Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Estimating forms, scaffolding
Uploaded by
Lorna Baclig0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
469 views11 pagesThe document discusses estimating forms, scaffolding, and staging used in construction projects. It defines different types of forms used to create the desired shape and size of concrete structural members. Methods for calculating the quantity of lumber needed for forms, scaffolding, and staging are presented along with an example quantity take-off problem.
Original Description:
Original Title
Estimates 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses estimating forms, scaffolding, and staging used in construction projects. It defines different types of forms used to create the desired shape and size of concrete structural members. Methods for calculating the quantity of lumber needed for forms, scaffolding, and staging are presented along with an example quantity take-off problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
469 views11 pagesEstimating forms, scaffolding
Uploaded by
Lorna BacligThe document discusses estimating forms, scaffolding, and staging used in construction projects. It defines different types of forms used to create the desired shape and size of concrete structural members. Methods for calculating the quantity of lumber needed for forms, scaffolding, and staging are presented along with an example quantity take-off problem.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
CENGR 3210– QUANTITY SURVEYING
Presentation 2 :
ESTIMATES
Formworks , Scaffolding Works
Engr. Ruel V. Vergara
FORMS
Form is a temporary boarding, sheathing, or pan to produce the desired shape
and size of concrete. The structural members of a building are built – up into its
desired shapes and dimensions through the use of form.
Common Types of Form:
Board Foot of Wood Frame For Column and Beam Per Plywood Form
Note: Size of 1 sheet of plywood is 4’ x 8’, that is 1.2 meters ( width ) by
2.4 meter ( length ) or 2.88 sq.m. of area per piece.
UNIT MEASURE OF LUMBER
Board Foot is the unit of measure used in computing the volume of lumber. Despite
the adoption of Metric System ( SI ), board foot for lumber is still in use for convenience
and practical use. One board foot simply mean, one square foot by one inch thick lumber
or an equivalent of 144 cubic inches.
The width and thickness of commercial lumber are expressed in inches while the
length is in feet of even numbers.
Board foot is found by dividing the product of the thickness, the width, and the
length by 12.
Example, to find the total board feet of 5 pieces 2” x 6” x 14 ft. lumber, that is:
5 ( 2 x 6 x 14 ) = 70 bd. ft.
12
SCAFFOLDING AND STAGING
Scaffolding is a temporary structure of wooden poles and planks providing
platforms for workers to stand on while erecting or repairing of building. It is
further defined as temporary framework for other purposes.
Staging on the other hand is more substantial framework progressively built
up as tall building rises up. The term staging is applied because it is built up in
stages one storey at a time.
The different parts of scaffolding to consider are:
1. Vertical Support
2. Base of Vertical Support ( if needed )
3. Horizontal Member
4. Diagonal Braces
5. Block and Wedges
6. Nails or Bolts
Quantity of Lumber for Scaffolding or Staging
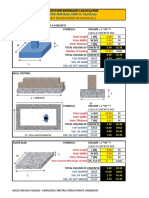
From the foundation plan of a 5m x 4m storage house, column
and column footing detail, and beam detail shown, determine
the following:
a. Compute for the quantity of ¼” marine plywood form for
columns.
b. Compute for the quantity in bd. ft. of 2” x 2” wood frame for
columns.
c. Compute for the quantity of ¼” marine plywood form for
beams.
d. Compute for the quantity in bd. ft. of 2” x 2” wood frame for
beams.
e. Compute for the quantity in bd. ft. of 2” x 3” wood scaffolding
for columns
f. Compute for the quantity in bd. ft. of 2” x 3” wood scaffolding
for beams.
The depth of col. ftg. and wall ftg. are 1.0m and 0.6m
respectively from NGL, and the top of beam and column are
located 3 m from the FFL.
You might also like
- Wood ConstructionDocument28 pagesWood ConstructionEzra GarciaNo ratings yet
- Covered Court EstimateDocument31 pagesCovered Court EstimateLizabelleNo ratings yet
- Const Estimate Made Easy by Engr. Ronald John R. CajillaDocument25 pagesConst Estimate Made Easy by Engr. Ronald John R. CajillaRonna Mae100% (2)
- Sample Estimate of Two Storey BLDGDocument14 pagesSample Estimate of Two Storey BLDGFaye HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Unit Cost DerivationDocument46 pagesUnit Cost Derivationapi-197535980% (1)
- The Prosecutor's HandbookDocument162 pagesThe Prosecutor's HandbooksamuelNo ratings yet
- Design N Cal. of FormworkDocument8 pagesDesign N Cal. of FormworkDENCONo ratings yet
- Estimating Concrete ReinforcementDocument19 pagesEstimating Concrete ReinforcementAl Patrick Dela Calzada100% (1)
- Final EstimateDocument60 pagesFinal EstimateChristian Paulo Cardinal TungolNo ratings yet
- CCST+Cybersecurity+Objecitve+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoDocument3 pagesCCST+Cybersecurity+Objecitve+Domain Cisco Final wCiscoLogoQazi ZayadNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials Price ListDocument12 pagesConstruction Materials Price ListChristian Gudino0% (1)
- Apollo Experience Report Lunar Module Landing Gear SubsystemDocument60 pagesApollo Experience Report Lunar Module Landing Gear SubsystemBob Andrepont100% (3)
- Bill of Quantities: Renovation of A Commercial BuildingDocument4 pagesBill of Quantities: Renovation of A Commercial BuildingIan Dalisay100% (1)
- CHB ReinforcementDocument16 pagesCHB ReinforcementMack Salazar0% (1)
- Construction PricesDocument5 pagesConstruction PricesGueanne ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- Excavation Works: 1. Excavation: A. Column FootingDocument43 pagesExcavation Works: 1. Excavation: A. Column FootingMichael Christ IcagoyNo ratings yet
- Construction Estimate Visuals Labor Cost For Painting WorksDocument8 pagesConstruction Estimate Visuals Labor Cost For Painting WorksLyn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Construction of Two Storey Residence with Roof DeckDocument34 pagesConstruction of Two Storey Residence with Roof DeckAamir GiverNo ratings yet
- Ceiling Works Estimate Tagbilaran City BoholDocument1 pageCeiling Works Estimate Tagbilaran City BoholRey TirolNo ratings yet
- CW3 - 4Document2 pagesCW3 - 4Rigel Zabate100% (1)
- TIMBERDocument4 pagesTIMBERjella21875% (4)
- Civil Engineer Cover Letter SampleDocument4 pagesCivil Engineer Cover Letter SampleLorna Baclig100% (1)
- Eastern Visayas State University Concrete Works ComputationsDocument18 pagesEastern Visayas State University Concrete Works ComputationsCole Jade DayoNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: John Lloyd B. Agapito - 201610485Document13 pagesPrepared By: John Lloyd B. Agapito - 201610485John Lloyd AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.a Analysis and Design of One-Way SlabDocument50 pagesLecture 3.a Analysis and Design of One-Way SlabMary Dominique OnateNo ratings yet
- CE155 Estimating Lecture 3 PDFDocument71 pagesCE155 Estimating Lecture 3 PDFArly Tolentino100% (1)
- Bill of Materials For Building PermitDocument3 pagesBill of Materials For Building PermitFitzgerard AgatonNo ratings yet
- Connections in Steel StructuresDocument4 pagesConnections in Steel StructuresLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- REINFORCEMENT, MORTAR AND PLASTERING OF CHBDocument13 pagesREINFORCEMENT, MORTAR AND PLASTERING OF CHBNuel LacionNo ratings yet
- Metal ReinforcementDocument91 pagesMetal Reinforcementjj75% (4)
- Ce 124 - Forms, Scaffoldings and StagingDocument13 pagesCe 124 - Forms, Scaffoldings and StagingJacob John100% (1)
- Reflection (Global Economy)Document2 pagesReflection (Global Economy)Lorna Baclig100% (3)
- Types of Cementitious MaterialsDocument9 pagesTypes of Cementitious MaterialsLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Spare Parts Catalog - Scooptram ST1030Document956 pagesSpare Parts Catalog - Scooptram ST1030Elvis RianNo ratings yet
- Event Management Study Material Free PDFDocument2 pagesEvent Management Study Material Free PDFKim0% (1)
- Lower Ceiling Estimation MaterialsDocument8 pagesLower Ceiling Estimation MaterialsMyla Riza Sintones NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Estimate S: I. EarthworksDocument58 pagesEstimate S: I. EarthworksRaul ArranguezNo ratings yet
- Calculate Steel Quantity For SlabDocument3 pagesCalculate Steel Quantity For SlabEMD DPWH-CAR0% (1)
- Embankment Price List Philippines - PHILCON PRICESDocument2 pagesEmbankment Price List Philippines - PHILCON PRICESGueanne ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- Consultation Research Investigations and ReportsDocument13 pagesConsultation Research Investigations and ReportsCJ L100% (2)
- 4 Storey With DeckDocument9 pages4 Storey With DeckFaye HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Tile Works Reyes EstimatesDocument4 pagesTile Works Reyes EstimatesVicent John ParedesNo ratings yet
- Bill of Materials: EarthworksDocument11 pagesBill of Materials: EarthworksJef Junio AlvarezNo ratings yet
- CONCRETE ESTIMATION MODULEDocument5 pagesCONCRETE ESTIMATION MODULEMac KYNo ratings yet
- ESTIMATESDocument13 pagesESTIMATESmelvin bautistaNo ratings yet
- Pre1 1Document43 pagesPre1 1Tooty FrootyNo ratings yet
- Excavation ToolsDocument41 pagesExcavation ToolsTejas Eknath PawarNo ratings yet
- 05 Hollow Core Ferrocement ProjectDocument19 pages05 Hollow Core Ferrocement ProjectDeo NievesNo ratings yet
- OJT RQMT MonitoringDocument4 pagesOJT RQMT MonitoringJerico VeranoNo ratings yet
- Metal Roofing Prices Philippines - PHILCON PRICESDocument1 pageMetal Roofing Prices Philippines - PHILCON PRICESjohn reyesNo ratings yet
- Constructing The RoadbedDocument15 pagesConstructing The RoadbedMoira Santos100% (1)
- Two-Storey Residential Building Bill of QuantitiesDocument20 pagesTwo-Storey Residential Building Bill of Quantitiespat cruzNo ratings yet
- Form WorksDocument13 pagesForm Worksmaryeonee12No ratings yet
- Item 1018Document5 pagesItem 1018Ester MarianNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1 (Visual Classification of Soil)Document2 pagesExperiment No.1 (Visual Classification of Soil)Stephanie BorcesNo ratings yet
- An Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010 )Document32 pagesAn Example Problem On Wind Load Calculation According To NSCP 2010 )joshua humirangNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two, Tension Members PDFDocument10 pagesChapter Two, Tension Members PDFZeleke TaimuNo ratings yet
- Bill of MaterialsDocument4 pagesBill of MaterialsCharles manezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8 - Ra544 ReflectionDocument3 pagesAssignment 8 - Ra544 ReflectionLuke MoraledaNo ratings yet
- Project: Standard Two-Storey School Building (12-Classrooms) Location: Various DPWH Proposed Projects Subject: Bill of MaterialsDocument5 pagesProject: Standard Two-Storey School Building (12-Classrooms) Location: Various DPWH Proposed Projects Subject: Bill of MaterialsFrances Sol TumulakNo ratings yet
- Table 5-4 Quantity of Lumber For Scaffolding and StagingDocument1 pageTable 5-4 Quantity of Lumber For Scaffolding and Stagingmark dominicNo ratings yet
- Using Long Span Color RoofDocument3 pagesUsing Long Span Color RoofMaria Rose Giltendez - BartianaNo ratings yet
- 4 LumberDocument18 pages4 LumberAbestano JadeNo ratings yet
- ABE Lecture 2Document40 pagesABE Lecture 2Lineth DomingoNo ratings yet
- REPORTINGDocument14 pagesREPORTINGxishiyanNo ratings yet
- Major Report Wood LumberDocument45 pagesMajor Report Wood LumberTorreja JonjiNo ratings yet
- Lumber: Wood Cut From Victorian Eucalyptus RegnansDocument9 pagesLumber: Wood Cut From Victorian Eucalyptus RegnansAlfredo RomeroNo ratings yet
- M.2. Carpentry WorksDocument26 pagesM.2. Carpentry WorksDominic Robiso DatuinNo ratings yet
- Carpentry Works (Ceiling and Partition Walls)Document26 pagesCarpentry Works (Ceiling and Partition Walls)Chris Ohlliver CuizonNo ratings yet
- Cockpit Plan 02Document11 pagesCockpit Plan 02sagitarius38No ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 2Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 2Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- 14p R8 - Baclig-SolomonDocument7 pages14p R8 - Baclig-SolomonLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Cengr 3210 - Quantity Surveying: Presentation 1Document13 pagesCengr 3210 - Quantity Surveying: Presentation 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Estimates 3Document16 pagesEstimates 3Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Analysis Template PDFDocument78 pagesAnalysis Template PDFLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 2Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Assignment # 2Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Chatoyancy': Minerals Igneous Metamorphic SedimentaryDocument3 pagesChatoyancy': Minerals Igneous Metamorphic SedimentaryLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Philippines plumbing code highlightsDocument195 pagesPhilippines plumbing code highlightsLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Baclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Document2 pagesBaclig, Lorna G. (Bsce 3-2) Quiz # 1Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- 7 Steel and Steel AlloysDocument3 pages7 Steel and Steel AlloysKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- The Rock CycleDocument1 pageThe Rock CycleLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Tests On Cement: IS: 4031 Part 4 1988 (Indian Standards)Document1 pageTests On Cement: IS: 4031 Part 4 1988 (Indian Standards)Lorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Steel Frame StructuresDocument2 pagesSteel Frame StructuresLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- Community Service MethodologiesDocument5 pagesCommunity Service MethodologiesLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- 7 Steel and Steel AlloysDocument3 pages7 Steel and Steel AlloysKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument1 pageAssignment 1 PDFLorna BacligNo ratings yet
- PSE Archery2015 RecurveDocument10 pagesPSE Archery2015 RecurvecarlheindlNo ratings yet
- What Is A Human Resources Strategy?Document8 pagesWhat Is A Human Resources Strategy?abdallah abdNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tentang Akuntansi Dengan Metode Kualitatif IDocument8 pagesJurnal Tentang Akuntansi Dengan Metode Kualitatif IAfni FebrianaNo ratings yet
- PTL Ls Programme HandbookDocument34 pagesPTL Ls Programme Handbooksalak946290No ratings yet
- REMMLOTDocument53 pagesREMMLOTarpit saraswat100% (1)
- Principles of Marketing Handout 4: Marketing Opportunity and Consumer AnalysisDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Handout 4: Marketing Opportunity and Consumer AnalysisAsset Dy100% (1)
- Impact On Cocoon Quality Improvement.1Document10 pagesImpact On Cocoon Quality Improvement.1Naveen NtrNo ratings yet
- OT Lawsuit CPDDocument20 pagesOT Lawsuit CPDDan LehrNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Swot and PDP AnalysisDocument4 pages1.3 Swot and PDP AnalysismiroyNo ratings yet
- Regulations 1-6 of 13Document2 pagesRegulations 1-6 of 13Leonardo RivasNo ratings yet
- MCMT 2 eDocument461 pagesMCMT 2 eRonNo ratings yet
- Engine Tune-UpDocument43 pagesEngine Tune-UpЮра ПетренкоNo ratings yet
- GPU, A Gnutella Processing UnitDocument27 pagesGPU, A Gnutella Processing UnitMengotti Tiziano FlavioNo ratings yet
- Nimt Institute of Method & Law, Greater Noida: "Legal Bases and Issues in Scrapping Article 370"Document12 pagesNimt Institute of Method & Law, Greater Noida: "Legal Bases and Issues in Scrapping Article 370"Preetish Sahu100% (1)
- Supreme Court: Arsenio C. Villalon, Jr. For Petitioner. Labaguis, Loyola, Angara & Associates For Private RespondentDocument43 pagesSupreme Court: Arsenio C. Villalon, Jr. For Petitioner. Labaguis, Loyola, Angara & Associates For Private RespondentpiaNo ratings yet
- United States Telecom Association v. Federal Communications Commission, US Court of Appeals, District of Columbia Circuit, 14 June 2016Document184 pagesUnited States Telecom Association v. Federal Communications Commission, US Court of Appeals, District of Columbia Circuit, 14 June 2016MowanNo ratings yet
- 5 Short MustWatch Motivational Videos For TeachersrccymDocument4 pages5 Short MustWatch Motivational Videos For Teachersrccymfoxpeak8No ratings yet
- 20 5880100Document2 pages20 5880100'Theodora GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- International Financial Law Reforms After Global CrisisDocument5 pagesInternational Financial Law Reforms After Global CrisisВладиславNo ratings yet
- Water Supply NED ArticleDocument22 pagesWater Supply NED Articlejulie1805No ratings yet
- TD102 Conductor - Standard ConductorsDocument2 pagesTD102 Conductor - Standard ConductorsHFandino1No ratings yet
- Patient-Centred CareDocument15 pagesPatient-Centred CareMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Tle 6 Ict Q4 M9Document16 pagesTle 6 Ict Q4 M9Christ Khayzee R. BacalsoNo ratings yet
- Educ 13C Questions For MidtermDocument9 pagesEduc 13C Questions For MidtermSannie MonoyNo ratings yet