Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Year 7 Juncture: Planning and Auditing Template
Uploaded by
Li NguyenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 7 Juncture: Planning and Auditing Template
Uploaded by
Li NguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 7 juncture
Planning and auditing template
All key learning areas
About this template Five processes that guide planning
This resource is intended to help you plan teaching, learning and
assessment of the Essential Learnings across the curriculum. It can be
used to:
audit existing units
plan new units of work.
The template provides a record of your units of work and their specific
teaching, learning and assessment of:
Ways of working
Knowledge and understandings (conceptual statements only)
Assessable elements.
Using the form features
This template is a protected MS Word form document — it allows you to
enter unit titles in the shaded areas and check and uncheck boxes by
clicking on them.
To make any other changes to the template, turn off the MS Word
protection feature:
Open the document in MS Word. This template can be used to identify curriculum and develop
Display the Forms toolbar: from the top menu, select View > assessment.
Toolbars > Forms.
On the Forms toolbar, click on the Protect forms icon (padlock). Additional planning and auditing resources
APEL is a QSA developed software application to help teachers audit
their curriculum and plan units of work using the Essential Learnings.
Available from the QSA website <www.qsa.qld.edu.au>.
Reactivate protection by clicking on padlock when needed.
1 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
Year 7 juncture — The Arts
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Ways of working Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Students are able to:
select and develop ideas for arts works, considering different
audiences and different purposes, using arts elements and
languages
create and shape arts works by modifying arts elements to
express purpose and to include influences from their own and
others cultures and times
modify and polish arts works, using interpretative and technical
skills
present arts works to informal and formal audiences for
intended purposes, using arts techniques, skills and processes
identify, apply and justify safe practices
respond by analysing and evaluating arts works in social,
cultural, historical and spiritual contexts, using arts elements
and languages
reflect on learning to apply new understandings and identify
future applications.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
2
Year 7 juncture — The Arts
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Dance: Dance involves using the human body to express ideas, considering different audiences and intended purposes,
by modifying dance elements in movement sequences.
Combinations of locomotor and non-locomotor movements
are used to create actions for movement sequences.
Directional focus is used to draw attention in space in
movement sequences.
Combinations of simple and compound time signatures are
used to modify timing of movements in sequences.
Suspending and vibrating movement qualities are used to
modify energy.
Structuring devices, including transitions, motifs and
improvisation forms, are used to organise movement
sequences.
Drama: Drama involves modifying dramatic elements and conventions to express ideas, considering intended audiences
and intended purposes, through dramatic action based on real or imagined events.
Roles and characters can be presented from different
perspectives and in different situations, using variations in
voice, movement and focus
Purpose and context are considered when modifying mood,
time frames, language, place and space, and are used to
express ideas.
Dramatic action is interpreted, prepared and shaped through
scenarios and scripts.
3 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
Year 7 juncture — The Arts
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Media: Media involves constructing meaning, considering intended audiences and intended purposes, by modifying
media languages and technologies to create representations.
Still and moving images, sounds and words are applied and
modified, using genre conventions, to construct media texts.
Media techniques and practices, including editing and
publishing, are used to create media texts.
Representations in media texts have specific purposes and
are modified to maximise audience impact.
Music: Music involves singing, playing instruments, listening, moving, improvising and composing by modifying
the music elements to express ideas, considering intended audiences and intended purposes, through sound.
Duration, beat, time values and metre are used to create
rhythm.
Pitch and intervals are used to create melody.
Tonalities and harmonies are used to organise music in
vertical arrangements.
Contemporary and traditional musical forms are used to
structure music.
Vocal, instrumental and electronic sound sources have
characteristic sound qualities (tone colour).
Relative softness and loudness and emphasis of sounds are
used to change dynamic levels and expression of music.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
4
Year 7 juncture — The Arts
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Visual Art: Visual Art involves selecting visual arts elements, concepts, processes and forms (both 2D and 3D) to express
ideas, considering different audiences and different purposes, through images and objects.
Blended, controlled and symbolic colour is used to create
depth, representation and symbolism.
Descriptive and emotive lines are used to create abstraction,
proportion and symbolism.
Negative space and positive shape are used to create
abstraction, non-representation and proportion.
Actual, invented and simulated textures are used to create
depth, representation and non-representation.
5 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
The Arts — Assessable elements
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Assessable elements
Unit title
Students demonstrate evidence of their learning over
time in relation to the following assessable elements:
Knowledge and understanding
Creating
Presenting
Responding
Reflecting
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
6
Year 7 juncture — HPE
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Ways of working Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Students are able to:
identify issues and plan investigations and activities
collect, analyse and evaluate information and evidence
draw conclusions and make decisions supported by
information and evidence
propose, justify, implement and monitor plans or actions to
promote health and wellbeing, movement capacities and
personal development
apply movement concepts and make purposeful refinements to
movement skills
create and perform movement sequences through modifying
and combining movement skills and applying movement
concepts
identify risks and justify and apply safe practices
select and demonstrate appropriate personal development
skills and strategies in team and group situations
reflect on and identify the impact of diverse influences on
health and well being, movement capacities and personal
development, including the best use of positive influences
reflect on learning, apply new understandings and identify
future applications.
7 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
Year 7 juncture — HPE
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Health: Health is multidimensional and influenced by individual and group actions and environments.
Health includes physical, social, emotional, cognitive and
spiritual (relating to beliefs) dimensions, which are interrelated.
Family, peers and the media influence health behaviours.
Individual, groups and communities act on the advice in health
promotion campaigns to promote health and wellbeing,
including safety, and contribute to management of health risks.
Food groups are rich in particular nutrients, and food intake
can be adapted to meet changing needs during adolescence.
Physical activity: Fundamental and specialised movement skills, movement concepts, tactics and strategies are elements of physical activity.
Modifying techniques and selectively applying movement
concepts can enhance physical performance and increase
enjoyment in physical activities.
Refining teamwork, tactics and strategies in a variety of
contexts improves movement capacities, and physical
performance, and enhances participation in physical activity.
Regular participation in physical activity can enhance cardio-
respiratory endurance, muscular strength and endurance,
flexibility, and health and wellbeing.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
8
Year 7 juncture — HPE
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Personal development: Beliefs, behaviours and social and environmental factors influence relationships and self-management and shape personal development.
Identity and self-image are influenced by environmental
factors, including the media, and social expectations of age,
gender and culture.
Assuming roles and responsibilities, experiencing leadership
opportunities, respecting cultural protocols and differences and
working well with others, develops positive identity and self-
esteem.
Life events and transitions can be dealt with through meaning-
making, resilience strategies, and use of personal and
community resources.
9 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
HPE — Assessable elements
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Assessable elements
Unit title
Students demonstrate evidence of their learning over
time in relation to the following assessable elements:
Knowledge and understanding
Investigating
Planning
Implementing and applying
Reflecting
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
10
Year 7 juncture — SOSE
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Ways of working Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Students are able to:
identify issues and use common and own focus questions
plan investigations using inquiry models
collect and organise information and evidence from primary
and secondary sources
evaluate sources of information and evidence for relevance,
reliability, origins and perspective
draw conclusions and make decisions based on information
and evidence by identifying patterns and connections
communicate descriptions, decisions and conclusions, using
different text types for specific purposes and the conventions of
research-based texts
respond to investigation findings and conclusions by planning
and implementing actions
apply strategies to contribute effectively to representative
groups and to participate in civic activities
reflect on and identify different perspectives, and recognise
and clarify beliefs and values relating to social justice, the
democratic process, sustainability and peace
reflect on learning, apply new understandings and identify
future applications.
11 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
Year 7 juncture — SOSE
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Time, continuity and change: Changes and continuities are linked to particular events and the achievements
of individuals and groups that attract different interpretations.
Events from pre-colonisation to Federation, including
Indigenous heritages, European colonisation, frontier conflicts,
the development of the economy, and the Federation
movement, have established the Australian nation and
contributed to Australian identities.
Australia’s relationship with its Asian and Pacific neighbours is
linked to events over a range of time periods, including events
associated with the “White Australia” policy, refugees and
immigration, free-trade agreements and military alliances.
National traditions, celebrations and commemorations have
evolved to reflect public sentiment and the perspectives,
values and interpretations of different groups.
Place and space: Environments are defined by physical characteristics and processes, and are connected
to human activities and decisions about resource management.
Australian environments are defined by patterns of natural
processes, by human activities and by the relationships
between them, including climate and natural resource
distribution, resource use, and settlement patterns.
Natural hazards are a result of natural processes, and human
activity can affect the impacts of these occurrences.
Sustainability requires a balance between using, conserving
and protecting environments, and involves decisions about
how resources are used and managed.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
12
Year 7 juncture — SOSE
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Place and space: Environments are defined by physical characteristics and processes, and are connected
to human activities and decisions about resource management.
Physical and human dimensions are used to define global
environments.
Distribution maps, climate zone maps and weather maps have
specific features to convey information, including latitude,
longitude, eight compass points, scale and distance, a legend
and shading and/or symbols.
Culture and identity: Cultures and identities consist of material and non-material elements and are affected by cross-cultural contacts.
Material and non-material elements influence personal identity
and sense of belonging of groups.
Perceptions of different cultures and groups are influenced by
local, national and world events and by representations.
Aboriginal people’s and Torres Strait Islander people’s diverse
social organisation, languages and lifestyles reflect the
importance of “country” — land, sea and places
Contact between Indigenous and non-Indigenous cultures in
Australia and in other places have had significant effects on
language, culture, land ownership, health and education of
Indigenous people.
Accessing Indigenous knowledge involves the protocols of
consultation with the local Aboriginal community and/or the
Torres Strait Islander community.
13 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
Year 7 juncture — SOSE
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Political and economic systems: Societies and economies have systems and institutions based on principles and values.
Australia’s government systems are characterised by
principles including civil society and representative democracy,
processes including free and fair elections, institutions
including parliaments and political parties, and instruments
including the Australian Constitution.
Australia’s legal system is founded on laws that reflect
community values, including fairness and impartiality, and the
courts to uphold the laws and protect rights and freedoms.
Local, state, national and Indigenous systems of government
in Australia have different roles, functions, ways of operating
and impacts on people and communities.
Australian citizenship involves values, attitudes and actions
related to political equality and civil and human rights.
Australia is connected to other nations through international
agreements, the responsibilities of global citizenship, and
shared commitments to security and environmental issues.
Economic systems involve primary, secondary, service and
knowledge industries that use resources and develop products
and services for sale to consumers.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
14
SOSE — Assessable elements
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Assessable elements
Unit title
Students demonstrate evidence of their learning over
time in relation to the following assessable elements:
Knowledge and understanding
Investigating
Communicating
Participating
Reflecting
15 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
Year 7 juncture — Technology
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Ways of working Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Students are able to:
investigate and analyse the purpose, context, specifications
and constraints for design ideas
generate and evaluate design ideas and determine suitability
based on purpose, specifications and constraints
communicate the details of designs showing relative
proportion, using labelled drawings, models and/or plans
select resources, techniques and tools to make products that
meet specifications
plan and manage production procedures and modify as
necessary
make products to meet specifications by manipulating and
processing resources
identify risks and justify and apply safe practices
evaluate the suitability of products and processes for the
purpose and context, and recommend improvements
reflect on and identify the impacts of products and processes
on people, their communities and environments
reflect on and identify the impacts of products and processes
on people, their communities and environments applications.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
16
Year 7 juncture — Technology
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Knowledge and understanding Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Key: Teaching and learning
Unit title
Assessment
Technology as a human endeavour: Technology influences and impacts on people, their communities and environments.
Design and development of products are influenced by
societies’ changing needs and wants, and include artefacts,
systems, environments and services.
Product design and production decisions are influenced by
specifications, constraints and aspects of appropriateness
including functions, aesthetics, ethics, culture, available
finances and resources, and sustainability.
Decisions made about the design, development and use of
products can impact positively or negatively on people, their
communities and environments.
Information, materials and systems (resources): The characteristics of resources are matched with tools and techniques
to make products to meet design challenges.
Resources are selected according to their characteristics, to
match requirements of design challenges and suit the user.
Techniques and tools are selected to manipulate or process
resources to enhance the quality of products and to match
design ideas, standards and specifications.
17 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
Technology — Assessable elements
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Assessable elements
Unit title
Students demonstrate evidence of their learning over
time in relation to the following assessable elements:
Knowledge and understanding
Investigating and designing
Producing
Evaluating
Reflecting
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
18
ICT Cross-curriculum priorities
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Inquiring with ICTs
Unit title
Students explore and use ICTs in the processes of
inquiry across key learning areas. They:
identify the inquiry focus, data and information requirements
and possible digital information sources
plan, conduct and manage structured searches and advanced
searches for data and information in response to questions
organise and analyse, experiment with and test data and
information from a variety of sources
evaluate data and information gathered for usefulness,
credibility, relevance, accuracy and completeness
reflect on, analyse and evaluate how ICTs have assisted in meeting
the inquiry purposes and in developing new understandings.
Creating with ICTs
Students experiment with, select and use ICTs to create a range of responses to suit the purpose and audience. They use ICTs to develop
understanding, demonstrate creativity, thinking, learning, collaboration and communication across key learning areas. They:
develop plans and proposals, considering common ICT design
feature
develop criteria to evaluate responses, plans and processes
express and creatively represent ideas, information and thinking
creatively document and present their planning, thinking and
learning using a combination of media
reflect on their use of ICTs as creative tools and evaluate the
quality of their ICT responses, plans and processes against
criteria.
19 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
ICT Cross-curriculum priorities
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Communicating with ICTs
Unit title
Students experiment with, select and use ICTs across key
learning areas to collaborate and enhance communication with
individuals, groups or wider audiences in local and global
contexts for an identified purpose and audience. They:
collaborate, develop, organise and present new ideas
consider how ICTs can be used to enhance interpersonal
relationships and empathise with people in different social and
cultural contexts
apply suitable or agreed communication conventions and
protocols
select and apply a variety of digital media to improve
communication
establish their own or a group image and identity in
communication
reflect on their use of ICTs and consider feedback to improve
collaboration and refine and communicate meaning.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
20
ICT Cross-curriculum priorities
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Ethics, issues and ICTs
Unit title
Students understand the role of some ICTs in society. They
develop and apply ethical, safe and responsible practices when
working with ICTs in online and stand-alone environments.
They
apply codes of practice for safe, secure and responsible use
of ICTs
review the use of ICTs in terms of safety, ethical practice,
legality and responsibility
apply values and codes of practice of the ICT environment
that respect individual rights and cultural differences when
accessing and delivering information online
apply protocols to acknowledge the owner(s)/creators(s) of
digital information sources and develop an awareness of
legislation relating to digital theft and plagiarism
apply a range of preventative strategies to address issues
relating to health and safety when using ICTs
develop and apply strategies for securing and protecting digital
information, including personal information
evaluate how their use of ICTs meets ethical and legal criteria
reflect on, analyse and evaluate the use of ICTs, assess their
impact in the workplace and society, and consider future
needs.
21 | Year 7 Juncture Planning and auditing template
ICT Cross-curriculum priorities
Units of work
Year 6 Year 7
Semester 1 Semester 2 Semester 1 Semester 2
Operating ICTs
Unit title
Students use a range of advanced ICT functions and
applications across key learning areas to inquire,
create, collaborate and communicate, and to manage
information and data. They:
develop operational skills and begin to use the extended
functionality of a range of ICT devices
investigate the main uses and processes of some input, output,
processing and storage devices
describe various ICT devices and processes using ICT-specific
terminology
apply operational conventions when using ICTs
develop strategies for learning new ICT operations and
consider different ways to perform tasks
identify operational advantages to manage personal ICT
resources and customise interfaces
apply agreed processes for personal management of digital
content and identify the advantages of customisation
reflect on, analyse and evaluate their operational skills to meet
the requirements of system resources, processes and
conventions.
Queensland Studies Authority March 2021 |
22
Queensland Studies Authority
295 Ann Street, Brisbane
PO Box 307 Spring Hill
QLD 4004 Australia
T +61 7 3864 0299
F +61 7 3221 2553
www.qsa.qld.edu.au
You might also like
- MC2 - Prototyping Phase Plan: Challenge OverviewDocument16 pagesMC2 - Prototyping Phase Plan: Challenge OverviewDelinda ShevyandaniNo ratings yet
- Seeds Lesson Plan Template Revised2 2 1Document5 pagesSeeds Lesson Plan Template Revised2 2 1api-548717522No ratings yet
- PC 9Document1 pagePC 9api-438470477No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 NotesDocument17 pagesChapter 7 NotesImran GureNo ratings yet
- PC 12Document1 pagePC 12api-438470477No ratings yet
- TOS Format1Document3 pagesTOS Format1Louchelle MacasasaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Components: Part A: PlanningDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Components: Part A: Planningapi-544654960No ratings yet
- CM402-Part 4 - Worksheet 7-2022-23Document5 pagesCM402-Part 4 - Worksheet 7-2022-23Sana SanaNo ratings yet
- ANL Business and Finance Training Curriculum GuideDocument2 pagesANL Business and Finance Training Curriculum GuideMuhammad Tassadaque ZiaNo ratings yet
- INTERNSHIP DIARY of DypatilDocument15 pagesINTERNSHIP DIARY of DypatilMac357GNo ratings yet
- CV. Stephani TasikDocument2 pagesCV. Stephani TasikStephani Wulandari TasikNo ratings yet
- (Individu) - Tugas SJODocument3 pages(Individu) - Tugas SJOeobikaskusNo ratings yet
- Annual Appraisal FormDocument7 pagesAnnual Appraisal FormSzabados SándorNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Ranking Research SkillsDocument1 page5.4 Ranking Research SkillsgetrindNo ratings yet
- Jatin R BhattDocument3 pagesJatin R BhattGuar GumNo ratings yet
- Certificate Grade - XII & XIDocument1 pageCertificate Grade - XII & XIAviraj RautNo ratings yet
- Dhaka, BD: Your NameDocument2 pagesDhaka, BD: Your NameFiroz AlamNo ratings yet
- Aimee Mancil Gapss Part B FinalDocument21 pagesAimee Mancil Gapss Part B Finalapi-189537139No ratings yet
- ps4 GridsDocument12 pagesps4 Gridsapi-302409237No ratings yet
- Amar Professional Competency Self Evaluation SheetsDocument12 pagesAmar Professional Competency Self Evaluation Sheetsapi-517831630No ratings yet
- Mate ComprobanteDocument375 pagesMate ComprobanteNatalia ArroyaveNo ratings yet
- 5S MethodologyDocument22 pages5S MethodologyAmandeep Singh GujralNo ratings yet
- PDF Self Evaluation Grid Fe3Document12 pagesPDF Self Evaluation Grid Fe3api-438611508No ratings yet
- Updated Information Brochure 14-05-2014Document126 pagesUpdated Information Brochure 14-05-2014Arjun lal KumawatNo ratings yet
- (NEW RELEASES) Northstar Listening and Speaking 3 With Myenglishlab - E-BOOKS LibraryDocument6 pages(NEW RELEASES) Northstar Listening and Speaking 3 With Myenglishlab - E-BOOKS Libraryalaa mmm67% (3)
- Microlearning Ebook AllencommDocument11 pagesMicrolearning Ebook AllencommMayra Alejandra CortesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Consulting Tools and TechnicquesDocument16 pagesModule 2 Consulting Tools and TechnicquesMARI DECE CRECHE BISCOCHONo ratings yet
- CM402-Part 3 - Worksheet 5-2021-22Document4 pagesCM402-Part 3 - Worksheet 5-2021-22Hong ChinNo ratings yet
- Assessment TemplateDocument2 pagesAssessment Templateapi-443558457No ratings yet
- Tyler MireDocument1 pageTyler Mireapi-650427295No ratings yet
- CooperativesDocument49 pagesCooperativesCarmella BelenNo ratings yet
- Advertisement Skills - III Semester (Study Materials)Document82 pagesAdvertisement Skills - III Semester (Study Materials)Gladwin Joseph E Nitte School of Fashion Technology and Interior DesignNo ratings yet
- Activities and Scores Log Sheet Date Topic Activity Scor E HPS Parent'S SignatureDocument1 pageActivities and Scores Log Sheet Date Topic Activity Scor E HPS Parent'S SignatureAlizza tanglibenNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management - Smarwatch AssigmentDocument11 pagesMarketing Management - Smarwatch AssigmentNguyen WoabeNo ratings yet
- Lab Homeostasis ExerciseDocument4 pagesLab Homeostasis Exerciseapi-259776843No ratings yet
- Facility Planning IntroDocument28 pagesFacility Planning Introsamar1976No ratings yet
- Student Name: Course Number: Assignment #: Project Name: Project PurposeDocument5 pagesStudent Name: Course Number: Assignment #: Project Name: Project PurposerrinessNo ratings yet
- Format 3. Objectives/ Guidelines/ Agreement: Internship Synopsis (This Will Be Prepared in Consultation With Faculty Mentor)Document3 pagesFormat 3. Objectives/ Guidelines/ Agreement: Internship Synopsis (This Will Be Prepared in Consultation With Faculty Mentor)johnNo ratings yet
- Abdallah Dahir - Architectural Technologist Portfolio 2022Document5 pagesAbdallah Dahir - Architectural Technologist Portfolio 2022Abdallah DahirNo ratings yet
- Hannah Sand ResumeDocument1 pageHannah Sand Resumeapi-543953942No ratings yet
- Registration FormDocument1 pageRegistration FormJeannifer MVNo ratings yet
- Global Digital HR Transformaiton & Analytics Virtual Forum 2022Document16 pagesGlobal Digital HR Transformaiton & Analytics Virtual Forum 2022SamiNo ratings yet
- General OrientationDocument7 pagesGeneral OrientationStacey SalvillaNo ratings yet
- Abdallah Dahir - Architectural Technologist Portfolio 2022Document5 pagesAbdallah Dahir - Architectural Technologist Portfolio 2022Abdallah DahirNo ratings yet
- Kelly Rakus Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesKelly Rakus Lesson Plan 1api-639732250No ratings yet
- Nurulsyazwani Ieps PDFDocument10 pagesNurulsyazwani Ieps PDFilhamhaziqNo ratings yet
- Template - Initial Job Training PlanDocument1 pageTemplate - Initial Job Training PlanJazper ComiaNo ratings yet
- 005 SkillFront Fundamentals of The ScrumDocument81 pages005 SkillFront Fundamentals of The ScrumMoanis HusseinNo ratings yet
- Teaching Model For Integrating CreativityDocument1 pageTeaching Model For Integrating CreativitySPONo ratings yet
- Brochure FinalDocument1 pageBrochure FinalAnand PaulNo ratings yet
- PMBOK 6 Data Flow DiagramDocument2 pagesPMBOK 6 Data Flow Diagram小瀬 淳一No ratings yet
- Idep Finance Policy PDFDocument18 pagesIdep Finance Policy PDFLaksmiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Urdu Ramadan Revelation of QuranDocument3 pages2015 Urdu Ramadan Revelation of QuranMuhammad Ali buttNo ratings yet
- Abdallah Dahir - Architectural Technologist Portfolio 2021Document5 pagesAbdallah Dahir - Architectural Technologist Portfolio 2021Abdallah DahirNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Java Programming: Java Basics: Manuel Oriol April 18, 2006Document31 pagesTechniques of Java Programming: Java Basics: Manuel Oriol April 18, 2006Sai VellankiNo ratings yet
- Employee Career Development PlanDocument1 pageEmployee Career Development PlanJenny CabuhatNo ratings yet
- Part 1-Stop-and-Check-2023Document5 pagesPart 1-Stop-and-Check-2023Sana SanaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security: Start Your Career inDocument2 pagesCyber Security: Start Your Career inMohamed Shafaathullah ShahNo ratings yet
- MATH 645 Homework Solutions for Dynamical Systems and ODEsDocument34 pagesMATH 645 Homework Solutions for Dynamical Systems and ODEsLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Finm33017hw2 PDFDocument2 pagesFinm33017hw2 PDFLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- FM 330: Homework 2 SolutionsDocument2 pagesFM 330: Homework 2 SolutionsLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Cryotherapy AftercareDocument1 pageCryotherapy AftercareLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- WW QLD 051022 NBCLNK6PDocument50 pagesWW QLD 051022 NBCLNK6PLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Echolocation in Dolphins and BatsDocument7 pagesEcholocation in Dolphins and BatsLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Plan - Australian Curriculum: Mathematics: Implementation Year: School Name: Year Level DescriptionDocument5 pagesYear 7 Plan - Australian Curriculum: Mathematics: Implementation Year: School Name: Year Level DescriptionLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Ideas for All LearnersDocument6 pagesLesson Plan Ideas for All LearnersLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Topic 03Document61 pagesTopic 03Li NguyenNo ratings yet
- Minimum Time ControlDocument6 pagesMinimum Time ControlLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Extension 2: MEX-V1 Further Work With VectorsDocument41 pagesMathematics Extension 2: MEX-V1 Further Work With VectorsLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Joint density function transforms to densities of products and ratiosDocument2 pagesJoint density function transforms to densities of products and ratiosLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Specialist Mathematics 2019 sample examDocument14 pagesSpecialist Mathematics 2019 sample examLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Extension 2 Year 12 Sample Unit VectorsDocument16 pagesMathematics Extension 2 Year 12 Sample Unit VectorsLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Specialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: IA3 Sample Assessment InstrumentDocument18 pagesSpecialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: IA3 Sample Assessment InstrumentLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- SNR Maths Specialist 19 SyllDocument86 pagesSNR Maths Specialist 19 SyllLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Tute 1 Notes PDFDocument5 pagesTute 1 Notes PDFLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Example 1Document1 pageExample 1Li NguyenNo ratings yet
- Specialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: IA2 Sample Assessment InstrumentDocument18 pagesSpecialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: IA2 Sample Assessment InstrumentLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Specialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: IA2 Sample Marking SchemeDocument12 pagesSpecialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: IA2 Sample Marking SchemeLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Specialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: Unit 2 Sample Assessment InstrumentDocument18 pagesSpecialist Mathematics 2019 v1.2: Unit 2 Sample Assessment InstrumentLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Finance 1 lecture notes on financial institutions and marketsDocument60 pagesFinance 1 lecture notes on financial institutions and marketsLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Work-1-6-Solutions 2015Document24 pagesTutorial-Work-1-6-Solutions 2015Li NguyenNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-Work-1-6-Questions 2014 PDFDocument25 pagesTutorial-Work-1-6-Questions 2014 PDFLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- ECE 313: Problem Set 12: Problems and Solutions Functions of Random Variables, Conditional PDFS, CovariancesDocument6 pagesECE 313: Problem Set 12: Problems and Solutions Functions of Random Variables, Conditional PDFS, CovariancesLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Application ChecklistDocument2 pagesApplication ChecklistLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2019 v1.3: General Senior SyllabusDocument103 pagesChemistry 2019 v1.3: General Senior SyllabusLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Math Note Sheet PDFDocument1 pageMath Note Sheet PDFLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Variance, Covariance, and Moment-Generating Functions: Practice Problems - SolutionsDocument2 pagesVariance, Covariance, and Moment-Generating Functions: Practice Problems - SolutionsLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Universalisation of Elementary Education in India Prof GovindaDocument44 pagesUniversalisation of Elementary Education in India Prof GovindaDevki MudaliarNo ratings yet
- Cultural and Diversity Characteristics Map AnalysisDocument4 pagesCultural and Diversity Characteristics Map AnalysisEvelyn Spikes HardingNo ratings yet
- Our Iceberg Is Melting EssayDocument3 pagesOur Iceberg Is Melting EssayMichael Angelo UyNo ratings yet
- LAC Evaluation ChecklistDocument2 pagesLAC Evaluation ChecklistBayoyong NhsNo ratings yet
- UCSP-Qrtr 1 - M3Document21 pagesUCSP-Qrtr 1 - M3Joshua Segismar100% (6)
- Complex Trauma Inventory (CTI) With Scoring Protocol and Psychometric InformationDocument4 pagesComplex Trauma Inventory (CTI) With Scoring Protocol and Psychometric InformationKhoyrunnisaa AnnabiilahNo ratings yet
- Educ216b - 2se - Siasol - 1Document22 pagesEduc216b - 2se - Siasol - 1Jeane Mae BooNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet On Translingual AutoethnographyDocument2 pagesAssignment Sheet On Translingual Autoethnographyapi-395950323No ratings yet
- Arts - Module 11Document2 pagesArts - Module 11Rodrick RamosNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Lifelong EducationDocument18 pagesInternational Journal of Lifelong EducationAlliance Consultancy PLCNo ratings yet
- Populism Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesPopulism Lesson PlanS.B.H.No ratings yet
- Simon Baron Cohen Mindblindness ExtractDocument13 pagesSimon Baron Cohen Mindblindness ExtractManuel Rizzello100% (1)
- Leadership and Corporate CultureDocument3 pagesLeadership and Corporate CultureGodfrey MakurumureNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument25 pagesTaxonomy of Educational ObjectivesAngelica AlejandroNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Spiritual Intelligence, Gender and Educational Background On Mental Health Among College StudentsDocument22 pagesThe Impact of Spiritual Intelligence, Gender and Educational Background On Mental Health Among College StudentsBabar MairajNo ratings yet
- Strati, Antonio - Aesthetics of Organization (2003)Document5 pagesStrati, Antonio - Aesthetics of Organization (2003)Jomes AunzoNo ratings yet
- Economic Burden and Reasons For Delay in First Psychiatric Consultation - An Observational StudyDocument11 pagesEconomic Burden and Reasons For Delay in First Psychiatric Consultation - An Observational StudyFaizan Ali UniqueNo ratings yet
- Personality Development Factors and TheoriesDocument46 pagesPersonality Development Factors and TheoriesMirafelNo ratings yet
- Reflections On The Diploma Disease Twenty Years LaterDocument19 pagesReflections On The Diploma Disease Twenty Years LaterMasliana SahadNo ratings yet
- Organization AND Management: Mr. Bernard Jay P. OroDocument10 pagesOrganization AND Management: Mr. Bernard Jay P. OroBernard Jay OroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in EthicsDocument9 pagesReviewer in EthicsIsla DianaNo ratings yet
- Differences Western EasternDocument2 pagesDifferences Western Easternmiki mikiNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquistion, Engagement and Retention Conclave - From NHRDDocument4 pagesTalent Acquistion, Engagement and Retention Conclave - From NHRDDeepak VinodNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Communication SkillsDocument19 pagesPresentation On Communication SkillsAditya JainNo ratings yet
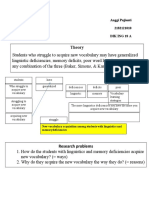
- DIK 18 A - Anggi Pujianti - Research Methodology - TR 15 (Revised)Document3 pagesDIK 18 A - Anggi Pujianti - Research Methodology - TR 15 (Revised)Fadli RafiNo ratings yet
- By Judy Kemp & Debby Toperoff: Guidelines For Portfolio AssessmentDocument27 pagesBy Judy Kemp & Debby Toperoff: Guidelines For Portfolio AssessmentJoshua LagonoyNo ratings yet
- Sleep is Crucial for Health, Mental Well-Being and PerformanceDocument3 pagesSleep is Crucial for Health, Mental Well-Being and PerformanceDes ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dictionary Psychology Oxford Quick ReferenceDocument3 pagesDictionary Psychology Oxford Quick ReferenceJust a GamerNo ratings yet
- Norway Education 2021: Key FiguresDocument37 pagesNorway Education 2021: Key FiguresKhallvina IzumiNo ratings yet
- Effective Communication & Barriers To It! - SomolekhaDocument17 pagesEffective Communication & Barriers To It! - SomolekhaZinneerah HibaNo ratings yet