Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G Transport (Plants I)
G Transport (Plants I)
Uploaded by
mjCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
G Transport (Plants I)
G Transport (Plants I)
Uploaded by
mjCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
1. The movement of water through xylem vessels is affected by external factors.
A decrease in which external factor would result in an increase in water movement?
A atmospheric humidity B external temperature C light intensity D wind velocity
2. The diagram shows the water potential (ψ) in some plant cells and in their environment.
Which statement describes the movement of water between these cells and between them and
their environment?
A All three cells are turgid, so no water moves.
B Water moves from cell 1, cell 3 and the environment into cell 2.
C Water moves from cell 3 to the environment, and from the environment to cell 1.
D Water moves from the environment into cells 1, 2 and 3.
3. Which statement describes the movement of water between these cells and between them
and their environment?
A All three cells are turgid, so no water moves.
B Water moves from cell 1, cell 3 and the environment into cell 2.
C Water moves from cell 3 to the environment, and from the environment to cell 1.
D Water moves from the environment into cells 1, 2 and 3.
4. What is the main function of a companion cell in mature phloem tissue?
A providing cytoplasmic contact with the sieve tube for loading
B providing structural support for the sieve tube element
C providing the nucleus for cell division in the phloem
D providing the source of assimilates for storage
5. The diagram shows a model which can be used to demonstrate mass flow.
X and Y are filled with sucrose solutions of different concentration, causing water to move in or
out of X and Y by osmosis or as a result of hydrostatic pressure. Sucrose solution then moves
through the tube T joining X and Y.
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
2 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
Which description of this is correct?
6. The graph shows the relationship between the loss of water vapour through stomata and an
environmental factor.
What is the environmental factor?
A air temperature
B atmospheric humidity
C light intensity
D wind velocity
7. The diagram shows a longitudinal section through transport tissue in a plant stem.
What are the names of the structure labelled X and the tissue in which it is found?
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
3 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
8. In which combination of environmental conditions are the stomata of a plant most likely to
close?
9. A water potential gradient causes water to move through xylem.
Which process is mainly responsible for this water potential gradient?
A active transport B osmosis C root pressure D transpiration
10. Which combination of features is characteristic of phloem sieve tubes?
11. A region of a stem of a plant is heated to kill the cells in the living vascular tissues. How will
this treatment affect the transport between roots and leaves via xylem and phloem?
12. Some soil-borne fungi cause wilting in crop plants by growing within the xylem vessels.
Which process will be directly affected by these fungi?
A conduction in the apoplast B development of root pressure
C stomatal movement D uptake of water by root hairs
13. The diagram shows some adjacent cells from the root of a plant. Which is the symplast
pathway of water movement?
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
4 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
14. Which organelles occur in large numbers in companion cells in phloem?
A chloroplasts B lysosomes C mitochondria D starch grains
15. A water potential gradient causes water to move through xylem.
Which process is mainly responsible for this water potential gradient?
A capillarity B osmosis C translocation D transpiration
16. During transpiration, what is the site of evaporation of water in the leaves?
A air spaces B mesophyll cell walls C stomata D walls of xylem vessels
17. The diagram represents the phloem pathway, with adjacent cells, from leaf to root in a plant.
Which process is occurring between 1 to 2 and what is the effect on the water potential at 2?
18. The diagram represents a transverse section through a part of the root of a plant.
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
5 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
Which values of water potential (kPa) in the xylem and soil water help to explain why water
passes from the soil into the xylem across the cortex?
19. Translocation in plants moves sucrose from sources to sinks. Which of the following can be
a source and which a sink?
20. What occurs in the apoplast and symplast pathways?
21. In an animal cell, which process is dependent upon cell surface area and which process is
dependent upon cell volume?
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
6 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
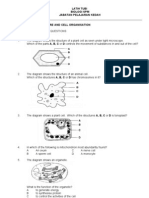
22. The diagrams show transverse sections of parts of a plant.
In the cross sections, what do 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 represent?
23. Land flooded by the sea is not suitable for growing plants long after the salty flood water has
drained away. The diagram represents a transverse section through a part of the root of a
plant.
Which values of water potential (kPa) in the xylem and soil water help to explain why the land
flooded with salty water is unsuitable for growth of plants?
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
7 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
Q1. Fig. 4.1 shows transverse sections of a root and a stem.
(a) (i) Shade in an area in the transverse section of the root where there are cells
specialised for the transport of water. [1]
(ii) Shade in an area in the transverse section of the stem where there are cells
specialised for the transport of sucrose. [1]
(b) Suggest why the vascular bundles in the stem are situated towards the outside.
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[1]
(c) Describe the process by which water passes from the soil into the root hairs.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
(d) Explain how water passes from the stem to the air surrounding a leaf.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
8 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
......................................................................................................................................[4]
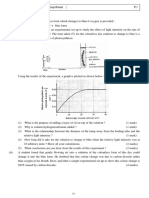
Q2. Fig. 3.1 shows a potometer that is used for measuring rates of water uptake by leafy
shoots.
A student used the potometer shown in Fig. 3.1 to investigate the rate of water uptake of a leafy
shoot under six different sets of conditions. The student changed two environmental conditions
around the plant:
• temperature
•wind speed.
For each experiment, the apparatus was left in the conditions until the rate of water uptake by
the leafy shoot became constant. The student took several measurements during each
experiment and calculated the mean rate of movement of the gas bubble. The results are
recorded in Table 3.1.
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
9 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
(a) Using the data in Table 3.1, describe and explain the effect of the two conditions that the
student changed during the investigation on the rate of water uptake.
temperature ......................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
wind speed . ......................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[4]
The rate of water movement up the leafy shoot was measured before it was cut from the plant.
The rate was found to be less than the rate of water uptake from the photometer when kept in
the same temperature and windspeed conditions.
(b) Suggest why the rate of water movement in an intact shoot is less than that measured in the
potometer.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
10 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
Q3. Fig. 2.1 is a drawing of a transverse section of a leaf.
(a) (i) Use label lines and the letters X, S, E and D to indicate the following on Fig. 2.1:
X – a xylem vessel
S – a phloem sieve tube
E – a lower epidermal cell
D – a palisade mesophyll cell [4]
(ii) Calculate the magnification of Fig. 2.1. Show your working and express your answer to the
nearest whole number.
Answer ........................................ [2]
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
11 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
(b) Name two assimilates that move from the palisade mesophyll cells to the vascular tissue to
be exported from the leaf.
1 .......................................................................................................................................
2 .................................................................................................................................. [2]
(c) Explain, using the term water potential, how water moves from the vascular tissue to the
atmosphere.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [4]
Q4. Fig. 2.1 shows part of a summer squash, Cucurbita pepo. Fig. 2.2 is a high power drawing
of an area of phloem from a transverse section of the stem of C. pepo.
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
12 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
(a) (i) Name G and H.
G ..............................................................................................................................
H ...........................................................................................................................[1]
(ii) Describe three ways in which the structure of a xylem vessel differs from the structure of
cell G.
1. ..............................................................................................................................
2. ..............................................................................................................................
3. ..........................................................................................................................[3]
(b) The liquid extracted from the phloem of C. pepo contains sucrose.
Explain how sucrose is transported in the phloem along the stem from the leaf to the fruit.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
13 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[4]
(c) Most of the sucrose transported in the phloem enters the fruit.
Suggest why summer squash fruits are not sweet.
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[1]
Q5. (a) Explain why transpiration is the inevitable consequence of gaseous exchange in land
plants.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[3]
Fig. 3.1 shows some of the cells from the lower part and under surface of a leaf. The water
potentials of three cells, A, B and C, are shown.
(b) Explain how water moves from the xylem vessel to cell B.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
14 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[3]
(c) Draw labelled arrows on Fig. 3.1 to show the direction in which
(i) water flows between the cells A, B and C; [2]
(ii) water vapour diffuses. [1]
(d) State two features of xerophytic plants that help to reduce the loss of water by transpiration
from their leaves.
1. ......................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
2. ......................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
Q6. Fig. 1.1 is a drawing made from an electron micrograph. It shows a longitudinal section
through a sieve tube element and a companion cell in the phloem of a flowering plant.
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
15 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
(a) Refer to Fig. 1.1.
(i) Name structures A to C.
A ...............................................................................................................................
B ...............................................................................................................................
C ...........................................................................................................................[3]
(ii) State the name given to the region labelled D that separates the two sieve tube elements.
...............................................................................................................................[1]
(iii) Name one assimilate that is transported in the phloem.
...............................................................................................................................[1]
(b) Explain how the structure of sieve tube elements helps the translocation of substances in the
phloem.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[3]
(c) Describe the role of companion cells in translocation in the phloem.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
16 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
Q7. Fig. 2.1 shows a transverse section of a root nodule of a legume. Fig. 2.2 is a drawing of a
cell from the centre of the nodule made from an electron micrograph.
(a) Name three structures that are present in cells in the cortex of the root that are not present in
bacterial cells.
1 .......................................................................................................................................
2 .......................................................................................................................................
3 ...................................................................................................................................[3]
(b) Explain the advantages of studying cell structure with an electron microscope rather than
with a light microscope.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
17 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
(c) Describe the role of Rhizobium in the root nodule.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[3]
(d) Cells in the centre of the root nodule have a high concentration of the pigment,
leghaemoglobin. This combines with oxygen in much the same way as haemoglobin in
mammals. Leghaemoglobin is responsible for maintaining anaerobic conditions around the
bacteria in the nodules. Leghaemoglobin is not found in the roots of other plants. The base
sequence in the gene that codes for the βpolypeptide of mammalian haemoglobin is similar to
that for leghaemoglobin. Suggest why this is so.
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................................[2]
Q8. Fig. 3.1 shows an electron micrograph of some xylem vessels in tobacco leaf fragments in a
cigarette.
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
18 Cambridge AS Level Biology Section: G Plant Transport
(i) Describe and explain two features of the xylem vessels, visible in Fig. 3.1, that are
adaptations for the transport of water in a plant.
feature ......................................................................................................................
explanation ...............................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
feature ......................................................................................................................
explanation ...............................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................[2]
(ii) Explain the mechanisms that cause movement of water in xylem vessels.
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................[4]
Waleed Ahmad Khan A Levels (ECP) 0347 – 4443879
You might also like
- Chapter 44 Test BankDocument9 pagesChapter 44 Test BankDonna BaluyotNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets As 062 (Practical Guide) (1) - See NowDocument6 pagesChemsheets As 062 (Practical Guide) (1) - See NowPrincess KimNo ratings yet
- DC-3 Operations ManualDocument20 pagesDC-3 Operations ManualGrzegorz PiasecznyNo ratings yet
- Eternals (2021) Google Drive MP4-HDDocument12 pagesEternals (2021) Google Drive MP4-HDAllan Abad0% (1)
- AnPhys3e Ch01 Test BankDocument22 pagesAnPhys3e Ch01 Test BankSuny Chavarria100% (1)
- Virtual Stomata LabDocument4 pagesVirtual Stomata Labapi-522847737No ratings yet
- TSSM Unit 1 Exam 2018Document28 pagesTSSM Unit 1 Exam 2018nisulNo ratings yet
- Respiration QuestionsDocument30 pagesRespiration Questionsadnan muridi100% (1)
- Korean Drama QuotesDocument19 pagesKorean Drama Quoteslucifer0% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence Report MS WordDocument11 pagesArtificial Intelligence Report MS Wordlucifer75% (4)
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderNo ratings yet
- Checked - Unit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and Health - Exam BookletDocument39 pagesChecked - Unit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and Health - Exam BookletEllane leeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Revision Exercise (Chap 5-8) Paper 2 1Document19 pagesIGCSE Biology Revision Exercise (Chap 5-8) Paper 2 1Sze Jack100% (1)
- Essential Biology 05 - Ecology, Evolution & ConservationDocument31 pagesEssential Biology 05 - Ecology, Evolution & ConservationManuel Torres100% (1)
- Biocomp Exam 2019Document10 pagesBiocomp Exam 2019nmNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsEva SugarNo ratings yet
- CH 13 EXCRETION IN HUMANS - QuestionsDocument10 pagesCH 13 EXCRETION IN HUMANS - QuestionsPranitha RaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26Document2 pagesChapter 26araneyaNo ratings yet
- B8 Photosynthesis Exam Pack: 132 Minutes 132 MarksDocument36 pagesB8 Photosynthesis Exam Pack: 132 Minutes 132 MarksDaniel's RevisionNo ratings yet
- Questions On Transport and Storage in PlantsDocument10 pagesQuestions On Transport and Storage in PlantsNathan mwapeNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Question PapreDocument12 pagesReproduction Question PapreIman DOTNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 - Cell StructureDocument52 pagesPaper 1 - Cell StructureShubin Pokhrel100% (2)
- 2015 Photosynthesis and Respiration Revision Tutorial AnsDocument18 pages2015 Photosynthesis and Respiration Revision Tutorial Ansliveaq100% (1)
- Sat II Real Evolution QuestionsDocument3 pagesSat II Real Evolution QuestionsMido MidoNo ratings yet
- Cell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Document6 pagesCell Nuclear Division Paper 1 (Multiple Choices)Tia wkwk100% (1)
- AQA GCSE Combined B7 Test 1 Beginner QP UnlockedDocument17 pagesAQA GCSE Combined B7 Test 1 Beginner QP Unlockedramloghun veer100% (1)
- Topical Past PapersDocument208 pagesTopical Past PapersShafaq RamzanNo ratings yet
- Transport 2Document2 pagesTransport 2Lyra Ane Ilagan100% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction Worksheet BoardWorksDocument2 pagesAsexual Reproduction Worksheet BoardWorksJohn Osborne0% (5)
- Paper 2 Data Interpretation Practice Questions & AnswersDocument17 pagesPaper 2 Data Interpretation Practice Questions & AnswersHanna “Hannaboo” YunNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 - Transport Across MembraneDocument5 pagesChapter3 - Transport Across MembraneBilly LamNo ratings yet
- Bio SPM Intervensi m1Document10 pagesBio SPM Intervensi m1teahockNo ratings yet
- A Level H2 Biology SyllabusDocument27 pagesA Level H2 Biology SyllabusTerry YauNo ratings yet
- Cell Division ReviewDocument7 pagesCell Division ReviewBLlahniesss Love Ken100% (1)
- Biocomp Exam 2009Document12 pagesBiocomp Exam 2009martynapet100% (1)
- KS3 Biology ReproductionDocument22 pagesKS3 Biology ReproductionMEHDI MAICHOUF100% (1)
- Photosynthesis & Mineral Nutrition: Question PaperDocument51 pagesPhotosynthesis & Mineral Nutrition: Question PaperWakif Khan Pranto100% (1)
- Worksheet Dna Class 12Document30 pagesWorksheet Dna Class 12BrindhaVasudevan100% (1)
- Year 7 Variation-WorksheetDocument17 pagesYear 7 Variation-WorksheetCally Chew100% (1)
- 2c Biotechnology Worksheet 2Document2 pages2c Biotechnology Worksheet 2api-263197810No ratings yet
- Topic 1 TestDocument11 pagesTopic 1 Testrania samirNo ratings yet
- Protein Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesProtein Multiple Choice QuestionsJohn Osborne100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/23Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/23Eain Thu100% (1)
- Protein and Enzyme WorksheetDocument8 pagesProtein and Enzyme Worksheetanahita kazemifar100% (1)
- 4.2 - Meiosis Revision QuestionsDocument6 pages4.2 - Meiosis Revision QuestionsCasper LuNo ratings yet
- Biology Higher Level Paper 1: International Baccalaureate Baccalauréat International Bachillerato InternacionalDocument15 pagesBiology Higher Level Paper 1: International Baccalaureate Baccalauréat International Bachillerato InternacionalJuan Fernando Velasco ForeroNo ratings yet
- 2011 Semifinal Exam QuestionsDocument42 pages2011 Semifinal Exam Questionsmartynapet100% (1)
- Diffusion and Osmosis QuestionsDocument2 pagesDiffusion and Osmosis QuestionsAlfred MwayutaNo ratings yet
- 9700 w15 QP 13Document16 pages9700 w15 QP 13Hew Li Yang100% (1)
- Inheritance Exam QDocument29 pagesInheritance Exam Qapi-422428700100% (1)
- CK-12 Biology Chapter WorksheetsDocument29 pagesCK-12 Biology Chapter WorksheetsNeacsu Mary50% (2)
- Bio 3.1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesBio 3.1 PhotosynthesisSuzuko YukinoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Homeostasis PDFDocument77 pages2.1 Homeostasis PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- CladogramDocument15 pagesCladogramJhoanna Paula BitorNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Function WorksheetsDocument24 pagesCellular Structure and Function WorksheetsLouiseNo ratings yet
- 2 Mem TransDocument6 pages2 Mem TransPhuong DoanNo ratings yet
- 2012 Semifinal Exam PartAandB QuestionsDocument39 pages2012 Semifinal Exam PartAandB Questionsmartynapet100% (3)
- 3.1.3 Cell and TransportDocument39 pages3.1.3 Cell and TransportHarshad Gadhvi100% (1)
- HL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingDocument192 pagesHL BIOLOGY PAST QUESTIONS PAPER PrintingFaizaNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 1 Molecules QuestionsDocument78 pagesBio Unit 1 Molecules Questionsareyouthere92100% (3)
- Metabolism WorksheetDocument6 pagesMetabolism WorksheetChristy Cook WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Immunity QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Document40 pagesImmunity QP New Syllabus (2010-2012)Ae Banpong100% (1)
- Unit 3 Grade 11 BiologyDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Grade 11 BiologyEva100% (1)
- Plant Transport Multiple Choice Qs PDFDocument7 pagesPlant Transport Multiple Choice Qs PDFMathula MuhundanNo ratings yet
- Movement Into & Out of The CellsDocument21 pagesMovement Into & Out of The Cellsvipprogamers7No ratings yet
- 36 Hours in SeoulDocument7 pages36 Hours in SeoulluciferNo ratings yet
- Canbridge Practical Exam Venue Schedule For June 2018Document8 pagesCanbridge Practical Exam Venue Schedule For June 2018luciferNo ratings yet
- Depiction of Victorian Era in The Novel Great Expectations by Charles DickensDocument6 pagesDepiction of Victorian Era in The Novel Great Expectations by Charles DickensluciferNo ratings yet
- InternetWalaLove 0Document2 pagesInternetWalaLove 0luciferNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Wolfman Study 1Document1 pageSummary of The Wolfman Study 1luciferNo ratings yet
- A Kushan-Period Sculpture: From The Reign of Jaya Varma-, A.D. 184/185 K NDocument7 pagesA Kushan-Period Sculpture: From The Reign of Jaya Varma-, A.D. 184/185 K NluciferNo ratings yet
- Jivan Kandola Completed Poster UrssDocument1 pageJivan Kandola Completed Poster UrssluciferNo ratings yet
- Event Date Week: Academic Calendar SPRING - 2021Document2 pagesEvent Date Week: Academic Calendar SPRING - 2021luciferNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 & 15Document16 pagesLecture 14 & 15luciferNo ratings yet
- Thermal StabilityDocument1 pageThermal StabilityluciferNo ratings yet
- Main Features of Romantic Poetry2393832108542687685Document3 pagesMain Features of Romantic Poetry2393832108542687685luciferNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Social MediaDocument5 pagesPresentation On Social MedialuciferNo ratings yet
- 5 Chemical EnergeticsDocument21 pages5 Chemical EnergeticsluciferNo ratings yet
- Just A Housewife by Arti ChopraDocument1 pageJust A Housewife by Arti ChopraluciferNo ratings yet
- C EnzymesDocument18 pagesC Enzymeslucifer100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document40 pagesChapter 2luciferNo ratings yet
- K Ecology-1Document16 pagesK Ecology-1luciferNo ratings yet
- 9A - Gas Exchange and SmokingDocument79 pages9A - Gas Exchange and SmokingluciferNo ratings yet
- Geological Applications of Wireline Logs: A Synopsis of Developments and TrendsDocument18 pagesGeological Applications of Wireline Logs: A Synopsis of Developments and Trendscunin12No ratings yet
- Surge Analysis: What Is Pressure Surge?Document2 pagesSurge Analysis: What Is Pressure Surge?Yang Gul Lee100% (1)
- ITE2 Worksheet UNIX and Linux On The Desktop enDocument2 pagesITE2 Worksheet UNIX and Linux On The Desktop enz233No ratings yet
- Designing A Container Terminal YardDocument108 pagesDesigning A Container Terminal Yardlim kang hai100% (5)
- KITCHENDocument3 pagesKITCHENAman RawatNo ratings yet
- My 101-Item Bucket ListDocument2 pagesMy 101-Item Bucket ListBasavaraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Overview LNG Central Java V.1.2.REV1Document10 pagesOverview LNG Central Java V.1.2.REV1sigit l.prabowoNo ratings yet
- Ac Servo Motor Trainer: - MechatronicsDocument1 pageAc Servo Motor Trainer: - MechatronicsatifNo ratings yet
- Soal Report 19Document18 pagesSoal Report 19SULARMANNo ratings yet
- Hardness Conversion TableDocument3 pagesHardness Conversion TableNisarg PandyaNo ratings yet
- Warren BuffeltDocument16 pagesWarren BuffeltsamkumNo ratings yet
- August 2010 NewsletterDocument9 pagesAugust 2010 Newsletterapi-239513807No ratings yet
- Financial Literacy Material-EnglishDocument55 pagesFinancial Literacy Material-EnglishAlamandha Madhan KumarNo ratings yet
- BBM401 Automata Theory and Formal Languages 1Document34 pagesBBM401 Automata Theory and Formal Languages 1Gautamkrishna ChintaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1110062117301939 Main PDFDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S1110062117301939 Main PDFbhavaniprasad478No ratings yet
- Supreme Student Government Awards 2012Document4 pagesSupreme Student Government Awards 2012Ramil Anton VillafrancaNo ratings yet
- Tugas MPSI P1-P14 - Kelompok 6 - 19.4A.04Document55 pagesTugas MPSI P1-P14 - Kelompok 6 - 19.4A.04kurniaalanNo ratings yet
- Enteral Nutrition Safety System With EnfitDocument12 pagesEnteral Nutrition Safety System With EnfitRenata OlmosNo ratings yet
- Repair My Life Nasty Bastards MC Book 6 Hayley Faiman All ChapterDocument67 pagesRepair My Life Nasty Bastards MC Book 6 Hayley Faiman All Chapterrachel.young780100% (19)
- Highway Design Handbook For Older Drivers and PedestriansDocument369 pagesHighway Design Handbook For Older Drivers and PedestriansfranciscovelaNo ratings yet
- Transcript of FGDDocument19 pagesTranscript of FGDGlensky Nadz NumbarNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - PepsicoDocument9 pagesHuman Resource Management - Pepsicoankitkmr25No ratings yet
- Undergraduate Programmes Offered: NotesDocument1 pageUndergraduate Programmes Offered: NotesWazaNo ratings yet
- TM12864H6CCOWADocument32 pagesTM12864H6CCOWASukumaran BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- How To Help Build The UK's Open Planning Database: Writing Scrapers - CountcultureDocument6 pagesHow To Help Build The UK's Open Planning Database: Writing Scrapers - CountcultureLara SalinasNo ratings yet
- Model Ysdc07Fs-Adg V/PH/HZ 220V/1Ph/60HzDocument10 pagesModel Ysdc07Fs-Adg V/PH/HZ 220V/1Ph/60HzJose Enrique Sanchez ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Self StudyDocument24 pagesWeek 9 Self Studyadegitegabriel7No ratings yet