Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3 Resistance Guide
Uploaded by
Yakub Channel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views18 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter 3. Resistance
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views18 pagesChapter 3 Resistance Guide
Uploaded by
Yakub ChannelCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 18
Chapter 3.
RESISTANCE
• 3.1 Resistance and resistivity
• 3.2 Temperature coefficient of resistance
• 3.3 Resistor colour coding and ohmic values
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 1
3.1 Resistance and resistivity
The resistance of an electrical conductor depends on four factors,
these being:
(a) the length of the conductor,
(b) the cross-sectional area of the conductor,
(c) the type of material and (d) the temperature of the material
Resistivity varies with temperature and some typical values of
resistivities measured at about room temperature are given
below:
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 2
Good conductors of electricity have a low value of resistivity and
good insulators have a high value of resistivity.
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 3
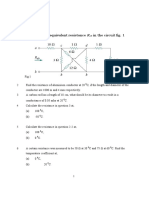
A piece of wire of cross-sectional area 2mm2 has a resistance
of 300. Find
(a) the resistance of a wire of the same length and material if the
cross-sectional area is 5mm2,
(b) The cross-sectional area of a wire of the same length and
material of resistance 750.
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 4
Determine the resistance of 1200m of copper cable having a
diameter of 12mm if the resistivity of copper is 1.7 X 10^-8 m.
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 5
Solution
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 6
3.2 Temperature coefficient of resistance
If the resistance of a material at 0°C is known the resistance at
any other temperature can be determined from,
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 7
Example: A coil of copper wire has a resistance of 100 when its
temperature is 0°C. Determine its resistance at 70°C if the temperature
coefficient of resistance of copper at 0°C is 0.0043/°C.
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 8
A coil of copper wire has a resistance of 10 at 20°C. If the temperature
coefficient of resistance of copper at 20°C is 0.004/°C determine the
resistance of the coil when the temperature rises to 100°C.
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 9
Example: Some copper wire has a resistance of 200 at 20°C. A current is
passed through the wire and the temperature rises to 90°C. Determine the
resistance of the wire at 90°C, correct to the nearest ohm, assuming that
the temperature coefficient of resistance is 0.004/°C at 0°C.
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 10
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 11
3.3 Resistor colour coding and ohmic values
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 12
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 13
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 14
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 15
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 16
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 17
1. Determine the colour coding for a 1M resistor having a tolerance of š10%
[brown-black-green-silver]
2. Determine the range of values expected for a resistor with colour coding: red-black-
greensilver [1.8M to 2.2M]
3. Determine the range of values expected for a resistor with colour coding: yellow-
blackorange-brown [39.6k to 40.4 k]
4. Determine the value of a resistor marked as
(a) R22G (b) 4K7F
*(a) 0.22 š 2% (b) 4.7 k š 1%+
5 Determine the letter and digit code for a resistor having a value of 100 k š 5%
[100 KJ]
6. Determine the letter and digit code for a resistor having a value of 6.8M š 20%
[6M8M]
Prepared by SURYA HARDI, PhD 18
You might also like
- Quiz For CircuitDocument3 pagesQuiz For CircuitGrace Panuelos OñateNo ratings yet
- Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesPractice ProblemsJayson Bryan MutucNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument39 pagesElectric CircuitsSoleil SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument33 pagesBasic ConceptsHNo ratings yet
- 2365 02 l2 202 Handout 7Document6 pages2365 02 l2 202 Handout 7dvm4yfptzmNo ratings yet
- 2 Resistance and Resistivity - 1Document9 pages2 Resistance and Resistivity - 1Genesis MenesesNo ratings yet
- Exercises ResistanceDocument5 pagesExercises ResistanceAldren IbarrondoNo ratings yet
- AP Resistance and ResistivityDocument4 pagesAP Resistance and ResistivityAdrian Humphrey PabloNo ratings yet
- 1 ResistanceDocument43 pages1 ResistanceSyu KurNo ratings yet
- 4 24573 360 PDFDocument3 pages4 24573 360 PDFrhap_0925060No ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles in DC CircuitsDocument25 pagesFundamental Principles in DC CircuitsGabriel Carl Alpuerto100% (1)
- Basic Ee Hw1Document2 pagesBasic Ee Hw1mon patrick pradoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document8 pagesChapter 3Jerome CansadoNo ratings yet
- Resistivity and Ohms Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesResistivity and Ohms Law WorksheetDavid BlakeNo ratings yet
- Selection of Spot Welding ElectrodesDocument2 pagesSelection of Spot Welding ElectrodesalenturskiNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 1 - Ee1 LecDocument27 pagesLecture No. 1 - Ee1 LecasapamoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Resistance: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument48 pagesChapter 3 - Resistance: Reference: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadMona SayedNo ratings yet
- FY7W04 Electrical Module 1 Lesson 6Document24 pagesFY7W04 Electrical Module 1 Lesson 6chudyaceNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document27 pagesQuestion 1Rammer PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Mesoviti Uzemljivac Schwarz PDFDocument10 pagesMesoviti Uzemljivac Schwarz PDFzdakonocevicNo ratings yet
- SMAW LessonDocument8 pagesSMAW LessonOJ DogplaceNo ratings yet
- It Depends Upon The Length of A ConductorDocument8 pagesIt Depends Upon The Length of A Conductorгульнур шахмановаNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument72 pagesResistanceParisDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Electrode Converted Into TextDocument14 pagesElectrode Converted Into TextNeha NimbarkNo ratings yet
- Es173 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesEs173 Tutorial 1steven ernestNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical CircuitsDocument6 pagesBasic Electrical CircuitsAllen Rhoe PuebloNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Problems Electrical CircuitsDocument2 pagesSupplementary Problems Electrical Circuitsmae50% (2)
- Current Electricity Assignment For JEE MAIN PDFDocument1 pageCurrent Electricity Assignment For JEE MAIN PDFMd IsfaqueNo ratings yet
- Chap3 ResistanceDocument40 pagesChap3 Resistancebree789No ratings yet
- AMIDON/Fair-Rite Ferrite InformationDocument48 pagesAMIDON/Fair-Rite Ferrite InformationskywroughtNo ratings yet
- 04 Temperature Resistance Effects Part 2 PDFDocument7 pages04 Temperature Resistance Effects Part 2 PDFMark Paul AñonuevoNo ratings yet
- Lab Resistivity 1. PurposeDocument2 pagesLab Resistivity 1. PurposeadylanNo ratings yet
- 14F3001X00 Welding Cable Wire Wisdom US enDocument2 pages14F3001X00 Welding Cable Wire Wisdom US enFelipe GustavoNo ratings yet
- Conductors Designed to Conform to Nominal AreasDocument12 pagesConductors Designed to Conform to Nominal AreasHashimi JuniNo ratings yet
- Copper Alloy (Bronze) and Bimetallic Power Connectors For S/S 150/20KvDocument10 pagesCopper Alloy (Bronze) and Bimetallic Power Connectors For S/S 150/20KvharrisvasNo ratings yet
- RESISTIVITY and CONDUCTIVITY of MaterialsDocument22 pagesRESISTIVITY and CONDUCTIVITY of Materialsbalweg mackyNo ratings yet
- ResistivityDocument19 pagesResistivityRoberta DalisayNo ratings yet
- ResistivityDocument20 pagesResistivityFebie Gail Pungtod ArenasNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Foundation Grounding ConsiderationsDocument28 pagesWind Turbine Foundation Grounding ConsiderationsDejanNo ratings yet
- PHY201 Physics II Review Problems Chapter 25 Current and ResistanceDocument5 pagesPHY201 Physics II Review Problems Chapter 25 Current and ResistanceNajmul Puda PappadamNo ratings yet
- Strain Gages (ME305)Document20 pagesStrain Gages (ME305)Ammar QaziNo ratings yet
- 1011 Chapter 3Document38 pages1011 Chapter 3Eman Sarmiento0% (1)
- CSWIP 3.1 Question With Answer and Explanation - Part 12Document9 pagesCSWIP 3.1 Question With Answer and Explanation - Part 12adel100% (3)
- Electrical Engineering MCQ Quiz on Color Codes, Ohm's Law, Resistors & CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectrical Engineering MCQ Quiz on Color Codes, Ohm's Law, Resistors & CircuitsHassan BilalNo ratings yet
- ResistanceDocument21 pagesResistanceOnii ChanNo ratings yet
- Resistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials: Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesResistivity of Electrical Conductor Materials: Standard Test Method ForAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- Resistance ThermometryDocument52 pagesResistance ThermometryRAJANo ratings yet
- Resistor Color CodesDocument14 pagesResistor Color CodesJeevan BasnyatNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Resistance VerifiedDocument28 pagesFactors Affecting Resistance VerifiedAyushi BishtNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature on Conductor ResistanceDocument29 pagesEffect of Temperature on Conductor ResistanceJM RaagasNo ratings yet
- Materials Science problems and conceptsDocument4 pagesMaterials Science problems and conceptsaoguNo ratings yet
- Creep and Creep Damage Assessment in P91 Weld JointsDocument12 pagesCreep and Creep Damage Assessment in P91 Weld JointsDeepakNo ratings yet
- BeeDocument22 pagesBeebiswajit7sarkarNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Practice ProblemsDocument26 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Practice ProblemsChris Thel May60% (5)
- ArthingDocument10 pagesArthingClémentNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"From EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 6, Slice 8 "Conduction, Electric"No ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred ExperimentsNo ratings yet
- The Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusFrom EverandThe Study of Elementary Electricity and Magnetism by Experiment: Containing Two Hundred Experiments Performed with Simple, Home-made ApparatusNo ratings yet
- Welding Craft Practice: Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding and Related StudiesFrom EverandWelding Craft Practice: Oxy-Acetylene Gas Welding and Related StudiesNo ratings yet
- Mitigating Energy Poverty: Mobilizing Climate Finance To Manage The Energy Trilemma in IndonesiaDocument18 pagesMitigating Energy Poverty: Mobilizing Climate Finance To Manage The Energy Trilemma in Indonesia조민기No ratings yet
- Soal Ujian Akhir Semester (Uas) Politeknik Kesehatan Medan Jurusan: Gizi Mata Kuliah: Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesSoal Ujian Akhir Semester (Uas) Politeknik Kesehatan Medan Jurusan: Gizi Mata Kuliah: Bahasa InggrisYakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsDocument29 pagesFundamentals of Electric CircuitsYakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- Materi 4 RL 2Document23 pagesMateri 4 RL 2Yakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9. Electromagnetism Induction - PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 9. Electromagnetism Induction - PDFYakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Electromagnetism: 8.1 Magnetic Field Due To An Electric CurrentDocument14 pagesChapter 8. Electromagnetism: 8.1 Magnetic Field Due To An Electric CurrentYakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Chemical ...Document13 pagesChapter 4. Chemical ...MImamNugrohoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5. Series and ParallelDocument13 pagesChapter 5. Series and ParallelYakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- 2119 2934 1 SMDocument15 pages2119 2934 1 SMVian Aditya SaputraNo ratings yet
- Studi Pengaruh Pembebanan Sebagai Dasar Scheduling Maintenance Untuk Meminimalisir Susut Umur Transformator 1 GI BlimbingDocument6 pagesStudi Pengaruh Pembebanan Sebagai Dasar Scheduling Maintenance Untuk Meminimalisir Susut Umur Transformator 1 GI BlimbingYakub ChannelNo ratings yet
- Banner Data Tables PDFDocument11 pagesBanner Data Tables PDFpotNo ratings yet
- 01 Experiment 1 - Familiarization of Components and InstrumentsDocument5 pages01 Experiment 1 - Familiarization of Components and InstrumentsNikita Mayee sahooNo ratings yet
- Lab # 3 Verifcation of CDR VDRDocument7 pagesLab # 3 Verifcation of CDR VDRKashif MujeebNo ratings yet
- Astm B267 07 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm B267 07 PDFCRISTIAN ANDRES MAYORGA CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Voltmeter AmperemeterDocument24 pagesVoltmeter Amperemeteryansenyang0% (1)
- EE8261 Electric Circuits Lab Manual EEE 1Document87 pagesEE8261 Electric Circuits Lab Manual EEE 1Bala Anderson0% (1)
- LM 334Document14 pagesLM 334Mai Van SyNo ratings yet
- Cabin Fan Controller ManualDocument18 pagesCabin Fan Controller ManualJohn DosherNo ratings yet
- 02 Datalink, J1939Document12 pages02 Datalink, J1939Ebied Yousif AlyNo ratings yet
- Electronics-Q2 M5Document27 pagesElectronics-Q2 M5Radleigh Vesarius RiegoNo ratings yet
- Tech Spec For NGR PDFDocument22 pagesTech Spec For NGR PDFnavneetNo ratings yet
- Led TV: Service ManualDocument32 pagesLed TV: Service ManualRuy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Applied Phy Lab ManualDocument109 pagesApplied Phy Lab Manualamirmehmood88No ratings yet
- Pioneer-VSX909RDS Service ManualDocument34 pagesPioneer-VSX909RDS Service Manualstephenstruk1No ratings yet
- Cell Phone Battery Flashlight DIY: Build a Bright LED Light Using Old Phone BatteriesDocument6 pagesCell Phone Battery Flashlight DIY: Build a Bright LED Light Using Old Phone Batteriesnita_alecsandruNo ratings yet
- Nominal Performance: Principal Dimensions - MMDocument1 pageNominal Performance: Principal Dimensions - MMمحمد صالحNo ratings yet
- E. v. Gray Analysis by William S. AlekDocument1 pageE. v. Gray Analysis by William S. Alekscribdsandu100% (1)
- Sharp Lc-60-70le745u C7450u Le845u C8470u Le847uDocument86 pagesSharp Lc-60-70le745u C7450u Le845u C8470u Le847uDan PrewittNo ratings yet
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 2Document17 pagesCurrent, Potential Difference & Resistance 2Juyeon NamNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Physics.soeDocument20 pagesLab Manual - Physics.soejhoyvanNo ratings yet
- 0185-1098-E 1V102 MA Tutorial LinMot DesignerDocument39 pages0185-1098-E 1V102 MA Tutorial LinMot DesignerTesfaye Utopia UtopiaNo ratings yet
- 10A Cu LM317Document6 pages10A Cu LM317Vali IgnatNo ratings yet
- Electronics RegularDocument169 pagesElectronics RegularNazeerNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of ElectricityDocument86 pagesFundamentals of ElectricityHersal fae Gerardo100% (1)
- 0-5 A, Single-Supply, 2 KV Isolated Current SensingDocument11 pages0-5 A, Single-Supply, 2 KV Isolated Current SensingjuanNo ratings yet
- JAR Part 66 Examination Mod 03Document126 pagesJAR Part 66 Examination Mod 03Shreyas PingeNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase Loco Item Review July 2020Document87 pages3-Phase Loco Item Review July 2020sumitshyamal100% (1)
- Carga Fantasma Bird 920-8251sDocument24 pagesCarga Fantasma Bird 920-8251sJorge AguilarNo ratings yet
- asset-v1-BerkeleyX+EE40LX+2T2015+type@asset+block@EE40LX PartsList Summer15 PDFDocument3 pagesasset-v1-BerkeleyX+EE40LX+2T2015+type@asset+block@EE40LX PartsList Summer15 PDFMuhammad HaroonNo ratings yet
- Jvs Manual JRD 011Document5 pagesJvs Manual JRD 011ashutosh20090% (1)