Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Activation Photochemical English
Uploaded by
plennyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Activation Photochemical English
Uploaded by
plennyCopyright:
Available Formats
5 CHEMICAL PROCESS ENGINEERING CATALYTIC AND PHOTOCHEMICAL ACTIVATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
PHOTOCHEMICAL ACTIVATION
In a photochemical activation, the activation
energy to enable or accelerate the reaction is
applied by means of electromagnetic radiation.
When the atoms or molecules absorb this radia-
tion, they achieve a higher energy level and are
activated. For an effective reaction process, the
emission spectrum (wavelength range) of the
light source used has to be as similar to the
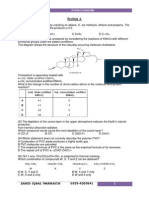
absorption spectra of the reacting substances as Spectrum of electromagnetic waves:
possible. 1 X-radiation, 2 ultraviolet radiation, 3 visible light,
4 infrared radiation
In industrial-scale photochemical reactions, the electro- The electromagnetic radiation is mostly generated by
magnetic radiation leads to the formation of radicals. The means of lamps working according to the electric discharge
most important property of radicals is that they have a an principle. The gas used is normally mercury vapour.
unpaired valence electron instead of an electron pair. This
The following lamp types are generally distinguished:
electron gives the radical its great reactivity and enables
the reaction rates necessary for the industrial process. Low-pressure lamps
One advantage of photochemical activation is the possi- These lamps generate a nearly monochromatic light
bility to activate specific chemical bonds by selecting a (light of a single wavelength) with a wavelength of
suitable emission spectrum. Another advantage is the fact 254nm (UV-C).
that the reaction rate can be easily influenced by switching
Medium-pressure lamps
light sources on or off.
These lamps emit radiation of various wavelengths in the
The following applications are examples of the industrial UV range and in the visible range. The emission spectrum
use of photochemical reactions: is in the range of 200...600nm.
chlorination of hydrocarbons High-pressure lamps
vitamin D production The spectrum of these lamps ranges from the short-wave
polyvinyl chloride (PVC) production UV range (V-UV) far into the visible range. It is used in
treatment of wastewater contents many photochemical reactions.
Example of a photochemically activated reaction to decompose organic, nonbiodegradable substances:
H2O2 hydrogen peroxide, ·OH hydroxyl radical, A organic, nonbiodegradable substance,
B organic intermediate products, C inorganic end products
You might also like
- PhotochemistryDocument22 pagesPhotochemistryJegadeeswaran SNo ratings yet
- Sterilization by RadiationDocument11 pagesSterilization by RadiationEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- PC 20166Document10 pagesPC 20166chopin.wlive.cnNo ratings yet
- Notes On UVRDocument3 pagesNotes On UVRVALDEZ, Kessia Faye Carmela R.No ratings yet
- UV CuringDocument31 pagesUV CuringAdesh GurjarNo ratings yet
- RD009EN00 - UV Technologies in Water Purification SystemsDocument12 pagesRD009EN00 - UV Technologies in Water Purification SystemsRonald SalasNo ratings yet
- Ultraviolet Lamps For Disinfection and OxidationDocument16 pagesUltraviolet Lamps For Disinfection and Oxidationdonnal47No ratings yet
- Basics of UV Curable Coatings - SelChemDocument14 pagesBasics of UV Curable Coatings - SelChemSatish ShenoyNo ratings yet
- A 1 Useful Terms and Expressions in The Photoreactivity Testing of DrugsDocument4 pagesA 1 Useful Terms and Expressions in The Photoreactivity Testing of DrugsMatthew WardNo ratings yet
- Photo Multipliers: By, MD Anas AhmadDocument16 pagesPhoto Multipliers: By, MD Anas AhmadPallav KumarNo ratings yet
- F Spectroscopic InstrumentationDocument21 pagesF Spectroscopic Instrumentationmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation: Sources of UV RadiationDocument16 pagesInstrumentation: Sources of UV Radiationexample2000No ratings yet
- Radiation Protection of Foods, and Nature of Microbial Radiation ResistanceDocument2 pagesRadiation Protection of Foods, and Nature of Microbial Radiation ResistanceMuhammad Fayiz HusainNo ratings yet
- Seminar II Recent Advances in Electrochemiluminescence By: Yegezu M. July, 2022 Addis AbabaDocument35 pagesSeminar II Recent Advances in Electrochemiluminescence By: Yegezu M. July, 2022 Addis AbabaYegezu MebratuNo ratings yet
- Experience With Optical Partial Discharge DetectionDocument4 pagesExperience With Optical Partial Discharge DetectionDaniel Tamata SolorioNo ratings yet
- Apeksha FinalDocument26 pagesApeksha FinalAshish MOHARENo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Opto-IsolationDocument8 pagesExperiment 3 Opto-IsolationasdfsafdasNo ratings yet
- Plastic Solar Cells Review Recent DevelopmentsDocument12 pagesPlastic Solar Cells Review Recent DevelopmentsjonbilbaoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry I Analytic Techniques: Violet BlueDocument5 pagesClinical Chemistry I Analytic Techniques: Violet BlueBenedict EntrampasNo ratings yet
- APPENDIX B: Sensor Types: A1. LDR (Light-Dependent Resistor)Document4 pagesAPPENDIX B: Sensor Types: A1. LDR (Light-Dependent Resistor)MostafaDilatyNo ratings yet
- L5 Research Conducted WorldwideDocument6 pagesL5 Research Conducted WorldwideOpreaNo ratings yet
- Single Photon DetectorsDocument8 pagesSingle Photon DetectorsAnonymous lsnDTjvNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation of Ultra Violet SpectrosDocument43 pagesInstrumentation of Ultra Violet Spectrosimam mahdi tv officialNo ratings yet
- Pulse Light Sterilizer SuperiorityDocument7 pagesPulse Light Sterilizer SuperiorityOtoy Mar-otoyNo ratings yet
- To Study Variation of Current Using A LDR - Physics Astronomy Project TopicsDocument7 pagesTo Study Variation of Current Using A LDR - Physics Astronomy Project Topicsashamishra01981No ratings yet
- CHE029 Spectroscopic-AnalysisDocument6 pagesCHE029 Spectroscopic-AnalysisCarla Mae OlvenarioNo ratings yet
- Organic Photochemistry BSCDocument21 pagesOrganic Photochemistry BSCZo Muana CXNo ratings yet
- Decker 1998 Polymer InternationalDocument9 pagesDecker 1998 Polymer InternationalreneNo ratings yet
- Introducing The Vapourtec UV-150 Photochemical ReactorDocument7 pagesIntroducing The Vapourtec UV-150 Photochemical ReactorAli TunaNo ratings yet
- IR Transmitter: Ir LedDocument14 pagesIR Transmitter: Ir LedPragna ThatipelliNo ratings yet
- Uv Visible SpectrosDocument48 pagesUv Visible SpectrosDhanvanth100% (7)
- Fourier Transform Infrared SpectrosDocument27 pagesFourier Transform Infrared Spectrosrmarin_90No ratings yet
- Optical PropertiesDocument31 pagesOptical PropertiesAhmed MalikNo ratings yet
- Light Cring SystemDocument16 pagesLight Cring SystemSaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Report On UV Visible Spectroscopy - CEP 506Document11 pagesReport On UV Visible Spectroscopy - CEP 506showravNo ratings yet
- FIBER IMP TOPICSDocument8 pagesFIBER IMP TOPICSAvik PalNo ratings yet
- Uv SPDocument17 pagesUv SPछेरबहादुर लेउवाNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0038109898002154 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0038109898002154 MainADXHYGFSXNo ratings yet
- 8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesDocument3 pages8.2. EMW-source, Frequency Range, UsesRamananNo ratings yet
- What Is UV LightDocument7 pagesWhat Is UV LightSupatmono NAINo ratings yet
- Flow Photochemistry PDFDocument28 pagesFlow Photochemistry PDFAli TunaNo ratings yet
- Uv Analysis Method Development For Diclofenac and Paracetamol in CombinationDocument28 pagesUv Analysis Method Development For Diclofenac and Paracetamol in Combination0921py100% (5)
- UV SpectrosDocument15 pagesUV Spectrosjatt da mukabalaNo ratings yet
- Lect7 - chemiluminescence - اجهزة معملية - الفرقة الثالثة - مختبراتDocument32 pagesLect7 - chemiluminescence - اجهزة معملية - الفرقة الثالثة - مختبراتamany mohamedNo ratings yet
- Grid-Connected PV SystemDocument42 pagesGrid-Connected PV SystemrevjangerNo ratings yet
- CollectionDocument6 pagesCollectionGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Code: PHA 305 UV-Visible SpectrophotometryDocument38 pagesCourse Code: PHA 305 UV-Visible SpectrophotometryMahadi Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- Instruments For Optical SpectrometryDocument2 pagesInstruments For Optical SpectrometrySean CollinsNo ratings yet
- Apeksha FinalDocument25 pagesApeksha FinalAshish MOHARENo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 PhotochemistryDocument18 pagesLesson 2 Photochemistryeunicedolphine2022No ratings yet
- Chan 2010Document14 pagesChan 2010Debasish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sterilization by RadiationDocument29 pagesSterilization by RadiationSadia AfrinNo ratings yet
- G2 - Residential Lighting LaboratoryDocument13 pagesG2 - Residential Lighting LaboratoryMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three-Sources and DetectorsDocument8 pagesChapter Three-Sources and DetectorsOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- SpectrrosDocument35 pagesSpectrrosvscdNo ratings yet
- Band GapDocument19 pagesBand Gapilham ditamaNo ratings yet
- Physics Project FileDocument17 pagesPhysics Project Filepantprakhar2No ratings yet
- UV VisDocument46 pagesUV VisWahyuni EkaNo ratings yet
- 17 en Produktbereich Niederspannungsschaltanlagen Neu EnglischDocument1 page17 en Produktbereich Niederspannungsschaltanlagen Neu EnglischplennyNo ratings yet
- 8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortDocument7 pages8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortplennyNo ratings yet
- Ed WP Automatic Commutation of Stepper MotorsDocument9 pagesEd WP Automatic Commutation of Stepper MotorsSelfiana UlfaNo ratings yet
- 947 E EGT 2 Wiring Installation For Lighting and Appliance Circuits ShortDocument8 pages947 E EGT 2 Wiring Installation For Lighting and Appliance Circuits ShortplennyNo ratings yet
- Lighting TechnologyDocument12 pagesLighting TechnologyplennyNo ratings yet
- WP Focus On Miniature Pumps Selecting The Right Motor TechnologyDocument4 pagesWP Focus On Miniature Pumps Selecting The Right Motor TechnologyplennyNo ratings yet
- 8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortDocument7 pages8498 E EPD Busbar Systems ShortplennyNo ratings yet
- WP Brush DC Motor Basics 0Document4 pagesWP Brush DC Motor Basics 0plennyNo ratings yet
- MeccalteDocument13 pagesMeccalteplennyNo ratings yet
- MAU2673 European Grid CodesDocument8 pagesMAU2673 European Grid CodesplennyNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide to Alternator Shaft StiffnessDocument9 pagesTechnical Guide to Alternator Shaft StiffnessplennyNo ratings yet
- Insulation SystemDocument8 pagesInsulation SystemplennyNo ratings yet
- En Engineering Definitions and FormulasDocument1 pageEn Engineering Definitions and FormulasplennyNo ratings yet
- Ed Engineers AppendixDocument28 pagesEd Engineers AppendixplennyNo ratings yet
- ECP 3-1S/4 Generator SpecsDocument5 pagesECP 3-1S/4 Generator SpecsplennyNo ratings yet
- Generator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesGenerator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsplennyNo ratings yet
- Ed Brushless DC Motors Timing RelattionshipDocument2 pagesEd Brushless DC Motors Timing RelattionshipplennyNo ratings yet
- 43 vl4Document5 pages43 vl4CristobalNo ratings yet
- Technical Guide to Alternator Shaft StiffnessDocument9 pagesTechnical Guide to Alternator Shaft StiffnessplennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp34 1l4Document5 pagesEcp34 1l4plennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp28 1VS4 ADocument5 pagesEcp28 1VS4 AplennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp34 1l4Document5 pagesEcp34 1l4plennyNo ratings yet
- ECP 3-1S/4 Generator SpecsDocument5 pagesECP 3-1S/4 Generator SpecsplennyNo ratings yet
- Test Motor Phase & Rotation DirectionDocument9 pagesTest Motor Phase & Rotation DirectionplennyNo ratings yet
- tdr-410 en 1.02 Druk KPLDocument24 pagestdr-410 en 1.02 Druk KPLplennyNo ratings yet
- Ecp28 1VS4 ADocument5 pagesEcp28 1VS4 AplennyNo ratings yet
- Generator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesGenerator Type Hco38 2L26 A: Electrical CharacteristicsplennyNo ratings yet
- vt-2 Ins Obs v10 GBDocument1 pagevt-2 Ins Obs v10 GBplennyNo ratings yet
- Phase Sequence Tester ManualDocument6 pagesPhase Sequence Tester ManualplennyNo ratings yet
- Safety recommendations for voltage indicator useDocument2 pagesSafety recommendations for voltage indicator useplennyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Reaction MechanismDocument15 pagesOrganic Chemistry Reaction Mechanismprem19999No ratings yet
- Heterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts 1Document117 pagesHeterogeneous Catalysis and Solid Catalysts 1lotannaNo ratings yet
- NSS Chemistry Part 9 Rate of ReactionsDocument26 pagesNSS Chemistry Part 9 Rate of ReactionsFelix YueNo ratings yet
- 1صناعاتDocument15 pages1صناعاتroaanaseem267No ratings yet
- HCL Temperature ExperimentDocument3 pagesHCL Temperature Experimentjosh ridesNo ratings yet
- Prep For Quiz 2: ChemistryDocument13 pagesPrep For Quiz 2: ChemistryAndreLiengNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of Antioxidant Action of Phosphite and Phosphonite EstersDocument38 pagesMechanisms of Antioxidant Action of Phosphite and Phosphonite EstersDuy Khánh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- A Reactive Distillation Process For A Cascade and Azeotropic Reaction System: Carbonylation of Ethanol With Dimethyl CarbonateDocument8 pagesA Reactive Distillation Process For A Cascade and Azeotropic Reaction System: Carbonylation of Ethanol With Dimethyl CarbonatePriyam NayakNo ratings yet
- X (Chem) Worksheet Half Yearly (Easy)Document3 pagesX (Chem) Worksheet Half Yearly (Easy)skyskyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Liquor Heat Treatment On The Lignin Carbohydrate ContentDocument96 pagesThe Effect of Liquor Heat Treatment On The Lignin Carbohydrate ContentHuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Problemas ICHO28 A ICHO24Document40 pagesProblemas ICHO28 A ICHO24Leonardo FagundesNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Reaction Engineering CHE 505Document42 pagesBiochemical Reaction Engineering CHE 505Haru MasaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 30A UCLA Fall 2009 Midterm Exam II KEY: On My Honor, I Have Neither Given Nor Received Any Aid On This ExamDocument7 pagesChemistry 30A UCLA Fall 2009 Midterm Exam II KEY: On My Honor, I Have Neither Given Nor Received Any Aid On This ExamViceregalNo ratings yet
- AQA Chemistry A-Level - Introduction to Organic Chemistry QuestionsDocument12 pagesAQA Chemistry A-Level - Introduction to Organic Chemistry QuestionsПолина ЩукаNo ratings yet
- 11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument39 pages11 Alcohols Phenols and EthersAishwarya Naidu100% (1)
- Belmar Dissertation Dec 2012Document191 pagesBelmar Dissertation Dec 2012jub164No ratings yet
- Ohtsuka 2010Document7 pagesOhtsuka 2010Rodrigo Regla MuñozNo ratings yet
- Aqa 74041 SQPDocument20 pagesAqa 74041 SQPAttique IftikharNo ratings yet
- Questioner For The Long Quiz (Grade 8)Document3 pagesQuestioner For The Long Quiz (Grade 8)Novie Mae ReambonanzaNo ratings yet
- Improved Methanol Yield and Selectivity From CO2 Hydrogenation Using A Novel Cu-ZnO-ZrO2 Catalyst Supported On Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH)Document8 pagesImproved Methanol Yield and Selectivity From CO2 Hydrogenation Using A Novel Cu-ZnO-ZrO2 Catalyst Supported On Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH)Nguyễn TuânNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Analysis of Alcohols and PhenolsDocument7 pagesExperiment 5: Analysis of Alcohols and PhenolsAnonymous 75TDy2yNo ratings yet
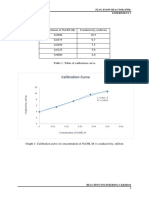
- Calibration Curve: Concentration of Naoh (M) Conductivity (MS/CM) 0.0500 10.7 0.0375 9.7 0.0250 7.5 0.0125 5.6 0.0000 4.0Document7 pagesCalibration Curve: Concentration of Naoh (M) Conductivity (MS/CM) 0.0500 10.7 0.0375 9.7 0.0250 7.5 0.0125 5.6 0.0000 4.0Kholidi ChooNo ratings yet
- 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument69 pages10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesSwayam ShrikondwarNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 10 Week7Document3 pagesQ4 Science 10 Week7Ma'am Jessica PambagoNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical EquationsDocument66 pagesModern Chemistry Chapter 8 Chemical EquationsanacercetNo ratings yet
- Hydro CarbonsDocument10 pagesHydro CarbonsLok Jun Hao100% (1)
- Syllabus CBEMS210Document1 pageSyllabus CBEMS210AnandNo ratings yet
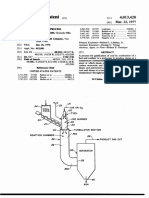
- No. of Patents US4013428 - Lurgi Gasification ProcessDocument8 pagesNo. of Patents US4013428 - Lurgi Gasification ProcessChristian ImanuelNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Kimia (Jurnal)Document11 pagesReaksi Kimia (Jurnal)Nur Rahayu Setiawati82% (51)
- Chemistry BBQDocument20 pagesChemistry BBQShaik nabi Farhath banuNo ratings yet