Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surge Tank Size and Cost Calculation: Virginia Falls
Uploaded by
psn_kylmOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surge Tank Size and Cost Calculation: Virginia Falls
Uploaded by
psn_kylmCopyright:
Available Formats
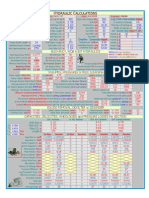
SURGE TANK SIZE AND COST CALCULATION
Enter data in blue cells only. Steel cost in cell E15
Virginia Falls
5 Flood level at dam, meters 457.00 Low supply level at dam, meters 454.00
6 Turbine rated head, m 140 Elevation at surge tank tee, meters 432.00
7 Design full load flow, m3/s 20.24 Upstream conduit length, meters 2100.00
8 Upstream conduit diameter, meters 3 Average Manning friction coefficient 0.011
9 Conduit velocity m/s 2.86 Tank diameter, meters 6.41
10 Elevation top of tank, meters 470.79 Elevation bottom of tank, meters 443.12
11 Tank height, top to bottom, meters 27.67 Tank volume, cubic meters 892
12 Steel weight in tank and legs, tonnes 58.917 Total height of tank, tee to roof, m 38.79
13 Cost of steel tank, millions of US$ 0.339 If in rock, total tank/ris. volume, m3 971
14 Rock excavation volume, allowing for a full concrete lining of tank and riser, m3 1323
15 Concrete lining volume, m3 351 Curved formwork area, m2 662
16 Conduit area, m2 7.07 Steel price $/kg. Erected 5.75
17 Acceleration n 0.01265 Deceleration n 0.01045
18 Accel. head loss, m 4.67 Decel. head loss, m 3.26
19 Acceleration c 0.569 Deceleration c 0.397
20 Tank area, F m2 25.19 Tank H/2 above tee. M 24.96
21 Acceleration Deceleration
22 N acc 29.74 N dec 20.76
23 K acc 45.97 K dec 19.69
24 y acc. = downsurge = m 5.71 Y dec. = upsurge = m 16.55
Ref: "Estimating weight of steel surge tank" HRW Vol.6, # 4, Sept. 1998, pages 26 - 29.
Ref: Hydroelectric Handbook. 2nd. Ed. 1950. W. P. Creager & J. D. Justin, page 734 - 743.
Note - this is a preliminary program, suitable for sizing and costing a restricted orifice surge tank.
For a simple tank, with no internal riser and no restricted orifice, increase the diameter by 25%
and keep the same high and low water levels. In such a case, the mimimum thickness of steel
plate in the tank wall, in millimeters = 21.0 Calculate steel weight manually. A simple
tank will be more expensive than a restricted orifice tank due to the larger diameter.
You might also like
- Pipeline Design for Water EngineersFrom EverandPipeline Design for Water EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Surge AnlysisDocument5 pagesSurge AnlysisnaveenaeeNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Simple Surge TankDocument7 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Simple Surge Tankbobmarley20161934No ratings yet
- Economic Surge Tank DesignDocument6 pagesEconomic Surge Tank DesigncsimsekNo ratings yet
- Trend of Surge DesignDocument34 pagesTrend of Surge DesignBalkrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Surge Calculation 1 - 373505Document7 pagesSurge Calculation 1 - 373505J A S JASNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Hydraulics Modification ReqdDocument6 pagesPipeline Hydraulics Modification ReqdchemtahirNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer Report (With Vacuum Air Valves)Document11 pagesWater Hammer Report (With Vacuum Air Valves)Ah Leng LauNo ratings yet
- Surge Shaft Design (First Edition) : SGI October 2005Document61 pagesSurge Shaft Design (First Edition) : SGI October 2005octatheweel100% (1)
- Mixing Time Jet MixerDocument9 pagesMixing Time Jet MixerLTE002No ratings yet
- CW Pump Intake Forebay Design As Per HIS 9.8.2Document4 pagesCW Pump Intake Forebay Design As Per HIS 9.8.2Amit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Grade LineDocument0 pagesHydraulic Grade LinemuazeemKNo ratings yet
- Selection and Sizing of Air Release Valves PDFDocument22 pagesSelection and Sizing of Air Release Valves PDFFredie Unabia100% (1)
- Water Hammer. Water and Slurry HammerDocument49 pagesWater Hammer. Water and Slurry HammerFari NazariNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Surge TankDocument7 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Surge TankUchirai Dede100% (3)
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Gate Valve (Through Conduit)Document25 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Gate Valve (Through Conduit)Eng-CalculationsNo ratings yet
- Water HamDocument226 pagesWater Hamp_ignatiusNo ratings yet
- Penstock CaalculationDocument3 pagesPenstock CaalculationGertjan DuniceriNo ratings yet
- Surge Shaft - Design ConceptDocument65 pagesSurge Shaft - Design Conceptpankaj100% (2)
- Surge AnalysisDocument2 pagesSurge AnalysisPraveen ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer: Design CriteriaDocument3 pagesWater Hammer: Design CriteriamazharimechNo ratings yet
- Surge TankDocument26 pagesSurge TankAmar WadoodNo ratings yet
- Surge AnalysisDocument35 pagesSurge AnalysisAh Leng Lau50% (2)
- Pump Station Design ManualDocument35 pagesPump Station Design ManualFrancis MitchellNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer. Examples Tyler - PehmcoDocument12 pagesWater Hammer. Examples Tyler - PehmcoZwingerfeltNo ratings yet
- Rising Main Design SheetDocument9 pagesRising Main Design SheetJaspal SinghNo ratings yet
- Computation of Penstock Pipe For Pinacanauan, Scheme BDocument6 pagesComputation of Penstock Pipe For Pinacanauan, Scheme BAziz ul HakeemNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Height of The Siphon SystemDocument2 pagesCalculation of Height of The Siphon SystemPhyu Mar Thein Kyaw100% (1)
- Surge Tank Design Calculation & AnalysisDocument9 pagesSurge Tank Design Calculation & AnalysisChris Angelo G Caadlawon0% (1)
- Anchor Block Stability AnalysisDocument9 pagesAnchor Block Stability AnalysisPrayas Subedi100% (1)
- Water Hammer. Water and Slurry HammerDocument57 pagesWater Hammer. Water and Slurry HammerDdNak Ydk SubangNo ratings yet
- Thrust Block CalculationDocument12 pagesThrust Block CalculationMegatech Engineering Consultants100% (1)
- Thrust Block CalcsDocument3 pagesThrust Block CalcsThiruvasagam Subramanian0% (1)
- Water Hammer Pressure/ Surge Pressure Calculation : Developed by Engr. Abiodun AsadeDocument2 pagesWater Hammer Pressure/ Surge Pressure Calculation : Developed by Engr. Abiodun Asadecoolsummer1112143100% (1)
- Tyrolean Weir PDFDocument148 pagesTyrolean Weir PDFRex ImperialNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer: Values For CalculationDocument3 pagesWater Hammer: Values For CalculationEng-CalculationsNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Buried Composite Fiberglass PipelineDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Buried Composite Fiberglass PipelineVinh Do ThanhNo ratings yet
- Air Release Valve Selection & SizingDocument1 pageAir Release Valve Selection & SizingMahmoud Eldusoky100% (1)
- Water HammerDocument3 pagesWater Hammerكرم عمروNo ratings yet
- Head Loss CalculationDocument7 pagesHead Loss CalculationCuong VuNo ratings yet
- Hammer Quick Lessons PDFDocument19 pagesHammer Quick Lessons PDFsebasfarsaNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer Pressure CalculatorDocument1 pageWater Hammer Pressure CalculatormohamedfirozNo ratings yet
- Water Hammer in Pumped Sewer MainsDocument45 pagesWater Hammer in Pumped Sewer MainsManikandanNo ratings yet
- Head Loss Calculation For HydropowerDocument9 pagesHead Loss Calculation For HydropowerBalkrishna Pangeni0% (1)
- Penstock Thickness CaclDocument44 pagesPenstock Thickness CaclAnonymous sfkedkym100% (1)
- Labyrinth Weir DesignDocument15 pagesLabyrinth Weir Designchutton681No ratings yet
- Surge Tank DesignDocument15 pagesSurge Tank Designdharanimadala100% (3)
- Closed Conduit Flow ExptDocument99 pagesClosed Conduit Flow ExptStephanie Anne FortinNo ratings yet
- PenstockDocument7 pagesPenstockmodest_dhuNo ratings yet
- Crane UbDocument20 pagesCrane UbBobor Emmanuel OfovweNo ratings yet
- Hfo Service Tank - ht003 Data Sheet r1 PDFDocument4 pagesHfo Service Tank - ht003 Data Sheet r1 PDFsocomenin2013No ratings yet
- A V H G: Calculation For Shell Thickness For Ms Pipeline - Clear Water Pumping Jayal To KERAP 1500 ØDocument1 pageA V H G: Calculation For Shell Thickness For Ms Pipeline - Clear Water Pumping Jayal To KERAP 1500 Øabhishek5810No ratings yet
- 6000m3 VST DesignDocument17 pages6000m3 VST Designjohney2No ratings yet
- Water Tank ReportDocument50 pagesWater Tank ReportDavin AzharNo ratings yet
- 1new PenstockDocument23 pages1new PenstockEr Harsh Mahato100% (1)
- Equalization TankDocument13 pagesEqualization Tanknataliepoison8917No ratings yet
- Watertank 3Document38 pagesWatertank 3api-297121029No ratings yet
- API 650 Design TanksDocument34 pagesAPI 650 Design TanksSyedZainAli100% (13)
- Bolt Tension & Torque CalculationDocument1 pageBolt Tension & Torque CalculationhuangjlNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis PDFDocument6 pagesVibration Analysis PDFBipin RohitNo ratings yet
- Bolt Torques For ASME B16.5 Flanges With Sheet Gaskets To ASME B16.21Document30 pagesBolt Torques For ASME B16.5 Flanges With Sheet Gaskets To ASME B16.21huangjlNo ratings yet
- Estimating TemplateDocument16 pagesEstimating TemplatehuangjlNo ratings yet
- Fuel Pump HP CalculationsDocument8 pagesFuel Pump HP CalculationshuangjlNo ratings yet
- GB5782 外形尺寸及重量表 六角头 -C级 GB5780Document2 pagesGB5782 外形尺寸及重量表 六角头 -C级 GB5780huangjlNo ratings yet
- Fuel Pump HP CalculationsDocument8 pagesFuel Pump HP CalculationshuangjlNo ratings yet
- Tank 2bDocument1 pageTank 2bMukeshSharmaNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument1 pageHeat TransferhuangjlNo ratings yet
- NPSH CalculationDocument1 pageNPSH CalculationhuangjlNo ratings yet
- Ydraulic Alculations: B W B HDocument1 pageYdraulic Alculations: B W B HhuangjlNo ratings yet
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument19 pagesShell and Tube Heat Exchangerhuangjl33% (3)
- 吊耳计算Document4 pages吊耳计算huangjlNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet For Cooling Tower PM Emissions Calculations (2012!03!09 Version)Document1 pageSpreadsheet For Cooling Tower PM Emissions Calculations (2012!03!09 Version)huangjlNo ratings yet
- Pump CalculationDocument4 pagesPump CalculationhuangjlNo ratings yet
- insulation cal (绝热厚度计算)Document4 pagesinsulation cal (绝热厚度计算)huangjlNo ratings yet
- Padeye CalDocument6 pagesPadeye Calhuangjl100% (1)
- External Pressure DesignDocument395 pagesExternal Pressure DesignrsubramaniNo ratings yet
- Tanks Hell Min ThicknessDocument1 pageTanks Hell Min ThicknesshuangjlNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Data SheetDocument1 pageAir Cooled Data SheethuangjlNo ratings yet
- 吊耳计算Document4 pages吊耳计算huangjlNo ratings yet