Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dermatomes Lateral Plate Mesoderm Neural Crest
Uploaded by
Ñäd Éèm0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesOriginal Title
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM-IUL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesDermatomes Lateral Plate Mesoderm Neural Crest
Uploaded by
Ñäd ÉèmCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
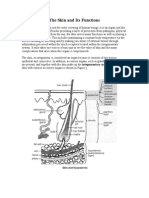
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
DERMIS (Surface ectoderm)
Initially, it is a single layer of ECTODERMAL cells
During 2nd month, two layers of cell develop from a single layer of cells
It consists of a superficial flattened cells called PERIDERM and deep cuboidal cells(Basal layer)
Further proliferation of cells of basal layer gives rise to third intermediate layer
During 3rd to 5th month , 5 layers are formed
Up to 5th month, there will be continuous desquamation and keratinization and replacement of
peridermal cells by those arising from basal layer
After 5th month, periderm disappears and is replaced by stratum corneum
Proliferation of stratum germinativum extends into dermis as EPIDERMAL RIDGES
EPIDERMIS
It develops from 3 sources
1. Paraxial mesoderm(DERMATOMES forming dorsal aspect of head and trunk)
2. Somatopleuric layer of lateral plate mesoderm (Limbs and ventral and lateral aspect of trunk)
3. Neural crest(HEAD AND NECK REGION)
Mesenchymal cells cause COLLAGEN AND ELASTIC FIBRES FORMATION
rd th
During 3 and 4 month, dermal papillae are formed
EPIDERMAL RIDGES – Epidermis projecting into dermis
DERMAL PAPILLAE-Dermis in between the epidermal ridges
HAIR (Surface Ectoderm)
Downgrowth of epidermis into underlying dermis occurs
Stratum germinativum form a solid oblique epithelial cord known as HAIR BUD
Hair bud(lower end) is invaginated by mesenchyme condensation and it forms the papilla
The proliferation of germinal cells overlying the papilla gives rise to the HAIR
As hair grows to surface, cells forming downgrowth surround the hair forming the EPITHELIAL
ROOT SHEATH
Surrounding the mesenchymal cells are the DERMAL ROOT SHEATH
NAILS (Surface Ectoderm)
Ectoderm at tip of each digit thickens and forms a primary nail field (10th week)
Thickening migrates to its dorsal aspect and is surrounded by U-shaped nail folds of epidermis
Cells in most proximal part of nail proliferate forming: Root of nail and cells of germinal layer:
germinal matrix
Cells in germinal matrix multiply and form the nail plate
Stratum corneum disappears from surface of nails EXCEPT from proximal part of nail plate
Epidermis overlapping proximal part of nail-EPONYCHIUM
Epidermis below free margin of nail plate-HYPONYCHIUM
SEBACEOUS GLANDS
It is formed as a bud arising from ectodermal cells forming the wall of hair follicle
Bud grows into adjacent dermis and divides into primordial of alveoli and ducts
Central cells of alveoli degenerates and release sebum
Arrector Pilli muscle arise from differentiation of mesenchyme adjacent to hair follicle
and it gets attached to dermal sheath of hair follicle
Note: Sebaceous from epidermis in glans penis and labia minora develop independent
from hair follicle
SWEAT GLANDS
ECCRINE
Develops as a downgrowth from epidermis into dermis(20 th week)
Downgrowth is solid at first but later gets canalized
Lower end- Secretory part of gland
Upper end- Ducts of sweat gland
Start functioning at time of birth(merocrine and involved in temp regulation)
APOCRINE
Begin to develop during puberty
Seen in axilla, areolae of nipples, pubic and perineal areas
Develop from hair follicles in form of buds
Open into hair follicle
Named as apocrine as part of secretory cell is shed as secretion
MAMMARY GLANDS (Ectodermal)
Appearance of a thickened line of epidermis extending from the base of the forelimb to the
region of the hind limb – MAMMARY RIDGE
It disappears but a small portion persists and penetrates the underlying mesenchyme
It forms 16 to 24 sprouts which later give rise to small, solid bud
By the end of prenatal life, they gets canalized and form lactiferous ducts(Proximal end)
Buds form small ducts and alveoli of the gland(terminal part of outgrowth)
Initially, the lactiferous ducts open into a small epithelial pit
Shortly after birth, this pit is transformed into the nipple by proliferation of the underlying
mesenchyme.
You might also like
- EmbryologyDocument39 pagesEmbryologyRukshan Ranatunga100% (1)
- The Integumentary System Development: Biene, Ellen Angelic Flores, Andrie BonDocument29 pagesThe Integumentary System Development: Biene, Ellen Angelic Flores, Andrie BonMu Lok100% (3)
- Drugs Used in Disorders of Endocrine System Ppt. Book (Lectures 1-6)Document467 pagesDrugs Used in Disorders of Endocrine System Ppt. Book (Lectures 1-6)Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (1)
- Physiology of The Thyroid GlandDocument28 pagesPhysiology of The Thyroid GlandSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- 001 Clinical Anatomy by Vishram SinghDocument180 pages001 Clinical Anatomy by Vishram SinghÑäd Éèm100% (1)
- Cushings DiseaseDocument17 pagesCushings Diseaserightspeaker22No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary Systemmao4evah0% (1)
- Thyroid StormDocument23 pagesThyroid Stormsadiq0% (1)
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument52 pagesIntegumentary Systemyasin oumer0% (1)
- Respiratory System ExaminationDocument46 pagesRespiratory System ExaminationÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- CPAC Nursing Course Syllabus for Competency Appraisal IIDocument10 pagesCPAC Nursing Course Syllabus for Competency Appraisal IIMary Janet Pinili100% (2)
- 02-1.WHO 2022-PitNETDocument21 pages02-1.WHO 2022-PitNETJihuhn YuNo ratings yet
- Lecture10 - The Skin and Its DerivativesDocument34 pagesLecture10 - The Skin and Its DerivativesSuresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Dev of Integumentary System and Appendages (Breast)Document4 pagesDev of Integumentary System and Appendages (Breast)Akachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ModifiedDocument34 pagesIntegumentary System Modifiedfarrah sorayah barodiNo ratings yet
- Development of Integumentary Sytem With AudioDocument36 pagesDevelopment of Integumentary Sytem With AudioRetrocasualty Find OutNo ratings yet
- Development of IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesDevelopment of IntegumentaryAkachukwu ObunikeNo ratings yet
- Histology: Nails Skin Glands Skin Repair Presented by Sultan Hafiz Adil Group 12Document15 pagesHistology: Nails Skin Glands Skin Repair Presented by Sultan Hafiz Adil Group 12Hafiz AdilNo ratings yet
- Embryology of the Integumentary System DevelopmentDocument3 pagesEmbryology of the Integumentary System DevelopmentJonathan PaghubasanNo ratings yet
- Skin (Integumentary System)Document16 pagesSkin (Integumentary System)sweet_toxiqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document7 pagesChapter 7Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument51 pagesIntegumentary SystemAuza Moses IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Hair and NailsDocument2 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Hair and NailsJosephine SNo ratings yet
- Integumen (Kulit Derivat) Organogenesis S2 2017Document58 pagesIntegumen (Kulit Derivat) Organogenesis S2 2017Desy NataliaNo ratings yet
- Skin Lecture 2Document7 pagesSkin Lecture 2bv2328002No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document31 pagesChapter 1cabdinuux32No ratings yet
- Integumantery STSMRDocument53 pagesIntegumantery STSMRamandagnaw19No ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument14 pagesHealth AssessmentAna MarieNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument32 pagesIntegumentary SystemRoman KhanNo ratings yet
- Histo ReportDocument8 pagesHisto ReportClaire GabionzaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pDocument4 pagesThe Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pdbelmerNo ratings yet
- L10 SkinDocument2 pagesL10 SkinalihusseinNo ratings yet
- Third To Eighth WeekDocument33 pagesThird To Eighth WeekGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Skin AppendagesDocument6 pagesIntegumentary System Skin AppendagespenshipNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesIntegumentary SystemxoxogeloNo ratings yet
- Gas Tru LationDocument53 pagesGas Tru LationSam MumoNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument17 pagesThe Integumentary SystemMoses BurgosNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument32 pagesThe Integumentary SystemDragan ZikicNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Anatomy in Under 40Document10 pagesIntegumentary System Anatomy in Under 40Bago CPSNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The Integumentary SystemChristine Joy MadronioNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Development and OrganogenesisDocument33 pagesEmbryonic Development and OrganogenesisMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Uni FileDocument10 pagesUni Filemuqadar khanNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period 4-8weekDocument25 pagesEmbryonic Period 4-8weekaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- Development of Eye-IulDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Eye-IulÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- 001 - ClassDocument26 pages001 - ClassLucas Victor AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerClarebelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Skin Appendages and Their Functions (40Document61 pagesSkin Appendages and Their Functions (40Arjohn VegaNo ratings yet
- "The Basics" - Origins of The Integumentary SystemDocument4 pages"The Basics" - Origins of The Integumentary SystemgerginNo ratings yet
- I) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueDocument44 pagesI) Skin Largest Organ of The Body in Surface Area and Weight. There Are Three Layers of The Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutaneous TissueSaralitaNo ratings yet
- Weeks 3 - 8Document32 pagesWeeks 3 - 8Stefan HutsonNo ratings yet
- The Third Week of Development: TH THDocument8 pagesThe Third Week of Development: TH THbarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument45 pagesIntegumentary SystemDASHNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - The Integumentary System - Hair and NailsDocument6 pagesLesson 2 - The Integumentary System - Hair and NailsAesthethic findsNo ratings yet
- Function of The SkinDocument69 pagesFunction of The SkinapermatagamaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesThe Integumentary SystemWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 009 Chapter 5Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 009 Chapter 5humanupgrade100% (1)
- Chapter 5 IntegumentaryDocument8 pagesChapter 5 IntegumentaryClark Jeth VicenteNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Integumrntary SystemDocument5 pagesUnit 2 Integumrntary Systemjayvee grace tuballaNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument38 pagesSkinrodelagapito100% (1)
- Dermatology Notes Handbook of Medical inDocument22 pagesDermatology Notes Handbook of Medical inMian BazanNo ratings yet
- LAYERS OF THE SKINDocument7 pagesLAYERS OF THE SKINJeah LourraineNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Skin FunctionDocument50 pagesPhysiology of Skin FunctionPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument8 pagesSkinsaraNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Structure and FunctionsDocument9 pagesThe Integumentary System: Structure and FunctionsJohn Paul ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Chapter 5Document13 pagesIntegumentary System Chapter 5lovj melNo ratings yet
- LG2 Histology of The SkinDocument26 pagesLG2 Histology of The SkinRawa AyubNo ratings yet
- Examination of Sensory SystemDocument27 pagesExamination of Sensory SystemÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- 18) Molecular Biology-SbDocument186 pages18) Molecular Biology-SbÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Descending Tracts: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeDocument39 pagesDescending Tracts: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- 22) Cancer SBDocument69 pages22) Cancer SBÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Descending Tracts: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeDocument39 pagesDescending Tracts: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Examination 2Document2 pagesRespiratory System Examination 2Ñäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- 3) Protein Chem IBDocument20 pages3) Protein Chem IBÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Posterior Pituitary: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeDocument60 pagesPosterior Pituitary: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamics: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeDocument31 pagesHemodynamics: DR Axelle Saverettiar Mbbs Physiology Department SSR Medical CollegeÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Basics: Views, Slides, ObjectsDocument15 pagesPowerPoint Basics: Views, Slides, ObjectsÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Lipid Chemistry - Case Based Q & ADocument18 pagesLipid Chemistry - Case Based Q & AÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Anterior Triangle of NeckDocument13 pagesAnterior Triangle of NeckÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Drain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesDocument3 pagesDrain The Central Portion of The Anterior Two-Third of The Tongue Bilaterally Into The Deep Cervical Lymph NodesÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Development of Body Cavities and Diaphragm: Pleuro-Pericardial and Pleuro-Peritoneal MembraneDocument14 pagesDevelopment of Body Cavities and Diaphragm: Pleuro-Pericardial and Pleuro-Peritoneal MembraneÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument23 pagesSpecial SensesÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- PANCREATIC SECRETION: HORMONAL AND NEURAL REGULATIONDocument46 pagesPANCREATIC SECRETION: HORMONAL AND NEURAL REGULATIONÑäd Éèm100% (2)
- Gastrointestin Al Hormones: Prof Suranjana RayDocument42 pagesGastrointestin Al Hormones: Prof Suranjana RayÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Development of Eye-IulDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Eye-IulÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Development of Eye-IulDocument4 pagesDevelopment of Eye-IulÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument23 pagesSpecial SensesÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- 7) Haemoglobin Chemistry-SbDocument39 pages7) Haemoglobin Chemistry-SbÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestin Al Hormones: Prof Suranjana RayDocument42 pagesGastrointestin Al Hormones: Prof Suranjana RayÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- 7) Haemoglobin Chemistry-SbDocument39 pages7) Haemoglobin Chemistry-SbÑäd ÉèmNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Endocrine SystemDocument39 pagesScience 6 Endocrine Systemcharmaine_olivia_1100% (1)
- Thyroid DiseasesDocument44 pagesThyroid DiseasesPLDT HOMENo ratings yet
- Homeostasis Practice QuizDocument2 pagesHomeostasis Practice QuizRofekiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System WorksheetDocument3 pagesEndocrine System WorksheetMa. Lourdes CarbonillaNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Endocrine Nursing: Muhammad Yaqoob Instructor Ion-DuhsDocument51 pagesUnit II: Endocrine Nursing: Muhammad Yaqoob Instructor Ion-DuhsyaqoobmdNo ratings yet
- Pituitary GlandDocument31 pagesPituitary GlandNeha BhartiNo ratings yet
- T3-T4-TSH Test Results for Harman SinghDocument2 pagesT3-T4-TSH Test Results for Harman SinghVaid Navdeep Singh100% (1)
- CH 5: Integumentary SystemDocument36 pagesCH 5: Integumentary SystemHurtlock HurtlockNo ratings yet
- Solitary Thyroid Nodule Evaluation and ManagementDocument50 pagesSolitary Thyroid Nodule Evaluation and ManagementMohammad BanisalmanNo ratings yet
- Unscramble menstrual cycle words and understand the processDocument58 pagesUnscramble menstrual cycle words and understand the processJoanBangitNo ratings yet
- Neonatal HyperthyroidismDocument30 pagesNeonatal HyperthyroidismVishal SidanaNo ratings yet
- Treating Thyroid Emergencies: Myxedema Coma and Thyroid StormDocument17 pagesTreating Thyroid Emergencies: Myxedema Coma and Thyroid StormMarlon UlloaNo ratings yet
- HypopituitarsimDocument24 pagesHypopituitarsimSetrax .sNo ratings yet
- Pancreatita Acuta Si Cancer de PancreasDocument10 pagesPancreatita Acuta Si Cancer de PancreasProdan SimonaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to EndocrinologyDocument19 pagesIntroduction to EndocrinologyVDiesel99No ratings yet
- Conn's SyndromeDocument10 pagesConn's SyndromeFathanah Yanti MphNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae 2020 2Document87 pagesCurriculum Vitae 2020 2api-325315995No ratings yet
- Patient XDocument2 pagesPatient XFatima Medriza DuranNo ratings yet
- Physiology and pathology of the estrous cycle of the bitchDocument5 pagesPhysiology and pathology of the estrous cycle of the bitchGajic NevenNo ratings yet
- Causes of Endocrine DisordersDocument8 pagesCauses of Endocrine DisordersKrystel Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology of Genitourinary SystemDocument4 pagesEndocrinology of Genitourinary SystemGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Normoz TabletDocument6 pagesNormoz TabletAmita VermaNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Communication in Humans: How Glands Coordinate the BodyDocument10 pagesHormonal Communication in Humans: How Glands Coordinate the BodyRuqayya ImranNo ratings yet
- Pituitary Adenomas: University of Fallujah Collage of Medicin Endocinology SurgeryDocument10 pagesPituitary Adenomas: University of Fallujah Collage of Medicin Endocinology SurgeryMohamed HamoodNo ratings yet