Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aspergillus
Aspergillus
Uploaded by
Kaviya Prakash0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesAspergillosis is caused by the fungus Aspergillus, which includes about 200 species. Aspergillus is widely distributed and can grow on decaying vegetables, fatty foods like butter, starchy foods like bread and rice, and preserved fruits. It requires only organic matter and moisture to grow. The fungus reproduces through conidia, which are produced in enormous numbers and give colonies their color. Its life cycle includes three phases: haplophase, dikaryophase, and transitory diplophase. Some potential virulence factors for different Aspergillus species are adhesions, pigments, and hydrolytic enzymes.
Original Description:
Aspergillosis
Original Title
aspergillus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAspergillosis is caused by the fungus Aspergillus, which includes about 200 species. Aspergillus is widely distributed and can grow on decaying vegetables, fatty foods like butter, starchy foods like bread and rice, and preserved fruits. It requires only organic matter and moisture to grow. The fungus reproduces through conidia, which are produced in enormous numbers and give colonies their color. Its life cycle includes three phases: haplophase, dikaryophase, and transitory diplophase. Some potential virulence factors for different Aspergillus species are adhesions, pigments, and hydrolytic enzymes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views6 pagesAspergillus
Aspergillus
Uploaded by
Kaviya PrakashAspergillosis is caused by the fungus Aspergillus, which includes about 200 species. Aspergillus is widely distributed and can grow on decaying vegetables, fatty foods like butter, starchy foods like bread and rice, and preserved fruits. It requires only organic matter and moisture to grow. The fungus reproduces through conidia, which are produced in enormous numbers and give colonies their color. Its life cycle includes three phases: haplophase, dikaryophase, and transitory diplophase. Some potential virulence factors for different Aspergillus species are adhesions, pigments, and hydrolytic enzymes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Aspergillosis
Aspergillus features
● This fungus is also called Eurotium.
● It is chiefly a saprophytic fungus which is widely
distributed.
● It grows on decaying vegetables; on fatty media
such as butter and ghee; on starchy media as
bread and rice; on preserved fruits as jams and
jellies.
● In all Aspergillus includes about 200 species
● At first when the connection between the two
stages was not fully established the sexual or
perfect stage was called Eurotium and the conidial
or imperfect stage as Aspergillus.
● All that the fungus requires are some organic
matter and little of moisture.
● The saprophytic forms are found almost on any decaying organic
matter.
● The chief means of multiplication are the conidia.
● They are produced in enormous numbers. It is the conidial mass
which gives hyphal mats their characteristic tint.
● The asci are globose or broadly club-shaped.
● They arise at different levels and thus are scattered irregularly
within a round closed ascocarp called the cleistothecium.
● The life history of Aspergillus consists of three phases. They are
the haplophase, the dikaryophase and the transitory diplophase.
Virulence factors of aspergillus
● Some putative virulence factors have been identified
for different Aspergillus species.
● These include adhesions e.g., biofilm production and
haemolysin, pigments hydrolytic enzymes such as
proteases, proteinase, lipase, phospholipases,
α-amylase, low-molecular-weight, non-protein
metabolites
You might also like
- Aspergillus and AspergillosisDocument35 pagesAspergillus and AspergillosissummiyaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument26 pagesReproduction in OrganismsRakesh S. GourNo ratings yet
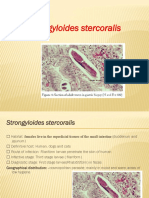
- Strongyloides StercoralisDocument30 pagesStrongyloides StercoralisEllagEsz100% (1)
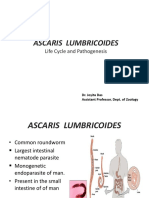
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: Ascariasis. Infections Most Often Seen in Young Children byDocument7 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides: Ascariasis. Infections Most Often Seen in Young Children byThea GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Classification of FungiDocument5 pagesClassification of FungiSoumit PaulNo ratings yet
- HouseflyDocument19 pagesHouseflyMoghi AngelNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabDocument64 pagesKingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument65 pagesFUNGILouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- AspergillusDocument53 pagesAspergillusማላያላም ማላያላም100% (1)
- Microorganisms Friend or Foe Part-4Document32 pagesMicroorganisms Friend or Foe Part-4rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of MucorDocument12 pagesLife Cycle of MucorHimanshi ShrresthaNo ratings yet
- FungusDocument31 pagesFungushadiya rehmanNo ratings yet
- Fungi - VII-ppt by VamikaDocument11 pagesFungi - VII-ppt by VamikaVamika BansalNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Hone College Lecture 5 2022 Fungi KingdomDocument30 pagesEvelyn Hone College Lecture 5 2022 Fungi KingdomJoyce KapembwaNo ratings yet
- 3..morphology Importance of FungiDocument21 pages3..morphology Importance of Fungichansadavid52No ratings yet
- Micro Organisms Important in Food Microbiology - 29maret 2012Document112 pagesMicro Organisms Important in Food Microbiology - 29maret 2012Hendra Pramana YNo ratings yet
- Round Worm Infection 1Document66 pagesRound Worm Infection 1Agochi CollinsNo ratings yet
- Ascaris 3Document13 pagesAscaris 3Rajanikanta MahatoNo ratings yet
- Zygospore: Phylum: ZygomycotaDocument16 pagesZygospore: Phylum: ZygomycotaDavid NindiNo ratings yet
- APPLIED ENTOMOLOGY-PESTS OF MAIZE and SORGHUMDocument26 pagesAPPLIED ENTOMOLOGY-PESTS OF MAIZE and SORGHUMTehreem AfzalNo ratings yet
- SMB3103Document147 pagesSMB3103xasantalan3No ratings yet
- FungiDocument15 pagesFungiKristine KrisNo ratings yet
- Kingdomfungi 170304171711Document34 pagesKingdomfungi 170304171711trisha abadNo ratings yet
- Para-Lab Practicals PDFDocument15 pagesPara-Lab Practicals PDFRizzy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Leaving Certificate Biology Notes: Kingdom FungiDocument29 pagesLeaving Certificate Biology Notes: Kingdom Fungisccscience0% (1)
- Miko SisDocument90 pagesMiko SisFahlevi QalbiNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-SayedDocument42 pagesKingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-Sayedomar mohamedNo ratings yet
- PCT 213 Power Point On FungiDocument20 pagesPCT 213 Power Point On Fungiezeudunicholas16No ratings yet
- Medical Helminthology-NematodesDocument134 pagesMedical Helminthology-NematodesKAYISIRE EMERYNo ratings yet
- Cestodes 1Document19 pagesCestodes 1ميمونه عبدالرحيم مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic MicroorganismDocument21 pagesEukaryotic MicroorganismEdie SilvergunsNo ratings yet
- Fascioliasis, TrematodesDocument31 pagesFascioliasis, Trematodesحسین جاسم ستارNo ratings yet
- Aedes Aegypti: B. Sc. 1 Year Zoology (Arthropoda)Document22 pagesAedes Aegypti: B. Sc. 1 Year Zoology (Arthropoda)yayeg rajaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 13 - Reproduction in Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadaliaDocument27 pagesUnit - 13 - Reproduction in Fungi by Dr. Kirtika PadaliaSurajit NaskarNo ratings yet
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument24 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesQonik Nuzulul FalakhiNo ratings yet
- Helminths PPTZDocument126 pagesHelminths PPTZShaina Gabrielle Balbiran (IHS)No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3Document45 pagesChapter 1.3Mr. NobodyNo ratings yet
- L21 - Fungi-Molds and YeastsDocument9 pagesL21 - Fungi-Molds and YeastsM Arfat YameenNo ratings yet
- SporeDocument3 pagesSporeapple crazypineappleNo ratings yet
- Botany PresentationDocument13 pagesBotany PresentationDevashish SawantNo ratings yet
- Importance of Insect Life Cycle: Pest Identification Guide For Pests in and Around BuildingsDocument1 pageImportance of Insect Life Cycle: Pest Identification Guide For Pests in and Around BuildingsFabian MataloNo ratings yet
- Ascariasis - MatoDocument27 pagesAscariasis - MatoofficialmwalusambaNo ratings yet
- GEN BIO II - MidtermsDocument14 pagesGEN BIO II - MidtermsVenniecine LopezNo ratings yet
- AscarisDocument43 pagesAscarisALBINUS AmbroseNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi: Part 6 Chapter 5Document37 pagesKingdom Fungi: Part 6 Chapter 5AtieyNoryhati-dzNo ratings yet
- Hymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpDocument7 pagesHymenolepis Nana Group 5 Write UpSusan GachukiaNo ratings yet
- Fungi-Definition, Examples, Structure, Classification & ReproductionDocument26 pagesFungi-Definition, Examples, Structure, Classification & Reproductionarissa noorNo ratings yet
- Host (S) Disease (S) : A.fumigatus A.niger A.flavusDocument3 pagesHost (S) Disease (S) : A.fumigatus A.niger A.flavusVedha VincyNo ratings yet
- Integrated Pest Management On Vegetables For Insect Pests and Vectors in South TexasDocument20 pagesIntegrated Pest Management On Vegetables For Insect Pests and Vectors in South TexasCharlote MontefalconNo ratings yet
- Pests of Maize and Sorghum: Presented By: Tehreem Afzal Roll No: 044 Presented To:Dr. Nousheen ZafeerDocument22 pagesPests of Maize and Sorghum: Presented By: Tehreem Afzal Roll No: 044 Presented To:Dr. Nousheen ZafeerTehreem AfzalNo ratings yet
- Rhizopus & MucorDocument11 pagesRhizopus & MucorManish SoniNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument13 pagesFUNGIFalen AriyandiNo ratings yet
- The Diverse World of ProtistsDocument63 pagesThe Diverse World of Protistsirene7008799016No ratings yet
- Molds YeastDocument8 pagesMolds YeastAnandNo ratings yet
- Fungus Chapter8Document13 pagesFungus Chapter8Chieng37No ratings yet
- Plant Kingdom Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)Document17 pagesPlant Kingdom Class 11 Notes NEET Biology (PDF)shusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Natural Enemy InformationDocument11 pagesNatural Enemy InformationRp PandeyNo ratings yet
- IPDocument19 pagesIPAnuj Abner Samuel BaskaranNo ratings yet