Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsQB106423 PDF
QB106423 PDF
Uploaded by
Jayed Ahmed LaskarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Electronics Circuits For Communications@Chapter 2Document104 pagesElectronics Circuits For Communications@Chapter 2Lee RitzNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PDFDocument33 pagesUnit 3 PDFreaper mochiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document33 pagesUnit 3Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- EC-II 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 4)Document2 pagesEC-II 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 4)Ganapathy RamadossNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers Two Marks Question & AnswerDocument9 pagesUnit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers Two Marks Question & AnswerGokulScribdNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Applications: Unit 1: Tunned Amplifier SubjectDocument47 pagesElectronic Devices & Applications: Unit 1: Tunned Amplifier SubjectmulushewaNo ratings yet
- EC II Unit 3Document33 pagesEC II Unit 3Thiyagarajan VelayuthamNo ratings yet
- Ec 1251 Electronics Circuits IIDocument17 pagesEc 1251 Electronics Circuits IIainugiri100% (1)
- Electronics Circuits II Two MarksDocument16 pagesElectronics Circuits II Two MarksB. AswiniNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit Analysis - U5Document29 pagesElectronic Circuit Analysis - U5RakshithNo ratings yet
- Tuned Amplifiers Unit 3Document15 pagesTuned Amplifiers Unit 3rageroshan933No ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Ii UnitDocument27 pagesElectronic Circuits Ii UnitMd. Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tuned Amplifiers SubbulakshmiDocument24 pagesTuned Amplifiers SubbulakshmiAshish Reddy100% (1)
- Analog Electronics Unit - 5Document66 pagesAnalog Electronics Unit - 5Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Scheme Eee Unit3 QBDocument35 pagesScheme Eee Unit3 QBMaaz S100% (2)
- Eca Unit 2 2024Document20 pagesEca Unit 2 2024Manchana PadamajaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Application of Operational AmplifiersDocument4 pagesUnit-Ii Application of Operational AmplifiersAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzNo ratings yet
- 1.classification of Amplifiers, Distortions in AmplifiersDocument12 pages1.classification of Amplifiers, Distortions in AmplifiersMrs. P. Ganga BhavaniNo ratings yet
- Ec II Q&A-Assign-6,10 Marks QuestionsDocument32 pagesEc II Q&A-Assign-6,10 Marks QuestionsJoshua Duffy100% (1)
- Tuned AmplifiersDocument66 pagesTuned AmplifiersHerald RufusNo ratings yet
- Q. Code: 578 Sub: Communication Engineering Course: ECE Sem: IV Part-ADocument24 pagesQ. Code: 578 Sub: Communication Engineering Course: ECE Sem: IV Part-ASabari Muthu RamanNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV: Electronics: II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IVDocument7 pagesUnit - IV: Electronics: II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IVanunilaNo ratings yet
- Tune Amp ProjectDocument10 pagesTune Amp ProjectVaibhav purushottam kaleNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions: Ec-41-Electronic Circuits IiDocument16 pagesTwo Mark Questions: Ec-41-Electronic Circuits IiashaambilyNo ratings yet
- Analog Exp 10Document4 pagesAnalog Exp 10Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Different Types of Coupled AmplifiersDocument15 pagesComparison of Different Types of Coupled AmplifiersDeval PareekNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Viva QuestionDocument8 pagesAnalog Communication Viva Questionsujithmrinal100% (4)
- Tuned AmplifiersDocument9 pagesTuned AmplifiersMadhu Krishna KarthanNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Analysis of Amplifiers (BJT & Fet) : Narayana Engineering College:: NelloreDocument12 pagesSmall Signal Analysis of Amplifiers (BJT & Fet) : Narayana Engineering College:: NelloreTharun kondaNo ratings yet
- Ie CP ReportDocument5 pagesIe CP ReportAnanya ChavanNo ratings yet
- 3 Single Tuned Voltage AmplifierDocument4 pages3 Single Tuned Voltage AmplifierdamasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Multistage AmplifiersDocument49 pagesLesson 5 Multistage AmplifiersSolomonNo ratings yet
- Aec 2 MarksDocument3 pagesAec 2 Markshemu70No ratings yet
- Frequency Response of BJT Single Stage AmplifierDocument8 pagesFrequency Response of BJT Single Stage AmplifierRonish SheoranNo ratings yet
- Tuned Amplifier PDFDocument40 pagesTuned Amplifier PDFRichik KashyapNo ratings yet
- Filters and Tuned AmplifiersDocument13 pagesFilters and Tuned AmplifiersLasantha AbeykoonNo ratings yet
- Oscillator CircuitDocument16 pagesOscillator CircuitSiddhartha PalNo ratings yet
- EC1311 Communication EngineeringDocument23 pagesEC1311 Communication EngineeringVidya NeemuNo ratings yet
- BE - NTL MaterialDocument17 pagesBE - NTL Materialsravan_451No ratings yet
- D - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-JkDocument20 pagesD - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-Jktinku990056% (9)
- Unit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & AnswerDocument4 pagesUnit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & Answerpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Viva Questons Exp 1 and Exp 2Document4 pagesViva Questons Exp 1 and Exp 2shrinidhi NNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONBANK EcadDocument19 pagesQUESTIONBANK EcadVarsha WaingankarNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Second Sem Complementary Electronics May 2023 - Ampliers, Oscillators and Power ElectronicsDocument16 pagesScheme of Second Sem Complementary Electronics May 2023 - Ampliers, Oscillators and Power ElectronicsabhinavsarasappanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Gain, Attenuation, and DecibelsDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Gain, Attenuation, and DecibelsMiscrits TRENo ratings yet
- Viva QuestionsDocument8 pagesViva QuestionsPrabinjose100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - OscillatorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - OscillatorJ A P SNo ratings yet
- Microwave & Optical Engineering Question BankDocument47 pagesMicrowave & Optical Engineering Question BankThiagu RajivNo ratings yet
- Comparison of BW For RC Coupled Single Stage and Multi Stage AmplifieDocument6 pagesComparison of BW For RC Coupled Single Stage and Multi Stage AmplifieFaras SmansaNo ratings yet
- Jntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca) Cracked by Mr.20Document21 pagesJntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca) Cracked by Mr.20kattlaNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Amplifire Lecture 1Document24 pagesSmall Signal Amplifire Lecture 1Mouzy McthyNo ratings yet
- Ec100 Model Question Paper With AnswersDocument35 pagesEc100 Model Question Paper With AnswersSanjay P NambiarNo ratings yet
- The Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyFrom EverandThe Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesFrom EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Kathrein 2017 Directional Antennas VPol 690-2690 MHZDocument8 pagesKathrein 2017 Directional Antennas VPol 690-2690 MHZRobertNo ratings yet
- Iot Lab ManualeditedDocument29 pagesIot Lab ManualeditedprashantNo ratings yet
- Decs 250 PDFDocument350 pagesDecs 250 PDFPritam SinghNo ratings yet
- 2SK3109 MosfetDocument8 pages2SK3109 MosfetJadi Marsahala HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Compact FlashDocument9 pagesCompact Flashenpr87reddyNo ratings yet
- IRFZ34N Datasheet - KDocument8 pagesIRFZ34N Datasheet - KNairo FilhoNo ratings yet
- C5440 PanasonicSemiconductorDocument2 pagesC5440 PanasonicSemiconductorteniNo ratings yet
- ST7MDTDocument5 pagesST7MDTIoan TivgaNo ratings yet
- Surge Protection For Frequency Converters - EEPDocument4 pagesSurge Protection For Frequency Converters - EEPRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- PalomaDocument16 pagesPalomaEmmanuel PalomaNo ratings yet
- Boss DR-770 Service NotesDocument18 pagesBoss DR-770 Service NotesFernando Gómez100% (1)
- MTE CatalogoDocument8 pagesMTE CatalogoCarlos Eduardo Caamaño RojasNo ratings yet
- Marantz CD6000 Service ManualDocument28 pagesMarantz CD6000 Service ManualZingarini AlessioNo ratings yet
- Blue 8x8x8 LED Cube Kit - PCB VersionDocument6 pagesBlue 8x8x8 LED Cube Kit - PCB VersionsiogNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Marco Cesar 203058 48Document12 pagesTask 3 Marco Cesar 203058 48asesorias academicasNo ratings yet
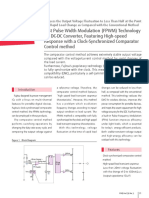
- Fast Pulse Width Modulation (FPWM) Technology For DC-DC Converter, Featuring High-Speed Response With A Clock-Synchronized Comparator Control MethodDocument2 pagesFast Pulse Width Modulation (FPWM) Technology For DC-DC Converter, Featuring High-Speed Response With A Clock-Synchronized Comparator Control MethodCan ERTANNo ratings yet
- Computer Class 4Document2 pagesComputer Class 4firojNo ratings yet
- MOBOT BTCarDocument5 pagesMOBOT BTCarElider Lucero HuamanNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument27 pagesEmbedded Systemsnavneet100% (1)
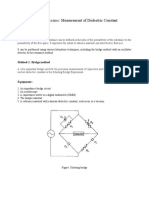
- Experiment Name:: Measurement of Dielectric ConstantDocument3 pagesExperiment Name:: Measurement of Dielectric Constantmuhtasim fuadNo ratings yet
- Agilent Tech., N5770A PW Supplies PDFDocument12 pagesAgilent Tech., N5770A PW Supplies PDFLulu Sweet ThingNo ratings yet
- AHP4518R3v06: Antenna SpecificationsDocument3 pagesAHP4518R3v06: Antenna SpecificationsDiogo AlvesNo ratings yet
- LCD Panel Repairing Book - Parte5Document40 pagesLCD Panel Repairing Book - Parte5Ricardo Nicolau WerlangNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Converter ICs SB Vol11 Issue5 PDFDocument12 pagesDigital-to-Analog Converter ICs SB Vol11 Issue5 PDFanggreiniayu666No ratings yet
- Appendix 2. Metrowerks Techarts 9S12C32 SetupDocument11 pagesAppendix 2. Metrowerks Techarts 9S12C32 SetupDev SuryaNo ratings yet
- 2ucd030000e009 C PCS100 SFCDocument38 pages2ucd030000e009 C PCS100 SFCSurendra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bga725l6 - V2 0 PDFDocument16 pagesBga725l6 - V2 0 PDFAnanda KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Analog Input Disturbance Fault Recorder: Description From DFR Terminal Source VIA (+) (-) Terminal To DFRDocument2 pagesAnalog Input Disturbance Fault Recorder: Description From DFR Terminal Source VIA (+) (-) Terminal To DFRHamdan IskandarNo ratings yet
- Polymer LedDocument14 pagesPolymer LedNaveenNo ratings yet
- 1102 - EPE Hybrid Computer - Part 1Document9 pages1102 - EPE Hybrid Computer - Part 1pelle svanslosNo ratings yet
QB106423 PDF
QB106423 PDF
Uploaded by
Jayed Ahmed Laskar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesOriginal Title
QB106423.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesQB106423 PDF
QB106423 PDF
Uploaded by
Jayed Ahmed LaskarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
SRI VIDYA COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH
DEPARTMENT OF ECE
EC 6401 – Electronic Circuits II
UNIT –III - TUNED AMPLIFIERS
Two Marks Question & Answer
1. What do you mean by tuned amplifiers?
The amplifiers which amplify only selected range of frequencies (narrow
band of frequencies) with the help of tuned circuits (parallel LC circuit) are called
tuned amplifiers.
2. What are the various types of tuned amplifiers?
(1) Small signal tuned amplifiers
a. Single tuned amplifiers
(i) Capacitive coupled
(ii) Inductively coupled (or) Transformer coupled
b. Double tuned amplifiers
c. Stagger tuned amplifiers
(2) Large signal tuned amplifiers
3. What is the response of tuned amplifiers?
The response of tuned amplifier is maximum at resonant frequency and it
falls sharply for frequencies below and above the resonant frequency.
4. When tuned circuit is like resistive, capacitive and inductive?
(1) At resonance, circuit is like resistive.
(2) For frequencies above resonance, circuit is like capacitive.
(3) For frequencies below resonance, circuit is like inductive.
5. What are the various components of coil losses?
(1) Copper loss
(2) Eddy current loss
(3) Hysteresis loss
6. Define Q factor of resonant circuit.
(1) It is the ratio of reactance to resistance.
(2) It also can be defined as the measure of efficiency with which inductor can
store the energy.
Q=2п *(Maximum Energy Stored per cycle / Energy dissipated per cycle)
7. What is dissipation factor?
(1) It is defined as 1/Q.
(2) It can be referred to as the total loss within a component.
8. Define unloaded and loaded Q of tuned circuit.
(1) The unloaded Q or QU is the ratio of stored energy to dissipated energy in
a reactor or resonator.
9. The loaded Q or QL of a resonator is determined by how tightly the
resonator is coupled to its terminations.Why quality factor is kept as high as
possible in tuned circuits?
1. When Q is high, bandwidth is low and we get better selectivity. Hence Q is
kept as high as possible in tuned circuits.
2. When Q is high inductor losses are less.
10. List various types of cascaded Small signal tuned amplifiers.
1. Single tuned amplifiers.
2. Double tuned amplifiers.
3. Stagger tuned amplifiers.
11. How single tuned amplifiers are classified?
1. Capacitance coupled single tuned amplifier.
2. Transformer coupled or inductively coupled single tuned amplifier.
12. What are single tuned amplifiers?
Single tuned amplifiers use one parallel resonant circuit as the load
impedance in each stage and all the tuned circuits are tuned to the same
frequency.
13. What are double tuned amplifiers?
Double tuned amplifiers use two inductively coupled tuned circuits per
stage, both the tuned circuits being tuned to the same frequency.
14. What are stagger tuned amplifiers?
Stagger tuned amplifiers use a number of single tuned stages in cascade,
the successive tuned circuits being tuned to slightly different frequencies.
(OR)
It is a circuit in which two single tuned cascaded amplifiers having certain
bandwidth are taken and their resonant frequencies are adjusted that they are
separated by an amount equal to the bandwidth of each stage. Since resonant
frequencies are displaced it is called stagger tuned amplifier.
15. What is the effect of cascading single tuned amplifiers on bandwidth?
Bandwidth reduces due to cascading single tuned amplifiers.
16. List the advantages and disadvantages of tuned amplifiers.
Advantages:
1. They amplify defined frequencies.
2. Signal to Noise ratio at output is good.
3. They are well suited for radio transmitters and receivers.
4. The band of frequencies over which amplification is required can be varied.
Disadvantages:
1. Since they use inductors and capacitors as tuning elements, the circuit is bulky
and costly.
2. If the band of frequency is increased, design becomes complex.
3. They are not suitable to amplify audio frequencies.
17. What are the advantages of double tuned amplifier over single tuned amplifier?
1. It provides larger 3 dB bandwidth than the single tuned amplifier and hence
provides the larger gain-bandwidth product.
2. It provides gain versus frequency curve having steeper sides and flatter top.
18. What the advantages are of stagger tuned amplifier?
The advantage of stagger tuned amplifier is to have better flat, wideband
characteristics.
19. Mention the applications of class C tuned amplifier.
1. Class C amplifiers are used primarily in high-power, high-frequency
applications such as Radio-frequency transmitters.
2. In these applications, the high frequency pulses handled by the amplifier are
not themselves the signal, but constitute what is called the Carrier for the
signal.
3. Amplitude modulation is one such example.
4. The principal advantage of class-C amplifier is that it has a higher efficiency
than the other amplifiers.
20. What is Neutralization?
The technique used for the elimination of potential oscillations is called
neutralization. (OR) The effect of collector to base capacitance of the transistor is
neutralized by introducing a signal that cancels the signal coupled through
collector base capacitance. This process is called neutralization.
21. What is the use of Neutralization?
1. BJT and FET are potentially unstable over some frequency range due to the
feedback parameter present in them.
2. If the feedback can be cancelled by an additional feedback signal that is equal in
amplitude and opposite in sign, the transistor becomes unilateral from input to
output the oscillations completely stop.
3. This is achieved by Neutralization.
22. What are the different types of neutralization?
1. Hazeltine neutralization
2. Rice neutralization
3. Neutrodyne neutralization.
23. What is rice neutralization?
It uses center tapped coil in the base circuit. The signal voltages at the end
of tuned base coil are equal and out of phase.
16 marks Question
1. Explain in detail about single tuned amplifier
2. Explain in detail about double tuned amplifier.
3. Explain in detail about stagger-tuned amplifier
4. Compare single tuned and double tuned amplifier
5. Explain the different types of neutralization?
You might also like
- Electronics Circuits For Communications@Chapter 2Document104 pagesElectronics Circuits For Communications@Chapter 2Lee RitzNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PDFDocument33 pagesUnit 3 PDFreaper mochiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document33 pagesUnit 3Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- EC-II 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 4)Document2 pagesEC-II 2marks (Q & A) (Unit 4)Ganapathy RamadossNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers Two Marks Question & AnswerDocument9 pagesUnit - Iii - Tuned Amplifiers Two Marks Question & AnswerGokulScribdNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Applications: Unit 1: Tunned Amplifier SubjectDocument47 pagesElectronic Devices & Applications: Unit 1: Tunned Amplifier SubjectmulushewaNo ratings yet
- EC II Unit 3Document33 pagesEC II Unit 3Thiyagarajan VelayuthamNo ratings yet
- Ec 1251 Electronics Circuits IIDocument17 pagesEc 1251 Electronics Circuits IIainugiri100% (1)
- Electronics Circuits II Two MarksDocument16 pagesElectronics Circuits II Two MarksB. AswiniNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit Analysis - U5Document29 pagesElectronic Circuit Analysis - U5RakshithNo ratings yet
- Tuned Amplifiers Unit 3Document15 pagesTuned Amplifiers Unit 3rageroshan933No ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Ii UnitDocument27 pagesElectronic Circuits Ii UnitMd. Mizanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tuned Amplifiers SubbulakshmiDocument24 pagesTuned Amplifiers SubbulakshmiAshish Reddy100% (1)
- Analog Electronics Unit - 5Document66 pagesAnalog Electronics Unit - 5Rohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Scheme Eee Unit3 QBDocument35 pagesScheme Eee Unit3 QBMaaz S100% (2)
- Eca Unit 2 2024Document20 pagesEca Unit 2 2024Manchana PadamajaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii Application of Operational AmplifiersDocument4 pagesUnit-Ii Application of Operational AmplifiersAnonymous 3yqNzCxtTzNo ratings yet
- 1.classification of Amplifiers, Distortions in AmplifiersDocument12 pages1.classification of Amplifiers, Distortions in AmplifiersMrs. P. Ganga BhavaniNo ratings yet
- Ec II Q&A-Assign-6,10 Marks QuestionsDocument32 pagesEc II Q&A-Assign-6,10 Marks QuestionsJoshua Duffy100% (1)
- Tuned AmplifiersDocument66 pagesTuned AmplifiersHerald RufusNo ratings yet
- Q. Code: 578 Sub: Communication Engineering Course: ECE Sem: IV Part-ADocument24 pagesQ. Code: 578 Sub: Communication Engineering Course: ECE Sem: IV Part-ASabari Muthu RamanNo ratings yet
- Unit - IV: Electronics: II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IVDocument7 pagesUnit - IV: Electronics: II yr/III Sem/Mech/EEE 2 Marks With Answers Unit-IVanunilaNo ratings yet
- Tune Amp ProjectDocument10 pagesTune Amp ProjectVaibhav purushottam kaleNo ratings yet
- Two Mark Questions: Ec-41-Electronic Circuits IiDocument16 pagesTwo Mark Questions: Ec-41-Electronic Circuits IiashaambilyNo ratings yet
- Analog Exp 10Document4 pagesAnalog Exp 10Farhan AliNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Different Types of Coupled AmplifiersDocument15 pagesComparison of Different Types of Coupled AmplifiersDeval PareekNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Viva QuestionDocument8 pagesAnalog Communication Viva Questionsujithmrinal100% (4)
- Tuned AmplifiersDocument9 pagesTuned AmplifiersMadhu Krishna KarthanNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Analysis of Amplifiers (BJT & Fet) : Narayana Engineering College:: NelloreDocument12 pagesSmall Signal Analysis of Amplifiers (BJT & Fet) : Narayana Engineering College:: NelloreTharun kondaNo ratings yet
- Ie CP ReportDocument5 pagesIe CP ReportAnanya ChavanNo ratings yet
- 3 Single Tuned Voltage AmplifierDocument4 pages3 Single Tuned Voltage AmplifierdamasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Multistage AmplifiersDocument49 pagesLesson 5 Multistage AmplifiersSolomonNo ratings yet
- Aec 2 MarksDocument3 pagesAec 2 Markshemu70No ratings yet
- Frequency Response of BJT Single Stage AmplifierDocument8 pagesFrequency Response of BJT Single Stage AmplifierRonish SheoranNo ratings yet
- Tuned Amplifier PDFDocument40 pagesTuned Amplifier PDFRichik KashyapNo ratings yet
- Filters and Tuned AmplifiersDocument13 pagesFilters and Tuned AmplifiersLasantha AbeykoonNo ratings yet
- Oscillator CircuitDocument16 pagesOscillator CircuitSiddhartha PalNo ratings yet
- EC1311 Communication EngineeringDocument23 pagesEC1311 Communication EngineeringVidya NeemuNo ratings yet
- BE - NTL MaterialDocument17 pagesBE - NTL Materialsravan_451No ratings yet
- D - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-JkDocument20 pagesD - Jayakumar Ece Ece Ece Viva Questions-Jktinku990056% (9)
- Unit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & AnswerDocument4 pagesUnit-Ii - Oscillators Two Marks Question & Answerpriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Viva Questons Exp 1 and Exp 2Document4 pagesViva Questons Exp 1 and Exp 2shrinidhi NNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONBANK EcadDocument19 pagesQUESTIONBANK EcadVarsha WaingankarNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Second Sem Complementary Electronics May 2023 - Ampliers, Oscillators and Power ElectronicsDocument16 pagesScheme of Second Sem Complementary Electronics May 2023 - Ampliers, Oscillators and Power ElectronicsabhinavsarasappanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Gain, Attenuation, and DecibelsDocument12 pagesModule 2 - Gain, Attenuation, and DecibelsMiscrits TRENo ratings yet
- Viva QuestionsDocument8 pagesViva QuestionsPrabinjose100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - OscillatorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - OscillatorJ A P SNo ratings yet
- Microwave & Optical Engineering Question BankDocument47 pagesMicrowave & Optical Engineering Question BankThiagu RajivNo ratings yet
- Comparison of BW For RC Coupled Single Stage and Multi Stage AmplifieDocument6 pagesComparison of BW For RC Coupled Single Stage and Multi Stage AmplifieFaras SmansaNo ratings yet
- Jntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca) Cracked by Mr.20Document21 pagesJntu Online Examinations (Mid 2 - Eca) Cracked by Mr.20kattlaNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Amplifire Lecture 1Document24 pagesSmall Signal Amplifire Lecture 1Mouzy McthyNo ratings yet
- Ec100 Model Question Paper With AnswersDocument35 pagesEc100 Model Question Paper With AnswersSanjay P NambiarNo ratings yet
- The Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyFrom EverandThe Technician's Radio Receiver Handbook: Wireless and Telecommunication TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesFrom EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: In Three VolumesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Kathrein 2017 Directional Antennas VPol 690-2690 MHZDocument8 pagesKathrein 2017 Directional Antennas VPol 690-2690 MHZRobertNo ratings yet
- Iot Lab ManualeditedDocument29 pagesIot Lab ManualeditedprashantNo ratings yet
- Decs 250 PDFDocument350 pagesDecs 250 PDFPritam SinghNo ratings yet
- 2SK3109 MosfetDocument8 pages2SK3109 MosfetJadi Marsahala HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Compact FlashDocument9 pagesCompact Flashenpr87reddyNo ratings yet
- IRFZ34N Datasheet - KDocument8 pagesIRFZ34N Datasheet - KNairo FilhoNo ratings yet
- C5440 PanasonicSemiconductorDocument2 pagesC5440 PanasonicSemiconductorteniNo ratings yet
- ST7MDTDocument5 pagesST7MDTIoan TivgaNo ratings yet
- Surge Protection For Frequency Converters - EEPDocument4 pagesSurge Protection For Frequency Converters - EEPRicardo A VergaraNo ratings yet
- PalomaDocument16 pagesPalomaEmmanuel PalomaNo ratings yet
- Boss DR-770 Service NotesDocument18 pagesBoss DR-770 Service NotesFernando Gómez100% (1)
- MTE CatalogoDocument8 pagesMTE CatalogoCarlos Eduardo Caamaño RojasNo ratings yet
- Marantz CD6000 Service ManualDocument28 pagesMarantz CD6000 Service ManualZingarini AlessioNo ratings yet
- Blue 8x8x8 LED Cube Kit - PCB VersionDocument6 pagesBlue 8x8x8 LED Cube Kit - PCB VersionsiogNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Marco Cesar 203058 48Document12 pagesTask 3 Marco Cesar 203058 48asesorias academicasNo ratings yet
- Fast Pulse Width Modulation (FPWM) Technology For DC-DC Converter, Featuring High-Speed Response With A Clock-Synchronized Comparator Control MethodDocument2 pagesFast Pulse Width Modulation (FPWM) Technology For DC-DC Converter, Featuring High-Speed Response With A Clock-Synchronized Comparator Control MethodCan ERTANNo ratings yet
- Computer Class 4Document2 pagesComputer Class 4firojNo ratings yet
- MOBOT BTCarDocument5 pagesMOBOT BTCarElider Lucero HuamanNo ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument27 pagesEmbedded Systemsnavneet100% (1)
- Experiment Name:: Measurement of Dielectric ConstantDocument3 pagesExperiment Name:: Measurement of Dielectric Constantmuhtasim fuadNo ratings yet
- Agilent Tech., N5770A PW Supplies PDFDocument12 pagesAgilent Tech., N5770A PW Supplies PDFLulu Sweet ThingNo ratings yet
- AHP4518R3v06: Antenna SpecificationsDocument3 pagesAHP4518R3v06: Antenna SpecificationsDiogo AlvesNo ratings yet
- LCD Panel Repairing Book - Parte5Document40 pagesLCD Panel Repairing Book - Parte5Ricardo Nicolau WerlangNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog Converter ICs SB Vol11 Issue5 PDFDocument12 pagesDigital-to-Analog Converter ICs SB Vol11 Issue5 PDFanggreiniayu666No ratings yet
- Appendix 2. Metrowerks Techarts 9S12C32 SetupDocument11 pagesAppendix 2. Metrowerks Techarts 9S12C32 SetupDev SuryaNo ratings yet
- 2ucd030000e009 C PCS100 SFCDocument38 pages2ucd030000e009 C PCS100 SFCSurendra sharmaNo ratings yet
- Bga725l6 - V2 0 PDFDocument16 pagesBga725l6 - V2 0 PDFAnanda KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Analog Input Disturbance Fault Recorder: Description From DFR Terminal Source VIA (+) (-) Terminal To DFRDocument2 pagesAnalog Input Disturbance Fault Recorder: Description From DFR Terminal Source VIA (+) (-) Terminal To DFRHamdan IskandarNo ratings yet
- Polymer LedDocument14 pagesPolymer LedNaveenNo ratings yet
- 1102 - EPE Hybrid Computer - Part 1Document9 pages1102 - EPE Hybrid Computer - Part 1pelle svanslosNo ratings yet