Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.2
Uploaded by
Dev KhattriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.2
Uploaded by
Dev KhattriCopyright:
Available Formats
RAY OPTICS: REFRACTION DPP 2
SINGLE CORRECT ANSWR TYPE
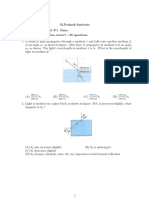
1. One side of a glass slab is silvered as shown. A ray of light is incident on the other side at angle
of incidence i = 45°. Refractive index of glass is given as 1.5. the deviation of the ray of light
from its initial path when it comes out of the slab is
a.90° b. 180° c. 120° d. 45°
2. When the rectangular metal tank is filled to the top with an unknown liquid, as observer with
eyes level with the top of the tank can just see the corner E; a ray that refracts towards the
observer at the top surface of the liquid is shown. The refractive index of the liquid will be
a.1.2 b. 1.4 c. 1.6 d. 1.9
3. A transparent cube of 15 cm edge contains a small air bubble. Its apparent depth when
viewed through one face is 6 cm and when viewed through the opposite face is 4 cm. Then
the refractive index of the material of the cube is
a.2.0 b. 2.5 c. 1.6 d. 1.5
4. A plane mirror is place at the bottom of the tank containing a liquid of refractive index μ. P is a
small object at a height h above the mirror. An observer O, vertically above P outside the liquid,
sees P and its image in the mirror. The apparent distance between these two will be
2ℎ 2ℎ 1
a.2μh b. c. 𝜇−1 d. h(1 + 𝜇)
𝜇
5. One face of a rectangular glass plate 6 cm thick is silvered. An object held 8 cm in front of the
first face forms an image 12 cm behind the silvered face. The refractive index of the glass is
a.0.4 b. 0.8 c. 1.2 d. 1.6
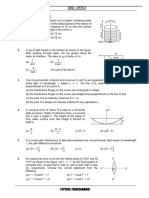
6. A concave mirror is placed at the bottom of an empty tank with face upwards and axis vertical. When sunlight falls
4
normally on the mirror, it is focussed at distance of 32 cm from the mirror. If the tank is filled with water (𝜇 = 3)
up to a height of 20 cm, then the sunlight will now get focussed at
a. 16 cm above water level b. 9 cm above water level
c. 24 cm below water level d. 9 cm below water level
7. A slab of glass, of thickness 6 cm and refractive index 1.5, is place in front of a concave mirror, the faces of the
slab being perpendicular to the principal axis of the mirror. If the radius of curvature of the mirror is 40 cm and the
reflected image coincides with the object, then the distance of the object from the mirror is
a. 30 cm b. 22 cm c. 42 cm d. 28 cm
8. A ray of light travels from an optically denser to rarer medium. The critical angle for the two media is C. the
maximum possible deviation of the ray will be
𝜋
a. ( 2 − 𝐶) b. 2C c. π – 2 C d. π – C
9. A point source of light S is placed at the bottom of a vessel containing a liquid of refractive
index 5/3. A person is viewing the source from above the surface. There is an opaque disc D of
radius 1 cm floating on the surface of the liquid. The centre of the disc lies vertically above the
source S. The liquid from the vessel is gradually drained out through a tap. The maximum
height of the liquid for which the source cannot be seen at all from the above is
a.1.50 cm b.1.64 cm c. 1.33 d. 1.86 cm
10. Light enters at an angle of incidence in a transparent rod of refractive index n. For what value of the refractive
index of the material of the rod the light once entered into it will not leave it through its lateral face whatsoever be
the value of angle of incidence
a. n > √2 b. n = 1 c. n = 1.1 d. n = 1.3
ANISH SIR & TEAM LUCKNOW-ASHOK MARG - 9919495931
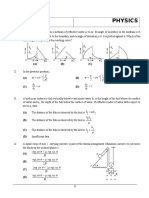
11. An optical fibre consists of core of μ1 surrounded by a cladding of by a cladding of
μ2 < μ1. A beam of light enters from air at an angle α with axis of fibre. The highest α
for which ray can be travelled through fibre is
a. cos – 1 √𝜇22 − 𝜇12 b. sin– 1 √𝜇12 − 𝜇22
c. tan – 1 √𝜇12 − 𝜇22 d. sec – 1 √𝜇22 − 𝜇12
12. A rod of glass (μ = 1.5) and of square cross section is bent into the shape shown in the
figure. A parallel beam of light falls on the plane flat surface A as shown in the figure. If d
𝑑
is the width of a side and R is the radius of circular arc then for what maximum value of 𝑅
light entering the glass slab through surface A emerges from the glass through B
a.1.5 b. 0.5 c. 1.3 d. None of these
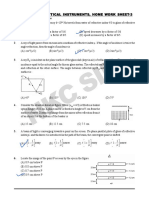
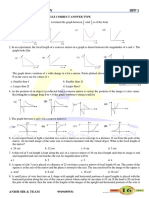
13. A ray of light travels from a medium of refractive index μ to air. Its angle of incidence in the medium is i,
measured from the normal to the boundary, and its angle of deviation is δ. δ is plotted against i ,which of the
following best represents the resulting curve
14. The apparent depth of water in cylindrical water tank of diameter 2R cm is reducing at the rate of x cm/minute
when water is being drained out at a constant rate. The amount of water drained in c.c. per minute is (n 1 = refractive
index of air, n2 = refractive index of water)
a.x π R2n1/n2 b. xπ R2n2/n1 c. 2π R n1 /n2 d. πR
MULTIPLE CORRECT ANSWERS TYPE
15. When light is incident on a medium at angle i and refracted into a second medium at an angle r, the graph of
sin i vs. sin r is as shown in the graph. From this, one can conclude that
a. velocity of light in the second medium is 1.73 times the velocity of light in the I medium
b. velocity of light in the I medium is 1.73 time the velocity in the II medium
1
c. the critical angle for the two media is given by sin 𝑖𝑐 =
√3
1
d. sin ic = 2
Answers key
Single correct answer type
1.a 2.a 3.d 4.b 5.c 6. b 7. c 8. c
9. c 10. a 11.b 12. B 13. a 14. b
Multiple correct answers type 15.(b, c)
ANISH SIR & TEAM LUCKNOW-ASHOK MARG - 9919495931
You might also like
- CBSE Class 10 Physics MCQs-All ChaptersDocument25 pagesCBSE Class 10 Physics MCQs-All ChaptersSiddharth Makkar100% (2)
- Summative Test in Grade-8Document5 pagesSummative Test in Grade-8ELVIS DOMINGO100% (1)
- Becke Line TestDocument1 pageBecke Line TestwessilissaNo ratings yet
- DPP-18 Geometrical Optics (QB) PDFDocument6 pagesDPP-18 Geometrical Optics (QB) PDFHarshit WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- OPtics Notes IITDocument18 pagesOPtics Notes IITMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- RAY OPTICS REFRACTION CURVE SURFACEDocument2 pagesRAY OPTICS REFRACTION CURVE SURFACEDev KhattriNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceDocument20 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceVivaan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 02 ExerciseDocument45 pages02 ExercisesocooltrishamNo ratings yet
- MCQ on Light Refraction and OpticsDocument20 pagesMCQ on Light Refraction and OpticsPritha KhannaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument14 pagesReviewerHeidi de LeonNo ratings yet
- ENGG1310, 2020-2021 Second Term Assignment 4 (Due Date: 10 Apr 2021) Answer All Questions. Show All Steps of Your Derivations and ReasoningDocument4 pagesENGG1310, 2020-2021 Second Term Assignment 4 (Due Date: 10 Apr 2021) Answer All Questions. Show All Steps of Your Derivations and Reasoningkant734No ratings yet
- College Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Test BankDocument20 pagesCollege Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Test Bankpaullanb7nch100% (32)
- Ebook College Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2Nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument41 pagesEbook College Physics Reasoning and Relationships 2Nd Edition Nicholas Giordano Test Bank Full Chapter PDFStevenMillersqpe100% (11)
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument8 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction GuideDocument68 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction GuideDzaky Zakiyal FawwazNo ratings yet
- IMP Geometrical - OpticsDocument24 pagesIMP Geometrical - OpticsPhantom1699No ratings yet
- Ray Optics Entrance Questions HannDocument4 pagesRay Optics Entrance Questions HannPHYSCO BOT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Optics RepDocument29 pagesOptics RepNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- X 2 O4 Z 5 A 1 V8 RF Je Ox 7 WSXD 0 OLpkmt N7 VC Ut AFcg SMDocument23 pagesX 2 O4 Z 5 A 1 V8 RF Je Ox 7 WSXD 0 OLpkmt N7 VC Ut AFcg SMdiscordewrNo ratings yet
- Optics Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesOptics Reflection and Refractionkabir ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Test: Reflection and RefractionDocument8 pagesTest: Reflection and RefractionRabia MehraNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssignmentDocument20 pagesRay Optics AssignmentApex Institute100% (1)
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument4 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- SANKALP - PsdfHASE VII - GO - 4Document5 pagesSANKALP - PsdfHASE VII - GO - 4Unfortunate GamerNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-3: Refraction From Plane Surface 1Document2 pagesRay Optics & Optical Instruments, Home Work Sheet-3: Refraction From Plane Surface 1Abhishek jainNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (In Reflection)Document13 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (In Reflection)Davinder SinghNo ratings yet
- RANKUP NEET (2019) DAY -1 (DPP) Geometrical Optics and Stoichiometry QuestionsDocument32 pagesRANKUP NEET (2019) DAY -1 (DPP) Geometrical Optics and Stoichiometry QuestionsYash bhartiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesWorksheet Ray OpticsYug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet 2426 Final ExamDocument19 pagesReview Sheet 2426 Final ExamperezromNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of Light MCQ & QuestionsDocument5 pagesReflection and Refraction of Light MCQ & Questionsajithrailway100% (1)
- Ray Optics Critical ThinkingDocument9 pagesRay Optics Critical Thinkingvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- Phy 1Document18 pagesPhy 1Garlapati Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice Questions I: Exemplar Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 9-Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsMohd SaquibNo ratings yet
- HW14-Light - 1 (学生版) - 021527Document14 pagesHW14-Light - 1 (学生版) - 021527Jun WuNo ratings yet
- Optics SheetDocument6 pagesOptics SheetDarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- OPTICS-05 - Objective UnSolvedDocument6 pagesOPTICS-05 - Objective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Learning Physics Through Simple Experiments: Quiz 1 (B)Document8 pagesLearning Physics Through Simple Experiments: Quiz 1 (B)TobiramaNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Conceptual QuestionsDocument16 pagesHapter: Conceptual QuestionsadelNo ratings yet
- Optics MCQ on Mirrors, Lenses and RefractionDocument5 pagesOptics MCQ on Mirrors, Lenses and RefractionAbhishek jainNo ratings yet
- MCQ Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesMCQ Ray OpticsDikshant SharmaNo ratings yet
- 50Q - Ray OpticsDocument10 pages50Q - Ray Opticskabir singhNo ratings yet
- Class 12Document6 pagesClass 12Sanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Optics AssignmentDocument9 pagesOptics AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- Refraction by AmanDocument24 pagesRefraction by Amanamanyadav885588No ratings yet
- Optics Mcq1Document7 pagesOptics Mcq1Manash SinghaNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document34 pagesCH 9Chetan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics QuestionsDocument3 pagesRay Optics QuestionsBAAP ka papaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics 1Document10 pagesGeometrical Optics 1S Prasad Shiva PulagamNo ratings yet
- WS - L2 - Diff - 12 - RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTSDocument3 pagesWS - L2 - Diff - 12 - RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTSSoul- HarryNo ratings yet
- Self Evalution Test-OpticsDocument5 pagesSelf Evalution Test-OpticsBHAAJI0001No ratings yet
- Ray Optics WSDocument7 pagesRay Optics WSYASHNo ratings yet
- Optics 27 YearsDocument15 pagesOptics 27 YearssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics ResonanceDocument8 pagesGeometrical Optics ResonanceArush Nagpal50% (2)
- Half Yearly Revision AssignmentDocument28 pagesHalf Yearly Revision AssignmentSidra QueenNo ratings yet
- LightsDocument4 pagesLightsDaniel GutierrezNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Document12 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- 5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionDocument51 pages5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionAnna Latifah CammryNo ratings yet
- Group Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkDocument5 pagesGroup Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkMadhvi ShardaNo ratings yet
- ExerciseDocument26 pagesExerciseRiyasat AnsariNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1Document2 pagesAssignment: 1Dev KhattriNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 3Document2 pagesAssignment: 3Dev KhattriNo ratings yet
- Assignment: 1Document2 pagesAssignment: 1Dev KhattriNo ratings yet
- RAY OPTICS REFLECTION GRAPHSDocument2 pagesRAY OPTICS REFLECTION GRAPHSDev KhattriNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Maths Lecture Plan and ScheduleDocument1 pageClass 12 Maths Lecture Plan and ScheduleDev KhattriNo ratings yet
- American International University-Bangladesh (Aiub) : Refractive Index of Prism Using A SpectrometerDocument11 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh (Aiub) : Refractive Index of Prism Using A SpectrometerShoaib Khan100% (2)
- QEE Review: Day 3: Chemistry PhysicsDocument48 pagesQEE Review: Day 3: Chemistry PhysicskangkongNo ratings yet
- (Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Physical Science (Phsc-112) - Grade 11 Week 11-20Document12 pages(Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Physical Science (Phsc-112) - Grade 11 Week 11-20James LazaroNo ratings yet
- Refractive Index Physics LabDocument6 pagesRefractive Index Physics LabAaliyah SeniorNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson PlanDocument22 pagesPhysics Form 5 Yearly Lesson PlanMohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- Cambridge Secondary Two Science: Chapter 12: LightDocument21 pagesCambridge Secondary Two Science: Chapter 12: LightarenestarNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 LightDocument165 pagesUnit 6 LightBlop100% (1)
- Light PDFDocument76 pagesLight PDFimposter131No ratings yet
- First Formal ReportDocument15 pagesFirst Formal ReportNana JilNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: RefractionDocument8 pagesStudent Exploration: RefractionJULISSA ROBLEDONo ratings yet
- Aakash FTS 12A (Only Eng)Document17 pagesAakash FTS 12A (Only Eng)evosgovind054No ratings yet
- 2.behaviour of SoundDocument45 pages2.behaviour of SoundSaransh ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- TWI UT Training Question Bank UltrasonicDocument85 pagesTWI UT Training Question Bank UltrasonicENOD CONTROL E INSPECCION S.A.C.No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document52 pagesChapter 11Mike JingNo ratings yet
- Standard-12 Science English Medium SANKALYA PAPERSET Download App For Best ResultsDocument31 pagesStandard-12 Science English Medium SANKALYA PAPERSET Download App For Best ResultsGaming CoreNo ratings yet
- Properties of Water WavesDocument22 pagesProperties of Water WavesEdgardo Leysa100% (1)
- EDMIDocument8 pagesEDMIMus'ab UsmanNo ratings yet
- 3B.Wave Optics (225-239)Document15 pages3B.Wave Optics (225-239)Rock656 RgNo ratings yet
- R.T.-1 P-08-05-2011 Paper-1 12th (ABCD) (English) Code-B WADocument12 pagesR.T.-1 P-08-05-2011 Paper-1 12th (ABCD) (English) Code-B WASushmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Presidium Refractive Index Meter II Reference ChartDocument6 pagesPresidium Refractive Index Meter II Reference ChartGems N Jewels PakistanNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion PDFDocument23 pagesWave Motion PDFFRANCES VISAYA100% (1)
- Fiber Optics GlossaryDocument164 pagesFiber Optics GlossarysbsfhlNo ratings yet
- Optical Phenomena RESEARCHDocument3 pagesOptical Phenomena RESEARCHMeganLeigh10% (1)
- Dispersion and SpectraDocument6 pagesDispersion and SpectrathinkiitNo ratings yet
- Module 2 QuestionsDocument49 pagesModule 2 QuestionsZain Hasan100% (1)
- SSLC Science Exam Prep: Key Questions on ElectricityDocument80 pagesSSLC Science Exam Prep: Key Questions on ElectricitySriNo ratings yet
- LTC Curvas en OriginDocument15 pagesLTC Curvas en OriginDiego CorreaNo ratings yet
- Diamond Design Marcel Tolkowsky 1919Document116 pagesDiamond Design Marcel Tolkowsky 1919Jorge Andres Glueck DazaNo ratings yet