficiency is 30% of
3,6x10-5 C -1. The mass of the cube that for a Carnot engine operating
1700g. between these temperatures limits.
218 kJ – Sol ∆W = P∆V, How many calories are absorbed each
∆Q = mC∆T second by the boiler?
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W 12.7 kCal/s – Sol 𝞰engine =
∆Q = mC∆T = 0.30𝞰carnot
1700g(0.11cal/g.C)(280C) =(0.30) [1- (Tcold/Thot) = 1 – (35 C +
= 52kcal 273)/ (220C + 273)
∆V = (3.6x10^-5.C)(280 C)(6x10^- =0.1125760649
3m)^3 W = J/s
= 2.17728x10^-9m Pi =Po/𝞰 = [7hp(746W)(1/4.2J)]/
P in exposed iron = 1x10^5N/m^2 0.1125760649
∆W = P∆V = (1x10^5N/m^2)( =12.622kcal/s
2.17728x10^-9m)
=2.17728x10^-4 J
∆U = ∆Q - ∆W = 52Kcal(4.2J/kcal) -
2.17728x10^-4 J= 218 kJ
56. What is true about the polytropic
exponent, n , for a perfect gas
undergoing an isobaric process?
n=0
57. Which of the following
thermodynamic cycles is the most
efficient?
Carnot
58. The ideal, reversible Carnot cycle
involves for basic processes. What
You might also like
- Thermodynamics 1Document72 pagesThermodynamics 1Victor CapistranoNo ratings yet
- EsasDocument38 pagesEsasRizza Yang100% (5)
- Fluids M3F1Document4 pagesFluids M3F1Ej ParañalNo ratings yet
- PC PH DiagramsDocument37 pagesPC PH DiagramsKenny Pabón Cevallos100% (1)
- Work sheet.1Document6 pagesWork sheet.1tfkthe46No ratings yet
- TDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IDocument11 pagesTDCE Question Bank - 2018 Unit IvinodNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Question and AnswerDocument10 pagesThermodynamics Question and AnswerKumaran PalaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Science Lecture - First Law ThermodynamicsDocument21 pagesMechanical Science Lecture - First Law ThermodynamicsNafiz Uddin NihalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3 E&EE Refrigeration System-1-4Document4 pagesExperiment No.3 E&EE Refrigeration System-1-4GauravNo ratings yet
- MET 220 Workshop #1 (CH1-CH2-CH3)Document4 pagesMET 220 Workshop #1 (CH1-CH2-CH3)zurita25No ratings yet
- Properties of Pure SubstanceDocument32 pagesProperties of Pure SubstanceMaherNo ratings yet
- MEG 212 Practise QuestionsdocxDocument11 pagesMEG 212 Practise Questionsdocxoyetunde ridwanNo ratings yet
- ME214_BTD_Tutorial_QuestionsDocument2 pagesME214_BTD_Tutorial_QuestionsKONDALRAONo ratings yet
- Chemical engineering thermodynamics I worksheetDocument4 pagesChemical engineering thermodynamics I worksheetTesfa negaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics QBDocument15 pagesThermodynamics QBrajasamygopalNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicDocument6 pagesThermodynamicWilliam Arthur MacklorenNo ratings yet
- Poveda Pachon Marlon Yesid Tarea #1Document12 pagesPoveda Pachon Marlon Yesid Tarea #1Marlon Yesid PovedaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet 1 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment Sheet 1 PDFRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer QuizDocument22 pagesThermodynamics and Heat Transfer QuizFeolo Riel TarayNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 4Document4 pagesLearning Activity 4Araiza FloresNo ratings yet
- Thermo DynamicsDocument21 pagesThermo DynamicsManas Ranjan JenaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics (LECTURE)Document117 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics (LECTURE)Arvind ArvindNo ratings yet
- Gen Phy Slem Week 8 2nd Q QateamDocument9 pagesGen Phy Slem Week 8 2nd Q QateamMharbin AsuncionNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument54 pagesThermodynamicsArbeeChrystelV.AleraNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document7 pagesSheet 1Bahaa RaghebNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Important QuestionsPrasobh ShamohanNo ratings yet
- Clean Energy Lecture 2Document28 pagesClean Energy Lecture 2Tze Long GanNo ratings yet
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesEngineering Thermodynamicsgyanimahato.4345No ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument57 pagesThermodynamicsMei Lamfao100% (1)
- MEM201Thermodynamics QB (2018-19) With Syllabus-1 PDFDocument10 pagesMEM201Thermodynamics QB (2018-19) With Syllabus-1 PDFRohan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (Numericals)Document12 pagesQuestion Bank (Numericals)Omid Karimi SadaghianiNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration 22.1Document29 pagesRefrigeration 22.1preceiuxNo ratings yet
- PomeDocument17 pagesPomeAnirudh KaushikNo ratings yet
- 13qus DME KecDocument4 pages13qus DME KecstrombornNo ratings yet
- AE321 Tut1Document4 pagesAE321 Tut1Prabhash singhNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Physics - ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesClass 11 - Physics - ThermodynamicsSha HNo ratings yet
- Chapter+1.Gases-part1 2023Document35 pagesChapter+1.Gases-part1 2023NOXOLO NOMBULELO WENDY NGXONGONo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics: (T C, M C)Document13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics: (T C, M C)ragunath LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics IntroductionDocument13 pagesThermodynamics IntroductionGissela BTNo ratings yet
- IDEAL GAS PROCESSESDocument2 pagesIDEAL GAS PROCESSESfitriNo ratings yet
- Vapor Precooling in A Pulse Tube Liquefier: E.D. Marquardt, Ray Radebaugh, and A.P. PeskinDocument5 pagesVapor Precooling in A Pulse Tube Liquefier: E.D. Marquardt, Ray Radebaugh, and A.P. PeskinANILNo ratings yet
- Thermo - First Second LawDocument35 pagesThermo - First Second LawPengintaiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics: Introduction and Basic ConceptsDocument44 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics: Introduction and Basic ConceptsMalav PurohitNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 3rdME BDocument1 pageAssignment-1 3rdME BShailesh PatraNo ratings yet
- Problem Set - Thermodynamics & ICEDocument2 pagesProblem Set - Thermodynamics & ICEBea Therese RadubanNo ratings yet
- 33 ch12Document19 pages33 ch12ZoyaNo ratings yet
- Basics of ThermodynamicsDocument36 pagesBasics of ThermodynamicsYeditha Satyanarayana MurthyNo ratings yet
- HW1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesHW1 SolutionsRunner ScottNo ratings yet
- ME150P ELecture 1 (04 January 2011)Document115 pagesME150P ELecture 1 (04 January 2011)engrjayasis200% (1)
- Behavior of Pure Substances: Than One Phase, But Each Phase Must Have The Same Chemical CompositionDocument18 pagesBehavior of Pure Substances: Than One Phase, But Each Phase Must Have The Same Chemical CompositionDharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Combus Eng'g Homework 1Document5 pagesCombus Eng'g Homework 1Alecsia NuguidNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 TermodinamikaDocument3 pagesTugas 1 TermodinamikaMega LialitaNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1ash jay100% (1)
- Me3391-Engineering Thermodynamics-805217166-Important Question For Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesMe3391-Engineering Thermodynamics-805217166-Important Question For Engineering ThermodynamicsRamakrishnan NNo ratings yet
- ME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Question BankDocument15 pagesME6301 Engineering Thermodynamics Question BankAnantha Kumar0% (1)
- Ol ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesOl ThermodynamicsMark Vincent Castillo ViloriaNo ratings yet
- FME Notes Unit3Document7 pagesFME Notes Unit3vishal shuklaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Moist Air PropertiesDocument9 pages2.2 Moist Air PropertiesMark MoraNo ratings yet
- Thermal expansion of steel I-beam and mercury thermometer problemsDocument2 pagesThermal expansion of steel I-beam and mercury thermometer problemsYancha PagdagdaganNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument5 pagesSampleMark Anthony RazonNo ratings yet
- Processes and Carnot CycleDocument4 pagesProcesses and Carnot CycleRagh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chem 73 PS1 2017 PDFDocument3 pagesChem 73 PS1 2017 PDFImee Kassandra Estomo CachoNo ratings yet
- Important Mcq-Single Phase Induction Motors - WWW - Allexamreview.comDocument14 pagesImportant Mcq-Single Phase Induction Motors - WWW - Allexamreview.comEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Enngcoa Data BankDocument55 pagesEnngcoa Data BankEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Engineering Economics Part 2 ECE Board ExamDocument17 pagesMCQ in Engineering Economics Part 2 ECE Board ExamEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Engineering Economics Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocument19 pagesMCQ in Engineering Economics Part 1 ECE Board ExamEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- 120 Top Most Current ELECTRICITY - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument59 pages120 Top Most Current ELECTRICITY - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Motor ObectivesDocument23 pagesSingle Phase Motor ObectivesEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Engineering Economics Part 3 ECE Board ExamDocument17 pagesMCQ in Engineering Economics Part 3 ECE Board ExamEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Simple Strain and Stress FormulasDocument6 pagesSimple Strain and Stress FormulasEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- EE116x EXIT EXAM Power Plant EngineeringDocument3 pagesEE116x EXIT EXAM Power Plant EngineeringEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- 110 TOP CONTROL SYSTEMS questionsDocument24 pages110 TOP CONTROL SYSTEMS questionsEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- 60 Top Most Cables - Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument14 pages60 Top Most Cables - Electrical Engineering Objective Type Questions and AnswersEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- 120 Top Most A.C. Fundamentals, Circuits and Circuit Theory Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument27 pages120 Top Most A.C. Fundamentals, Circuits and Circuit Theory Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Assistant and Sub Assistant Job Question With AnswerDocument10 pagesAssistant and Sub Assistant Job Question With AnswerEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Important Mcq-Single Phase Induction Motors - WWW - Allexamreview.comDocument14 pagesImportant Mcq-Single Phase Induction Motors - WWW - Allexamreview.comEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Motor ObectivesDocument23 pagesSingle Phase Motor ObectivesEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank in Control SystemsDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank in Control SystemsEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- AC Mach Module 3 Problems Parallel Alternators Load Current PFDocument3 pagesAC Mach Module 3 Problems Parallel Alternators Load Current PFEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank in Transformers EfficiencyDocument17 pagesQuestion Bank in Transformers EfficiencyMarbyDadivasNo ratings yet
- Study Guide#1 Ee Computer ApplicationDocument5 pagesStudy Guide#1 Ee Computer ApplicationEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Q. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3Document13 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark Each.: GATE 2019 General Aptitude (GA) Set-3pulkit patelNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Transmission and Distribution System Engineering 1 - RBCDocument12 pagesElectric Power Transmission and Distribution System Engineering 1 - RBCEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Solid Geom FormulaDocument8 pagesSolid Geom FormulaEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Session 2 Trigonometry - HandoutDocument1 pageSession 2 Trigonometry - HandoutConan EdogawaNo ratings yet
- Fluids Forma 1 M 2Document3 pagesFluids Forma 1 M 2Ej ParañalNo ratings yet
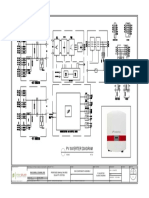
- PV Inverter Diagram: E 1 1 Proposed 264Kwp On-Grid Solar PV SystemDocument1 pagePV Inverter Diagram: E 1 1 Proposed 264Kwp On-Grid Solar PV SystemEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Practice Problems Online ReviewDocument8 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Practice Problems Online ReviewEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- August 2020 Monthly Market Assessment Report Highlights Declining Demand and Over-GenerationDocument20 pagesAugust 2020 Monthly Market Assessment Report Highlights Declining Demand and Over-GenerationEj ParañalNo ratings yet
- PAC Report On MRA Final 1Document20 pagesPAC Report On MRA Final 1Ej ParañalNo ratings yet
- Organic Compounds Separation TechniquesDocument6 pagesOrganic Compounds Separation TechniquesKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Cbiescss 07Document6 pagesCbiescss 07Ayush BeheraNo ratings yet
- A Simple HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Analysis of Phosphatidylcholine and Its Partial Hydrolysis Products 1-And 2-Acyl LysophosphatidylcholineDocument5 pagesA Simple HPLC Method For The Simultaneous Analysis of Phosphatidylcholine and Its Partial Hydrolysis Products 1-And 2-Acyl LysophosphatidylcholineChang Woo JongNo ratings yet
- Alhoty Pre QualificationDocument91 pagesAlhoty Pre QualificationSridhar ShankarNo ratings yet
- The Consep AcaciaDocument7 pagesThe Consep AcaciaPrincess Ruwarashe Courteney MunyoroNo ratings yet
- Sulfide Stress CrackingDocument5 pagesSulfide Stress Crackingsyahril siddiq arelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Scab Formation On Castings SurfacesDocument57 pagesLecture 4 Scab Formation On Castings SurfacesLuis Arturo RamirezNo ratings yet
- GG General - Guidelines - Glass - Embedding - v1 - 10-11Document16 pagesGG General - Guidelines - Glass - Embedding - v1 - 10-11Manuel GallardoNo ratings yet
- Modeling Premixed Combustion in FLUENTDocument18 pagesModeling Premixed Combustion in FLUENTXabi TrifolNo ratings yet
- Iron International StandardsDocument2 pagesIron International StandardsAmir MusaibNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 231 Tutorial Session #5 QuestionsDocument8 pagesChemistry 231 Tutorial Session #5 QuestionsFiqkyAkbarNo ratings yet
- Tantalum: Arihant Jain 6 PeriodDocument7 pagesTantalum: Arihant Jain 6 PeriodbudyNo ratings yet
- SCM25 steel alloy properties and applicationsDocument1 pageSCM25 steel alloy properties and applicationsPeterWayNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-Metals 1Document32 pagesMetals and Non-Metals 1MindOfPrinceNo ratings yet
- Agilent HPLC and UHPLC Application HighlightsDocument159 pagesAgilent HPLC and UHPLC Application HighlightsHeather Fleming100% (1)
- Tema ExcelDocument8 pagesTema ExcelTeodor OlaruNo ratings yet
- Distillation LabDocument18 pagesDistillation LabWong XimeiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics 11th Edition Halliday Test BankDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Physics 11th Edition Halliday Test Bankdorissamuelqpnrrz100% (32)
- Ica 2 Reviewer For MidtermDocument17 pagesIca 2 Reviewer For Midtermjohn kyleNo ratings yet
- EVreporter October 2021 e MagazineDocument36 pagesEVreporter October 2021 e MagazinekarthikNo ratings yet
- Actuator StepbystepDocument53 pagesActuator StepbystepQuang Huy VũNo ratings yet
- Peek vs. MetalDocument3 pagesPeek vs. MetalAzizol WahabNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Bronze Properties and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesAluminum Bronze Properties and ApplicationsAbbasNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry: Physical ChemistryDocument22 pagesThermochemistry: Physical ChemistryAaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- bổ trợ đọcDocument35 pagesbổ trợ đọcCao HảiNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 Rocks Minerals NotesDocument45 pagesTopic 11 Rocks Minerals NotesPlayer One100% (1)
- Marshall Stability Test PDFDocument8 pagesMarshall Stability Test PDFAnonymous FO4sHLLONo ratings yet
- Basic Instrument SymbolsDocument7 pagesBasic Instrument Symbolssushant_jhawer100% (1)
- Quantifying Member Slenderness RatioDocument14 pagesQuantifying Member Slenderness RatiobethNo ratings yet