Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparison of Markets Structures - 1458613952630
Uploaded by
Vaanazhagan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views2 pagesOriginal Title
COMPARISON OF MARKETS STRUCTURES_1458613952630
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views2 pagesComparison of Markets Structures - 1458613952630
Uploaded by
VaanazhaganCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
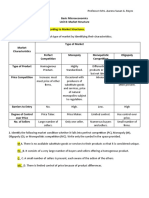
COMPARISON OF MARKETS STRUCTURES
Factors Monopoly Oligopoly Perfect Competition Monopolistic Competition
1. Number of Only one seller for A few large sellers supply the Many sellers, and many Large number of sellers
sellers the entire market bulk of the industry output buyers
2. Degree of Zero competition Less competition regarding High degree f Relatively less price
competition price. Non-price competition competition competition when compared
exists to perfect competition. Non-
price competition exists
3. Price level Highest as there is Higher due to a lower level of As determined by the Depends upon the extent to
no competition competition market forces of demand which products can be
and supply. differentiated.
4. Knowledge of A monopolist Buyers are relatively better All buyers have perfect Buyers are aware of the
buyers about controls market. informed about market information about the market conditions.
the market Buyers are not conditions. price and the market
conditions much aware of the conditions.
market conditions.
5. Entry and exit There are high Relatively less barriers for There is a high degree of High degree of freedom to
barriers for other
traders to enter the market freedom for buyers and enter and exit.
traders to enter the sellers to enter or exit
market the market.
6. Control on price Monopolist Relatively less freedom to A seller in perfect Sellers have control over
determines the
decide the price. Because competition has to take price to some extent which
price. So he is athere is more than one that price which the depends upon the degree of
price maker. trader. Often there could be market decides for him. product differentiation.
a price-lobby among the So he is a price taker.
tellers to charge a particular
price.
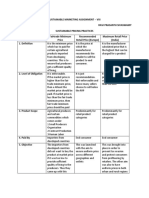
7. Degree of There is only one Mutual interdependence Each seller is Each seller is independent
dependency seller. Dependency among bulk suppliers independent
among sellers question does not
arise.
8. Nature of Relatively inelastic There is kink in the demand Perfectly elastic Relatively inelastic or elastic
demand curve curve depends upon the degree of
product differentiation
9. Type of Unique Homogeneous or Homogeneous Differentiated
products differentiated
10. Individual firm’s Very high Reasonable high if there No control over price as Some control persists
control over even depending.
price
11. Consumer Least Relatively less Consumers are powerful Relatively higher as there is
sovereignty at they are fully informed a large number of firms
12. Choice for No choice Less Choice Customer is free to buy Maximum choice due to
consumer from any producer, but product differentiation
the product is
homogeneous
13. Predatory Does not apply Applies No chance Remote chance
pricing (a price
that will throw
the rivals out of
the market)
14. Economies of Occur Occur May not occur May not occur
scale
15. Relationship AR > MR AR > MR AR = MR AR > MR
between AR
and MR
16. Examples of Rare but found in In homogenous oligopoly, Rare but sometimes Branded foods, retail stores,
products / public utility agricultural products, raw found in the case of beauty parlours, etc.
services services such as materials, etc. In case of agricultural products, raw
Indian Railways differentiated oligopoly, materials, etc.
automobiles, detergents,
audio and video equipment,
refrigerators, etc.
17. Real life Rarely exists Commonly found Rarely found Commonly found
relevance
You might also like
- Option Market Making : Part 1, An Introduction: Extrinsiq Advanced Options Trading Guides, #3From EverandOption Market Making : Part 1, An Introduction: Extrinsiq Advanced Options Trading Guides, #3No ratings yet
- Practical CS ProcessingDocument483 pagesPractical CS ProcessinganAMUstudent100% (2)
- CA-idms Ads Alive User Guide 15.0Document142 pagesCA-idms Ads Alive User Guide 15.0svdonthaNo ratings yet
- Talent-Olympiad 9 Science SampleDocument12 pagesTalent-Olympiad 9 Science SampleFire GamingNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Feeding Mechanism in Sewing MachinesDocument21 pagesDifferent Types of Feeding Mechanism in Sewing MachinesVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Computerized Pattern MakingDocument18 pagesComputerized Pattern MakingVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Computerized Pattern MakingDocument18 pagesComputerized Pattern MakingVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Economics - Market Structures (From The Book Understanding Economics)Document9 pagesEconomics - Market Structures (From The Book Understanding Economics)Pauline EllaNo ratings yet
- 28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsDocument14 pages28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsniallNo ratings yet
- Perfect CompetitionDocument23 pagesPerfect Competitionsamrulezzz80% (5)
- Loan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseDocument2 pagesLoan Agreement: Acceleration ClauseSomething SuspiciousNo ratings yet
- Chapt 5 Market StructureDocument54 pagesChapt 5 Market StructureAnnaLiyana50% (2)
- Textilecalculations 131030144207 Phpapp01Document15 pagesTextilecalculations 131030144207 Phpapp01jazzlovey100% (1)
- Activity 21 Table of Structure Regarding To M.S.Document2 pagesActivity 21 Table of Structure Regarding To M.S.Kerby Geroza AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Types of OligopolyDocument3 pagesTypes of OligopolyIvan Dennis SalupanNo ratings yet
- Monopoly Market 2Document5 pagesMonopoly Market 2Pradyumna KansariNo ratings yet
- Name of Learner: - Quarter 1-Week 5 Section: - DateDocument8 pagesName of Learner: - Quarter 1-Week 5 Section: - DateNicolette SaangNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Eco, C) Classification of Markets.Document15 pagesUnit 3 Eco, C) Classification of Markets.khushbooNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Exercises 3Document1 pageTutorial Exercises 3SITI MARIAM MAILNo ratings yet
- Hum 2229 - Lecture 2Document14 pagesHum 2229 - Lecture 2NASIF BIN NAZRULNo ratings yet
- Types of Market StructureDocument5 pagesTypes of Market Structureaznairah.malicNo ratings yet
- Eco Finals - Lesson 1Document6 pagesEco Finals - Lesson 1Rodessa CacayuranNo ratings yet
- Monopoly MarketDocument5 pagesMonopoly Market15 - JAIN DEEPSHIKHA - ANo ratings yet
- Socstud Q2summa2Document1 pageSocstud Q2summa2CRAIG MIKEL P YUNo ratings yet
- Market Structure 1Document20 pagesMarket Structure 1Yuwon Angelo AguilarNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous 8Document1 pageAsynchronous 8swaroopppatra2002No ratings yet
- Document (2) RDocument3 pagesDocument (2) Rmatomanaluvo7No ratings yet
- Monopolistic Competition: Names of Sub-UnitsDocument11 pagesMonopolistic Competition: Names of Sub-UnitssarthaksenNo ratings yet
- MarketDocument3 pagesMarketSuny JubayerNo ratings yet
- Eco1 Module 4Document3 pagesEco1 Module 4Jamaeca Abat EdraNo ratings yet
- BOOKDocument3 pagesBOOKAnand RahulNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument2 pagesMarket StructuresMhelfe Bayeng Tabao-icanNo ratings yet
- NAME: Muhammad Adil Javed CLASS: BBA-II Section A SUBJECT: Microeconomics Roll No: Fa-2019-016Document11 pagesNAME: Muhammad Adil Javed CLASS: BBA-II Section A SUBJECT: Microeconomics Roll No: Fa-2019-016Esha KulsoomNo ratings yet
- 4 Market Structures ModifiedDocument4 pages4 Market Structures ModifiedDanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Monopoly: Price and Output Decisions: 10.0 ObjectivesDocument22 pagesUnit 10 Monopoly: Price and Output Decisions: 10.0 ObjectivesSaid Abdi MohamudNo ratings yet
- UNIT V - Market BehaviourDocument11 pagesUNIT V - Market Behaviourdarun17076No ratings yet
- Oligopoly - Olig-FewDocument4 pagesOligopoly - Olig-Fewmia cadenNo ratings yet
- Chapt 5 Market Structure OldDocument50 pagesChapt 5 Market Structure OldAnnaLiyanaNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument19 pagesMarket StructuresKeen DjnNo ratings yet
- 5-7 - Market Structures and EfficiencyDocument83 pages5-7 - Market Structures and EfficiencySamiyah Irfan 2023243No ratings yet
- EME-4 NotesDocument17 pagesEME-4 NotesAakriti DubeyNo ratings yet
- Bm2da Module#4Document5 pagesBm2da Module#4Arielle Nichole SombilonNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Marketing Assignment - 8-1Document2 pagesSustainable Marketing Assignment - 8-1Sudhanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Market StructuresDocument11 pagesUnit 2 Market StructuresFausto Da GamaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 MARKETDocument16 pagesClass 11 MARKETTim_GnsNo ratings yet
- Market StructureDocument12 pagesMarket StructureYashwant MisaleNo ratings yet
- Main Market Forms HandoutsDocument6 pagesMain Market Forms HandoutsKishor CharsiNo ratings yet
- Me 4 (Part A)Document6 pagesMe 4 (Part A)Anuj YadavNo ratings yet
- Economics Monopoly NewDocument19 pagesEconomics Monopoly NewBhavin patelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 25Document7 pagesLecture 25RohitPatialNo ratings yet
- Principles of Economics Chapter 09Document28 pagesPrinciples of Economics Chapter 09Lu CheNo ratings yet
- Me 2Document13 pagesMe 2vikrantsachdeva03No ratings yet
- Market Structures & CompetitionDocument20 pagesMarket Structures & CompetitionJames BondNo ratings yet
- The Firm and Market StructuresDocument36 pagesThe Firm and Market StructuresPrince AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 6 EthicsDocument18 pages6 Ethicsgyoyo9797No ratings yet
- Block 4 MS 9 Unit 2Document14 pagesBlock 4 MS 9 Unit 2vinay kaithwasNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: Market StructureDocument11 pagesChapter Five: Market StructurefaNo ratings yet
- Econ Homework # 5Document3 pagesEcon Homework # 5Alfonso Jr. BusaNo ratings yet
- Market StructureDocument12 pagesMarket Structurekannan sunilNo ratings yet
- Marketstructureupdated 191014150142Document41 pagesMarketstructureupdated 191014150142Soobin ChoiNo ratings yet
- Economics AIP - Monopolies, Duopolies and OligopoliesDocument10 pagesEconomics AIP - Monopolies, Duopolies and OligopoliesSiya HedaNo ratings yet
- Types of Market and Price DeterminationDocument4 pagesTypes of Market and Price DeterminationSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Basis Perfect Competition Monopoly Monopolistic Competition OligopolyDocument2 pagesBasis Perfect Competition Monopoly Monopolistic Competition OligopolyAnthony Tunying MantuhacNo ratings yet
- 1 Market StructureDocument11 pages1 Market StructureArallaeNo ratings yet
- Report Topic:: Market StructureDocument4 pagesReport Topic:: Market StructureAyisOgaNo ratings yet
- TECHNOPRENEURSHIPDocument13 pagesTECHNOPRENEURSHIPLeana Victoria EspanolaNo ratings yet
- Price DeterminationDocument16 pagesPrice DeterminationMD. TasneemNo ratings yet
- EME-4 NotesDocument17 pagesEME-4 NotesAnivesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Market StructuresDocument1 pageMarket Structuresizzy9zyzyNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis and Development of Card-Spinning SystemDocument10 pagesDynamic Analysis and Development of Card-Spinning SystemVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Ring SpinningDocument4 pagesRecent Developments in Ring SpinningVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Comber: Salient FeaturesDocument2 pagesComber: Salient FeaturesVaanazhagan100% (5)
- Draw Frame: Salient FeaturesDocument2 pagesDraw Frame: Salient FeaturesVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in Spinning, Weaving and Wet Processing Industry - Textile LearnerDocument10 pagesRecent Developments in Spinning, Weaving and Wet Processing Industry - Textile LearnerVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Multiple Activity Chart: Group - 1Document27 pagesMultiple Activity Chart: Group - 1VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 4 NewDocument12 pagesEconomics Unit 4 NewKumaran SgNo ratings yet
- Two Handed Process Chart & Ergonomics in Textile and ApparelDocument32 pagesTwo Handed Process Chart & Ergonomics in Textile and ApparelVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- String Diagram and Plant Layout: Group - 2Document25 pagesString Diagram and Plant Layout: Group - 2VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 5 - 1457145468349Document5 pagesEconomics Unit 5 - 1457145468349VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Group 7Document28 pagesGroup 7VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 5 - 1457145468349Document5 pagesEconomics Unit 5 - 1457145468349VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 6 - 1457605509458Document9 pagesEconomics Unit 6 - 1457605509458VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 8 - 1461428222405Document14 pagesEconomics Unit 8 - 1461428222405VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Buying House & Buying AgenciesDocument17 pagesBuying House & Buying AgenciesVaanazhagan0% (1)
- Types of Fabric UsedDocument17 pagesTypes of Fabric UsedVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Folding and PackingDocument27 pagesFolding and PackingVaanazhagan0% (1)
- Seams and StitchesDocument21 pagesSeams and StitchesVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Mechanics CA 3Document27 pagesMechanics CA 3VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Mechanics CA 2Document50 pagesMechanics CA 2VaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Mechanics CA 1 NotesDocument48 pagesMechanics CA 1 NotesVaanazhaganNo ratings yet
- Admission Test For Programme 2009-11: B C D B C ADocument51 pagesAdmission Test For Programme 2009-11: B C D B C ATuku SinghNo ratings yet
- Why Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedDocument16 pagesWhy Do Kashmiris Need Self-Determination?: UncategorizedFarooq SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Trend in Agricultural ProductivityDocument1 pageTrend in Agricultural ProductivityGiaNo ratings yet
- Wa200-8 Venss06304 1904 PDFDocument24 pagesWa200-8 Venss06304 1904 PDFOktiano BudiNo ratings yet
- DD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogDocument46 pagesDD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogAndres Fdo Mora D100% (2)
- WHITE TOWN GROUP-4 FinalDocument112 pagesWHITE TOWN GROUP-4 Finalaswath manojNo ratings yet
- Grammar Review A2-B1Document5 pagesGrammar Review A2-B1Lena Silva SouzaNo ratings yet
- Why You MeDocument18 pagesWhy You MeFira tubeNo ratings yet
- Molecules of Life PDFDocument113 pagesMolecules of Life PDFArpit Pradhan100% (1)
- Cinnamon RollDocument1 pageCinnamon RollMaria Manoa GantalaNo ratings yet
- Sorting Algorithms in Fortran: Dr. Ugur GUVENDocument10 pagesSorting Algorithms in Fortran: Dr. Ugur GUVENDHWANIT MISENo ratings yet
- Cell Structure, Cellular Respiration, PhotosynthesisDocument14 pagesCell Structure, Cellular Respiration, PhotosynthesisAmr NasserNo ratings yet
- AC MachinesDocument32 pagesAC Machinesjoeney guardiarioNo ratings yet
- Tip Sheet March 2017Document2 pagesTip Sheet March 2017hoangvubui4632No ratings yet
- 88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareDocument1 page88 Year Old Man Missing in SC - Please ShareAmy WoodNo ratings yet
- DTS Nozzles R3Document2 pagesDTS Nozzles R3meilia teknikNo ratings yet
- 7 ApportionmentDocument46 pages7 Apportionmentsass sofNo ratings yet
- 10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupDocument4 pages10 Problem For The Topic 9 & 10 Hicao GroupArvin ArmojallasNo ratings yet
- Unseen Passage 2Document6 pagesUnseen Passage 2Vinay OjhaNo ratings yet
- Professional Development Objectives Related To Modalities Specific TopicsDocument3 pagesProfessional Development Objectives Related To Modalities Specific TopicsCris100% (1)
- Individual Reflection ScribdDocument4 pagesIndividual Reflection ScribdJamie Chan JieminNo ratings yet
- SRM 7 EHP 4 Release Notes PDFDocument18 pagesSRM 7 EHP 4 Release Notes PDFMOHAMMED SHEHBAAZNo ratings yet
- Damask: by ChenoneDocument17 pagesDamask: by ChenoneYasir IjazNo ratings yet
- NUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsDocument2 pagesNUFLO Low Power Pre-Amplifier: SpecificationsJorge ParraNo ratings yet
- Towards A Brighter Ecological Future: Group 2Document24 pagesTowards A Brighter Ecological Future: Group 2As YangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemDocument3 pagesChapter 3 Mine Ventialtion ProblemfahimNo ratings yet