Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microorganisms Friend or Foe Part-4
Uploaded by
rajesh dua0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views32 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views32 pagesMicroorganisms Friend or Foe Part-4
Uploaded by
rajesh duaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 32
MICROORGANISMS: FRIEND OR FOE
You shall be able to
• Understand the general characteristic
features of Fungi.
• Gain knowledge about the structure of
Rhizopus.
• Understand the useful and harmful activities
of fungi.
FUNGI
GENERAL CHARACTERISTIC FEATURES
• Fungi can be unicellular as well as multicellular. Example-
Yeast is a unicellular fungi and Rhizopus is multicellular
fungi.
• The body of multicellular fungi consists of long thread like
structures called hyphae which form a network called
mycelium.
• Cell wall is composed of chitin. Some fungal cell wall also
contain cellulose.
• They show heterotrophic mode of nutrition as they lack
chlorophyll pigment. They can be saprotrophic, parasitic or
symbionts.
• They reproduce by budding, fission and spore formation.
• Their size varies from few microns to few centimeter.
TYPES OF FUNGI
Mushroom (Agaricus), Yeast( Saccharomyces), Bread mould ( Rhizopus)
STRUCTURE OF RHIZOPUS
STRUCTURE OF RHIZOPUS
• It grows on stale bread in warm and moist
conditions.
• The body of rhizopus consists of a network of
hyphae called mycelium.
• The mycelium is composed of three types of
hyphae-
Rhizoidal hyphae
Stoloniferous hyphae
Sporangiferous hyphae
TYPES OF HYPHAE IN RHIZOPUS
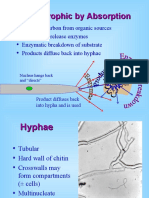
1. Rhizoids or Rhizoidal hyphae are branched, penetrate the
substratum and absorb nutrients.
• They secrete digestive enzymes on the substratum which
convert complex organic matter into simpler compounds.
2. Stoloniferous hyphae are sub-aerial, arched and
unbranched.
• They help in transportation of food and provides support.
3. Sporangiferous hyphae are unbranched, aerial and develop
at the time of asexual reproduction.
• Their tip bears a swollen sac like structures called
sporangium which bear spores.
TYPES OF HYPHAE IN RHIZOPUS
• When spores are mature, the sporangium
burst to release spores.
• Spores are carried by the air currents.
• On falling on a suitable medium ( bread) ,
spores germinate into a new mycelium.
TYPES OF HYPHAE IN RHIZOPUS
RHIZOIDAL HYPAHE STOLONIFEROUS HYPHAE SPORANGIFEROUS
HYPHAE
They are branched, anchor They are sub-aerial, They are aerial, and
the mycelium to the arched and unbranched. unbranched.
substratum. Develop during asexual
reproduction.
They secrete digestive They help in Their tip bears swollen
enzymes on the medium transportation of food and sac- like structure called
which convert complex provides support. sporangium which bears
substances into simpler spores.
form and absorb nutrients
USEFUL ACTIVITIES OF FUNGI
• IN THE FIELD OF MEDICINE- (Antibiotic
production)
THE FIRST ANTIBIOTIC ‘PENICILLIN’ WAS DISCOVERED BY
ALEXANDER FLEMING IN 1929 (when he was working on
Staphylococcus.) Penicillin is obtained from fungus Penicillium
notatum.
USEFUL ACTIVITIES OF FUNGI
• In Food industry-
• Some species of Yeast and Penicillum are
used for flavouring cheese.
• Yeast is used in baking and brewing
industries as they respire anaerobically by
the process of fermentation.
FERMENTATION
• It is a type of anaerobic respiration which
involves incomplete breakdown of glucose in the
absence of oxygen to produce ethyl alcohol and
carbon dioxide and small amount of energy.
• Louis Pasteur discovered fermentation in 1857.
EQUATION FOR FERMENTATION
YEAST IN BAKING INDUSTRY
• During fermentation, carbon dioxide is
produced by yeast.
• Co2 forms bubbles in the dough and
increases the volume of dough.
• When dough is heated, carbon dioxide
escapes. This makes the bread soft and
spongy.
YEAST IN BAKING INDUSTRY
YEAST IN BREWING INDUSTRY
• In a dark closed bottle, yeast is added to
sugar solution of grains like barley, wheat,
rice or crushed fruit juices.
• Yeast converts sugar( Glucose) into ethyl
alcohol and carbon dioxide. ( Anaerobic
respiration/ Fermentation).
• Thus, ethyl alcohol is produced.
YEAST IN BREWING INDUSTRY
USEFUL ACTIVITIES OF FUNGI
•Some fungi are edible. e.g Mushroom ( Agaricus)
USEFUL ACTIVITIES OF FUNGI
•Some fungi along with bacteria help in decomposition of
biodegradable waste. They also help in formation of manure.
HARMFUL ACTIVITIES OF FUNGI
•Some fungi spoil food, clothes and leather articles
during hot and humid conditions.
HARMFUL ACTIVITIES OF FUNGI
Diseases-
• Fungi cause a number of diseases in man,
animals and plants.
• Rust of wheat- is caused by Puccinia . It
spreads through air or infected seeds carrying
the spores of fungi.
RUST OF WHEAT caused by Puccinia
Fungi can be unicellular as well as multicellular.
Fungal cell wall is composed of chitin. Some fungal cell wall also contain cellulose.
Fungi show heterotrophic mode of nutrition as they lack chlorophyll pigment.
They can be saprotrophic, parasitic or symbionts.
Fungi reproduce by budding, fission and spore formation.
The body of multicellular fungi consists of long thread like structures called
hyphae which form a network called mycelium.
The mycelium is composed of three types of hyphae- Rhizoidal hyphae,
Stoloniferous hyphae, Sporangiferous hyphae.
Some species of Yeast and Penicillum are used for flavouring cheese.
Yeast is used in baking and brewing industries as they respire anaerobically by the
process of fermentation.
Some fungi are edible. e.g Mushroom ( Agaricus)
Some fungi along with bacteria help in decomposition of biodegradable waste.
Some fungi spoil food, clothes and leather articles during hot and humid
conditions.
Rust of wheat- is caused by Puccinia . It spreads through air or infected seeds
carrying the spores of fungi.
Oral questions-
• State the mode of nutrition in Fungi.
• Heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
• What is the composition of cell wall of Fungi?
• It is made up of Chitin.
• Name and define the process in yeast that
converts sugar into alcohol.
• Fermentation is the breakdown of sugar in the
absence of oxygen to produce ethanol/ ethyl
alcohol and carbon dioxide.
• Name an edible fungus.
• Mushroom ( Agaricus)
ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS
Q14. Define Fermentation.
Q 15. Differentiate between: Fungi and
Bacteria.
Q 16. Compare the structure and function of
three types of hyphae in Rhizopus.
Q17. Discuss the use of yeast in brewing
industry.
Q 18. Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of
‘Rhizopus’.
Experiential Learning
Aim: To grow microbes/ fungi on different substrata and observe the favourable conditions for
their growth.
Experiential Learning
Aim: To grow microbes/ fungi on different substrata and observe the
favourable conditions for their growth.
Q.1 Observe the figure given below and answer the following
questions.
a) Name the microorganism and the group to which it belongs.
b) Name the food item on which this microorganism usually grows.
c) Label stoloniferous hyphae in the picture and state its function.
Q.2 In which of the following conditions can Rhizopus grow well?
A) Condition 1 B) Condition 2
C) Condition 3 D) Both conditions 1 and 2.
Q.3 In order to survive unfavourable conditions, microorganisms form a hard
protective covering called:
A) Cell membrane B) Chloroplast
C) Mesosome D) Cyst
Q.4 Which of the following is absent in Rhizopus?
A) Rhizoidal hyphae B) Sporangiferous hyphae
C) Sporangium D) None of these.
Q.5 Antibiotic penicillin is obtained from which fungus?
A) Rhizopus sp. B) Acetobacter sp.
C) Penicillium notatum D) Agaricus
You might also like
- Kingdom Fungi: Part 6 Chapter 5Document37 pagesKingdom Fungi: Part 6 Chapter 5AtieyNoryhati-dzNo ratings yet
- 3..morphology Importance of FungiDocument21 pages3..morphology Importance of Fungichansadavid52No ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3Document45 pagesChapter 1.3Mr. NobodyNo ratings yet
- Kingdomfungi 170304171711Document34 pagesKingdomfungi 170304171711trisha abadNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument27 pagesFUNGILyrra Jorramie Rull GragedaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 FungiDocument57 pages1.5 FungiaixyaehNo ratings yet
- PCT 213 Power Point On FungiDocument20 pagesPCT 213 Power Point On Fungiezeudunicholas16No ratings yet
- 5 - FungiDocument8 pages5 - FungiPrazwal RegmiNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of MucorDocument12 pagesLife Cycle of MucorHimanshi ShrresthaNo ratings yet
- FungusDocument31 pagesFungushadiya rehmanNo ratings yet
- Fungi - VII-ppt by VamikaDocument11 pagesFungi - VII-ppt by VamikaVamika BansalNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-SayedDocument42 pagesKingdom: FUNGI: DR /amr El-Sayedomar mohamedNo ratings yet
- 6 - FungiDocument32 pages6 - FungiRUSSEL MAE CATIMBANGNo ratings yet
- Evelyn Hone College Lecture 5 2022 Fungi KingdomDocument30 pagesEvelyn Hone College Lecture 5 2022 Fungi KingdomJoyce KapembwaNo ratings yet
- L4 FungiDocument54 pagesL4 Fungif22b0054No ratings yet
- TOPIC 5 The Kingdom of The Fungi (Part 2)Document35 pagesTOPIC 5 The Kingdom of The Fungi (Part 2)Ally AbadeoNo ratings yet
- King Faisal University Nursing DepartmentDocument62 pagesKing Faisal University Nursing DepartmentzanderNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument33 pagesFUNGIGabz Gabby50% (6)
- FungiDocument38 pagesFungiRamayono RayNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabDocument64 pagesKingdom Fungi Group 3 Post LabClemence Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- By Retno Wati SMPN I SalatigaDocument22 pagesBy Retno Wati SMPN I SalatigaAziza ZulfaNo ratings yet
- Nutrisi Kultivasi Mikologi 2021Document55 pagesNutrisi Kultivasi Mikologi 2021Irfan YonataNo ratings yet
- General Biology Ii (Bly 102) - FungiDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology Ii (Bly 102) - FungiTolani Ayo100% (1)
- MycologyDocument25 pagesMycologyShahid BashirNo ratings yet
- Fungi Kingdom: By: Tio Magdalena Manurung, B.SCDocument50 pagesFungi Kingdom: By: Tio Magdalena Manurung, B.SCClara ClarestaNo ratings yet
- ActinomycetesDocument10 pagesActinomycetes09ANKIT MISHRANo ratings yet
- Basic Mycology: Russell G. Panem, RMT School of Medical Technology Chinese General Hospital CollegesDocument47 pagesBasic Mycology: Russell G. Panem, RMT School of Medical Technology Chinese General Hospital CollegesJaellah MatawaNo ratings yet
- Fungal Isolation: Learning Activity No. 11Document25 pagesFungal Isolation: Learning Activity No. 11Christine RanoaNo ratings yet
- Fungi Spring 2011Document23 pagesFungi Spring 2011Kenzie SmithNo ratings yet
- MBC 305 Pat 1and 2Document19 pagesMBC 305 Pat 1and 2Usman SurajNo ratings yet
- Note 5 Fungi PDFDocument2 pagesNote 5 Fungi PDFRufaida TaahaNo ratings yet
- Mycology - The Study of Fungi: Fungi - Singular Fungus - PluralDocument18 pagesMycology - The Study of Fungi: Fungi - Singular Fungus - PluralPutri SeptiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Microbial Growth Characteristics - Morphology of FungiDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Microbial Growth Characteristics - Morphology of Fungisarveshmhatre88No ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form 2 Teacher - Ac TZDocument134 pagesBiology Notes Form 2 Teacher - Ac TZSamweliNo ratings yet
- Module On FungiDocument10 pagesModule On FungiIsha GishNo ratings yet
- Food Biotechnology 3Document22 pagesFood Biotechnology 3Thomas MugaboNo ratings yet
- Leaving Certificate Biology Notes: Kingdom FungiDocument29 pagesLeaving Certificate Biology Notes: Kingdom Fungisccscience0% (1)
- Microorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyDocument39 pagesMicroorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyKumkum CRNo ratings yet
- Fungi ClassificationDocument8 pagesFungi ClassificationNAYAN JYOTI KALITA100% (1)
- Kingdom FungiDocument51 pagesKingdom FungiRISHIKHESANNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: Protista MoneraDocument11 pagesBiodiversity: Protista MoneraridwanNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument31 pagesKingdom Fungiraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- DeutromycetesDocument10 pagesDeutromyceteshendra_s_backNo ratings yet
- The Fungi Kingdom: Chairotunnisa Sma Negeri 5 Kota BekasiDocument52 pagesThe Fungi Kingdom: Chairotunnisa Sma Negeri 5 Kota Bekasisepuluhtiga100% (1)
- Introduction To Fungi: General MicrobiologyDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Fungi: General MicrobiologyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Mycology - : The Study of Fungi Singular PluralDocument18 pagesMycology - : The Study of Fungi Singular PluralfaizNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument52 pagesFUNGIkeira raishaNo ratings yet
- Biology #KautilyaDocument79 pagesBiology #KautilyapankajNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 FUNGIDocument56 pagesBab 6 FUNGIjakyNo ratings yet
- FUNGI - 6-Sem112Document42 pagesFUNGI - 6-Sem112menNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic MicrobesDocument46 pagesEukaryotic Microbeslouie tibarNo ratings yet
- 3.1 The FungiDocument40 pages3.1 The FungiMohammed Faraaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To MycologyPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Domain Eukarya (Kingdom Fungi)Document47 pagesDomain Eukarya (Kingdom Fungi)Mazlisya Nadhirah100% (1)
- Fungi: Prepared by Elina Shrestha M.SC - MM Pokhara UniversityDocument45 pagesFungi: Prepared by Elina Shrestha M.SC - MM Pokhara UniversityElena ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotes CH 12Document8 pagesEukaryotes CH 12qwivy.comNo ratings yet
- Micro Organisms Important in Food Microbiology - 29maret 2012Document112 pagesMicro Organisms Important in Food Microbiology - 29maret 2012Hendra Pramana YNo ratings yet
- l2 ch20Document4 pagesl2 ch20fatimaabdullahalarfajNo ratings yet
- The Mycophile's Handbook: From Spores to Harvest: Your Comprehensive Guide to MushroomFrom EverandThe Mycophile's Handbook: From Spores to Harvest: Your Comprehensive Guide to MushroomNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 1Document20 pagesLight Lesson 1rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Ftre-2021-C-Viii-P1-At+s&m-Sample PaperDocument21 pagesFtre-2021-C-Viii-P1-At+s&m-Sample Paperrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Unit2 (Class 8)Document1 pageSyllabus - Unit2 (Class 8)rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Revolt of 1857-2Document6 pagesRevolt of 1857-2rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Revolt of 1857 - 1Document6 pagesRevolt of 1857 - 1rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 4Document22 pagesLight Lesson 4rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- TelescopingDocument4 pagesTelescopingrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 3Document13 pagesLight Lesson 3rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Map - Centre of RevoltDocument2 pagesMap - Centre of Revoltrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 1Document20 pagesLight Lesson 1rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Social Science PortfolioDocument2 pagesSocial Science Portfoliorajesh duaNo ratings yet
- E H Sculpt: Let's Reduce, Reuse and RecycleDocument12 pagesE H Sculpt: Let's Reduce, Reuse and Recyclerajesh duaNo ratings yet
- A Worksheet On Cop 26Document1 pageA Worksheet On Cop 26rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Civilizing The Native Educating The NationDocument22 pagesCivilizing The Native Educating The Nationrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Navsrijan Worksheet Biology Class 8Document6 pagesNavsrijan Worksheet Biology Class 8rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Some Natural Phenomena M.C.Q. and WorksheetDocument20 pagesSome Natural Phenomena M.C.Q. and Worksheetrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Somebody's MotherDocument15 pagesSomebody's Motherrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- MESSAGE WRITING & EditingDocument14 pagesMESSAGE WRITING & Editingrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms Friend or Foe Part-5Document28 pagesMicroorganisms Friend or Foe Part-5rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- 8geo Chap6 2021Document34 pages8geo Chap6 2021rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms Friend or Foe Part - 3Document25 pagesMicroorganisms Friend or Foe Part - 3rajesh dua0% (1)
- 37 Aryabhatta Inter-School Mathematics Competition - 2020 Class - ViiiDocument15 pages37 Aryabhatta Inter-School Mathematics Competition - 2020 Class - Viiirajesh dua100% (1)
- Non Finite 1Document21 pagesNon Finite 1rajesh dua100% (1)
- E H Sculpt: Let's Reduce, Reuse and RecycleDocument12 pagesE H Sculpt: Let's Reduce, Reuse and Recyclerajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Some Natural Phenomena Lesson 5Document18 pagesSome Natural Phenomena Lesson 5rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Light Lesson 1Document20 pagesLight Lesson 1rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Triangles: Class - Viii AryabhattaDocument46 pagesTriangles: Class - Viii Aryabhattarajesh duaNo ratings yet
- CONJUNCTIONSDocument19 pagesCONJUNCTIONSrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- A Worksheet On Cop 26Document1 pageA Worksheet On Cop 26rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Assignment CM Final PDFDocument9 pagesAssignment CM Final PDFRefisa JiruNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Your Data and Drawing Conclusions Worksheet Without AnswersDocument3 pagesAnalyzing Your Data and Drawing Conclusions Worksheet Without AnswersNur ShaNo ratings yet
- Scheme and Syllabus of B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering) 3 TO8 Semester 2017-2018Document170 pagesScheme and Syllabus of B.E. (Computer Science and Engineering) 3 TO8 Semester 2017-2018pratik YadavNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Software AcceptanceDocument6 pagesCertificate of Software AcceptanceVince PepañaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 6Document6 pagesCase Study 6Shaikh BilalNo ratings yet
- Halftrack Track Chains InstructionsDocument4 pagesHalftrack Track Chains Instructionsddlevy0% (1)
- Dialer AdminDocument5 pagesDialer AdminNaveenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Montenegrin LanguageDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Montenegrin LanguageSanja MacutNo ratings yet
- Agrasar Lecture and Demonstration Programme On Water, Food and Climate ChangeDocument20 pagesAgrasar Lecture and Demonstration Programme On Water, Food and Climate ChangeMinatiBindhaniNo ratings yet
- VISTA LAND AND LIFESCAPES INC FinalDocument9 pagesVISTA LAND AND LIFESCAPES INC Finalmarie crisNo ratings yet
- GSPANN Returns To Adobe Summit 2021 As A Showcase SponsorDocument2 pagesGSPANN Returns To Adobe Summit 2021 As A Showcase SponsorPR.comNo ratings yet
- Relationship Marketing & International RetailingDocument17 pagesRelationship Marketing & International Retailingpriyarp5075No ratings yet
- Math 7 LAS W1&W2Document9 pagesMath 7 LAS W1&W2Friendsly TamsonNo ratings yet
- SM QuestionDocument7 pagesSM QuestionPRiNCEMagNus100% (1)
- Case Study-Cereal PartnersDocument5 pagesCase Study-Cereal PartnersTariq MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Chilis Allergen Vegetarian GenericDocument6 pagesChilis Allergen Vegetarian Genericsuresh jkNo ratings yet
- Scenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Document7 pagesScenario - Taxation 2019 UNISA - Level 1 Test 4Tyson RuvengoNo ratings yet
- Sika Comfor PorefillerDocument5 pagesSika Comfor Porefillerrangarajan1989No ratings yet
- PRACTICES AND CHALLENGES IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF BASIC EDUCATION LEARNING CONTINUITY PLAN-Authored By: Reynaldo C. CruzDocument71 pagesPRACTICES AND CHALLENGES IN THE IMPLEMENTATION OF BASIC EDUCATION LEARNING CONTINUITY PLAN-Authored By: Reynaldo C. CruzInternational Intellectual Online PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Regulatory Guide 1.71Document5 pagesRegulatory Guide 1.71Siis IngenieriaNo ratings yet
- 1 MergedDocument81 pages1 MergedCHEN XIAN YANG MoeNo ratings yet
- RCB Dealers PHDocument3 pagesRCB Dealers PHJing AbionNo ratings yet
- World CurrenciesDocument7 pagesWorld Currenciespraiseonyinye3No ratings yet
- Open World First B2 Students BookDocument257 pagesOpen World First B2 Students BookTuan Anh Bui88% (8)
- MQ SSL/TLS Channels Including V8 ChangesDocument23 pagesMQ SSL/TLS Channels Including V8 ChangesAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Advance Strategic Marketing: Project Report of Nayatel.Document46 pagesAdvance Strategic Marketing: Project Report of Nayatel.Omer Abbasi60% (15)
- Gears DifferentialDocument13 pagesGears Differentialpulkitymcaust_112907100% (1)
- Dallas Symphony Orchestra 2009 Annual ReportDocument14 pagesDallas Symphony Orchestra 2009 Annual ReportCharlie StephensonNo ratings yet