Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Networks: More Information
Networks: More Information
Uploaded by
zentaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Networks: More Information
Networks: More Information
Uploaded by
zentaCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-70300-0 - Infotech: English for Computer Users, Fourth Edition - Teacher’s Book
Santiago Remancha Esteras
Excerpt
More information
Unit 28 Networks
Topics Abbreviations: PAN, LAN, MAN, WAN, GSM
Networking basics Phrasal verbs / verbs with particles: look at, consist
Types of network of, carry out, turn on/off, switch on/off, log in/on, log
Wired networks versus wireless networks out /off, plug into, set up, sign up, try out, find out, take
up, make up, fill in
Learning objectives
To understand the basics of networking Skills
To discuss the advantages of using networks Listening: Labelling a diagram of a mixed wired/
To describe networks, both in speaking and writing wireless LAN based on information from a lecture
To use phrasal verbs common in ICT Speaking: Discussing the advantages of using
networks
Language
Describing a WAN connected via satellite
Grammar: Verbs with particle (phrasal verbs)
Reading: Understanding general and specific
Vocabulary: wired network, wireless network, network
information from a text about networking
architecture (client-server, peer-to-peer), network
Writing: Describing a network
topology (bus, ring, star), protocol, router, Ethernet
cables, fibre optic cable, wireless access point, Wi-Fi, Technical help is given on page 127.
Bluetooth
Plan
Teacher’s activities Students’ activities Comments
1 Small networks
A Elicit ideas from SS and write A SS brainstorm ideas and try You may like to write the word network on
them on the board. to define computer network. the board and elicit ideas about networks
B Play track 34 of the CD. SS then discuss the benefits in real life: TV network, telephone network,
C Play the CD twice more if of using networks. radio network, spy network, railway network,
necessary. B SS listen to the description neural network, computer network, etc.
of a LAN and answer the
Make sure SS understand these basic
questions.
concepts: Local area network (LAN), wired vs.
C SS listen again and label the
wireless, router, wireless access point
elements of the network.
2 Networking FAQs
A Ask SS to only look at the FAQs A SS look at the FAQs without You may like to set C as a game. The
for now. They will be reading reading the whole text and winners are the group that answers the
the whole text in Task B. answer as many of them as most questions correctly in three minutes.
B Monitor the task, helping with they can.
Make sure SS understand the different ways
any vocabulary problems. B SS read the whole text
of classifying networks.
C Let SS do the network quiz in and find answers to the
pairs or trios. questions.
C SS choose the correct
answers in the network quiz.
124
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-70300-0 - Infotech: English for Computer Users, Fourth Edition - Teacher’s Book
Santiago Remancha Esteras
Excerpt
More information
Unit 28 Networks
3 Language work: phrasal verbs
A Refer SS to the HELP box, A SS study the HELP box and
providing more examples if translate the phrasal verbs
necessary. Encourage SS to into their own language.
explain how these verbs are B SS complete some sentences
formed in their mother tongue. with the correct form of
B and C phrasal verbs from the HELP
Monitor the tasks, helping box.
where needed. C SS then practise some
phrasal verbs by matching
questions and answers in
short exchanges.
4 WANs and satellites
A Draw SS’ attention to the picture A SS look at the illustration
and refer them to the Useful of a wide area network
language box. Remind SS that and then prepare a written
this is a good opportunity to description.
use the technical terms and the B Some SS present their
phrasal verbs learnt throughout description to the class,
the unit. either as an oral report or as
Encourage SS to prepare a a PowerPoint presentation.
PowerPoint presentation of the
description.
Monitor the activity, helping
where needed.
B Ask some students to present
their description to the class.
Evaluation of the unit:
Answer key B
1 Small networks 1 Local Area Network
2 LANs are usually located within a relatively small
A geographical area, such as an office or building.
Possible answers 3 A wired LAN is connected with cables; a wireless LAN
uses electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves,
1 A computer network is a system of interconnected
instead of cables.
computers that share files and other resources.
2 They enable us to get the most from our peripherals.
For example, printers, scanners and high-speed C
modems or routers can be shared by a great number of 1 mixed
users on the same network. In the same way, networks 2 Central computer (or File server)
allow us to send and receive messages, have access
3 cables
to large databases, and transfer files to and from other
4 Broadband modem
computers. This implies faster communications, and
flexible and interactive work between users. 5 Router
6 Wireless access point (or wireless router)
125
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-70300-0 - Infotech: English for Computer Users, Fourth Edition - Teacher’s Book
Santiago Remancha Esteras
Excerpt
More information
2 Networking FAQs 4 WANs and satellites
A A
Open task Possible answer
L� The diagram represents a wide area network, or WAN,
B connecting two networks via satellite.
L� The wired network in Barcelona is made up of a
1 Personal Area Network
desktop PC and a PDA connected with Ethernet cables.
2 A network protocol is the language or set of rules that
A central computer acts as a file server, allowing the
computers use to communicate with each other.
PCs to access common files and resources.
3 To log on to an Internet Service Provider, you need to
L� The wireless network in Los Angeles consists of a
type in your username and password.
wireless access point (a wireless router), which links
4 WiMAX has greater range than Wi-Fi and is used to
multiple computers (a central computer, a laptop and
connect various Wi-Fi hotspots with each other.
a PDA) without using cables.
(WiMAX is short for Worldwide Interoperability for
L� In Barcelona, the network is connected by a modem
Microwave Access)
to fibre optic cables. In Los Angeles, however, the
5 To set up a wireless LAN, you need computers computers are linked up by ordinary telephone lines.
equipped with a wireless adapter or wireless card,
L� The satellite receives signals from a disk aerial. The
a wireless access point (a wireless router) and a
signals are then amplified and sent on to workstations
broadband internet connection.
in Barcelona or Los Angeles.
6 Wireless networks are easier to install; they let you
L� The purpose of this integrated network may be to
move, or roam, from one access point to another.
establish information and communications services on
However, they are less secure than wired networks and
a transcontinental scale. It allows large companies and
are subject to interference.
institutions to exchange information, transfer files and
communicate – for example, via videoconferencing
C – over long distances.
1b 2a 3b 4c 5c 6b 7a 8c
B
3 Language work: verbs with particle Open task
A
Open task
B
1 fill in
2 carries out
3 takes up
4 make up
5 find out
C
1c 2a 3e 4b 5d 6f
126
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
Cambridge University Press
978-0-521-70300-0 - Infotech: English for Computer Users, Fourth Edition - Teacher’s Book
Santiago Remancha Esteras
Excerpt
More information
Unit 28 Networks
Audio script
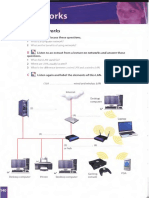
Let’s begin by talking about small networks, which are transmits and receives radio frequencies from wireless-
called local area networks, or LANs. These are groups of enabled devices. Each device that operates over the
computers within a small physical area, like a home or an network is equipped with a wireless card or adapter.
office building.
Many wireless LANs use Wi-Fi, a wireless technology that
In this diagram, we see a mixed wired and wireless uses radio waves to enable communication between
LAN, a typical solution for small businesses that already devices in a limited area. This gives users flexibility and
have a wired LAN and decide to expand it with wireless mobility. Another popular technology is Bluetooth, used
technologies to accommodate new needs. for short distances.
In the existing fixed, wired LAN, the central computer is a The whole network is linked to the Internet via a
file server with a large hard drive used to store common broadband modem. This modem is plugged into a
files and application programs. The computers, acting as router, or hub, which splits the internet connection
clients, are connected to the file server and to a printer into parts and allows all users to access email and web
via Ethernet cables. resources. With appropriate networking software, users
on the wireless LAN can share files and the printer
In the wireless part of the network, several devices,
located on the wired LAN.
including desktops, laptops, PDAs and a gaming console,
are connected to each other without cables. This part Photocopiable © Cambridge University Press 2008
is controlled by a wireless access point – also called a
wireless router. This access point is like a base station that
Technical Help: Network topology
Topology refers to the shape of
a network. There are three main
topologies or configurations used in
LANs:
In a Star network, all devices are
connected to a central station, called
a star controller. The central station
functions as a switching centre.
Computers cannot pass messages
directly to one another; instead, they
have to communicate via the central
station, which prevents messages Star
from colliding.
A Bus network consists of one Bus
cable to which all the devices are
connected.
In a Ring network, all devices are
connected to the same circuit,
forming a continuous loop, or ring. A
token (a piece of software) circulates
continuously along the ring and is Ring
read through an adapter card in each
machine as it passes by.
127
© Cambridge University Press www.cambridge.org
You might also like
- Smartoptics DWDM CWDMDocument22 pagesSmartoptics DWDM CWDMsrotenstein3114No ratings yet
- Scientific Inquiry 1 2 3Document5 pagesScientific Inquiry 1 2 3Lucky Gale BastianNo ratings yet
- Microwave Material List Album-20110629-ADocument90 pagesMicrowave Material List Album-20110629-AMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- G10 - DALISAY - Daily Lesson Log 2 FINALDocument4 pagesG10 - DALISAY - Daily Lesson Log 2 FINALMam Lorna Es Gee50% (2)
- Alcatel Lucent 7750 Service Router OverviewDocument60 pagesAlcatel Lucent 7750 Service Router OverviewZahid AKhoon0% (1)
- Top 20 Networking Interview Questions (March 2022)Document19 pagesTop 20 Networking Interview Questions (March 2022)cutieedivyaNo ratings yet
- Spms Master 20160704Document60 pagesSpms Master 20160704Steffe ArbiniNo ratings yet
- 1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationDocument3 pages1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationmonicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Wired and Wireless NetworksDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Wired and Wireless NetworksTek CasoneteNo ratings yet
- COMNETS CSS11 Week 1Document3 pagesCOMNETS CSS11 Week 1Julius ColminasNo ratings yet
- GRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School ADocument10 pagesGRADES 1 TO 12 DAILY LESSON LOG School Ajecelyn mae BaluroNo ratings yet
- Huawei IP Transport Network 2010 Oct 12Document62 pagesHuawei IP Transport Network 2010 Oct 12Kicsihuszar85100% (2)
- UMTS RNC Overview and IntegrationDocument40 pagesUMTS RNC Overview and IntegrationRwayda NadimNo ratings yet
- 3rd DLL Lan CablingDocument13 pages3rd DLL Lan CablingRachelle MosqueteNo ratings yet
- What Is Networking?Document2 pagesWhat Is Networking?Jesselyn Dacdac Llantada-BautistaNo ratings yet
- G8 Computing Mid Term Revision Tool Kit - 2023Document9 pagesG8 Computing Mid Term Revision Tool Kit - 2023cherry.20.2004No ratings yet
- B7 Comp WK7Document6 pagesB7 Comp WK7Nana Yaw Poku JuniorNo ratings yet
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Document4 pagesNetwork Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateways and Brouter)Roy ThomasNo ratings yet
- 1.5.5 Packet Tracer Network RepresentationDocument2 pages1.5.5 Packet Tracer Network RepresentationzssfbgsNo ratings yet
- UQ-II Outline (1) - 1Document10 pagesUQ-II Outline (1) - 1daudNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v7 Modules 4 - 7 - Ethernet Concepts Exam AnswersDocument27 pagesCCNA 1 v7 Modules 4 - 7 - Ethernet Concepts Exam AnswersBagus Fajariyanto 21.01.4647No ratings yet
- Computer Concepts Illustrated Introductory 9th Edition Parsons Solutions ManualDocument13 pagesComputer Concepts Illustrated Introductory 9th Edition Parsons Solutions Manualjezebeldouglasz3n100% (37)
- Intro To Data Comms & NetworkingDocument2 pagesIntro To Data Comms & NetworkingJacob100% (1)
- Act 7Document5 pagesAct 7Check OndesNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking From Lans To Wans Hardware Software and Security 1st Edition Mansfield Test BankDocument25 pagesComputer Networking From Lans To Wans Hardware Software and Security 1st Edition Mansfield Test BankMeganJonesjwbp100% (56)
- 1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationDocument3 pages1.5.7 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationDo LeeNo ratings yet
- Specialization: Quarter 2 - Week 4Document11 pagesSpecialization: Quarter 2 - Week 4Lendrei QuerimitNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.1.9a Communications Circuits: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesLab 3.1.9a Communications Circuits: Objectiveamna mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Course Code: CT-123 Course Title: Basic Networking Course DescriptionDocument3 pagesCourse Code: CT-123 Course Title: Basic Networking Course Descriptiondmcjr_stiNo ratings yet
- A Symbol Set For Diagramming NetworksDocument5 pagesA Symbol Set For Diagramming NetworksbiouwayNo ratings yet
- TLE11-ICT-Computer Systems Servicing-Q1 - Q2-W3-LeaPDocument3 pagesTLE11-ICT-Computer Systems Servicing-Q1 - Q2-W3-LeaPNomer FloresNo ratings yet
- TLE-IA-EP9-Week 3Document4 pagesTLE-IA-EP9-Week 3Guianne MaigueNo ratings yet
- Tle10 Ict Chs q2 Week 1-4 ModuleDocument32 pagesTle10 Ict Chs q2 Week 1-4 Modulegerlie22No ratings yet
- CCNA-200-301 Vol1-317-400Document84 pagesCCNA-200-301 Vol1-317-400enrique salazarNo ratings yet
- IT-212-213 - 214CS-212-DCN-4 - Course - Outline Spring 2017Document6 pagesIT-212-213 - 214CS-212-DCN-4 - Course - Outline Spring 2017Waleed HussainNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationDocument4 pagesLab 1 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationZulaikha ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The New Perspectives Collection Microsoft Office 365 Office 2019 1st Edition Patrick Carey DownloadDocument15 pagesTest Bank For The New Perspectives Collection Microsoft Office 365 Office 2019 1st Edition Patrick Carey Downloadsarahwatsonmfjtabceri100% (13)
- Final LP Install Network Cables S. AltaDocument3 pagesFinal LP Install Network Cables S. AltaAsan BarhamaNo ratings yet
- Formato Planeación IMMA Literature NovemberDocument7 pagesFormato Planeación IMMA Literature Novemberricardo.acatitla.rNo ratings yet
- Networking and Phrasal Verbs 2Document5 pagesNetworking and Phrasal Verbs 2Angel Fernandez AvilesNo ratings yet
- Network Systems: BriefingDocument8 pagesNetwork Systems: BriefingLeo KrekNo ratings yet
- 1.5.5 Packet Tracer - Network Representation - VelascoDocument3 pages1.5.5 Packet Tracer - Network Representation - Velascoallyssanicolevelasco07No ratings yet
- Reg. No.: Name:: Q.No. Sub. Sec. Question Description MarksDocument1 pageReg. No.: Name:: Q.No. Sub. Sec. Question Description MarksXodiNo ratings yet
- Certified Wireless Network AdministratorDocument2 pagesCertified Wireless Network AdministratorJacobNo ratings yet
- Definitive WANs For EngineersDocument2 pagesDefinitive WANs For EngineersJacobNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Tutorial - Network Representation - ILMDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Tutorial - Network Representation - ILMSteliosDoumasNo ratings yet
- Developing A Networking LexiconDocument2 pagesDeveloping A Networking LexiconMichael HsiaoNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Foundation For Engineers: RF FundamentalsDocument2 pagesTCP/IP Foundation For Engineers: RF FundamentalsJacobNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Communication (Recovered)Document80 pagesChapter 2 - Communication (Recovered)Hamad Shahid HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Quiz - 5th - CEA - Module - 1 - 2019 PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 1 Quiz - 5th - CEA - Module - 1 - 2019 PDFJaydip KyadaNo ratings yet
- Local Area Network Week2 (3.2)Document4 pagesLocal Area Network Week2 (3.2)REYMOND SUMAYLONo ratings yet
- 1.5.5 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationDocument2 pages1.5.5 Packet Tracer - Network RepresentationAndre LightNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Networks WorksheetDocument3 pagesYear 7 Networks WorksheetjasmineNo ratings yet
- 11.6.1.1 Class Activity - Design and Build A Small Network Instructions PDFDocument1 page11.6.1.1 Class Activity - Design and Build A Small Network Instructions PDFRakibuzzahanNo ratings yet
- Layers of OSI Model: Related ArticlesDocument1 pageLayers of OSI Model: Related ArticlesKh JlNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in TLE 10 (ICT-Computer Systems Servicing) I. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in TLE 10 (ICT-Computer Systems Servicing) I. ObjectivesJayvie Galang RaquelNo ratings yet
- Network Essentials General Might Include OS Relate To NetworkingDocument8 pagesNetwork Essentials General Might Include OS Relate To NetworkingDastan ArysbayNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Network Representation: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesPacket Tracer - Network Representation: ObjectivesGiroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Internet ResearchDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Internet ResearchAndyNo ratings yet
- Application Delivery FundamentalsDocument2 pagesApplication Delivery FundamentalsJacobNo ratings yet
- TLE-ICT 9 LAN Cabling LPDocument5 pagesTLE-ICT 9 LAN Cabling LPcjalboladoraNo ratings yet
- CYB NetworkEssentials 03 LessonPlan NetworkMediaHardwareDocument7 pagesCYB NetworkEssentials 03 LessonPlan NetworkMediaHardwareperezmanny0614No ratings yet
- TLE Grade9CSS Module1 Quarter3 Week1Document4 pagesTLE Grade9CSS Module1 Quarter3 Week1Axel Nicerio RoveloNo ratings yet
- Network Interview Question With AnswerDocument39 pagesNetwork Interview Question With AnswerSanket MuleyNo ratings yet
- DLL CSS12 2qtr Week5Document5 pagesDLL CSS12 2qtr Week5glenn0805No ratings yet
- BTI-7000 System OverviewDocument1 pageBTI-7000 System OverviewSal InguaggiatoNo ratings yet
- Optec Catalogue PDFDocument98 pagesOptec Catalogue PDFVijay Lakshmipathy0% (1)
- Point-To-point Protocol Over EthernetDocument7 pagesPoint-To-point Protocol Over EthernetsrujanNo ratings yet
- Ccie Notes MMDocument6 pagesCcie Notes MMmauriziomoroniNo ratings yet
- Nexus FP PDFDocument48 pagesNexus FP PDFPeter MkamaNo ratings yet
- 5.4.1.1 MAC and Choose InstructionsDocument2 pages5.4.1.1 MAC and Choose Instructionsstuntboy090% (1)
- ZTE F680 Brochure 20140715 EN PDFDocument2 pagesZTE F680 Brochure 20140715 EN PDFAlexander PischulinNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA 1 v6.0 Chapter 5 Exam Answers Score 100%: The Frame Is Dropped.Document7 pagesCisco CCNA 1 v6.0 Chapter 5 Exam Answers Score 100%: The Frame Is Dropped.Webber JonxNo ratings yet
- AO DataSheet SFP ReferenciaDocument2 pagesAO DataSheet SFP ReferenciaAntero CasaniNo ratings yet
- 1 - TS MC210MM SM 10 100M Media Converter PDFDocument2 pages1 - TS MC210MM SM 10 100M Media Converter PDFKheireddine BelhadiaNo ratings yet
- Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q TrunkingDocument12 pagesConfiguring EtherChannel and 802.1Q TrunkingSAGALOGNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions PDFDocument3 pages3.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring VLANs Instructions PDFShaun75% (4)
- Spare Count in MAN Location 101007Document52 pagesSpare Count in MAN Location 101007api-3804296No ratings yet
- Ch2-Physical Layer PDFDocument30 pagesCh2-Physical Layer PDFDali BelaibaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Prime Support DevicesDocument181 pagesCisco Prime Support DevicesjoNo ratings yet
- Nokia Umts PCIDocument105 pagesNokia Umts PCIRockyNo ratings yet
- Wireless Mod4 WirelessTopologiesDocument50 pagesWireless Mod4 WirelessTopologiesEngr Suleman MemonNo ratings yet
- Regarding Listing All Hardware Network InterfacesDocument2 pagesRegarding Listing All Hardware Network InterfacestummalapallyNo ratings yet
- LS-Fiber Optical Interface Mini Card For Loop-AM3440: FeaturesDocument4 pagesLS-Fiber Optical Interface Mini Card For Loop-AM3440: FeaturesAmrNo ratings yet
- Huawei AR G3 Enterprise Router Comparison ListDocument2 pagesHuawei AR G3 Enterprise Router Comparison ListS. M. Arifinul KarimNo ratings yet
- OLT1408A ZyxelDocument4 pagesOLT1408A ZyxelJanilson LopesNo ratings yet
- ML700 and BBA TestDocument56 pagesML700 and BBA TestmounaachourNo ratings yet
- External Modem Indicator LightsDocument2 pagesExternal Modem Indicator LightsJyotindraNo ratings yet
- Definition - What Does Cellular Network Mean?Document2 pagesDefinition - What Does Cellular Network Mean?Sunny KumarNo ratings yet