Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 - BIO310
Uploaded by
Ilham Amni Amanina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter 9_BIO310
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views2 pagesChapter 9 - BIO310
Uploaded by
Ilham Amni AmaninaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chapter 9 (Senses)
1. Illustrate how sound is transmitted into the inner ear.
2. Explain visual disorders myopia and hyperopia and their corrections by specific
lenses.
=Myopia disorders is nearsightedness. Distant images are brought to a point of focus
in front of retina. The image will appear blurry. Near images is brought into focus on
retina without accommodation. They with Myopia has better near vision than far
vision. Its often due to an elongated eyeball. It can be corrected by concave lenses in
eyeglasses.
Hyperopia disorder is farsightedness. Near images are focused behind retina even
with accommodation which image will appear blurry. They has better far vision than
near vision. Its often due to a short eyeball. It can be corrected by lenses that are
convex.
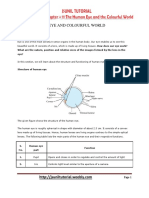
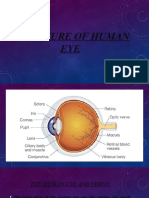
3. List three layers of the eye with respective structures.
-Outermost: Sclera, cornea
-Middle: Choroid, ciliary body, iris.
-Innermost: Retina
4. Describe two types of photoreceptor on the retina of human eyes.
The two types of photoreceptors are rods and cones. Rods allow black and white
vision in low light. It numerous , far sensitive to light, but do not provide sharp
images or color vision. Contain the pigment rhodopsin. Absorption causes rhodopsin
to dissociate into retinaldehyde and opsin.
Cones is receptor for bright light and provide high-resolution color vision.Light pass
through the ganglion and bipolar layers before reaching the photoreceptors in all
areas in retina except fovea (most distinct vision).
5. Explain pathway of the light as it passes into the eyes.
When light passes from one medium to another, it bends. Curvature at the point of
refraction can also bend light. Changing the curvature of the lens allows fine control
of focus. The image is flipped upside down in this process.
6. Compare the accommodation by eyes when focusing near and distant object.
Near Far
Ciliary muscle Contract, pulling border Relax
of choroid toward the
lens
Suspensory ligaments Relax Pulls on the suspensory
ligament
Lens Thicker and rounder Thin, not so curvature
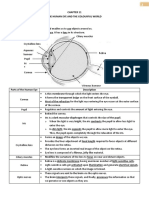
7. Explain the structures and functions of the parts in human ear.
External part- transmit airborne sound waves to middle ear (amplify sound) and to
fluid-filled inner ear.
Inner- houses 2 different sensory system:
The cochlea: receptors for conversion of sound waves into nerve impulses.
Vestibular apparatus: for sense of equilibrium
Middle ear- contains three bones called ossicle which is malleus, incus and stapes.
Vibrations are transmitted and amplified along the bones. The stapes is attached to
the oval window which transfers the vibrations into the inner ear.
You might also like
- 27 Physiology of Visual Analyzer (2)Document39 pages27 Physiology of Visual Analyzer (2)siwap34656No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueDocument33 pagesUnit 2 Sense Organs Eyes Skin and TongueBONGISIPHO HLOPHENo ratings yet
- The Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionDocument5 pagesThe Main Parts of The Eye and Their FunctionJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Human Visual System (Disowner)Document4 pagesHuman Visual System (Disowner)Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Lab Act Special SensesDocument7 pagesLab Act Special SensesJhia TorreonNo ratings yet
- 2.07 Tutorial Week 3Document4 pages2.07 Tutorial Week 3GraciaNo ratings yet
- Eye and VisionDocument20 pagesEye and VisionshyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Perception and SensationDocument6 pagesChapter 4 - Perception and Sensationecaber.a12343991No ratings yet
- Sense Organs Guide: Classification, Structure & FunctionsDocument26 pagesSense Organs Guide: Classification, Structure & FunctionsArpan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- 6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Document35 pages6.lessons, The Senses, pp472Lazare ChNo ratings yet
- Sensation: I. Eye: VisionDocument15 pagesSensation: I. Eye: VisionAvie Tablatin De LeonNo ratings yet
- An Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainDocument59 pagesAn Organ That Receives and Relays Information About The Body's Senses To The BrainIsarra AmsaluNo ratings yet
- Biology Eye NotesDocument12 pagesBiology Eye NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Light - Class NotesDocument6 pagesLight - Class Noteskirankarnawat29No ratings yet
- Resumen Semana 1 Clase de OftalmologiaDocument3 pagesResumen Semana 1 Clase de OftalmologiaIsis MartinezNo ratings yet
- Eyes Health AssessmenttDocument34 pagesEyes Health AssessmenttMhiaBuenafeNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument33 pagesThe Human Eye and The Colourful WorldHarshit GoelNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Sense OrganDocument8 pages3.2 Sense OrganMod HollNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida CH. 10. The Human Eye and The Colorful World RESOURCE SHEET: 1Document3 pagesAmity International School, Noida CH. 10. The Human Eye and The Colorful World RESOURCE SHEET: 1dreAdNo ratings yet
- Olfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESDocument23 pagesOlfactory, Eye, Ear'nOTESTida TpNo ratings yet
- OLD Human Eye and The Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesOLD Human Eye and The Colourful WorldRadhika GargNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Sense Organ - EyeDocument28 pages13.2 Sense Organ - EyeMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of VisionDocument49 pagesPhysiology of VisionPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- اخطاء انكسار 3&4Document6 pagesاخطاء انكسار 3&4Hassan AljaberiNo ratings yet
- For Lab ConclusionDocument10 pagesFor Lab ConclusionChippy RabeNo ratings yet
- Sense of VisionDocument34 pagesSense of VisionqqqqqNo ratings yet
- 11.human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument22 pages11.human Eye and Colourful WorldMalancha high school HSNo ratings yet
- Ch-11-Human Eye and The Colouful World 285-307 Physics Sem-1Document22 pagesCh-11-Human Eye and The Colouful World 285-307 Physics Sem-1MAYUR DESAI II BeingMD in PHYSICS IINo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument9 pagesThe Human Eyegiana 4e100% (1)
- Sense Organs NotesDocument13 pagesSense Organs NotesVijay Laxmi MundhraNo ratings yet
- Eye LectureDocument38 pagesEye LectureAMR WALIDNo ratings yet
- Sensory and Perceptual Process NotesDocument10 pagesSensory and Perceptual Process NotesSarah KimNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Biology The EyeDocument5 pagesGrade 11 Biology The EyeDexter TorringtonNo ratings yet
- Exp 11Document3 pagesExp 11Soler HeusaffNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Human Eye Notes FinalDocument27 pagesCh-10 Human Eye Notes Finalkilemas494No ratings yet
- Sense Organs: Structure of Human EyeDocument8 pagesSense Organs: Structure of Human EyeRanveer SinghNo ratings yet
- CHP 2Document22 pagesCHP 2Muskaan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye: A Simple CameraDocument18 pagesThe Human Eye: A Simple CameraljieNo ratings yet
- 187 RefractionDocument5 pages187 RefractionShabir KhanNo ratings yet
- 5 Special SensesDocument8 pages5 Special SensesEdel GapasinNo ratings yet
- Humans, and Other Animals, Are Able To Detect A Range of Stimuli From The External Environment, Some of Which Are Useful For CommunicationDocument13 pagesHumans, and Other Animals, Are Able To Detect A Range of Stimuli From The External Environment, Some of Which Are Useful For CommunicationYouieeeNo ratings yet
- The Colourful WorldDocument9 pagesThe Colourful WorldShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Physiology of SightDocument3 pagesPhysiology of SightDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteDocument13 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteJay MakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 f3Document113 pagesChapter 1 f3FAthiyah Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Visual and AuditoryDocument7 pagesVisual and AuditoryChristi EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Structure of the Human Eye in 40 CharactersDocument10 pagesStructure of the Human Eye in 40 Charactersvineet_knwrNo ratings yet
- GCSE OCR GATEWAYBiology - YOUR SENSES AND NERVOUS SYSTEM (Includes About Eyes)Document16 pagesGCSE OCR GATEWAYBiology - YOUR SENSES AND NERVOUS SYSTEM (Includes About Eyes)m4a1_attiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Windows of KnowledgeDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Windows of Knowledgesajith kumar VariathNo ratings yet
- 5 Assessment and Diagnostic Procedures For Visual and Eye DisordersDocument5 pages5 Assessment and Diagnostic Procedures For Visual and Eye DisordersNica EnriquezNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument16 pagesCommunicationbitchass niggaNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear - 2019Document3 pagesEye and Ear - 2019Mr. RWord100% (1)
- 11 Human Eye and Colorful World NotesDocument9 pages11 Human Eye and Colorful World NotesvenkatNo ratings yet
- SENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Document5 pagesSENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Said SakerNo ratings yet
- HME 2209-wk - 2Document7 pagesHME 2209-wk - 2frank kipkoech bettNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument3 pagesThe Human EyeKajetano GraucosNo ratings yet
- Psychobiology Ch. 6 Vision Lecture NotesDocument23 pagesPsychobiology Ch. 6 Vision Lecture NotesGabriel CardozaNo ratings yet
- Pupil: Photopupillary ReflexDocument24 pagesPupil: Photopupillary ReflexAyra Nakrish Alvarez100% (3)
- Physics CH 10Document12 pagesPhysics CH 10Zeel GajeraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 3 - Lymphatic SystemDocument1 pageTutorial - 3 - Lymphatic SystemIlham Amni AmaninaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - 4 - Immune SystemDocument1 pageTutorial - 4 - Immune SystemIlham Amni AmaninaNo ratings yet
- FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE BIO320 CASE STUDY: LEPTOSPIROSIS IN MALAYSIADocument12 pagesFACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE BIO320 CASE STUDY: LEPTOSPIROSIS IN MALAYSIAIlham Amni AmaninaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Determination of Ethanoic Acid Content in VinegarDocument5 pagesExperiment 2 Determination of Ethanoic Acid Content in VinegarIlham Amni AmaninaNo ratings yet
- What Is PresbycusisDocument4 pagesWhat Is PresbycusisNisa UcilNo ratings yet
- Nervous System and Special Senses OverviewDocument90 pagesNervous System and Special Senses Overviewjayc lopezNo ratings yet
- Cholesteatoma Pic 2013 05Document90 pagesCholesteatoma Pic 2013 05Asiya ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Haematoma in Farm Animals and Its Management.Document7 pagesHaematoma in Farm Animals and Its Management.Pratap Kafle100% (3)
- HearingDocument15 pagesHearingdisha mangeNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Reading: I-Reading Comprehension TextDocument4 pagesUnit 3: Reading: I-Reading Comprehension Textabdelaziz hmidatNo ratings yet
- Only Residents AllowedDocument12 pagesOnly Residents AllowedKucluk KuclukNo ratings yet
- Our Sense OrganDocument58 pagesOur Sense OrganAlanie Grace Beron TrigoNo ratings yet
- Batson2017 OtosclerosisDocument6 pagesBatson2017 OtosclerosisnuhajazminNo ratings yet
- Bone Clones 2011 WebDocument132 pagesBone Clones 2011 WebToha PutraNo ratings yet
- ORAL REVALIDA AND COMPREHENSIVE EXAM! METABOLISM AND UPPER GI PROBLEMSDocument13 pagesORAL REVALIDA AND COMPREHENSIVE EXAM! METABOLISM AND UPPER GI PROBLEMSlovelove DayoNo ratings yet
- Mastoidectomy Various TypesDocument33 pagesMastoidectomy Various TypesDr. T. BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Newborn: Submitted To:-Submitted ByDocument17 pagesAssessment of Newborn: Submitted To:-Submitted BySAYMABANU100% (1)
- ENT Conditions: Hearing Loss, Balance Issues, Tinnitus & MoreDocument24 pagesENT Conditions: Hearing Loss, Balance Issues, Tinnitus & MoreBalakrishnan DoraisamiNo ratings yet
- Health 6 Quarter 1 Module1Document12 pagesHealth 6 Quarter 1 Module1Cindy EsperanzateNo ratings yet
- Eustachian Tube DysfunctionDocument34 pagesEustachian Tube DysfunctiondestiNo ratings yet
- Human Body (Eyewitness Workbooks) (Claire Watts)Document115 pagesHuman Body (Eyewitness Workbooks) (Claire Watts)Despoina AjlaNo ratings yet
- Human Perf. OXFORD PPLDocument31 pagesHuman Perf. OXFORD PPLStefania TamasNo ratings yet
- Human Factors in AviationDocument103 pagesHuman Factors in AviationJustus JosephNo ratings yet
- Academic rigor, journalistic flair: The physics, anatomy, and psychology behind choosing great headphonesDocument4 pagesAcademic rigor, journalistic flair: The physics, anatomy, and psychology behind choosing great headphonesLiar LiarNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 Audio Edtech 1Document9 pagesTopic 7 Audio Edtech 1Nicole ApitanNo ratings yet
- Ear MathesDocument66 pagesEar Mathes1lluminatt1No ratings yet
- The Listening Skill Between Theory and Practice in EFL Classrooms (By Benhamed Afrah)Document102 pagesThe Listening Skill Between Theory and Practice in EFL Classrooms (By Benhamed Afrah)Fariha FoufaNo ratings yet
- Ear Irrigation: Nurs 516 Emergency Nursing Care 1 PracticalDocument28 pagesEar Irrigation: Nurs 516 Emergency Nursing Care 1 PracticalMarianne Laylo100% (1)
- The Development of The Middle Ear Spaces and Their Surgical SignificanceDocument15 pagesThe Development of The Middle Ear Spaces and Their Surgical SignificanceDrTarek Mahmoud Abo Kammer100% (2)
- Light and Sound Revision ChecklistDocument8 pagesLight and Sound Revision ChecklisthafizNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Sound, Music, and HearingDocument5 pagesThe Physics of Sound, Music, and HearingSun Hee ParkNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Ears - StudentDocument8 pagesAssessment of The Ears - StudentSherinne Jane CariazoNo ratings yet
- Susanna Oroyan - Fantastic FiguresDocument122 pagesSusanna Oroyan - Fantastic Figuresladyghost100% (20)
- Cutaneous Sensory Deficit Following Post-Auricular IncisionDocument17 pagesCutaneous Sensory Deficit Following Post-Auricular IncisionAbhilash AntonyNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (76)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombFrom EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)