Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gas Laws: Gas Law Formula Constant Application/Example
Gas Laws: Gas Law Formula Constant Application/Example
Uploaded by
John Reigh Catipay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThe document summarizes five gas laws - Boyle's law, Charles' law, Gay-Lussac's law, the combined gas law, and the ideal gas law. For each law, it provides the formula, constant, and an example application or calculation involving changes in pressure, volume, temperature, moles, or some combination of these factors for an ideal gas. The document is intended to review the key gas laws and how they can be applied to different gas behavior scenarios.
Original Description:
Original Title
sda
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes five gas laws - Boyle's law, Charles' law, Gay-Lussac's law, the combined gas law, and the ideal gas law. For each law, it provides the formula, constant, and an example application or calculation involving changes in pressure, volume, temperature, moles, or some combination of these factors for an ideal gas. The document is intended to review the key gas laws and how they can be applied to different gas behavior scenarios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageGas Laws: Gas Law Formula Constant Application/Example
Gas Laws: Gas Law Formula Constant Application/Example
Uploaded by
John Reigh CatipayThe document summarizes five gas laws - Boyle's law, Charles' law, Gay-Lussac's law, the combined gas law, and the ideal gas law. For each law, it provides the formula, constant, and an example application or calculation involving changes in pressure, volume, temperature, moles, or some combination of these factors for an ideal gas. The document is intended to review the key gas laws and how they can be applied to different gas behavior scenarios.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
CATIPAY, JOHN REIGH D.
STEM – 1 CE
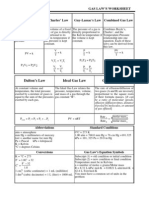
GAS LAWS
GAS LAW FORMULA CONSTANT APPLICATION/EXAMPLE
BOYLE'S LAW P1V1=P2V2 TEMPERATURE 2.30 L of a gas is at 725.0 mmHg
pressure.What is its volume at
standard pressure? Recall that
standard pressure is 760 mmHg.
CHARLES’ LAW V1/T1=V2/T2 PRESSURE A gas is collected and found to fill
4.73 L at 35.0°C. What will be its
volume at standard temperature
GAY-LUSSAC'S P1/T1=P2/T2 VOLUME 9.0 L of a gas is found to exert 83.0
LAW kPa at 35.0°C. What would be the
required temperature (in Celsius)
to change the pressure to
standard pressure
COMBINED P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 This type of combined gas law
GAS LAW problem is frequently
encountered, especially when
values are calculated at "standard
temperature and pressure" or STP
conditions. So let's say that 3.00 L
of a gas is collected at 35.0°C and
705.0 mmHg. What is the volume
at STP
IDEAL GAS LAW PV=nRT A sample of dry gas weighing
3.1134 grams is found to occupy
3.650 L at 22.0°C and 740.0
mmHg. How many moles of the
gas are present
You might also like
- 4.1 Open Channels - Uniform FlowDocument14 pages4.1 Open Channels - Uniform FlowJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Gay Lussac's LawDocument15 pagesGay Lussac's LawAngelyn BarzanaNo ratings yet
- Questions G1 and 2Document5 pagesQuestions G1 and 2John Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet GasesDocument6 pagesWorksheet GasesakladffjaNo ratings yet
- The Gas LawsDocument40 pagesThe Gas LawsLailanie PinedaNo ratings yet
- Gas Law WorksheetDocument3 pagesGas Law WorksheetRonaldo Manaoat50% (2)
- Physics II - EngineeringG PDFDocument110 pagesPhysics II - EngineeringG PDFRami JarrarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Discharge, Engergy and Head, Power and EfficiencyDocument14 pages1.1 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow - Discharge, Engergy and Head, Power and EfficiencyJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument9 pagesGas LawsGineNo ratings yet
- PP 1 Intellicare Orientation SM PDFDocument59 pagesPP 1 Intellicare Orientation SM PDFJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument41 pagesGas LawsGrey TapesNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument2 pagesGas LawsRaleen GenerNo ratings yet
- 4th QTR PPT Week 2Document7 pages4th QTR PPT Week 2RSTuzuNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument32 pagesGas LawssureshrockzNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - BEHAVIOR OF GASESDocument24 pagesUnit 8 - BEHAVIOR OF GASESsoileeartsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineering - Class 1: 1. GasesDocument9 pagesChemistry For Engineering - Class 1: 1. GasesMai Sơn DươngNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument22 pagesGas LawsMatsuri VirusNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - Behavior of GasesDocument24 pagesUnit 8 - Behavior of GasesJessie Montes JrNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Review Sheet Answers RenoDocument2 pagesGas Laws Review Sheet Answers RenoERICA BURNSNo ratings yet
- Lecture II Part 1Document19 pagesLecture II Part 1badeth.pagcaliwagan23No ratings yet
- Ideal & Combined Gas LawsDocument13 pagesIdeal & Combined Gas LawsJihan LuNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Jacques Charles (1746 - 1823)Document5 pagesGas Laws: Jacques Charles (1746 - 1823)cj lequinNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - Behavior of GasesDocument24 pagesUnit 8 - Behavior of GasesNenbon NatividadNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 - BEHAVIOR OF GASESDocument24 pagesUnit 8 - BEHAVIOR OF GASESMerrie Anne BagsicNo ratings yet
- ES III/ADGE 1 - Final - Module 10/week 10Document6 pagesES III/ADGE 1 - Final - Module 10/week 10Oct Toberey MendozaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument4 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryG-Ann N. BorjaNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas LawDocument1 pageIdeal Gas LawLarry BugaringNo ratings yet
- GLWS9Document6 pagesGLWS9Vince HernándezNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountDocument9 pagesGas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountArun KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document8 pagesChapter 2J.K HomerNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 q1 w7Document56 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 q1 w7NicoleNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument13 pagesChemical ReactionsAprilyn LaribaNo ratings yet
- Student CH 13 GasesDocument51 pagesStudent CH 13 GasesMichael MaglaqueNo ratings yet
- Paula Reviewer ThermoDocument14 pagesPaula Reviewer ThermoMICHELLE CAPISTRANONo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument10 pagesGas LawsJornalyn PalaganasNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Ideal GasesDocument4 pages2.2 Ideal GasesJoana MendoNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Chapter 10Document87 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 10Debalina DassNo ratings yet
- Properties of GasDocument12 pagesProperties of GasRaghaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Document47 pagesTopic 1 - Gas Laws (Part 1)Joshua LaBordeNo ratings yet
- Eeac 104 Handout 2Document1 pageEeac 104 Handout 2moclarit2212601No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry (Recovered)Document62 pagesPhysical Chemistry (Recovered)Ahmed Mohammed salaadNo ratings yet
- 1 - GasesDocument5 pages1 - GasesVon Joby RomeroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 KimiaDocument3 pagesChapter 5 KimiaelmishaenandaeNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument3 pagesGas LawsJsn JsnNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws PresentationDocument8 pagesGas Laws Presentationapi-305244853No ratings yet
- GasesDocument1 pageGasesAlgem Cris CrusisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2A Gas Laws 2Document22 pagesLesson 2A Gas Laws 2Desiree FranciscoNo ratings yet
- GasesDocument84 pagesGasesmdnishathasan141No ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument33 pagesGas LawspopiscanzNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Gas LawsDocument27 pagesLesson 2 - Gas LawsJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleDocument4 pagesBoyle's Law: Volume and Pressure: Temperature Must Be Expressed On The Absolute Temperature or Kelvin ScaleChris HeydenrychNo ratings yet
- Gay Lussac Combined Avogadro Ideal Gas Law ApplicationDocument28 pagesGay Lussac Combined Avogadro Ideal Gas Law ApplicationAlexandra Venice Ann M. PerezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1: Quarter 4: Module 4Document3 pagesChemistry 1: Quarter 4: Module 4Rain AlmsNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument64 pagesGas LawsALECXANDER COLLERANo ratings yet
- Gay Lussac's Law - Group1Document15 pagesGay Lussac's Law - Group1dandoycedrickjayNo ratings yet
- CH 11 GasesDocument67 pagesCH 11 Gasesman supermanNo ratings yet
- The Gas Laws Boyle's LawDocument4 pagesThe Gas Laws Boyle's LawFrancis Alfred DanaoNo ratings yet
- Properties of Gases: University of Zakho Collage of Education General Science DepartmentDocument16 pagesProperties of Gases: University of Zakho Collage of Education General Science DepartmentNihad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sept13Document57 pagesChapter 10 Sept13chandro57No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Gas LawsDocument55 pagesChapter 11 - Gas Lawsjim tannerNo ratings yet
- MELC G Ihi 43 50 GasesDocument54 pagesMELC G Ihi 43 50 GasesAmber MontesNo ratings yet
- Hand Out 4Document5 pagesHand Out 4Shawty YeshiNo ratings yet
- Gases and Gas LawsDocument49 pagesGases and Gas LawsArianne LaruscainNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The PhilippinesDocument7 pagesTechnological University of The PhilippinesJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 3Document36 pagesLecture No. 3John Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Techno Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesTechno Reflection PaperJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesTechnological University of The PhilippinesJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesTechnological University of The PhilippinesJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesTechnological University of The PhilippinesJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Plate No. 2 VolumeDocument4 pagesPlate No. 2 VolumeJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Polytechnic University of The Philippines College of Communications Department of Broadcast CommunicationDocument4 pagesPolytechnic University of The Philippines College of Communications Department of Broadcast CommunicationJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Course Title (Course Code) : Fluid Flow MeasurementDocument9 pagesCourse Title (Course Code) : Fluid Flow MeasurementJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Technological University of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesTechnological University of The PhilippinesJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment: LATENT HEAT: Q ML Q J Cal M KG L L L J KGDocument6 pagesLaboratory Experiment: LATENT HEAT: Q ML Q J Cal M KG L L L J KGJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Reading Comprehension PDFDocument1 pageAnswer Key Reading Comprehension PDFJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Application Permit: Waiver For CredentialDocument1 pageApplication Permit: Waiver For CredentialJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Background Check Form and Letter of ConsentDocument3 pagesBackground Check Form and Letter of ConsentJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- A Fund-Raising Cause in Support of Jeepney Drivers Who Lost Income Sources During The PandemicDocument9 pagesA Fund-Raising Cause in Support of Jeepney Drivers Who Lost Income Sources During The PandemicJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- A Fund-Raising Cause in Support of Jeepney Drivers Who Lost Income Sources During The PandemicDocument9 pagesA Fund-Raising Cause in Support of Jeepney Drivers Who Lost Income Sources During The PandemicJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- CATIPAY, John Reigh D. Assignment No. 2 Bsce - 3A 10/14/2020Document4 pagesCATIPAY, John Reigh D. Assignment No. 2 Bsce - 3A 10/14/2020John Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Plate Format PDFDocument2 pagesPlate Format PDFJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Plato Girls PDFDocument30 pagesPlato Girls PDFJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet